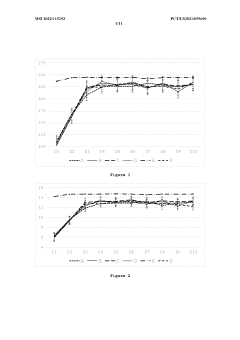
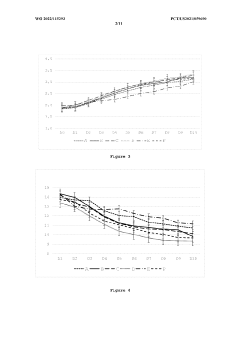
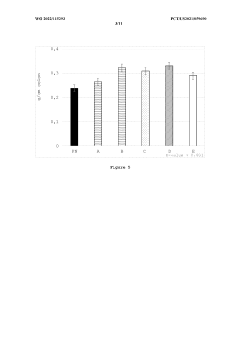
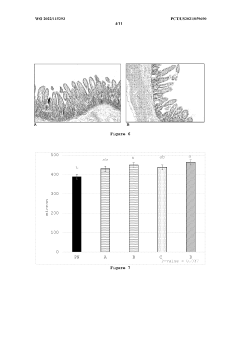
Sodium Butyrate Supplementation Enhances Growth, Gut Integrity, and Antimicrobial Response in Turbot on High Soybean Meal Diets
Sodium Butyrate in Aquaculture: Background and Objectives
Sodium butyrate has emerged as a promising feed additive in aquaculture, particularly in the context of sustainable fish farming practices. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring alternatives to antibiotics in animal nutrition. As the aquaculture industry faced challenges with disease outbreaks and the need for improved feed efficiency, sodium butyrate gained attention for its potential benefits.
The development of sodium butyrate as a feed supplement in aquaculture has been driven by several key factors. First, the increasing demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly aquaculture practices has led to a search for natural growth promoters. Second, the rise of antibiotic resistance and regulatory restrictions on antibiotic use in animal production have necessitated alternative solutions for maintaining fish health and growth performance.
Sodium butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid salt, has shown promise in addressing these challenges. Its mechanisms of action include enhancing gut health, improving nutrient absorption, and modulating the immune system. These properties make it particularly relevant for species like turbot, which are often raised in intensive aquaculture systems and face challenges related to diet composition and disease susceptibility.
The technological evolution of sodium butyrate supplementation has seen advancements in formulation and delivery methods. Early studies focused on simple dietary inclusion, while more recent research has explored protected forms of sodium butyrate to enhance its efficacy throughout the gastrointestinal tract. This progression reflects the industry's growing understanding of the compound's potential and the need for optimized application strategies.
In the context of high soybean meal diets, which are increasingly used as a sustainable protein source in aquaculture, sodium butyrate supplementation addresses specific challenges. Soybean meal can cause intestinal inflammation and reduced nutrient absorption in some fish species. The objectives of current research focus on leveraging sodium butyrate's properties to mitigate these negative effects, thereby improving growth performance, gut integrity, and disease resistance in turbot and other commercially important fish species.
The goals of sodium butyrate research in aquaculture extend beyond immediate growth enhancement. Long-term objectives include developing more resilient and efficient aquaculture systems, reducing the environmental impact of fish farming, and improving the overall sustainability of the industry. By enhancing fish health and feed utilization, sodium butyrate technology aims to contribute to the broader goals of food security and sustainable protein production in the face of growing global demand.
Market Analysis for Sustainable Aquafeed Additives
The global aquaculture industry has been experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for seafood and the need for sustainable protein sources. This growth has led to a surge in demand for aquafeed additives, particularly those that promote sustainability and improve fish health. The market for sustainable aquafeed additives is expected to expand rapidly in the coming years, with a focus on products that enhance growth, improve gut health, and boost immune responses in farmed fish species.
Sodium butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid salt, has emerged as a promising aquafeed additive, particularly for species like turbot that are increasingly being fed plant-based diets. The shift towards plant-based ingredients, such as soybean meal, in aquaculture feeds has created new challenges in fish nutrition and health management. This transition has opened up opportunities for additives that can mitigate the negative effects of plant-based diets on fish growth and gut health.
The market for sodium butyrate as an aquafeed additive is poised for substantial growth, driven by its potential to enhance growth performance, improve gut integrity, and strengthen antimicrobial responses in fish fed high soybean meal diets. This aligns with the broader trend in the aquaculture industry towards more sustainable and efficient feed solutions that can support the production of healthy fish while reducing environmental impacts.
Key market drivers include the increasing adoption of plant-based protein sources in aquafeeds, growing concerns about antibiotic resistance, and the need for improved feed efficiency in aquaculture operations. The demand for sodium butyrate is expected to be particularly strong in regions with developed aquaculture industries, such as Asia-Pacific, Europe, and North America.
The market for sustainable aquafeed additives like sodium butyrate is characterized by a growing emphasis on research and development, with both academic institutions and private companies investing in studies to demonstrate the efficacy of these products. This research focus is likely to lead to the development of more targeted and effective formulations, further driving market growth.
Challenges in the market include regulatory hurdles, the need for extensive efficacy testing across different fish species, and competition from alternative feed additives. However, the potential benefits of sodium butyrate in addressing key issues in modern aquaculture, such as improving feed utilization and reducing the environmental impact of fish farming, position it as a promising solution with significant market potential.
Current Challenges in High Soybean Meal Diets for Turbot
The use of high soybean meal diets in turbot aquaculture presents several significant challenges that have hindered its widespread adoption. One of the primary issues is the presence of anti-nutritional factors in soybean meal, which can negatively impact nutrient absorption and digestibility. These factors, including protease inhibitors, lectins, and phytic acid, interfere with protein utilization and mineral availability, potentially leading to reduced growth rates and feed efficiency in turbot.
Another major challenge is the potential for intestinal inflammation and compromised gut health. Soybean meal contains compounds that can cause enteritis in some fish species, including turbot. This condition is characterized by changes in the intestinal morphology, such as shortening of the mucosal folds and increased infiltration of inflammatory cells. Such alterations can disrupt the normal digestive and absorptive functions of the gut, ultimately affecting the overall health and performance of the fish.
The high inclusion of soybean meal in turbot diets may also lead to imbalances in the amino acid profile. While soybean meal is a good source of protein, its amino acid composition does not perfectly match the requirements of turbot. This mismatch can result in suboptimal growth and protein utilization, necessitating careful diet formulation and potential supplementation with limiting amino acids.
Furthermore, the palatability of high soybean meal diets can be a concern for turbot. These fish are known to be sensitive to dietary changes and may exhibit reduced feed intake when presented with diets containing high levels of plant-based proteins. This can lead to decreased growth rates and increased feed waste, affecting both the economic efficiency of production and environmental sustainability.
The potential for reduced immune function is another challenge associated with high soybean meal diets in turbot. Some studies have suggested that plant-based protein sources may not provide the same immunostimulatory effects as fish meal, potentially leaving the fish more susceptible to diseases and environmental stressors. This is particularly crucial in intensive aquaculture systems where disease outbreaks can have severe economic consequences.
Lastly, the environmental impact of high soybean meal diets must be considered. While replacing fish meal with plant-based proteins can reduce the pressure on wild fish stocks, the cultivation and processing of soybeans have their own environmental footprint. Balancing the need for sustainable feed sources with the ecological consequences of soybean production remains a challenge for the aquaculture industry.
Existing Solutions for Enhancing Fish Growth and Gut Integrity
01 Sodium butyrate promotes growth and development
Sodium butyrate has been shown to enhance growth and development in various organisms. It acts as a source of energy for intestinal cells and stimulates cell proliferation. This compound can improve feed efficiency and weight gain in livestock and aquaculture species, making it a valuable feed additive.- Sodium butyrate promotes growth and development: Sodium butyrate has been shown to enhance growth and development in various organisms. It acts as a source of energy for intestinal cells and stimulates cell proliferation. This compound can improve feed efficiency and weight gain in livestock and aquaculture species, contributing to overall growth performance.
- Enhancement of gut integrity and barrier function: Sodium butyrate plays a crucial role in maintaining and improving gut integrity. It strengthens the intestinal barrier by promoting tight junction protein expression and reducing intestinal permeability. This action helps prevent the translocation of harmful bacteria and toxins, thereby supporting overall gut health and function.
- Antimicrobial properties and immune modulation: Sodium butyrate exhibits antimicrobial properties against various pathogens, including bacteria and viruses. It can modulate the immune response by influencing the production of cytokines and enhancing the activity of immune cells. This dual action helps in maintaining a balanced gut microbiome and improving overall disease resistance.
- Application in animal feed and aquaculture: Sodium butyrate is widely used as a feed additive in animal husbandry and aquaculture. It improves feed conversion efficiency, promotes growth, and enhances disease resistance in livestock and aquatic species. The compound's beneficial effects on gut health make it a valuable tool for sustainable animal production practices.
- Therapeutic potential in gastrointestinal disorders: Research suggests that sodium butyrate has therapeutic potential in treating various gastrointestinal disorders. It may help alleviate symptoms of inflammatory bowel diseases, reduce the risk of colorectal cancer, and improve overall gut health. The compound's ability to modulate inflammation and support gut barrier function contributes to its therapeutic effects.
02 Enhancement of gut integrity and barrier function
Sodium butyrate plays a crucial role in maintaining and improving gut integrity. It strengthens the intestinal barrier by promoting tight junction protein expression and reducing intestinal permeability. This action helps prevent the translocation of harmful bacteria and toxins, contributing to overall gut health.Expand Specific Solutions03 Antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties
Sodium butyrate exhibits antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects in the gut. It can inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria while promoting beneficial microbiota. Additionally, it modulates the immune response and reduces inflammation in the intestinal tract, potentially alleviating symptoms of various gastrointestinal disorders.Expand Specific Solutions04 Modulation of gene expression and epigenetic regulation
As a histone deacetylase inhibitor, sodium butyrate influences gene expression and epigenetic regulation. This property affects various cellular processes, including cell differentiation, apoptosis, and immune function. The compound's ability to modulate gene expression contributes to its diverse biological effects on growth, gut health, and antimicrobial response.Expand Specific Solutions05 Formulations and delivery methods for enhanced efficacy
Various formulations and delivery methods have been developed to enhance the efficacy of sodium butyrate. These include microencapsulation techniques, slow-release formulations, and combination with other bioactive compounds. Such approaches aim to improve the stability of sodium butyrate, ensure its targeted delivery to the intestine, and maximize its beneficial effects on growth, gut integrity, and antimicrobial response.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Aquaculture Feed Additives Industry
The research on sodium butyrate supplementation in turbot diets represents an emerging field in aquaculture nutrition, currently in its early development stage. The market for this technology is relatively small but growing, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable aquaculture practices. The technical maturity is still evolving, with academic institutions like Ocean University of China and Shandong University leading the research efforts. Industry players such as Norel SA and MP Gokyo Food & Chemical Co. Ltd. are beginning to explore commercial applications, while established companies like Baxter International, Inc. and Nestlé SA may leverage their expertise in nutrition to enter this space. The collaboration between research institutions and industry partners is likely to accelerate the development and adoption of this technology in aquaculture.
Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences
MP Gokyo Food & Chemical Co. Ltd.
Innovations in Sodium Butyrate Supplementation for Aquaculture
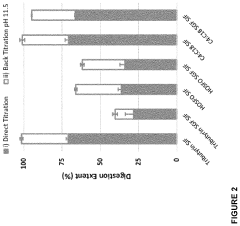
- A composition comprising arginine butyrate is used to improve intestinal health by maintaining or ameliorating local immunity, reducing inflammation, and enhancing intestinal barrier function, which is stable and safe for central or peripheral administration in pediatric and adult patients.
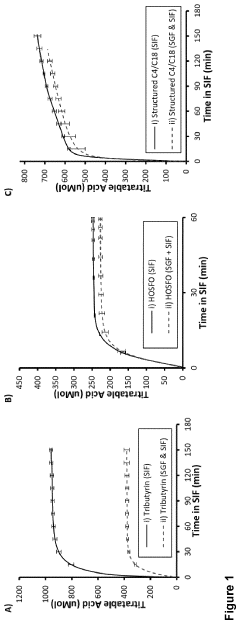
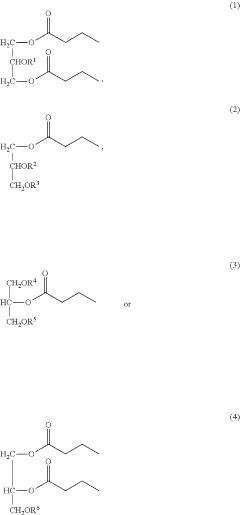
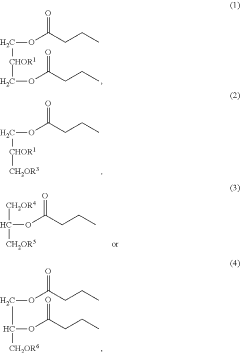
- Development of butyrate moiety containing triglycerides with improved organoleptic properties, such as 1,3-dibutyryl-2-palmitoylglycerol, which are synthesized through interesterification of tributyrin with high oleic sunflower oil, providing a dairy-free, cholesterol-free, and vegan alternative with reduced bitterness and odor, allowing effective delivery of butyric acid to the intestinal compartment.
Environmental Impact of Sodium Butyrate in Aquaculture
The environmental impact of sodium butyrate in aquaculture is a critical consideration as the industry seeks sustainable practices. Sodium butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid salt, has gained attention for its potential to enhance growth, gut health, and disease resistance in fish species, including turbot. However, its widespread use raises questions about its effects on aquatic ecosystems.
One primary concern is the potential for sodium butyrate to alter water chemistry. As a salt, it may contribute to increased salinity in freshwater systems or modify the pH balance in both fresh and marine environments. These changes could have cascading effects on aquatic flora and fauna, potentially disrupting local ecosystems. Additionally, the organic nature of sodium butyrate may lead to increased biological oxygen demand (BOD) in water bodies, potentially affecting dissolved oxygen levels critical for aquatic life.
The impact on sediment composition and benthic communities is another area of concern. Excess sodium butyrate that is not metabolized by fish may settle in sediments, potentially altering microbial communities and nutrient cycling processes. This could lead to changes in the benthic ecosystem structure and function, affecting bottom-dwelling organisms and the overall food web.
Furthermore, the use of sodium butyrate may influence the microbial ecology of aquaculture systems. While it can promote beneficial gut microbiota in fish, its presence in water may also affect environmental microorganisms. This could potentially lead to shifts in microbial populations, with unknown consequences for water quality and ecosystem balance.
The potential for bioaccumulation and biomagnification of sodium butyrate or its metabolites in the food chain is another aspect that requires investigation. Although sodium butyrate is generally considered safe, its long-term accumulation in aquatic organisms and potential transfer to higher trophic levels, including humans, needs careful assessment.
Lastly, the environmental footprint of sodium butyrate production and transportation should be considered. As demand for this supplement grows in aquaculture, the energy and resources required for its manufacture and distribution may contribute to broader environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion.
Regulatory Framework for Aquafeed Additives
The regulatory framework for aquafeed additives plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of supplements like sodium butyrate in aquaculture. In the context of turbot farming with high soybean meal diets, understanding these regulations is essential for implementing research findings and developing new feed formulations.
At the international level, organizations such as the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) provide guidelines and standards for aquaculture practices, including feed additives. These guidelines often serve as a basis for national regulations and help harmonize global practices in aquafeed production and use.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety and efficacy of feed additives. The EU maintains a register of authorized feed additives, which includes specific categories for zootechnical additives and gut flora stabilizers. Sodium butyrate, as a potential growth enhancer and gut health promoter, would likely fall under these categories and require thorough evaluation before approval.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates animal feed additives through the Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM). The FDA's regulatory process includes evaluating the safety and effectiveness of feed additives, as well as their environmental impact. For novel additives like sodium butyrate in turbot diets, manufacturers would need to submit a food additive petition or seek approval through the Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) notification process.
In Asia, major aquaculture producers like China and Vietnam have their own regulatory bodies overseeing aquafeed additives. China's Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (MARA) is responsible for feed additive regulations, while Vietnam's Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (MARD) oversees similar processes. These countries often have specific requirements for product registration, safety assessments, and efficacy trials.
Regulatory frameworks typically require extensive documentation on the additive's composition, manufacturing process, intended use, and safety data. For sodium butyrate supplementation in turbot diets, researchers and manufacturers would need to provide evidence of its effects on growth, gut integrity, and antimicrobial response, as well as any potential risks to fish health, human consumers, and the environment.
Many regulatory bodies also consider the sustainability aspects of feed additives. Given the use of high soybean meal diets in this research, regulators may evaluate the environmental impact of increased plant-based ingredients in aquafeeds and how additives like sodium butyrate might mitigate any negative effects.
As research progresses and the benefits of sodium butyrate supplementation become more established, regulatory frameworks may evolve to accommodate this and similar feed additives. This could potentially lead to streamlined approval processes or specific guidelines for butyrate-based products in aquaculture, facilitating their adoption in commercial turbot farming and other aquaculture sectors.