Butyrate and its Potential in Diabetes Prevention
Butyrate in Diabetes Prevention: Background and Objectives
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut microbiota through fermentation of dietary fibers, has emerged as a promising compound in the prevention and management of diabetes. The rising global prevalence of diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, has spurred extensive research into novel therapeutic approaches and preventive strategies. In this context, butyrate has garnered significant attention due to its multifaceted effects on metabolic health.
The historical background of butyrate research dates back to the early 20th century when it was first identified as a product of microbial fermentation. However, its potential role in diabetes prevention has only gained traction in recent decades, coinciding with the growing understanding of the gut microbiome's influence on human health. The evolution of this field has been marked by significant technological advancements in microbiome analysis and metabolomics, enabling researchers to elucidate the complex interactions between diet, gut bacteria, and host metabolism.
Recent epidemiological studies have consistently shown an inverse relationship between dietary fiber intake and the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This association has partly been attributed to the production of short-chain fatty acids, including butyrate, highlighting the need for a deeper understanding of butyrate's mechanisms of action in glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity.
The primary objectives of current research on butyrate in diabetes prevention are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a focus on elucidating the molecular pathways through which butyrate influences glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and pancreatic β-cell function. Secondly, researchers aim to determine the optimal dosage and delivery methods for butyrate supplementation to maximize its therapeutic potential. Thirdly, there is a growing interest in identifying specific dietary interventions that can enhance endogenous butyrate production through modulation of the gut microbiome.
Furthermore, the research aims to explore the potential synergistic effects of butyrate with other diabetes prevention strategies, such as lifestyle modifications and pharmacological interventions. Long-term clinical trials are being designed to assess the efficacy and safety of butyrate-based interventions in high-risk populations. Additionally, there is a concerted effort to develop novel butyrate derivatives or prodrugs that can overcome the limitations of butyrate's pharmacokinetics and improve its bioavailability.
As the field progresses, researchers are also investigating the broader implications of butyrate in metabolic health, including its effects on obesity, inflammation, and cardiovascular risk factors, all of which are closely intertwined with diabetes pathophysiology. The ultimate goal is to translate these findings into practical, effective strategies for diabetes prevention and management, potentially revolutionizing the approach to this global health challenge.
Market Analysis for Butyrate-Based Diabetes Solutions
The market for butyrate-based diabetes solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing prevalence of diabetes worldwide and the growing interest in innovative treatment approaches. The global diabetes market is projected to reach $78 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate of 6.1%. Within this broader market, butyrate-based solutions are emerging as a promising niche segment.
Consumer demand for natural and preventive diabetes management options is fueling interest in butyrate-based products. As awareness of the gut microbiome's role in metabolic health grows, consumers are seeking alternatives to traditional pharmaceuticals. This trend aligns well with butyrate's potential as a naturally occurring short-chain fatty acid that can be produced by gut bacteria.
The market for butyrate-based diabetes solutions spans several product categories, including dietary supplements, functional foods, and potential pharmaceutical applications. Dietary supplements containing butyrate or its precursors are gaining traction, with several brands already offering products targeting gut health and metabolic support. The functional food sector is also exploring butyrate-enriched products, such as fortified dairy and bakery items.
Geographically, North America and Europe are leading the market for butyrate-based diabetes solutions, owing to higher awareness of gut health and greater willingness to adopt novel preventive approaches. However, Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by the rapidly increasing diabetes prevalence in countries like China and India.
Key market drivers include the rising healthcare costs associated with diabetes management, growing consumer preference for natural health solutions, and increasing research supporting the link between gut health and metabolic disorders. The potential for butyrate to address multiple aspects of diabetes, including insulin sensitivity and inflammation, positions it as a versatile solution in the market.
Challenges in the market include the need for more extensive clinical trials to validate butyrate's efficacy in diabetes prevention, regulatory hurdles in positioning butyrate-based products as medical treatments, and competition from established diabetes management solutions. Additionally, educating healthcare providers and consumers about the role of butyrate in metabolic health remains a crucial task for market players.
Despite these challenges, the market outlook for butyrate-based diabetes solutions is promising. As research continues to elucidate the mechanisms by which butyrate influences glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, opportunities for innovative product development are likely to expand. The potential for personalized nutrition approaches incorporating butyrate supplementation also presents a significant growth avenue for the market.
Current State and Challenges in Butyrate Research
Butyrate research has made significant strides in recent years, particularly in understanding its potential role in diabetes prevention. Currently, the field is characterized by a growing body of evidence supporting butyrate's beneficial effects on glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that butyrate supplementation can improve glycemic control and reduce inflammation in animal models of diabetes.
However, the translation of these findings to human clinical applications faces several challenges. One major obstacle is the limited bioavailability of oral butyrate supplements due to rapid absorption and metabolism in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Researchers are exploring various delivery methods, including encapsulation technologies and prodrug approaches, to enhance butyrate's therapeutic potential.
Another significant challenge lies in elucidating the precise mechanisms by which butyrate exerts its anti-diabetic effects. While studies have implicated pathways involving G-protein coupled receptors, histone deacetylase inhibition, and modulation of the gut microbiome, the complex interplay between these mechanisms remains to be fully understood. This knowledge gap hinders the development of targeted interventions and optimized dosing strategies.
The heterogeneity of diabetes pathophysiology also presents a challenge in butyrate research. Different subtypes of diabetes may respond differently to butyrate-based interventions, necessitating personalized approaches. Additionally, the long-term effects of butyrate supplementation on metabolic health and potential side effects require further investigation through longitudinal studies.
From a geographical perspective, butyrate research is conducted globally, with notable contributions from North America, Europe, and Asia. However, there is a need for more diverse population studies to account for genetic and environmental factors that may influence butyrate's efficacy in diabetes prevention.
Technological limitations in accurately measuring butyrate levels in various tissues and bodily fluids pose another challenge. Developing sensitive and specific analytical methods for butyrate quantification is crucial for advancing research and monitoring treatment efficacy.
Lastly, regulatory hurdles and the need for large-scale clinical trials present significant obstacles in translating butyrate research into approved therapeutic interventions for diabetes prevention. Overcoming these challenges will require collaborative efforts between academia, industry, and regulatory bodies to establish butyrate's safety and efficacy in human populations.
Current Approaches to Butyrate-Mediated Diabetes Prevention
01 Butyrate as a therapeutic agent for diabetes prevention
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid, has shown potential in preventing diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. It may help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce inflammation associated with diabetes development.- Butyrate as a therapeutic agent for diabetes prevention: Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid, has shown potential in preventing diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. It may help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce inflammation associated with diabetes development.
- Dietary supplements containing butyrate for diabetes prevention: Formulations of dietary supplements incorporating butyrate or its derivatives have been developed to aid in diabetes prevention. These supplements may enhance gut health and metabolic function, potentially reducing the risk of developing diabetes.
- Butyrate-producing probiotics for diabetes prevention: Probiotic strains capable of producing butyrate in the gut have been identified and studied for their potential in preventing diabetes. These probiotics may help maintain a healthy gut microbiome and improve metabolic health.
- Combination therapies using butyrate for diabetes prevention: Research has explored the use of butyrate in combination with other compounds or therapies for enhanced diabetes prevention. These combinations may target multiple pathways involved in diabetes development, potentially offering more effective prevention strategies.
- Butyrate-based pharmaceutical compositions for diabetes prevention: Pharmaceutical compositions containing butyrate or its derivatives have been developed specifically for diabetes prevention. These formulations may be designed for targeted delivery or enhanced absorption to maximize the potential benefits of butyrate in preventing diabetes.
02 Dietary supplements containing butyrate for diabetes prevention
Formulations of dietary supplements incorporating butyrate or its derivatives have been developed to aid in diabetes prevention. These supplements may enhance gut health and metabolic function, potentially reducing the risk of developing diabetes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Butyrate-producing probiotics for diabetes prevention
Probiotic strains capable of producing butyrate in the gut have been identified and studied for their potential in preventing diabetes. These probiotics may help maintain a healthy gut microbiome and improve metabolic health.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination therapies using butyrate for diabetes prevention
Research has explored combining butyrate with other compounds or treatments to enhance its effectiveness in preventing diabetes. These combination therapies may target multiple pathways involved in diabetes development.Expand Specific Solutions05 Butyrate-based pharmaceutical compositions for diabetes prevention
Pharmaceutical compositions containing butyrate or its derivatives have been developed specifically for diabetes prevention. These formulations may be designed for targeted delivery or enhanced absorption to maximize the beneficial effects of butyrate on metabolic health.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Butyrate and Diabetes Research
The research on butyrate and its potential in diabetes prevention is in an emerging phase, with growing market potential due to increasing diabetes prevalence worldwide. The technology is still developing, with varying levels of maturity among key players. Companies like Merck Patent GmbH, Astellas Pharma, Inc., and Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH are at the forefront, leveraging their pharmaceutical expertise. Academic institutions such as The University of Michigan and Monash University are contributing significant research. Smaller biotech firms like BioKier, Inc. and Pendulum Therapeutics, Inc. are also making strides, focusing on innovative approaches. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established pharmaceutical companies and emerging startups vying for breakthroughs in this promising field.
BioKier, Inc.
Seed Health, Inc.
Critical Patents and Studies on Butyrate in Diabetes
- Delivering butyrate directly to the colon using a colon-targeted delivery system that bypasses the upper digestive system, allowing for a time-released formulation over 0 to 5 hours to stimulate gut hormone secretion from L-cells, thereby increasing GLP-1, GLP-2, and oxyntomodulin production.
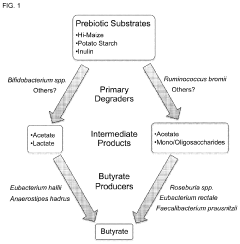
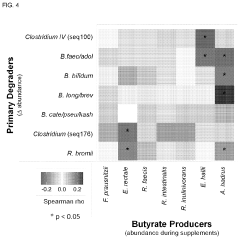
- Administering a carbohydrate source, such as resistant starch, combined with specific bacteria like Bifidobacterium spp., Clostridium seq 176, or Ruminococcus bromii, to promote butyrate production in the intestine, either orally or rectally, to increase butyrate levels and treat associated diseases.
Regulatory Landscape for Butyrate-Based Therapeutics
The regulatory landscape for butyrate-based therapeutics is complex and evolving, reflecting the growing interest in harnessing butyrate's potential for diabetes prevention and treatment. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the development and approval of such therapeutics. The FDA's regulatory framework for butyrate-based products depends on their intended use and formulation.
For butyrate supplements marketed as dietary supplements, they fall under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This allows for a relatively streamlined path to market, provided manufacturers comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) and ensure product safety. However, claims regarding diabetes prevention or treatment are strictly regulated and require substantial scientific evidence.
In contrast, butyrate-based drugs aimed at treating or preventing diabetes would be subject to the rigorous New Drug Application (NDA) process. This involves extensive preclinical and clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. The FDA's guidance on developing drugs for diabetes management emphasizes the need for long-term safety data and clear evidence of glycemic control or other clinically meaningful outcomes.
Internationally, regulatory bodies such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) have similar stringent requirements for diabetes therapeutics. However, there may be variations in specific clinical trial designs or endpoints required for approval.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses quality control and manufacturing standards. For butyrate-based products, this includes ensuring consistent potency, stability, and bioavailability. Given butyrate's volatile nature, innovative formulations and delivery systems may require additional regulatory scrutiny to ensure they meet safety and efficacy standards.
As research on butyrate's role in diabetes prevention advances, regulatory agencies are likely to refine their guidance. This may include specific considerations for microbiome-modulating therapies or precision medicine approaches that leverage individual variations in butyrate metabolism. Manufacturers and researchers must stay abreast of these evolving regulations to navigate the path from discovery to market successfully.
Collaboration between regulatory bodies, academic institutions, and industry stakeholders is crucial in shaping a regulatory environment that balances innovation with patient safety. This includes developing standardized protocols for assessing butyrate's effects on diabetes-related outcomes and establishing clear guidelines for combination therapies that may include butyrate alongside traditional diabetes medications.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations for Butyrate Interventions
The safety and efficacy of butyrate interventions in diabetes prevention are critical considerations for researchers and healthcare professionals. Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut microbiota, has shown promising potential in metabolic health improvement. However, its use as a therapeutic agent requires careful evaluation of both its benefits and potential risks.
Safety considerations for butyrate interventions primarily focus on gastrointestinal tolerability and potential systemic effects. Oral administration of butyrate supplements may cause mild to moderate gastrointestinal discomfort, including bloating, flatulence, and abdominal pain in some individuals. These side effects are generally dose-dependent and tend to subside with continued use. However, long-term safety data on high-dose butyrate supplementation is limited, necessitating further research.
Systemic effects of butyrate interventions, particularly on liver function and blood parameters, require careful monitoring. While butyrate has shown beneficial effects on liver metabolism in preclinical studies, its impact on hepatic function in humans with diabetes or pre-diabetes needs thorough investigation. Additionally, potential interactions with other medications commonly used in diabetes management should be evaluated to ensure safe co-administration.
Efficacy considerations for butyrate interventions in diabetes prevention are multifaceted. Current evidence suggests that butyrate may improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and enhance glucose homeostasis. However, the optimal dosage, formulation, and duration of butyrate supplementation for maximal efficacy in diabetes prevention remain to be established. Variability in individual responses to butyrate interventions, potentially due to differences in gut microbiota composition or genetic factors, adds complexity to efficacy assessments.
The route of administration is another crucial factor affecting both safety and efficacy. While oral supplementation is the most common approach, targeted delivery systems that release butyrate in the colon may enhance its efficacy and reduce systemic side effects. Novel formulations, such as esterified forms of butyrate or microencapsulated preparations, are being explored to improve bioavailability and tolerability.
Long-term efficacy of butyrate interventions in diabetes prevention requires extensive clinical trials with adequate follow-up periods. Current studies have primarily focused on short-term outcomes, and the sustainability of butyrate's beneficial effects over extended periods needs further investigation. Moreover, the potential for butyrate to synergize with lifestyle interventions or other pharmacological treatments in diabetes prevention should be explored to optimize its therapeutic potential.
In conclusion, while butyrate shows promise in diabetes prevention, careful consideration of safety and efficacy is paramount. Rigorous clinical trials, long-term safety monitoring, and personalized approaches to butyrate interventions are necessary to fully harness its potential in metabolic health improvement.