How Butyrate Supports Cardiometabolic Health
Butyrate and Cardiometabolic Health Overview
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut microbiota through fermentation of dietary fiber, has emerged as a key player in supporting cardiometabolic health. This compound has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its multifaceted effects on various physiological processes that influence cardiovascular and metabolic well-being.
The relationship between butyrate and cardiometabolic health is rooted in its ability to modulate several critical pathways. Primarily, butyrate acts as an energy source for colonic epithelial cells, maintaining the integrity of the gut barrier. This function is crucial in preventing the translocation of harmful bacteria and endotoxins into the bloodstream, which can trigger systemic inflammation – a key factor in the development of cardiometabolic disorders.
Furthermore, butyrate exhibits potent anti-inflammatory properties, suppressing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhancing the expression of anti-inflammatory mediators. This anti-inflammatory action extends beyond the gut, potentially mitigating low-grade chronic inflammation associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Butyrate also plays a significant role in glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity. Studies have shown that it can improve insulin signaling and glucose uptake in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. By enhancing insulin sensitivity, butyrate may help prevent the development of insulin resistance, a hallmark of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
In the context of cardiovascular health, butyrate has been found to have beneficial effects on blood pressure regulation and lipid metabolism. It may contribute to the reduction of hypertension by modulating the renin-angiotensin system and improving endothelial function. Additionally, butyrate has been associated with decreased levels of total cholesterol and triglycerides, potentially reducing the risk of atherosclerosis.
The impact of butyrate on energy metabolism and body weight regulation is another area of interest in cardiometabolic health. Research suggests that butyrate can increase energy expenditure and fat oxidation, potentially aiding in weight management and reducing obesity-related cardiometabolic risks.
As research in this field progresses, the intricate connections between gut health, butyrate production, and cardiometabolic outcomes are becoming increasingly apparent. The potential of butyrate as a therapeutic target or supplement for improving cardiometabolic health is an exciting avenue for future investigations, with implications for both preventive strategies and treatment approaches in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.
Market Analysis for Butyrate-Based Products
The market for butyrate-based products is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing awareness of the compound's potential benefits for cardiometabolic health. Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut bacteria during fiber fermentation, has garnered attention for its role in supporting heart health, metabolic function, and overall well-being.
The global market for butyrate supplements and related products is expanding rapidly, with a particular focus on developed countries where lifestyle-related health issues are prevalent. North America and Europe currently lead the market, with Asia-Pacific regions showing promising growth potential. The market encompasses various product forms, including dietary supplements, functional foods, and beverages fortified with butyrate or its precursors.
Consumer demand for natural and preventive health solutions has been a key driver of market growth. As more individuals seek alternatives to traditional pharmaceuticals for managing cardiometabolic health, butyrate-based products have gained traction. This trend aligns with the broader shift towards personalized nutrition and gut health optimization.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established nutraceutical companies and emerging startups specializing in microbiome-focused products. Key players are investing in research and development to create innovative delivery mechanisms that enhance butyrate's bioavailability and efficacy. Partnerships between ingredient suppliers and product manufacturers are becoming increasingly common to leverage expertise and accelerate product development.
Market segmentation reveals distinct consumer groups, including health-conscious individuals, those with existing cardiometabolic conditions, and athletes seeking performance benefits. Each segment presents unique opportunities for targeted product development and marketing strategies.
Regulatory environments vary across regions, influencing market dynamics. While some countries have embraced butyrate-based products, others maintain stricter regulations on health claims, impacting market entry and product positioning strategies.
The competitive landscape is intensifying as more companies recognize the potential of butyrate in addressing cardiometabolic health. This has led to increased investment in clinical trials and scientific research to substantiate product claims and differentiate offerings in a crowded market.
Looking ahead, the market for butyrate-based products is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Factors such as the rising prevalence of cardiometabolic disorders, growing consumer interest in gut health, and ongoing research into butyrate's mechanisms of action are likely to sustain market growth. However, challenges such as taste issues, stability concerns, and the need for consumer education on butyrate's benefits must be addressed to fully capitalize on market opportunities.
Current Research on Butyrate's Cardiometabolic Effects
Recent research on butyrate's effects on cardiometabolic health has revealed promising insights into its potential as a therapeutic agent. Studies have demonstrated that butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut bacteria during fiber fermentation, plays a crucial role in maintaining cardiovascular and metabolic health.
One of the primary mechanisms through which butyrate supports cardiometabolic health is by improving insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Several clinical trials have shown that butyrate supplementation can enhance insulin signaling pathways, leading to better glucose uptake and utilization in peripheral tissues. This effect is particularly significant in individuals with metabolic syndrome or type 2 diabetes.
Butyrate has also been found to have anti-inflammatory properties, which are essential for cardiovascular health. Research has indicated that butyrate can suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines and activate anti-inflammatory pathways, potentially reducing the risk of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases. These anti-inflammatory effects extend to adipose tissue, where butyrate has been shown to decrease inflammation and improve metabolic function.
Furthermore, studies have highlighted butyrate's role in regulating lipid metabolism. Experiments in animal models and human cell lines have demonstrated that butyrate can inhibit lipogenesis and promote fatty acid oxidation, potentially leading to reduced triglyceride levels and improved lipid profiles. This effect may contribute to the prevention of obesity and related cardiometabolic disorders.
Recent investigations have also focused on butyrate's impact on blood pressure regulation. Some studies suggest that butyrate may help lower blood pressure by modulating the renin-angiotensin system and improving endothelial function. While these findings are promising, more research is needed to fully elucidate the mechanisms and potential clinical applications.
Another area of active research is butyrate's influence on the gut-heart axis. Emerging evidence suggests that butyrate can strengthen the intestinal barrier, reducing the translocation of harmful bacteria and endotoxins into the bloodstream. This effect may indirectly benefit cardiovascular health by reducing systemic inflammation and oxidative stress.
While the current body of research on butyrate's cardiometabolic effects is encouraging, it is important to note that many studies have been conducted in animal models or in vitro settings. More large-scale, long-term clinical trials are needed to confirm these findings in humans and establish optimal dosing and administration methods for potential therapeutic applications.
Existing Butyrate Supplementation Strategies
01 Butyrate for improving cardiometabolic health
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid, has been found to have beneficial effects on cardiometabolic health. It can improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and regulate lipid metabolism, potentially lowering the risk of cardiovascular diseases and metabolic disorders.- Butyrate supplementation for cardiometabolic health: Butyrate supplementation has shown potential benefits for cardiometabolic health. It may help improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and support gut health, which are all factors contributing to better cardiovascular and metabolic outcomes. Butyrate can be administered in various forms, including oral supplements or through dietary interventions that promote its production in the gut.
- Butyrate-producing bacteria for metabolic disorders: Probiotic formulations containing butyrate-producing bacteria have been developed to address metabolic disorders. These bacteria can colonize the gut and produce butyrate in situ, potentially improving metabolic parameters such as glucose tolerance, lipid profiles, and body weight regulation. This approach leverages the gut microbiome's role in cardiometabolic health.
- Butyrate derivatives for targeted delivery: Novel butyrate derivatives have been developed to enhance the delivery and efficacy of butyrate for cardiometabolic health. These derivatives may have improved stability, absorption, or tissue-specific targeting compared to free butyrate. Such modifications aim to overcome the limitations of butyrate's rapid metabolism and poor bioavailability, potentially leading to more effective treatments for cardiometabolic disorders.
- Combination therapies with butyrate for cardiometabolic health: Combination therapies that include butyrate along with other active ingredients have been explored for comprehensive cardiometabolic health benefits. These combinations may include other short-chain fatty acids, antioxidants, or specific nutrients that work synergistically with butyrate to improve various aspects of cardiovascular and metabolic function.
- Butyrate in personalized nutrition for cardiometabolic health: Personalized nutrition approaches incorporating butyrate or butyrate-promoting strategies have been developed for cardiometabolic health. These approaches consider individual genetic, metabolic, and microbiome profiles to tailor dietary recommendations or supplement regimens that optimize butyrate production or utilization for improved cardiometabolic outcomes.
02 Butyrate-producing bacteria for gut health
Certain probiotic strains that produce butyrate in the gut have been identified as potential therapeutic agents for improving cardiometabolic health. These bacteria can enhance the gut barrier function, modulate the immune system, and contribute to overall metabolic homeostasis.Expand Specific Solutions03 Butyrate derivatives for targeted delivery
Novel butyrate derivatives and formulations have been developed to enhance the delivery and efficacy of butyrate in improving cardiometabolic health. These modifications aim to increase bioavailability, stability, and tissue-specific targeting of butyrate compounds.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination therapies with butyrate
Combining butyrate or butyrate-producing compounds with other active ingredients has shown synergistic effects in improving various aspects of cardiometabolic health. These combinations may include other short-chain fatty acids, antioxidants, or specific nutrients that complement butyrate's actions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Butyrate in metabolic syndrome management
Research has focused on the potential of butyrate and related compounds in managing metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Butyrate supplementation or stimulation of endogenous butyrate production has shown promise in addressing multiple components of metabolic syndrome simultaneously.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Butyrate Research and Development
The research on butyrate's role in cardiometabolic health is in a growth phase, with increasing market potential as awareness of gut health's impact on overall wellness rises. The global market for gut health products is expanding rapidly, driven by consumer interest in preventive health measures. Technologically, the field is advancing but still evolving, with varying levels of maturity among key players. Companies like Nestlé SA, DSM IP Assets BV, and Seed Health, Inc. are at the forefront, investing in research and product development. Academic institutions such as The University of Chicago and Zhejiang University are contributing significant research, while pharmaceutical companies like Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corp. are exploring therapeutic applications. This diverse ecosystem of players indicates a dynamic and competitive landscape with ample room for innovation and market growth.
Société des Produits Nestlé SA
Seed Health, Inc.
Innovative Butyrate Delivery Mechanisms
- Development of oral, systemically bioavailable butyrate conjugates with amino acids like serine, threonine, and tyrosine, which enhance bioavailability and allow butyrate to bypass initial metabolism, facilitating its transport into the bloodstream and across the blood-brain barrier.
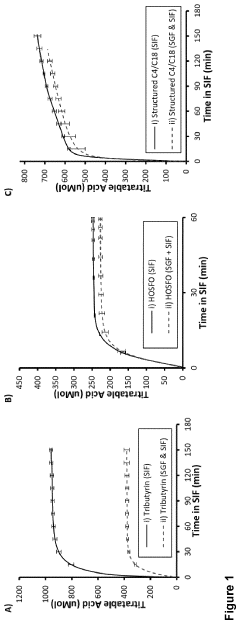
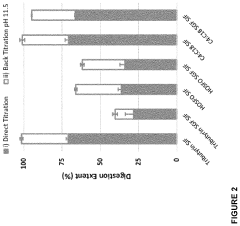
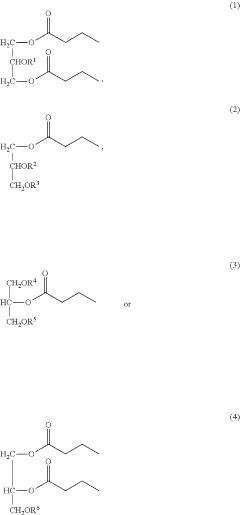
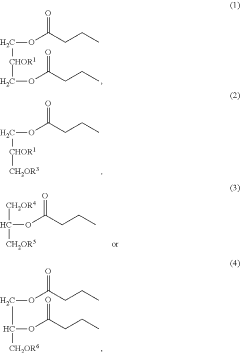
- Development of butyrate moiety containing triglycerides with improved organoleptic properties, such as 1,3-dibutyryl-2-palmitoylglycerol, which are synthesized through interesterification of tributyrin with high oleic sunflower oil, providing a dairy-free, cholesterol-free, and vegan alternative with reduced bitterness and odor, allowing effective delivery of butyric acid to the intestinal compartment.
Regulatory Landscape for Butyrate Supplements
The regulatory landscape for butyrate supplements is complex and evolving, reflecting the growing interest in their potential health benefits, particularly in cardiometabolic health. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies butyrate supplements as dietary supplements, falling under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This classification allows manufacturers to produce and sell butyrate supplements without prior FDA approval, provided they comply with good manufacturing practices and do not make disease treatment claims.
However, the regulatory framework becomes more intricate when considering the various forms of butyrate supplements available. Sodium butyrate, calcium butyrate, and tributyrin are among the common forms, each potentially subject to different regulatory scrutiny. Manufacturers must ensure that their products contain the ingredients listed on the label in the stated amounts and are free from contaminants.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) oversees the regulation of butyrate supplements. The EFSA requires scientific evidence to support any health claims made about these supplements. To date, no specific health claims related to butyrate and cardiometabolic health have been approved, highlighting the need for more robust clinical research in this area.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses quality control and safety measures. Manufacturers are required to report any serious adverse events associated with their products to the FDA in the United States. Similar pharmacovigilance systems exist in other regions, such as the European Union's EudraVigilance system.
As research into butyrate's role in cardiometabolic health progresses, regulatory bodies may need to reassess their approach. The potential for butyrate to be considered a novel food ingredient in some jurisdictions could lead to more stringent approval processes. Additionally, the growing interest in microbiome-based therapies may prompt regulatory agencies to develop new frameworks for assessing the safety and efficacy of butyrate and similar compounds.
Internationally, regulations vary significantly. Some countries may classify butyrate supplements as pharmaceuticals, requiring more rigorous clinical trials and approval processes. This regulatory diversity creates challenges for global distribution and marketing of butyrate supplements, necessitating careful navigation of different regulatory environments.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
When considering the safety and efficacy of butyrate supplementation for cardiometabolic health, several key factors must be taken into account. Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut bacteria, has shown promising results in preclinical and clinical studies. However, its widespread use as a therapeutic agent requires careful evaluation of potential risks and benefits.
Safety considerations for butyrate supplementation are generally favorable. Natural production of butyrate in the gut is well-tolerated, and exogenous supplementation has shown minimal adverse effects in most studies. Common side effects, when reported, are typically mild and include gastrointestinal discomfort, bloating, and flatulence. These effects are often transient and dose-dependent, suggesting that proper dosing strategies can mitigate potential issues.
Long-term safety data for butyrate supplementation is limited, necessitating further research to establish its safety profile for extended use. Additionally, interactions with medications and other supplements should be carefully evaluated, particularly in patients with pre-existing cardiometabolic conditions who may be on multiple therapies.
Efficacy considerations for butyrate in supporting cardiometabolic health are promising but require further validation. Preclinical studies have demonstrated butyrate's potential to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and enhance lipid metabolism. These effects are thought to be mediated through various mechanisms, including modulation of gut microbiota, regulation of gene expression, and improvement of intestinal barrier function.
Clinical studies, while limited in number and scale, have shown encouraging results. Some trials have reported improvements in markers of insulin resistance, lipid profiles, and body composition following butyrate supplementation. However, the magnitude of these effects and their long-term sustainability remain areas of active investigation.
Dosage and delivery methods are critical factors in determining butyrate's efficacy. The optimal dose for cardiometabolic benefits has not been firmly established, and may vary depending on the specific health outcome targeted. Various delivery systems, including encapsulated forms and prodrugs, are being explored to enhance butyrate's bioavailability and targeted delivery to specific tissues.
Individual variability in response to butyrate supplementation is an important consideration. Factors such as baseline gut microbiome composition, diet, and genetic background may influence the efficacy of butyrate interventions. Personalized approaches, potentially incorporating microbiome analysis and metabolic profiling, may be necessary to optimize treatment outcomes.
In conclusion, while butyrate shows promise for supporting cardiometabolic health, careful consideration of safety and efficacy is essential. Ongoing research is needed to fully elucidate the long-term effects, optimal dosing strategies, and potential interactions of butyrate supplementation. As the field advances, a balanced approach considering both the potential benefits and risks will be crucial in determining the role of butyrate in cardiometabolic health management.