The Future of Butyrate in Functional Foods
Butyrate in Functional Foods: Background and Objectives
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid, has emerged as a significant player in the realm of functional foods, garnering increased attention from researchers and food industry professionals alike. The evolution of butyrate in functional foods can be traced back to the early 2000s when scientists began to uncover its potential health benefits. As research progressed, the understanding of butyrate's role in gut health, inflammation reduction, and metabolic regulation has expanded considerably.
The primary objective of incorporating butyrate into functional foods is to harness its therapeutic properties and deliver them to consumers in a palatable and convenient form. This goal aligns with the growing consumer demand for foods that not only provide nutrition but also offer specific health benefits. The development of butyrate-enhanced functional foods aims to address various health concerns, including digestive disorders, inflammatory conditions, and metabolic syndromes.
The technological evolution in this field has been driven by the need to overcome butyrate's inherent limitations, such as its strong odor and rapid metabolism in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Initial efforts focused on simple supplementation, but as the field progressed, more sophisticated delivery systems were developed. These include microencapsulation techniques, targeted release formulations, and the use of butyrate-producing bacteria as probiotics.
Market trends indicate a rising interest in gut health and microbiome-modulating foods, creating a favorable environment for butyrate-enhanced products. This has led to increased research and development efforts by both academic institutions and food industry players. The global functional food market, valued at $177.7 billion in 2019, is expected to reach $267.9 billion by 2027, with gut health products playing a significant role in this growth.
Current technological challenges in butyrate incorporation include maintaining stability during food processing, ensuring targeted delivery to the colon, and masking its unpleasant sensory properties. Overcoming these hurdles is crucial for the widespread adoption of butyrate in functional foods. Additionally, regulatory considerations and the need for clinical validation of health claims present further challenges that need to be addressed.
Looking ahead, the future of butyrate in functional foods appears promising. Emerging research is exploring novel applications beyond gut health, including potential benefits for brain function, cardiovascular health, and cancer prevention. As technology advances and consumer awareness grows, butyrate is poised to become a key ingredient in the next generation of functional foods, offering targeted health benefits and contributing to the broader trend of personalized nutrition.
Market Analysis for Butyrate-Enhanced Foods
The market for butyrate-enhanced functional foods is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of gut health and its impact on overall well-being. Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut bacteria during fiber fermentation, has gained attention for its potential health benefits, including improved digestive health, enhanced immune function, and possible anti-inflammatory properties.
The global functional food market, valued at approximately $260 billion in 2022, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% through 2028. Within this broader market, butyrate-enhanced foods are carving out a niche, with particular interest in dairy products, cereals, and beverages fortified with butyrate or its precursors.
Consumer demand for butyrate-enhanced foods is primarily driven by health-conscious individuals seeking natural ways to improve their gut health. This trend aligns with the growing popularity of probiotics and prebiotics, as consumers become more educated about the importance of a balanced gut microbiome. Market research indicates that over 60% of consumers are willing to pay a premium for foods with proven health benefits, creating a favorable environment for butyrate-enhanced products.
The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a key market for butyrate-enhanced foods, with Japan and South Korea leading in product innovation and consumer adoption. In North America and Europe, the market is seeing steady growth, particularly in the natural and organic food sectors. Major food and beverage companies are investing in research and development to create palatable and effective butyrate-enhanced products, recognizing the potential for long-term market growth.
Challenges in the market include the need for more clinical studies to substantiate health claims, potential regulatory hurdles, and the development of stable, palatable formulations. The distinct odor and taste of butyrate pose challenges in product development, driving innovation in encapsulation and delivery technologies.
Despite these challenges, the market outlook for butyrate-enhanced foods remains positive. Industry analysts predict that the segment could reach a market value of $1.5 billion by 2025, with potential for further growth as research continues to uncover new health benefits and applications for butyrate in functional foods.
Current Challenges in Butyrate Incorporation
Despite the promising potential of butyrate in functional foods, several significant challenges hinder its widespread incorporation. One of the primary obstacles is the unpleasant organoleptic properties of butyrate, particularly its strong, rancid odor and taste. This characteristic makes it difficult to incorporate butyrate into food products without compromising their sensory appeal, which is crucial for consumer acceptance.
Another major challenge is the stability of butyrate during food processing and storage. Butyrate is a volatile compound that can easily degrade or evaporate under various conditions, such as high temperatures, exposure to light, or oxidation. This instability poses significant hurdles in maintaining the desired concentration of butyrate in functional foods throughout their shelf life, potentially reducing their efficacy and value.
The bioavailability of butyrate presents another complex issue. When consumed orally, butyrate is rapidly absorbed in the upper gastrointestinal tract, limiting its beneficial effects in the colon where it is most needed. Developing effective delivery systems that can protect butyrate and ensure its targeted release in the colon remains a significant technological challenge.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape surrounding the use of butyrate in functional foods is still evolving. Different countries have varying regulations regarding the classification and permissible use of butyrate as a food ingredient or additive. This regulatory uncertainty can impede product development and market entry for butyrate-enriched functional foods.
The cost-effectiveness of butyrate incorporation is also a considerable challenge. High-quality, food-grade butyrate can be expensive to produce, and the additional processing required to overcome its sensory and stability issues further increases production costs. This economic factor can limit the commercial viability of butyrate-enriched functional foods, especially in price-sensitive markets.
Lastly, there is a need for more comprehensive human clinical trials to fully establish the efficacy and safety of butyrate-enriched functional foods. While animal studies and limited human trials have shown promising results, larger-scale, long-term studies are necessary to convince both regulatory bodies and consumers of the benefits and safety of these products. The lack of such extensive clinical evidence currently hampers the widespread acceptance and adoption of butyrate in functional foods.
Existing Butyrate Delivery Technologies
01 Butyrate as a therapeutic agent
Butyrate is explored as a potential therapeutic agent for various health conditions. It has shown promise in treating inflammatory disorders, metabolic diseases, and gastrointestinal issues. Research indicates that butyrate may have beneficial effects on gut health, immune function, and cellular metabolism.- Butyrate as a therapeutic agent: Butyrate is being investigated as a potential therapeutic agent for various health conditions. It has shown promise in treating inflammatory disorders, metabolic diseases, and certain types of cancer. Research suggests that butyrate may have anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and epigenetic effects, making it a versatile compound for medical applications.
- Butyrate in gut health and microbiome modulation: Butyrate plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health and modulating the gut microbiome. It serves as an energy source for colonic epithelial cells and has been shown to enhance intestinal barrier function. Studies indicate that butyrate supplementation may help in managing gastrointestinal disorders and improving overall gut health by promoting beneficial bacteria growth.
- Butyrate production by microorganisms: Various microorganisms, particularly certain strains of bacteria, are capable of producing butyrate through fermentation processes. Research is focused on identifying and optimizing these microbial strains for enhanced butyrate production. This approach has potential applications in the development of probiotics, functional foods, and industrial production of butyrate.
- Butyrate in animal nutrition and livestock management: Butyrate supplementation in animal feed has shown benefits in livestock management. It has been found to improve growth performance, enhance gut health, and reduce the need for antibiotics in animal husbandry. Research is ongoing to optimize butyrate formulations and delivery methods for various animal species.
- Butyrate derivatives and delivery systems: Development of butyrate derivatives and novel delivery systems aims to enhance the stability, bioavailability, and targeted release of butyrate. These innovations include encapsulation techniques, prodrug formulations, and controlled-release mechanisms. Such advancements are crucial for improving the efficacy of butyrate-based therapies and expanding their potential applications.
02 Butyrate production in the gut microbiome
Studies focus on enhancing butyrate production in the gut microbiome. This involves investigating the role of specific bacteria in butyrate synthesis, developing prebiotic compounds to stimulate butyrate-producing bacteria, and exploring dietary interventions to increase butyrate levels in the intestine.Expand Specific Solutions03 Butyrate derivatives and formulations
Research is conducted on developing novel butyrate derivatives and formulations to improve its bioavailability and targeted delivery. This includes creating prodrugs, encapsulation techniques, and controlled-release systems to enhance the therapeutic potential of butyrate.Expand Specific Solutions04 Industrial applications of butyrate
Butyrate and its derivatives find applications in various industrial processes. These include their use as flavoring agents, solvents, and intermediates in the production of plastics, textiles, and pharmaceuticals. Research focuses on improving production methods and exploring new industrial uses for butyrate compounds.Expand Specific Solutions05 Butyrate in animal nutrition and agriculture
Butyrate is investigated for its potential benefits in animal nutrition and agriculture. Studies explore its use as a feed additive to improve growth performance, gut health, and disease resistance in livestock. Additionally, research examines the role of butyrate in plant growth promotion and soil health enhancement.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Butyrate Functional Food Industry
The butyrate functional food market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing consumer awareness of gut health benefits. The market size is expanding, with major players like Nestlé, Reckitt Benckiser, and Baxter International investing in research and development. Technological maturity varies, with companies at different stages of innovation. Zhejiang University, The University of Chicago, and Ghent University are contributing to academic research, while PharmaBiome AG and Clasado Research Services are focusing on commercial applications. Companies like Südzucker AG and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. are exploring industrial-scale production methods, indicating a trend towards scalability and cost-effectiveness in butyrate production for functional foods.
Société des Produits Nestlé SA
Südzucker AG
Innovative Approaches in Butyrate Formulation
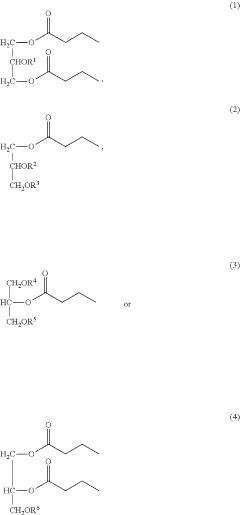
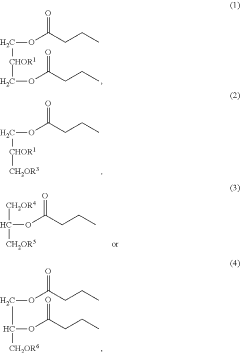
- Development of oral, systemically bioavailable butyrate conjugates with amino acids like serine, threonine, and tyrosine, which enhance bioavailability and allow butyrate to bypass initial metabolism, facilitating its transport into the bloodstream and across the blood-brain barrier.
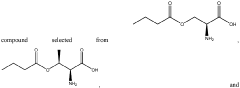
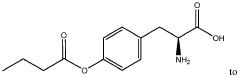
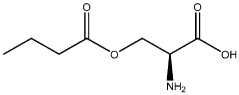
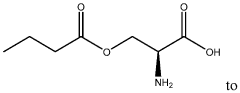
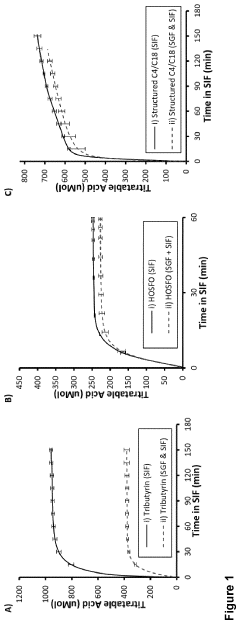
- Development of butyrate moiety containing triglycerides with improved organoleptic properties, such as 1,3-dibutyryl-2-palmitoylglycerol, which are synthesized through interesterification of tributyrin with high oleic sunflower oil, providing a dairy-free, cholesterol-free, and vegan alternative with reduced bitterness and odor, allowing effective delivery of butyric acid to the intestinal compartment.
Regulatory Framework for Butyrate in Foods
The regulatory framework for butyrate in foods is a complex and evolving landscape that plays a crucial role in shaping the future of functional foods. As butyrate gains recognition for its potential health benefits, regulatory bodies worldwide are working to establish guidelines for its use in food products.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of food additives and functional ingredients. Currently, butyrate is not explicitly listed as a Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) substance. However, certain forms of butyrate, such as tributyrin, have been granted GRAS status for specific applications. Manufacturers seeking to incorporate butyrate into functional foods must navigate the FDA's premarket approval process or pursue a GRAS notification pathway.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has a more stringent approach to novel food ingredients. Butyrate and its derivatives would likely fall under the Novel Food Regulation (EU) 2015/2283, requiring a comprehensive safety assessment before market authorization. This process involves submitting detailed scientific evidence on the safety and proposed uses of butyrate in food products.
In Asia, regulatory frameworks vary significantly between countries. Japan's Foods for Specified Health Uses (FOSHU) system provides a potential pathway for butyrate-enhanced functional foods, but requires extensive clinical data to support health claims. China's State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) has been increasingly focused on functional food regulations, and any butyrate-based products would need to comply with their evolving standards.
Globally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the FAO and WHO, provides international food standards that influence national regulations. While butyrate is not currently addressed in Codex standards, future developments may lead to the establishment of specific guidelines for its use in functional foods.
A key challenge in the regulatory landscape is the classification of butyrate-containing products. Depending on the concentration and intended use, these products may be categorized as conventional foods, dietary supplements, or even borderline pharmaceutical products. This classification significantly impacts the regulatory requirements and marketing possibilities.
As research on butyrate's health benefits continues to expand, regulatory bodies are likely to refine their approaches. Industry stakeholders and researchers are advocating for clearer guidelines and streamlined approval processes for butyrate-enhanced functional foods. The future regulatory framework will need to balance consumer safety with innovation, potentially leading to the development of specific regulations for butyrate and similar bioactive compounds in functional foods.
Consumer Acceptance and Education Strategies
The successful integration of butyrate into functional foods hinges on consumer acceptance and effective education strategies. As butyrate gains traction in the functional food market, it is crucial to address potential barriers to consumer adoption and implement targeted educational initiatives.
Consumer acceptance of butyrate-enhanced functional foods may face challenges due to unfamiliarity with the compound and its benefits. Many consumers are unaware of butyrate's role in gut health and its potential impact on overall well-being. To overcome this hurdle, food manufacturers and marketers must develop clear, concise messaging that highlights the specific health benefits of butyrate in easily understandable terms.
Taste and sensory attributes play a significant role in consumer acceptance. Butyrate's naturally pungent odor and taste can be off-putting to some consumers. Therefore, food scientists and product developers must focus on masking or neutralizing these sensory characteristics without compromising the compound's efficacy. Innovative formulation techniques and flavor masking technologies will be essential in creating palatable butyrate-enriched functional foods.
Education strategies should focus on raising awareness about the importance of gut health and the role of butyrate in maintaining a healthy microbiome. This can be achieved through various channels, including social media campaigns, informative packaging, and partnerships with healthcare professionals and nutritionists. Engaging influencers and thought leaders in the health and wellness space can help amplify the message and lend credibility to butyrate-enhanced products.
Transparency in labeling and marketing is crucial for building consumer trust. Clear information about the source of butyrate, its production methods, and any potential side effects should be readily available to consumers. This transparency will help address any concerns about safety and efficacy, particularly for those with specific dietary restrictions or health conditions.
Targeted education efforts should also focus on different consumer segments, tailoring messages to address the specific needs and interests of various demographics. For example, athletes may be interested in butyrate's potential role in improving exercise performance, while older adults might be more concerned with its impact on cognitive function and digestive health.
Collaborations between food companies, research institutions, and health organizations can further enhance consumer education efforts. By supporting and disseminating scientific research on butyrate's health benefits, these partnerships can provide credible, evidence-based information to consumers and healthcare professionals alike.