How to Increase Butyrate in Gut: Nutritional and Lifestyle Modifications
Butyrate Production Mechanisms and Targets
Butyrate production in the gut is primarily driven by the fermentation of dietary fibers by specific gut bacteria. The main mechanisms involve the breakdown of complex carbohydrates that are resistant to digestion in the upper gastrointestinal tract. These fibers reach the colon, where they serve as substrates for bacterial fermentation, resulting in the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), including butyrate.
The primary targets for increasing butyrate production are the butyrate-producing bacteria in the gut microbiome. These include species from the Firmicutes phylum, such as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Eubacterium rectale, and Roseburia species. These bacteria possess specific enzymes and metabolic pathways that enable them to convert complex carbohydrates into butyrate.
One key mechanism involves the butyryl-CoA:acetate CoA-transferase pathway, which is the predominant route for butyrate synthesis in the human gut. This pathway utilizes acetate as a co-substrate, highlighting the importance of cross-feeding interactions among different bacterial species in the gut ecosystem.
Another important target is the stimulation of bacterial growth and activity through the provision of appropriate substrates. Resistant starches, inulin, and other fermentable fibers serve as crucial energy sources for butyrate-producing bacteria. By increasing the availability of these substrates, it is possible to enhance the population and metabolic activity of butyrate-producing microorganisms.
The gut environment itself is also a critical target for optimizing butyrate production. Factors such as pH, transit time, and the presence of other metabolites can significantly influence the growth and activity of butyrate-producing bacteria. Maintaining a slightly acidic pH in the colon, for instance, can favor the growth of butyrate producers over potentially harmful bacteria.
Furthermore, the mucus layer of the gut epithelium serves as an important niche for many butyrate-producing bacteria. Strategies that support the integrity of this mucus layer can indirectly promote butyrate production by providing a favorable habitat for these beneficial microorganisms.
Lastly, the host's genetic factors and immune system play a role in shaping the gut microbiome composition and, consequently, butyrate production. Targeting the host-microbe interactions through dietary interventions or lifestyle modifications can potentially modulate these factors to create a more favorable environment for butyrate-producing bacteria.
Market Analysis for Gut Health Products
The gut health products market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of the importance of gut health and its impact on overall well-being. This market encompasses a wide range of products, including probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and other dietary supplements aimed at improving gut microbiome balance and function.
The global gut health products market was valued at approximately $36 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $66 billion by 2026, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.9% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to factors such as rising health consciousness, growing prevalence of digestive disorders, and increasing research on the gut-brain axis.
North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, dominates the market due to high consumer awareness and a well-established health and wellness industry. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to witness the fastest growth rates in the coming years.
The market is segmented into various product categories, with probiotics leading the pack. Probiotic supplements and probiotic-fortified foods and beverages account for the largest market share, driven by their well-established benefits for digestive health. Prebiotics, which serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria, are gaining traction as consumers become more educated about their role in supporting a healthy microbiome.
Key players in the gut health products market include multinational corporations such as Danone, Nestlé, and Yakult Honsha, as well as specialized companies like Chr. Hansen, DuPont, and BioGaia. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative products and expand their market presence.
Consumer trends indicate a growing preference for natural and plant-based gut health solutions. This has led to an increase in the development of products containing plant-based probiotics and prebiotics, as well as fermented foods and beverages. Additionally, personalized nutrition is emerging as a significant trend, with companies offering customized gut health solutions based on individual microbiome profiles.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth, as consumers have become more health-conscious and interested in products that support immune function, which is closely linked to gut health. This has resulted in increased demand for gut health products and a surge in online sales channels for these products.
Current Challenges in Butyrate Enhancement
Despite the growing recognition of butyrate's importance in gut health, several challenges persist in effectively increasing its levels through nutritional and lifestyle modifications. One primary obstacle is the variability in individual gut microbiomes, which significantly influences butyrate production. The complex interplay between diet, lifestyle factors, and the gut ecosystem makes it difficult to predict and consistently enhance butyrate levels across diverse populations.
Another challenge lies in the limited understanding of the optimal dietary composition for maximizing butyrate production. While high-fiber diets are generally associated with increased butyrate levels, the specific types and combinations of fibers that yield the most significant benefits remain unclear. Moreover, the bioavailability and effectiveness of different butyrate precursors in various food sources are not fully elucidated, complicating dietary recommendations.
The modern Western diet, characterized by low fiber intake and high consumption of processed foods, presents a significant hurdle in butyrate enhancement efforts. Overcoming ingrained dietary habits and promoting sustained changes in eating patterns is a complex task that requires addressing both individual behaviors and broader societal factors.
Furthermore, the impact of lifestyle factors such as stress, sleep patterns, and physical activity on butyrate production is not yet fully understood. While these factors are known to influence gut health, their specific effects on butyrate levels and the mechanisms involved require further investigation.
The lack of standardized, non-invasive methods for measuring butyrate levels in the gut poses a challenge in assessing the effectiveness of interventions. Current techniques often involve invasive procedures or rely on indirect markers, limiting the ability to conduct large-scale studies and provide personalized recommendations.
Additionally, the potential interactions between butyrate-enhancing strategies and existing medical conditions or medications are not well-characterized. This gap in knowledge raises concerns about the safety and efficacy of butyrate enhancement approaches in certain patient populations.
Lastly, the translation of research findings into practical, sustainable lifestyle modifications remains a significant challenge. Developing evidence-based, user-friendly guidelines that can be easily adopted by the general public while accounting for individual variations in diet, lifestyle, and gut microbiome composition is a complex task that requires ongoing research and refinement.
Existing Strategies for Butyrate Increase
01 Butyrate production and regulation
Methods and compositions for increasing butyrate production in the gut microbiome. This includes strategies for enhancing butyrate-producing bacteria and regulating butyrate levels through dietary interventions or probiotic supplementation.- Butyrate production and regulation: Methods and compositions for increasing butyrate production in the gut microbiome. This includes strategies for enhancing butyrate-producing bacteria and regulating butyrate levels through dietary interventions or probiotic supplementation.
- Butyrate in metabolic disorders: The role of butyrate in treating metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes. Research focuses on how butyrate levels affect metabolism and potential therapeutic applications.
- Butyrate and gut health: Investigations into the relationship between butyrate levels and gut health, including its effects on intestinal barrier function, inflammation, and the prevention of gastrointestinal diseases.
- Butyrate measurement and analysis: Development of methods and technologies for accurately measuring and analyzing butyrate levels in biological samples, including blood, feces, and gut microbiome samples.
- Butyrate in cancer research: Exploration of butyrate's potential anti-cancer properties and its role in cancer prevention and treatment, particularly in colorectal cancer. Studies focus on how butyrate levels affect cancer cell growth and apoptosis.
02 Butyrate in metabolic health
The role of butyrate in improving metabolic health, including its effects on insulin sensitivity, glucose metabolism, and lipid profiles. Research focuses on developing therapies that leverage butyrate's metabolic benefits.Expand Specific Solutions03 Butyrate in gut health and inflammation
Investigations into butyrate's anti-inflammatory properties and its impact on gut health. This includes studies on how butyrate levels affect intestinal barrier function, immune response, and the prevention of gastrointestinal disorders.Expand Specific Solutions04 Butyrate delivery systems
Development of novel delivery systems to enhance butyrate absorption and efficacy. This includes encapsulation technologies, controlled-release formulations, and targeted delivery methods to specific areas of the gastrointestinal tract.Expand Specific Solutions05 Butyrate in neurological health
Exploration of butyrate's potential neuroprotective effects and its role in brain health. Research focuses on how butyrate levels may influence cognitive function, neurodegenerative diseases, and mood disorders.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Gut Health Industry
The market for increasing butyrate in the gut through nutritional and lifestyle modifications is in a growth phase, driven by rising consumer awareness of gut health. The global prebiotic market, a key component in butyrate production, is expected to reach $9.5 billion by 2027. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Société des Produits Nestlé SA, Baxter International, Inc., and DSM IP Assets BV leading research and product development. These firms are investing in microbiome science and developing targeted prebiotics and synbiotics. Emerging players such as Seed Health, Inc. and PharmaBiome AG are bringing innovative approaches to market, focusing on personalized gut health solutions. The technology's maturity varies, with established dietary interventions coexisting with cutting-edge microbiome modulation techniques.
Seed Health, Inc.
PharmaBiome AG
Innovative Approaches in Butyrate Research
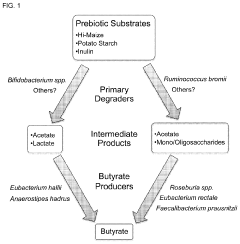
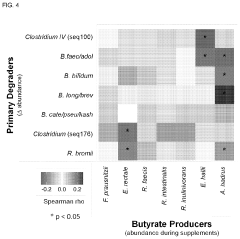
- Administering a carbohydrate source, such as resistant starch, in combination with specific bacteria like Bifidobacterium spp., Clostridium seq 176, or Ruminococcus bromii, to increase butyrate levels in the intestine, potentially treating or preventing diseases associated with low butyrate levels.
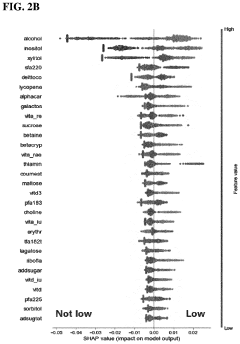
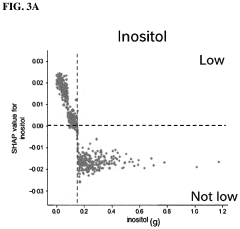
- A composition comprising inositol, erythritol, or sorbitol, optionally combined with polyphenols like coumestrol and quercetin, and vitamins such as Vitamin B5, B6, B12, A, or D, administered orally to enhance the growth of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, thereby treating or preventing related pathological conditions.
Regulatory Framework for Gut Health Claims
The regulatory framework for gut health claims is a complex and evolving landscape that significantly impacts the development and marketing of products aimed at increasing butyrate in the gut. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of health claims related to dietary supplements and functional foods. The FDA requires substantial scientific evidence to support any health claims made about gut health or butyrate production.
For products targeting butyrate production, manufacturers must adhere to strict guidelines when making health claims. These claims are typically categorized as structure/function claims, which describe the role of a nutrient or dietary ingredient intended to affect the structure or function of the body. However, they cannot claim to treat, prevent, or cure any disease.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating health claims. The EFSA has established a rigorous process for assessing scientific evidence supporting gut health claims. To date, no specific health claims related to butyrate production have been approved by the EFSA, highlighting the challenges in meeting the required scientific standards.
Globally, there is increasing scrutiny of probiotic and prebiotic products, which are often marketed for their potential to enhance butyrate production. Regulatory bodies are demanding more robust clinical trials and mechanistic studies to substantiate these claims. This has led to a surge in research focusing on the specific strains of bacteria and types of dietary fibers that may promote butyrate production.
The regulatory landscape also extends to the labeling and marketing of foods and supplements. Claims must be clear, truthful, and not misleading to consumers. This has prompted many companies to invest in consumer education initiatives to explain the complex relationship between diet, gut microbiome, and butyrate production.
As research in gut health and butyrate production continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. There is a growing recognition of the importance of personalized nutrition, which may lead to more nuanced regulations that account for individual variations in gut microbiome composition and metabolism. This could potentially open new avenues for tailored gut health products and claims.
Personalized Nutrition for Butyrate Optimization
Personalized nutrition for butyrate optimization represents a cutting-edge approach to enhancing gut health through targeted dietary interventions. This strategy recognizes that individual variations in genetics, microbiome composition, and lifestyle factors significantly influence butyrate production in the gut. By tailoring nutritional recommendations to an individual's unique profile, it becomes possible to maximize butyrate synthesis and its associated health benefits.
One key aspect of personalized nutrition for butyrate optimization involves the analysis of an individual's microbiome composition. Advanced sequencing techniques allow for the identification of specific bacterial strains present in the gut, particularly those known to produce butyrate. This information can be used to develop targeted prebiotic and probiotic strategies that support the growth and activity of these beneficial bacteria.
Dietary fiber intake plays a crucial role in butyrate production, but the type and quantity of fiber that is most effective can vary between individuals. Personalized nutrition plans may recommend specific fiber-rich foods or supplements based on an individual's gut microbiome profile and their ability to ferment different types of fiber. For example, some individuals may benefit more from resistant starch, while others may see better results with inulin or pectin.
Genetic factors also influence butyrate metabolism and should be considered in personalized nutrition strategies. Genetic testing can reveal variations in genes related to butyrate production and utilization, allowing for more precise dietary recommendations. For instance, individuals with certain genetic variants may require higher intake of specific nutrients that support butyrate synthesis or absorption.
Lifestyle factors, such as stress levels, sleep patterns, and physical activity, can significantly impact gut health and butyrate production. A comprehensive personalized nutrition plan for butyrate optimization would take these factors into account, potentially incorporating stress management techniques, sleep hygiene recommendations, and tailored exercise regimens to complement dietary interventions.
The implementation of personalized nutrition for butyrate optimization often involves the use of advanced technologies and data analytics. Wearable devices and mobile apps can track dietary intake, physical activity, and other relevant metrics, providing real-time feedback and allowing for continuous optimization of the nutrition plan. Machine learning algorithms can analyze this data alongside microbiome and genetic information to generate increasingly accurate and effective personalized recommendations over time.
As research in this field progresses, the potential for personalized nutrition to optimize butyrate production and improve overall gut health continues to grow. This approach holds promise not only for enhancing digestive health but also for addressing a wide range of systemic health issues linked to gut dysbiosis and low butyrate levels.