Latest Research on Butyrate’s Anti-Obesity Effects
Butyrate Research Background and Objectives
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut microbiota through fermentation of dietary fiber, has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential anti-obesity effects. The research on butyrate's role in obesity management has evolved from initial observations of its metabolic benefits to more comprehensive studies exploring its mechanisms of action and therapeutic potential.
The historical context of butyrate research dates back to the early 2000s when scientists first began to investigate the relationship between gut microbiota, their metabolites, and host metabolism. As obesity rates continued to rise globally, researchers sought novel approaches to combat this epidemic, leading to increased interest in the gut-brain axis and its influence on energy homeostasis.
Over the past decade, technological advancements in microbiome analysis and metabolomics have significantly accelerated our understanding of butyrate's functions. These developments have enabled researchers to elucidate the complex interactions between butyrate, gut microbiota, and host metabolism, paving the way for more targeted investigations into its anti-obesity effects.
The primary objectives of current butyrate research in the context of obesity are multifaceted. Firstly, researchers aim to fully characterize the mechanisms through which butyrate exerts its anti-obesity effects, including its impact on energy expenditure, appetite regulation, and adipose tissue metabolism. Secondly, there is a focus on identifying optimal strategies to increase butyrate production or delivery in the gut, whether through dietary interventions, probiotic supplementation, or direct butyrate administration.
Another key goal is to translate preclinical findings into human clinical trials, assessing the efficacy and safety of butyrate-based interventions for obesity management. This includes determining effective dosages, delivery methods, and potential synergistic effects with other therapeutic approaches.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring the broader implications of butyrate's effects on metabolic health, including its potential to mitigate obesity-related comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. This holistic approach aims to position butyrate not just as an anti-obesity agent, but as a comprehensive metabolic health modulator.
As the field progresses, there is also a growing emphasis on personalized approaches, recognizing that individual variations in gut microbiota composition and genetic factors may influence the effectiveness of butyrate-based interventions. This tailored strategy aligns with the broader trend towards precision medicine in obesity management.
In conclusion, the latest research on butyrate's anti-obesity effects represents a convergence of microbiology, nutrition, and metabolic science. By elucidating the intricate relationships between diet, gut microbiota, and host metabolism, this field holds promise for developing novel, targeted therapies to combat the global obesity epidemic.
Market Analysis of Anti-Obesity Solutions
The global anti-obesity market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing prevalence of obesity worldwide and growing awareness of its associated health risks. As of 2021, the market was valued at approximately $2.5 billion and is projected to reach $3.9 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.2% during this period.
The market for anti-obesity solutions can be segmented into pharmaceutical interventions, dietary supplements, and medical devices. Pharmaceutical interventions currently dominate the market, accounting for over 60% of the total market share. However, dietary supplements, including those targeting gut health and metabolism, are gaining traction due to their perceived safety and natural approach.
The latest research on butyrate's anti-obesity effects has sparked interest in the potential for gut microbiome-based solutions. This aligns with the growing consumer preference for natural and holistic approaches to weight management. The global probiotics market, which includes butyrate-producing strains, is expected to reach $94.48 billion by 2027, with a CAGR of 7.9%.
Geographically, North America leads the anti-obesity market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, represents the largest market due to its high obesity rates and advanced healthcare infrastructure. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years due to increasing disposable incomes and changing lifestyles.
Key market players in the anti-obesity sector include pharmaceutical giants like Novo Nordisk, Roche, and GlaxoSmithKline, as well as emerging biotech companies focusing on microbiome-based solutions. The potential of butyrate in obesity management has attracted attention from both established players and startups, leading to increased research and development investments in this area.
Consumer trends indicate a shift towards personalized nutrition and gut health solutions for weight management. This presents an opportunity for butyrate-based products to gain market share, especially if supported by robust clinical evidence. The growing interest in the gut-brain axis and its role in metabolism further supports the market potential for butyrate and other gut microbiome modulators.
Challenges in the anti-obesity market include stringent regulatory requirements, high development costs, and potential side effects of pharmaceutical interventions. These factors contribute to the growing appeal of dietary supplements and natural solutions, which face less regulatory scrutiny. However, the lack of standardization and quality control in the supplement industry remains a concern for both consumers and healthcare providers.
Current State of Butyrate Research in Obesity Treatment
Butyrate research in obesity treatment has gained significant momentum in recent years, with numerous studies highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent. The current state of research focuses on understanding the mechanisms by which butyrate exerts its anti-obesity effects and exploring various delivery methods to maximize its efficacy.
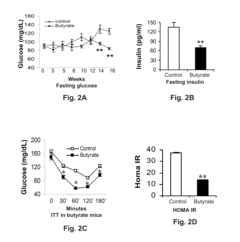
One of the primary areas of investigation is butyrate's role in modulating gut microbiota composition and function. Studies have shown that butyrate supplementation can increase the abundance of beneficial bacteria, such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, while reducing the prevalence of potentially harmful microbes. This shift in microbial composition is associated with improved metabolic health and reduced obesity risk.
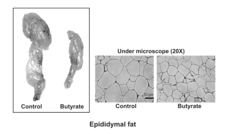
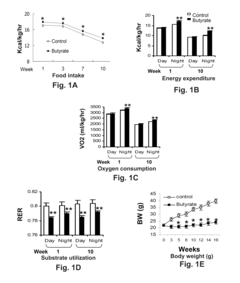
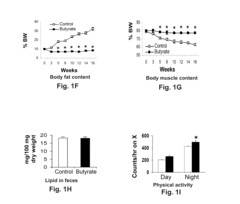
Researchers are also exploring butyrate's impact on energy metabolism and fat storage. Recent findings suggest that butyrate can enhance mitochondrial function and promote fatty acid oxidation in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle. These effects contribute to increased energy expenditure and reduced fat accumulation, making butyrate a promising candidate for obesity management.
Another critical aspect of current research is the investigation of butyrate's effects on appetite regulation and food intake. Studies have demonstrated that butyrate can modulate the expression of appetite-regulating hormones, such as leptin and ghrelin, potentially leading to reduced caloric intake and improved satiety. This line of research is particularly important for developing strategies to address overeating and promote sustainable weight loss.
Inflammation and oxidative stress are key contributors to obesity-related complications. Recent studies have shown that butyrate possesses potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which may help mitigate obesity-induced inflammation and oxidative damage. These findings suggest that butyrate could play a role in preventing or treating obesity-related comorbidities, such as insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease.
The development of novel butyrate delivery systems is another active area of research. Traditional oral supplementation of butyrate is limited by its rapid absorption in the upper gastrointestinal tract. To overcome this challenge, scientists are exploring various formulations, including microencapsulation, nanoparticle-based delivery, and prodrug approaches, to enhance butyrate's bioavailability and targeted delivery to the colon.
Clinical trials investigating the efficacy of butyrate supplementation in obese individuals are ongoing. While preliminary results are promising, larger-scale studies are needed to establish optimal dosing regimens, long-term safety profiles, and potential synergistic effects with other therapeutic interventions.
Current Approaches to Butyrate-Based Obesity Interventions
01 Butyrate as an anti-obesity agent
Butyrate has been identified as a potential anti-obesity agent due to its ability to regulate metabolism and reduce fat accumulation. Research suggests that butyrate supplementation can help in weight management and improve overall metabolic health.- Butyrate as an anti-obesity agent: Butyrate has been found to have anti-obesity effects by regulating metabolism, reducing fat accumulation, and improving insulin sensitivity. It may act by modulating gene expression related to lipid metabolism and energy expenditure.
- Butyrate in combination with other compounds: The anti-obesity effects of butyrate can be enhanced when combined with other compounds such as probiotics, prebiotics, or specific nutrients. These combinations may have synergistic effects on weight management and metabolic health.
- Butyrate delivery methods for anti-obesity treatment: Various delivery methods have been developed to enhance the efficacy of butyrate as an anti-obesity agent. These include encapsulation techniques, controlled-release formulations, and targeted delivery systems to improve bioavailability and effectiveness.
- Butyrate's effect on gut microbiota and obesity: Butyrate has been shown to positively influence gut microbiota composition, which in turn can contribute to its anti-obesity effects. It may promote the growth of beneficial bacteria and improve gut barrier function, leading to better metabolic health.
- Mechanisms of butyrate's anti-obesity action: Research has revealed various mechanisms through which butyrate exerts its anti-obesity effects. These include modulation of appetite-regulating hormones, increased energy expenditure, reduced inflammation, and improved glucose homeostasis.
02 Butyrate-producing probiotics for obesity treatment
Probiotics that produce butyrate have shown promise in treating obesity. These beneficial bacteria can increase butyrate levels in the gut, potentially leading to improved metabolic function and reduced fat storage.Expand Specific Solutions03 Butyrate in combination with other compounds for enhanced anti-obesity effects
Combining butyrate with other compounds, such as specific nutrients or bioactive substances, has been explored to enhance its anti-obesity effects. These combinations may work synergistically to improve metabolic health and promote weight loss.Expand Specific Solutions04 Butyrate's role in regulating appetite and energy expenditure
Research has shown that butyrate can influence appetite regulation and energy expenditure, which are crucial factors in obesity management. By modulating these processes, butyrate may help in reducing calorie intake and increasing energy utilization.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel delivery methods for butyrate in obesity treatment
Innovative delivery methods for butyrate have been developed to enhance its effectiveness in obesity treatment. These may include controlled-release formulations, targeted delivery systems, or novel compounds that can increase butyrate production in the body.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Butyrate and Anti-Obesity Research
The research on butyrate's anti-obesity effects is gaining momentum in a rapidly evolving market. The industry is in its growth phase, with increasing interest from both academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies. The market size is expanding as obesity remains a global health concern. Technologically, the field is progressing from basic research to potential therapeutic applications. Companies like Nestlé, Baxter International, and DSM IP Assets are actively involved, indicating a growing commercial interest. Academic institutions such as The University of Chicago and New York University are contributing significant research, while pharmaceutical companies like Japan Tobacco and Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma are exploring potential drug developments. This collaborative ecosystem suggests a maturing field with promising future applications.
DSM IP Assets BV
Seed Health, Inc.
Breakthrough Studies on Butyrate's Anti-Obesity Mechanisms
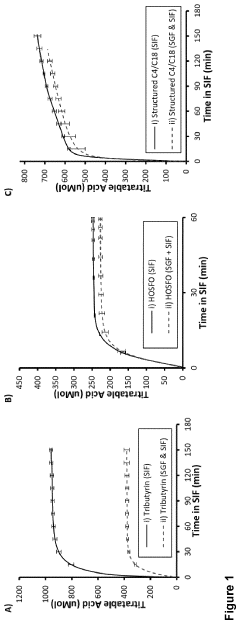
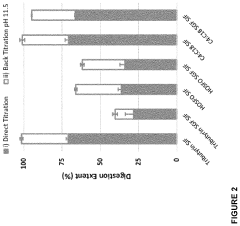
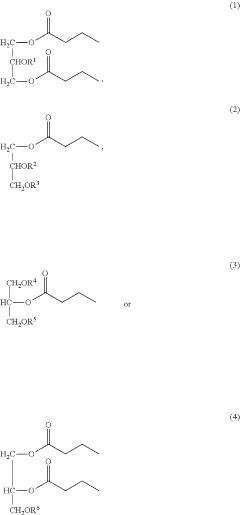
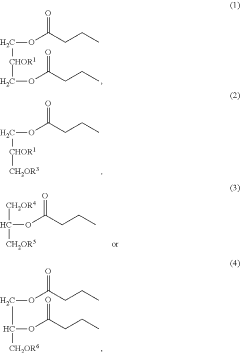
- Development of butyrate moiety containing triglycerides with improved organoleptic properties, such as 1,3-dibutyryl-2-palmitoylglycerol, which are synthesized through interesterification of tributyrin with high oleic sunflower oil, providing a dairy-free, cholesterol-free, and vegan alternative with reduced bitterness and odor, allowing effective delivery of butyric acid to the intestinal compartment.
- Chronic administration of dietary sodium butyrate, which inhibits histone deacetylases, enhances PGC-1α activity, leading to increased insulin sensitivity, reduced body weight, and improved metabolic parameters in non-ruminant mammals on a high-fat diet.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations for Butyrate Supplementation
The safety and efficacy of butyrate supplementation are critical considerations in its potential use as an anti-obesity intervention. Recent research has shown promising results regarding butyrate's effects on weight management and metabolic health, but several factors must be carefully evaluated before widespread implementation.
Safety considerations for butyrate supplementation primarily revolve around gastrointestinal tolerability and potential interactions with existing medications or health conditions. Some studies have reported mild gastrointestinal discomfort, including bloating and flatulence, in a subset of participants. However, these effects are generally transient and dose-dependent. Long-term safety data is still limited, necessitating further research to establish the optimal dosage and duration of supplementation.
Efficacy considerations focus on the bioavailability and delivery methods of butyrate. Oral supplementation faces challenges due to rapid absorption in the upper gastrointestinal tract, potentially limiting its effectiveness in reaching the colon where it exerts its primary effects. Researchers are exploring various formulations, including microencapsulation and targeted delivery systems, to enhance butyrate's bioavailability and ensure its release in the desired intestinal regions.
The optimal dosage for butyrate supplementation remains a subject of ongoing investigation. Studies have utilized a wide range of doses, typically between 4-10 grams per day, with varying results. Determining the most effective dose while minimizing potential side effects is crucial for maximizing the anti-obesity benefits of butyrate supplementation.
Individual variability in response to butyrate supplementation is another important consideration. Factors such as gut microbiome composition, diet, and genetic predisposition may influence the efficacy of butyrate in weight management. Personalized approaches, potentially involving microbiome analysis and tailored supplementation strategies, may be necessary to optimize outcomes.
The long-term sustainability of butyrate's anti-obesity effects also requires further investigation. While short-term studies have demonstrated promising results, the durability of these effects and the potential for adaptive responses over extended periods of supplementation need to be thoroughly evaluated.
Lastly, the integration of butyrate supplementation with other lifestyle interventions, such as diet and exercise, should be explored to determine potential synergistic effects and develop comprehensive anti-obesity strategies. This holistic approach may enhance the overall efficacy of butyrate supplementation in addressing obesity and related metabolic disorders.
Potential Applications in Personalized Nutrition
The latest research on butyrate's anti-obesity effects opens up exciting possibilities for personalized nutrition strategies. As our understanding of the gut microbiome's role in metabolism and weight management deepens, butyrate emerges as a key player in tailoring dietary interventions to individual needs.
One potential application lies in developing personalized prebiotic and probiotic supplements. By analyzing an individual's gut microbiome composition, nutritionists could recommend specific fiber-rich foods or prebiotic supplements that promote the growth of butyrate-producing bacteria. This approach would optimize butyrate production based on each person's unique microbial profile, potentially enhancing its anti-obesity effects.
Customized meal plans represent another promising avenue. Nutritionists could design diets rich in resistant starch and other butyrate-promoting compounds, taking into account an individual's genetic predisposition to obesity, current metabolic health, and gut microbiome status. These tailored meal plans would aim to maximize butyrate production and its beneficial effects on metabolism and appetite regulation.
The development of personalized functional foods enriched with butyrate or its precursors offers another exciting possibility. Food manufacturers could create products that cater to specific metabolic needs, potentially incorporating microencapsulated butyrate or engineered probiotics that enhance butyrate production in the gut. These products could be tailored to different age groups, activity levels, or specific health conditions related to obesity.
Wearable technology and mobile apps could play a crucial role in implementing personalized butyrate-based nutrition strategies. These tools could track dietary intake, physical activity, and even real-time markers of gut health, providing users with personalized recommendations to optimize their butyrate levels and support weight management goals.
In clinical settings, healthcare providers could use butyrate-focused personalized nutrition as part of comprehensive obesity treatment plans. By combining genetic testing, microbiome analysis, and metabolic profiling, clinicians could develop highly targeted interventions that leverage butyrate's anti-obesity effects alongside other therapeutic approaches.
As research in this field progresses, we may see the emergence of precision nutrition clinics specializing in butyrate-based interventions for obesity management. These clinics could offer comprehensive assessments and long-term personalized nutrition plans that evolve with an individual's changing health status and goals.