Innovative Methods for Butyrate Delivery Systems
Butyrate Delivery Background and Objectives
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential health benefits and therapeutic applications. The development of innovative methods for butyrate delivery systems represents a crucial area of research aimed at harnessing the full potential of this compound. Historically, butyrate has been recognized for its role in maintaining gut health and regulating various physiological processes.
The evolution of butyrate delivery systems has been driven by the need to overcome the limitations associated with traditional oral administration. These limitations include rapid absorption in the upper gastrointestinal tract, unpleasant taste, and poor bioavailability. As a result, researchers have been exploring novel approaches to enhance the targeted delivery and sustained release of butyrate throughout the gastrointestinal tract.
The primary objective of developing innovative butyrate delivery systems is to maximize its therapeutic efficacy while minimizing potential side effects. This involves designing delivery mechanisms that can protect butyrate from degradation in the stomach and small intestine, ensuring its release in the colon where it exerts its beneficial effects. Additionally, researchers aim to improve patient compliance by addressing issues related to taste and odor.
Recent technological advancements have paved the way for more sophisticated delivery systems, including microencapsulation, nanoparticle-based carriers, and pH-responsive formulations. These approaches offer the potential for controlled release, enhanced stability, and improved targeting of butyrate to specific regions of the gastrointestinal tract.
The development of innovative butyrate delivery systems also aligns with the growing interest in personalized medicine and targeted therapies. By tailoring delivery mechanisms to individual patient needs and specific disease conditions, researchers aim to optimize the therapeutic outcomes of butyrate supplementation.
Furthermore, the exploration of novel delivery methods extends beyond oral administration, with ongoing research into alternative routes such as rectal suppositories, enemas, and transdermal applications. These diverse approaches reflect the multifaceted nature of butyrate's potential applications and the need for versatile delivery solutions.
As research in this field progresses, the goals include not only enhancing the efficacy of butyrate delivery but also addressing scalability and cost-effectiveness to ensure widespread accessibility. The development of innovative delivery systems is expected to unlock new possibilities for butyrate in various therapeutic areas, including inflammatory bowel diseases, colorectal cancer prevention, and metabolic disorders.
Market Analysis for Butyrate Delivery Systems
The market for butyrate delivery systems has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of the health benefits associated with butyrate supplementation. This market encompasses various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and animal feed industries. The global butyrate market size was valued at approximately $329 million in 2020 and is projected to reach $425 million by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 4.5% during the forecast period.
The pharmaceutical sector represents a substantial portion of the butyrate delivery systems market, with applications in treating inflammatory bowel diseases, colorectal cancer, and other gastrointestinal disorders. The rising prevalence of these conditions, coupled with the growing body of research supporting butyrate's therapeutic potential, is fueling demand in this sector. Additionally, the nutraceutical industry is witnessing increased interest in butyrate supplements for gut health and overall well-being, contributing to market expansion.
In the animal feed industry, butyrate delivery systems are gaining traction as alternatives to antibiotic growth promoters. With the global push towards reducing antibiotic use in livestock, butyrate-based feed additives are becoming increasingly popular for improving animal gut health and performance. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions with stringent regulations on antibiotic use in animal husbandry, such as the European Union.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the butyrate delivery systems market, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure, higher consumer awareness, and stringent regulations favoring natural feed additives. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing disposable incomes, growing health consciousness, and rapid expansion of the animal feed industry in countries like China and India.
Key market players in the butyrate delivery systems industry include Kemin Industries, Innovad, Palital Feed Additives, and Nutriad (now part of Adisseo). These companies are focusing on developing innovative delivery technologies to enhance the stability and bioavailability of butyrate. Encapsulation techniques, such as microencapsulation and nanoencapsulation, are gaining prominence as they protect butyrate from degradation in the upper gastrointestinal tract and ensure targeted release in the colon.
The market is characterized by intense competition and ongoing research and development activities. Companies are investing in novel formulations and delivery mechanisms to differentiate their products and gain a competitive edge. Collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are also becoming more common, aiming to explore new therapeutic applications of butyrate and develop advanced delivery systems.
Current Challenges in Butyrate Delivery
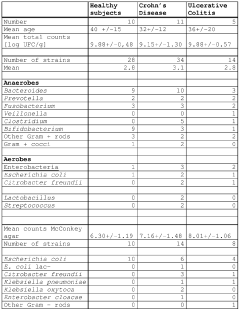
Butyrate delivery systems face several significant challenges that hinder their widespread application and efficacy. One of the primary obstacles is the rapid absorption and metabolism of butyrate in the upper gastrointestinal tract, which limits its availability in the colon where it exerts its beneficial effects. This premature absorption reduces the therapeutic potential of butyrate and necessitates higher doses, potentially leading to adverse effects.
Another major challenge is the unpleasant taste and odor of butyrate, which can significantly impact patient compliance and acceptability. The strong, rancid smell of butyrate makes it difficult to formulate into palatable oral dosage forms, limiting its use in clinical settings and consumer products.
The stability of butyrate in various delivery systems poses another hurdle. Butyrate is prone to degradation under acidic conditions, such as those found in the stomach, which can compromise its effectiveness. Developing stable formulations that can protect butyrate from degradation while ensuring its release at the target site remains a significant technical challenge.
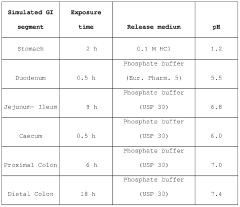
Furthermore, achieving controlled and targeted release of butyrate in the colon is complex. The diverse physiological conditions along the gastrointestinal tract, including varying pH levels and enzymatic activities, make it challenging to design delivery systems that can selectively release butyrate in the colon while remaining intact in the upper GI tract.
The low permeability of butyrate across intestinal epithelial cells also presents a barrier to its effective delivery. This limited absorption capacity necessitates the development of innovative strategies to enhance butyrate uptake and retention in the colon.
Additionally, the scalability and cost-effectiveness of butyrate delivery systems are significant concerns. Many promising delivery technologies developed in laboratory settings face challenges in scaling up for commercial production, often due to complex manufacturing processes or the use of expensive materials.
Regulatory hurdles also pose challenges for the development and approval of novel butyrate delivery systems. The classification of butyrate-based products as drugs, medical foods, or dietary supplements can impact the regulatory pathway and requirements for market entry, potentially slowing down the development process.
Lastly, the lack of standardized methods for evaluating the efficacy and safety of butyrate delivery systems hampers the comparison of different approaches and the translation of preclinical results to clinical applications. Developing robust and reproducible assessment protocols remains an important challenge in advancing butyrate delivery technologies.
Existing Butyrate Delivery Solutions
01 Encapsulation techniques for butyrate delivery
Various encapsulation methods are used to improve the delivery efficiency of butyrate. These techniques include microencapsulation, nanoencapsulation, and liposomal formulations. Encapsulation protects butyrate from degradation in the gastrointestinal tract and allows for controlled release, enhancing its bioavailability and therapeutic effects.- Encapsulation techniques for butyrate delivery: Various encapsulation methods are used to improve the delivery efficiency of butyrate. These techniques include microencapsulation, nanoencapsulation, and liposomal formulations. Encapsulation protects butyrate from degradation in the gastrointestinal tract and allows for controlled release, enhancing its bioavailability and therapeutic effects.
- pH-responsive delivery systems: pH-responsive delivery systems are developed to target butyrate release in specific regions of the gastrointestinal tract. These systems utilize pH-sensitive polymers or coatings that dissolve at specific pH levels, allowing for site-specific delivery of butyrate. This approach improves the efficiency of butyrate delivery to the desired location in the gut.
- Prodrug approaches for butyrate delivery: Prodrug strategies are employed to enhance the delivery efficiency of butyrate. These approaches involve chemically modifying butyrate to improve its stability, solubility, or permeability. The prodrug is then converted to active butyrate in the body, allowing for more efficient delivery and absorption.
- Combination with other delivery enhancers: Butyrate delivery systems are formulated with other delivery enhancers to improve efficiency. These may include permeation enhancers, mucoadhesive agents, or absorption promoters. The combination approach aims to overcome barriers to butyrate absorption and increase its bioavailability.
- Targeted delivery using nanocarriers: Nanocarrier-based systems are developed for targeted delivery of butyrate. These include nanoparticles, nanoemulsions, and nanofibers designed to improve the stability and delivery efficiency of butyrate. The nanocarriers can be functionalized to target specific cells or tissues, enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of butyrate.
02 Targeted delivery systems for butyrate
Targeted delivery systems are developed to enhance the efficiency of butyrate delivery to specific sites in the body. These systems utilize various mechanisms such as pH-responsive polymers, receptor-mediated targeting, and tissue-specific carriers. Targeted delivery improves the therapeutic index of butyrate by increasing its concentration at the desired site of action while minimizing systemic exposure.Expand Specific Solutions03 Prodrug approaches for butyrate delivery
Prodrug strategies are employed to enhance the delivery efficiency of butyrate. These approaches involve chemical modification of butyrate to improve its physicochemical properties, such as solubility and stability. The prodrug is designed to be metabolized into active butyrate upon reaching the target site, thereby increasing its bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination therapies for enhanced butyrate delivery
Combination therapies are explored to improve the delivery efficiency of butyrate. These approaches involve co-administration of butyrate with other compounds that can enhance its absorption, stability, or therapeutic effects. Examples include combining butyrate with absorption enhancers, enzyme inhibitors, or complementary therapeutic agents to achieve synergistic effects and improved delivery outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel formulation strategies for butyrate delivery
Innovative formulation strategies are developed to enhance the delivery efficiency of butyrate. These include the use of advanced drug delivery systems such as hydrogels, nanofibers, and smart polymers. Novel formulations aim to improve the stability, solubility, and controlled release properties of butyrate, leading to enhanced bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Butyrate Delivery Industry
The innovative methods for butyrate delivery systems market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing research into gut health and microbiome modulation. The market size is expanding, with potential applications in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and functional foods. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with varying degrees of maturity across different delivery approaches. Companies like DURECT Corp., Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and Roquette Frères SA are at the forefront, developing novel formulations and delivery mechanisms. Academic institutions such as Duke University and Texas A&M University are contributing significant research, while pharmaceutical companies like Zydus Lifesciences Ltd. and Baxter International, Inc. are exploring clinical applications. The competitive landscape is diverse, with a mix of established players and innovative startups vying for market share and technological breakthroughs.
DURECT Corp.
EyePoint Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Core Innovations in Butyrate Delivery
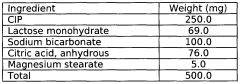
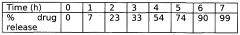
- A controlled release pharmaceutical dosage form using a polymeric mixture of a water-insoluble polymer and an indigestible water-soluble polysaccharide, such as ethyl cellulose and branched maltodextrin, which provides gastric resistance and site-specific drug release in the colon by utilizing enzyme degradation differences between the upper gastrointestinal tract and the colon, ensuring effective drug delivery even under pathophysiological conditions.
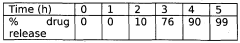
- A gastroretentive drug delivery system comprising a core of a drug and a gas generating agent coated with a novel pH-sensitive polymer, specifically formulated with methyl methacrylate, n-butyl methacrylate, and 4-vinyl pyridine, which swells at pH 3.5, allowing for controlled release in both sustained and pulsatile manners.
Regulatory Landscape for Butyrate Delivery
The regulatory landscape for butyrate delivery systems is complex and multifaceted, involving various agencies and guidelines across different regions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the development and approval of butyrate delivery methods. The FDA categorizes butyrate-based products depending on their intended use, which can range from dietary supplements to pharmaceutical drugs.
For dietary supplements, butyrate products fall under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This framework allows for a relatively streamlined path to market, provided manufacturers comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) and ensure product safety. However, strict limitations exist on the health claims that can be made without clinical evidence.
When butyrate delivery systems are developed for therapeutic purposes, they are subject to more rigorous regulatory scrutiny. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) oversees the approval process for new drug applications, which requires extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. This pathway is considerably more time-consuming and costly but allows for specific health claims if approved.
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) governs the approval of butyrate-based pharmaceuticals. The EMA's centralized procedure offers a single application process for marketing authorization across all EU member states. For dietary supplements, regulations vary by country, but generally fall under the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) guidelines.
Globally, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on innovative drug delivery systems, including those for butyrate. The International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) provides guidelines that aim to harmonize regulatory requirements across different regions, potentially streamlining the approval process for novel butyrate delivery methods.
As research continues to uncover the potential benefits of butyrate, regulatory agencies are adapting their frameworks to accommodate emerging delivery technologies. This includes considerations for targeted delivery systems, controlled-release formulations, and novel routes of administration. Manufacturers must navigate these evolving regulations carefully, ensuring compliance while pushing the boundaries of innovation in butyrate delivery.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
Safety and efficacy considerations are paramount when developing innovative methods for butyrate delivery systems. The primary concern is ensuring that the delivery system can effectively transport butyrate to the intended target site within the body while minimizing potential adverse effects.
One of the key safety considerations is the stability of the delivery system. Butyrate is a volatile compound that can easily degrade under certain conditions. Therefore, the delivery system must be designed to protect butyrate from premature degradation in the stomach and upper gastrointestinal tract. This often involves encapsulation techniques or the use of pH-sensitive polymers that release butyrate only when the appropriate conditions are met in the lower intestine.
The biocompatibility of the materials used in the delivery system is another critical safety aspect. Any carriers, coatings, or excipients employed must be non-toxic and well-tolerated by the body. This includes ensuring that these materials do not trigger immune responses or cause local irritation in the gastrointestinal tract.
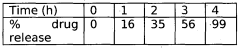
Efficacy considerations focus on the ability of the delivery system to release butyrate at the desired location and rate. Controlled release mechanisms are often employed to maintain therapeutic levels of butyrate over an extended period. This may involve the use of matrix systems, reservoir devices, or stimuli-responsive materials that can modulate butyrate release based on environmental cues.
The bioavailability of butyrate is a crucial factor in determining the efficacy of the delivery system. Innovative methods must address the challenge of enhancing butyrate absorption in the colon, where it exerts its primary beneficial effects. This may involve strategies such as increasing the residence time of butyrate in the colon or improving its permeability across the intestinal epithelium.
Potential interactions between the delivery system and the gut microbiome must also be considered. While butyrate is known to have positive effects on gut health, it is essential to ensure that the delivery method does not disrupt the delicate balance of the intestinal microbiota.
Long-term safety and efficacy studies are necessary to evaluate the chronic effects of butyrate supplementation using these innovative delivery systems. This includes monitoring for any potential systemic effects, as well as assessing the impact on gut health markers and overall well-being.
Regulatory considerations play a significant role in the development of butyrate delivery systems. Depending on the intended use and claims, these systems may be classified as drugs, medical devices, or dietary supplements, each with its own set of regulatory requirements for safety and efficacy demonstration.