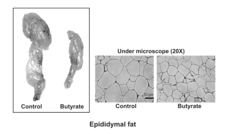
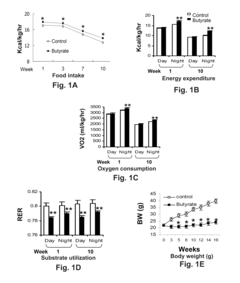
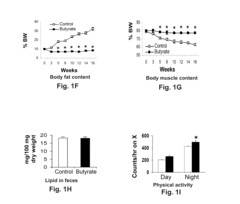
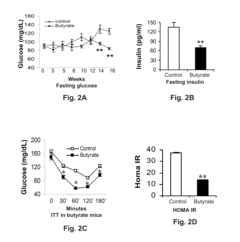
Comparative Analysis of Oral and Fiber-Derived Butyrate Supplementation in Obesity Management
Butyrate Supplementation Background and Objectives
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut microbiota through fermentation of dietary fiber, has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential role in obesity management. The evolution of butyrate supplementation as a therapeutic approach stems from the growing understanding of the gut-brain axis and its influence on metabolic health.
Historically, the focus on butyrate emerged from observations of its beneficial effects on colonic health and its role as an energy source for colonocytes. As research progressed, scientists uncovered butyrate's broader systemic impacts, including its potential to modulate energy metabolism, inflammation, and insulin sensitivity. This led to increased interest in exploring butyrate supplementation as a strategy for addressing obesity and related metabolic disorders.
The technological advancements in butyrate supplementation have followed two main paths: oral supplementation and fiber-derived butyrate production. Oral supplementation involves direct intake of butyrate or its derivatives, while fiber-derived approaches aim to stimulate endogenous butyrate production through the consumption of specific dietary fibers or prebiotics.
The primary objective of this comparative analysis is to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and practical implications of oral versus fiber-derived butyrate supplementation in the context of obesity management. This investigation seeks to determine which approach may offer superior benefits in terms of weight reduction, improvement in metabolic parameters, and overall health outcomes.
Key technological goals include assessing the bioavailability and targeted delivery of butyrate through different supplementation methods, optimizing dosage and formulation for maximum efficacy, and exploring potential synergistic effects with other dietary interventions or medications. Additionally, the analysis aims to identify any differences in the physiological responses elicited by exogenous butyrate supplementation compared to endogenously produced butyrate from fiber fermentation.
Furthermore, this research endeavors to elucidate the mechanisms by which butyrate exerts its effects on obesity-related parameters, including its impact on gut microbiota composition, intestinal barrier function, and systemic inflammation. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing more targeted and effective butyrate-based interventions for obesity management.
By comprehensively examining the technological aspects, physiological effects, and clinical outcomes of oral and fiber-derived butyrate supplementation, this analysis aims to provide valuable insights for future research directions and potential therapeutic applications in the field of obesity management.
Market Analysis for Obesity Management Solutions
The obesity management solutions market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing prevalence of obesity worldwide and the growing awareness of its associated health risks. This market encompasses a wide range of products and services, including pharmaceuticals, medical devices, dietary supplements, and lifestyle interventions.
The global obesity management market was valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.9 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 7.8% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to factors such as the rising incidence of obesity-related comorbidities, increasing healthcare expenditure, and the development of novel treatment options.
Within this market, the dietary supplements segment, which includes butyrate supplementation, has been gaining traction. The global market for weight loss supplements was estimated at $6.3 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach $9.1 billion by 2027, with a CAGR of 5.4%. This growth is driven by consumer preference for natural and non-invasive weight management solutions.
The comparative analysis of oral and fiber-derived butyrate supplementation represents a niche but promising segment within the obesity management market. While specific market data for butyrate supplements is limited, the broader prebiotics market, which includes fiber-derived butyrate precursors, was valued at $4.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $8.5 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 11.2%.
Geographically, North America dominates the obesity management market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, holds the largest market share due to its high obesity rates and advanced healthcare infrastructure. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing urbanization, changing lifestyles, and rising disposable incomes.
Key players in the obesity management market include pharmaceutical companies like Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Roche, as well as medical device manufacturers such as Medtronic and ReShape Lifesciences. In the dietary supplement space, companies like Nestlé Health Science, Glanbia, and Herbalife Nutrition are significant contributors.
The market for butyrate supplementation, both oral and fiber-derived, is still in its early stages but shows promise for growth. As research continues to demonstrate the potential benefits of butyrate in obesity management, it is likely to attract increased attention from both consumers and industry players, potentially leading to the development of new products and expanded market opportunities.
Current Challenges in Butyrate Supplementation
Despite the promising potential of butyrate supplementation in obesity management, several challenges currently hinder its widespread adoption and efficacy. One of the primary obstacles is the poor bioavailability of oral butyrate supplements. The human digestive system rapidly absorbs butyrate in the upper gastrointestinal tract, leading to a significant reduction in its concentration before reaching the colon, where it exerts its beneficial effects. This absorption pattern limits the therapeutic potential of oral butyrate supplementation.
Another challenge lies in the unpleasant taste and odor of butyrate, which can significantly impact patient compliance. The strong, rancid smell of butyrate makes it difficult for many individuals to consistently consume oral supplements, potentially compromising the long-term effectiveness of the treatment. This sensory issue has prompted researchers to explore alternative delivery methods and formulations.
The optimal dosage and duration of butyrate supplementation for obesity management remain unclear. Current studies show variability in dosing protocols, making it challenging to establish standardized treatment guidelines. This lack of consensus complicates the design of clinical trials and hinders the development of evidence-based recommendations for healthcare providers.
Furthermore, the long-term safety profile of butyrate supplementation, especially at higher doses, requires further investigation. While short-term studies have shown promising results, the potential side effects and interactions with other medications or dietary components over extended periods are not fully understood. This uncertainty poses a challenge for healthcare professionals in prescribing butyrate supplements for chronic conditions like obesity.
The comparative efficacy of different forms of butyrate supplementation, such as oral versus fiber-derived, presents another challenge. While fiber-derived butyrate production through the gut microbiome offers a more natural approach, controlling the precise amount of butyrate produced and ensuring consistent delivery to the colon remains difficult. This variability in butyrate production from dietary fibers complicates the assessment of its effectiveness compared to direct oral supplementation.
Lastly, the complex interplay between butyrate, the gut microbiome, and host metabolism adds another layer of complexity to butyrate supplementation strategies. Individual variations in gut microbiota composition and metabolic profiles may influence the response to butyrate supplementation, necessitating a more personalized approach to treatment. Developing methods to predict and optimize individual responses to butyrate supplementation represents a significant challenge in the field of obesity management.
Oral vs Fiber-Derived Butyrate Delivery Mechanisms
01 Butyrate supplementation for obesity management
Butyrate supplementation has shown potential in managing obesity by regulating metabolism, reducing inflammation, and improving gut health. It may help in weight loss and fat reduction by influencing energy expenditure and fat oxidation. The supplementation can be administered through various forms such as oral supplements or dietary modifications.- Butyrate supplementation for obesity management: Butyrate supplementation has shown potential in managing obesity by regulating metabolism, reducing inflammation, and improving gut health. It may help in weight loss and fat reduction by influencing energy expenditure and fat oxidation.
- Combination of butyrate with other active ingredients: Combining butyrate with other active ingredients such as probiotics, prebiotics, or specific nutrients can enhance its effectiveness in obesity management. These combinations may target multiple pathways involved in weight regulation and metabolic health.
- Formulations and delivery methods for butyrate: Various formulations and delivery methods have been developed to improve the bioavailability and efficacy of butyrate for obesity management. These include encapsulation techniques, controlled-release formulations, and targeted delivery systems.
- Butyrate's effects on gut microbiota and metabolism: Butyrate supplementation can modulate gut microbiota composition and function, which in turn affects host metabolism and energy balance. This mechanism plays a crucial role in its potential for obesity management.
- Butyrate in combination with lifestyle interventions: Integrating butyrate supplementation with lifestyle interventions such as diet and exercise may provide synergistic effects in obesity management. This approach addresses multiple aspects of weight control and metabolic health.
02 Combination of butyrate with other compounds for enhanced obesity management
Combining butyrate with other bioactive compounds or medications can potentially enhance its effectiveness in obesity management. These combinations may target multiple pathways involved in weight regulation, metabolism, and appetite control, leading to more comprehensive obesity treatment strategies.Expand Specific Solutions03 Butyrate-producing probiotics for obesity treatment
Probiotics capable of producing butyrate in the gut have been explored as a potential approach for obesity management. These beneficial bacteria can increase butyrate levels in the intestine, potentially leading to improved metabolic health and weight regulation through modulation of the gut microbiome.Expand Specific Solutions04 Butyrate's role in regulating appetite and food intake
Research has investigated butyrate's potential in regulating appetite and food intake, which are crucial factors in obesity management. Butyrate supplementation may influence hormones and neural pathways involved in satiety signaling, potentially leading to reduced caloric intake and improved weight control.Expand Specific Solutions05 Delivery systems for butyrate in obesity treatment
Various delivery systems have been developed to improve the efficacy and bioavailability of butyrate for obesity management. These may include encapsulation technologies, controlled-release formulations, or targeted delivery methods to ensure optimal absorption and effectiveness of butyrate in the body.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Butyrate Supplement Industry
The comparative analysis of oral and fiber-derived butyrate supplementation in obesity management is currently in a nascent stage of development, with a growing market driven by increasing obesity rates worldwide. The global market for obesity management is projected to reach significant value in the coming years, attracting both established pharmaceutical companies and innovative startups. Companies like Nestlé, Abbott Laboratories, and Mead Johnson Nutrition are leveraging their expertise in nutrition to explore butyrate supplementation. Emerging players such as Pendulum Therapeutics and TargEDys are focusing on microbiome-based approaches. The technology is still in early stages of maturity, with ongoing clinical trials and research collaborations involving institutions like New York University and Louisiana State University to establish efficacy and safety profiles.
Société des Produits Nestlé SA
Abbott Laboratories
Innovations in Butyrate Supplementation Research
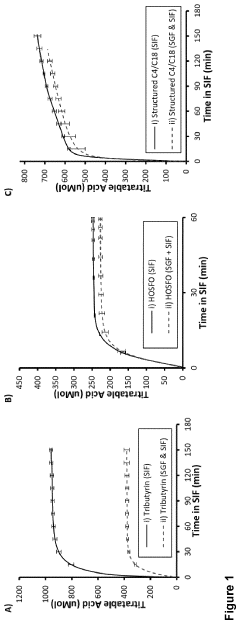
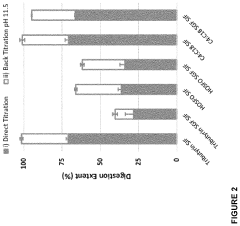
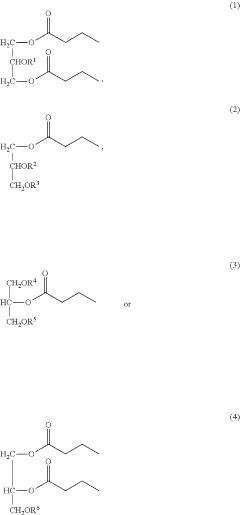
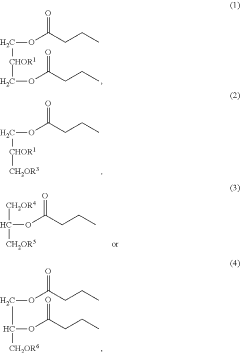
- Development of butyrate moiety containing triglycerides with improved organoleptic properties, such as 1,3-dibutyryl-2-palmitoylglycerol, which are synthesized through interesterification of tributyrin with high oleic sunflower oil, providing a dairy-free, cholesterol-free, and vegan alternative with reduced bitterness and odor, allowing effective delivery of butyric acid to the intestinal compartment.
- Chronic administration of dietary sodium butyrate, which inhibits histone deacetylases, enhances PGC-1α activity, leading to increased insulin sensitivity, reduced body weight, and improved metabolic parameters in non-ruminant mammals on a high-fat diet.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
When considering the safety and efficacy of oral and fiber-derived butyrate supplementation in obesity management, several key factors must be examined. The safety profile of butyrate supplementation is generally favorable, with minimal reported adverse effects in clinical trials. However, long-term safety data for both oral and fiber-derived forms are limited, necessitating further research.
Oral butyrate supplementation has shown promising results in reducing body weight and improving metabolic parameters in obese individuals. Studies have demonstrated its ability to modulate gut microbiota composition, enhance insulin sensitivity, and reduce inflammation. However, the optimal dosage and duration of oral butyrate supplementation for obesity management remain unclear, warranting additional investigation.
Fiber-derived butyrate supplementation, on the other hand, offers a more natural approach to increasing butyrate levels in the gut. This method relies on the fermentation of dietary fibers by gut bacteria to produce butyrate. While this approach may be more physiologically relevant, its efficacy can vary depending on an individual's gut microbiome composition and fiber intake.
Comparative studies between oral and fiber-derived butyrate supplementation have shown mixed results. Some research suggests that oral supplementation may provide more immediate and consistent effects, while fiber-derived butyrate production offers sustained benefits over time. The choice between these two approaches may depend on individual patient factors, such as gut microbiome health and dietary habits.
Efficacy considerations also extend to the bioavailability of butyrate. Oral supplementation faces challenges related to absorption and degradation in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Various formulations, including enteric-coated tablets and microencapsulation techniques, have been developed to improve butyrate delivery to the colon. Fiber-derived butyrate production circumvents these issues but may be less predictable in terms of dosage control.
The potential for synergistic effects when combining oral butyrate supplementation with dietary interventions that promote fiber-derived butyrate production is an area of growing interest. This combined approach may offer enhanced benefits for obesity management by addressing multiple aspects of gut health and metabolism simultaneously.
In conclusion, while both oral and fiber-derived butyrate supplementation show promise in obesity management, further research is needed to fully elucidate their comparative safety and efficacy profiles. Long-term studies, standardized dosing protocols, and personalized approaches based on individual gut microbiome profiles will be crucial in optimizing the use of butyrate supplementation for obesity treatment.
Regulatory Landscape for Dietary Supplements
The regulatory landscape for dietary supplements in the context of butyrate supplementation for obesity management is complex and multifaceted. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates dietary supplements under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This legislation defines dietary supplements as products intended to supplement the diet, containing vitamins, minerals, herbs, amino acids, or other dietary substances.
For butyrate supplements, whether oral or fiber-derived, manufacturers must ensure compliance with FDA regulations. This includes adhering to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) to ensure product quality, safety, and proper labeling. Labels must include a Supplement Facts panel, listing all ingredients and their amounts, as well as the statement "This statement has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease."
The regulatory framework also requires manufacturers to notify the FDA before marketing a new dietary ingredient (NDI) not present in the food supply before October 15, 1994. This process involves submitting safety data to demonstrate that the ingredient is reasonably expected to be safe under the conditions of use.
In the European Union, dietary supplements are regulated under the Food Supplements Directive (2002/46/EC). This directive harmonizes rules for labeling and introduces specific rules on vitamins and minerals in food supplements. For novel ingredients like certain forms of butyrate, manufacturers may need to go through the Novel Food approval process, which involves a rigorous safety assessment by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA).
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing health claims made by supplement manufacturers. In both the US and EU, any claims regarding the effects of butyrate supplements on obesity management must be substantiated by scientific evidence. Structure-function claims, which describe the role of a nutrient or dietary ingredient intended to affect the structure or function of the body, are allowed in the US but must be accompanied by a disclaimer.
As research on butyrate supplementation in obesity management progresses, regulatory agencies may update their guidelines. Manufacturers and researchers must stay informed about these changes to ensure compliance and maintain consumer trust. The evolving nature of this field underscores the importance of ongoing dialogue between regulatory bodies, researchers, and industry stakeholders to balance innovation with consumer safety.