Butyrate’s Impact on Chronic Disease Management
Butyrate Research Background and Objectives
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut microbiota through fermentation of dietary fibers, has emerged as a significant focus in chronic disease management research. The exploration of butyrate's potential therapeutic effects has gained momentum over the past two decades, driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the growing understanding of the gut-brain axis.
The primary objective of butyrate research in chronic disease management is to elucidate its mechanisms of action and potential applications in treating various chronic conditions. These include but are not limited to inflammatory bowel diseases, metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and certain types of cancer. Researchers aim to uncover how butyrate influences cellular processes, gene expression, and immune responses to mitigate disease progression and improve patient outcomes.
The historical context of butyrate research dates back to the late 20th century when scientists first recognized the importance of gut microbiota in human health. However, it was not until the early 2000s that butyrate's specific role in chronic disease management began to be extensively studied. This shift was prompted by advancements in microbiome research and a deeper understanding of the complex interactions between diet, gut bacteria, and human health.
Recent technological developments, such as high-throughput sequencing and metabolomics, have significantly accelerated butyrate research. These tools have enabled scientists to more accurately measure butyrate levels in the gut, identify butyrate-producing bacteria, and analyze the effects of butyrate on host physiology at a molecular level. This has led to a more comprehensive understanding of butyrate's multifaceted roles in maintaining gut health and potentially alleviating chronic diseases.
The current research landscape is characterized by a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from microbiology, immunology, nutrition, and clinical medicine. This collaborative effort aims to translate laboratory findings into practical therapeutic strategies. Key areas of investigation include optimizing dietary interventions to enhance butyrate production, developing butyrate-based pharmaceuticals, and exploring the potential of butyrate-producing probiotics.
As research progresses, the scientific community anticipates that butyrate could play a pivotal role in personalized medicine approaches to chronic disease management. The ultimate goal is to harness butyrate's beneficial properties to develop novel, targeted therapies that can effectively prevent, manage, or even reverse certain chronic conditions, thereby improving the quality of life for millions of patients worldwide.
Market Analysis for Butyrate-Based Therapeutics
The market for butyrate-based therapeutics is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing awareness of the potential benefits of butyrate in managing chronic diseases. The global market for microbiome-based therapeutics, which includes butyrate-related products, is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years. This growth is fueled by rising incidences of chronic diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), diabetes, and obesity, where butyrate has shown promising results in preclinical and clinical studies.
The demand for butyrate-based therapeutics is particularly strong in regions with high prevalence of gastrointestinal disorders and metabolic diseases. North America and Europe currently lead the market, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher adoption rates of novel therapies. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth due to improving healthcare access and rising disposable incomes.
One of the key drivers of market growth is the increasing focus on gut health and its connection to overall well-being. As research continues to unveil the importance of the gut microbiome in various aspects of health, including immune function and metabolism, the demand for butyrate-based products is likely to surge. This trend is further supported by the growing consumer preference for natural and preventive healthcare solutions.
The market is segmented based on product type, including oral supplements, topical formulations, and prescription medications. Oral supplements currently dominate the market share, driven by ease of administration and growing consumer awareness. However, prescription medications are expected to witness the highest growth rate, as more clinical trials validate the efficacy of butyrate-based drugs in treating specific chronic conditions.
Key players in the butyrate-based therapeutics market include pharmaceutical companies, biotech firms, and nutraceutical manufacturers. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create novel formulations and delivery methods that enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of butyrate. Strategic partnerships between academic institutions and industry players are also contributing to market expansion by accelerating the translation of research findings into commercial products.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical validation. The complex nature of microbiome-based therapies requires rigorous testing and approval processes, which can extend development timelines and increase costs. Additionally, educating healthcare providers and consumers about the benefits of butyrate-based therapies remains crucial for market penetration and sustained growth.
Current Challenges in Butyrate Research
Despite the growing interest in butyrate's potential for chronic disease management, several significant challenges persist in the field of butyrate research. One of the primary obstacles is the difficulty in maintaining stable and effective butyrate concentrations in the body. Butyrate is rapidly metabolized and absorbed in the gut, making it challenging to achieve therapeutic levels in target tissues.
Another major hurdle is the limited understanding of butyrate's precise mechanisms of action in different chronic diseases. While its anti-inflammatory and epigenetic effects are well-documented, the specific pathways and molecular targets involved in various conditions remain unclear. This knowledge gap hinders the development of targeted therapies and optimal dosing strategies.
The variability in individual responses to butyrate supplementation poses another challenge. Factors such as gut microbiome composition, diet, and genetic background can significantly influence butyrate production and efficacy. This heterogeneity complicates the design of clinical trials and the interpretation of results, making it difficult to establish standardized treatment protocols.
Furthermore, the delivery of butyrate to specific sites of action within the body remains problematic. Oral administration often results in poor bioavailability due to rapid absorption and metabolism in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Developing effective delivery systems that can bypass these barriers and target specific tissues or organs is a critical area of ongoing research.
The lack of long-term safety data on butyrate supplementation is another concern. While short-term studies have shown promising results, the potential side effects and risks associated with prolonged use of butyrate in chronic disease management are not fully understood. This gap in knowledge necessitates careful monitoring and extended follow-up studies.
Additionally, the complex interplay between butyrate and other short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in the gut microbiome ecosystem presents a challenge in isolating butyrate's specific effects. The synergistic or antagonistic interactions with other metabolites and microbial species need to be elucidated to optimize therapeutic strategies.
Lastly, the translation of preclinical findings to clinical applications remains a significant hurdle. Many studies demonstrating butyrate's beneficial effects have been conducted in vitro or in animal models, and replicating these results in human clinical trials has proven challenging. Bridging this gap requires more robust and well-designed human studies that account for the complexities of chronic disease pathophysiology and individual variability.
Existing Butyrate Delivery Methods
01 Butyrate's impact on gut health and microbiome
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid, plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health and regulating the microbiome. It serves as an energy source for colonocytes, strengthens the intestinal barrier, and modulates the composition of gut bacteria. Research indicates that butyrate supplementation can improve gut integrity and reduce inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract.- Butyrate's impact on gut health and microbiome: Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid, plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health and regulating the microbiome. It serves as an energy source for colonocytes, strengthens the intestinal barrier, and modulates the composition of gut bacteria. Research suggests that butyrate supplementation can improve digestive health and potentially alleviate symptoms of various gastrointestinal disorders.
- Butyrate's effects on metabolism and obesity: Studies indicate that butyrate has significant metabolic effects, particularly in relation to obesity and insulin sensitivity. It has been shown to increase energy expenditure, reduce fat accumulation, and improve glucose homeostasis. These findings suggest potential applications in the treatment and prevention of metabolic disorders such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.
- Butyrate's role in inflammation and immune regulation: Butyrate exhibits potent anti-inflammatory properties and plays a role in immune system regulation. It has been shown to suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines, enhance the production of regulatory T cells, and modulate the innate immune response. These effects suggest potential therapeutic applications in inflammatory bowel diseases, autoimmune disorders, and other inflammatory conditions.
- Butyrate's impact on cancer prevention and treatment: Research indicates that butyrate may have anticancer properties, particularly in colorectal cancer. It has been shown to induce apoptosis in cancer cells, inhibit cell proliferation, and promote differentiation. These findings suggest potential applications in cancer prevention strategies and as an adjunct to conventional cancer treatments.
- Butyrate's effects on neurological function and brain health: Emerging evidence suggests that butyrate may have neuroprotective effects and influence brain function. It has been shown to cross the blood-brain barrier, modulate neurotransmitter levels, and potentially improve cognitive function. These findings indicate possible applications in the treatment of neurological disorders and the maintenance of brain health.
02 Butyrate's effects on metabolism and obesity
Studies have shown that butyrate can influence metabolism and potentially aid in weight management. It has been found to increase energy expenditure, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce fat accumulation. These effects may be attributed to butyrate's ability to regulate gene expression related to lipid metabolism and energy homeostasis.Expand Specific Solutions03 Butyrate's role in immune system modulation
Butyrate has been observed to have immunomodulatory properties, affecting both innate and adaptive immune responses. It can suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines, enhance the production of regulatory T cells, and improve the function of the intestinal immune system. These effects contribute to its potential in managing inflammatory conditions and autoimmune disorders.Expand Specific Solutions04 Butyrate's neuroprotective and cognitive effects
Research suggests that butyrate may have neuroprotective properties and positive effects on cognitive function. It has been shown to cross the blood-brain barrier, influence neurotransmitter levels, and potentially reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Studies indicate that butyrate supplementation may improve memory and learning capabilities.Expand Specific Solutions05 Butyrate production and delivery methods
Various methods have been developed to enhance butyrate production in the gut or deliver it effectively to target tissues. These include the use of butyrate-producing probiotics, prebiotic fibers that promote butyrate production, and novel drug delivery systems for targeted butyrate release. Researchers are exploring ways to overcome the rapid metabolism of butyrate and improve its bioavailability.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Butyrate Research and Development
The butyrate market for chronic disease management is in a growth phase, driven by increasing research into its potential health benefits. The market size is expanding as more companies and institutions explore butyrate's therapeutic applications. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with varying levels of maturity across different applications. Key players like Société des Produits Nestlé SA, The University of Chicago, and Zhejiang University are at the forefront of research and development. Other significant contributors include The Regents of the University of Michigan, Seed Health, Inc., and Synlogic Operating Co., Inc., each bringing unique expertise to the field. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established pharmaceutical companies and innovative startups vying for market share and scientific breakthroughs in butyrate-based therapies for chronic diseases.
Seed Health, Inc.
Synlogic Operating Co., Inc.
Innovative Approaches in Butyrate Research
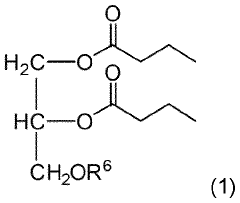
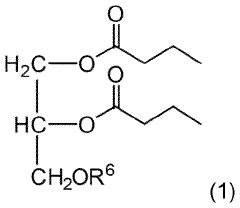
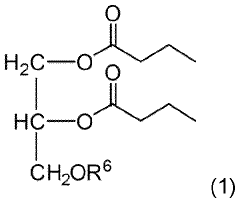
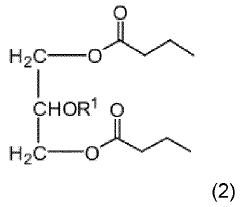
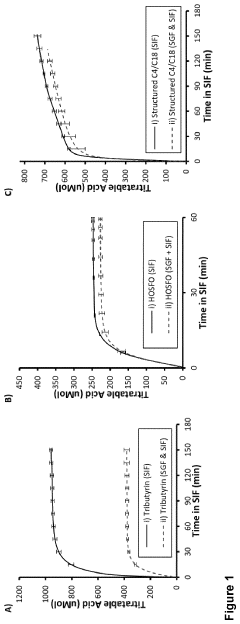
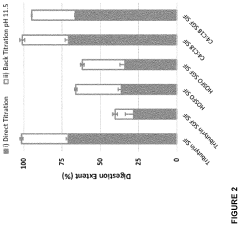
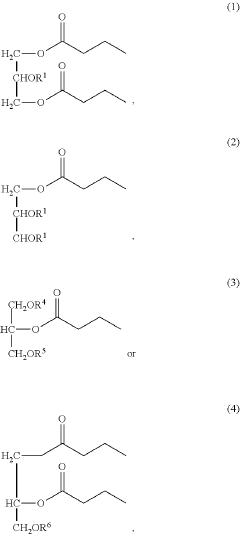
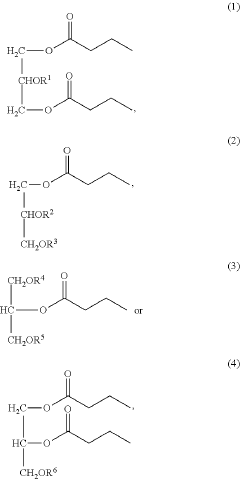
- Development of triglycerides with a long chain fatty acid moiety, specifically oleic acid, as the main butyrate source, providing improved organoleptic properties and effective delivery of butyrate to the intestinal compartment, potentially comprising 95% or more of the butyrate moiety in nutritional compositions.
- Development of butyrate moiety containing triglycerides with improved organoleptic properties, specifically designed to have reduced gastric lipolysis and enhanced delivery of butyric acid, using compounds like 1,3-dibutyryl-2-palmitoylglycerol and combinations thereof, for use in nutritional compositions and dietary supplements.
Regulatory Landscape for Microbiome-Based Therapies
The regulatory landscape for microbiome-based therapies, including those involving butyrate for chronic disease management, is complex and evolving. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has been working to establish a framework for regulating microbiome-based products. These therapies often fall into a gray area between traditional drugs and dietary supplements, presenting unique challenges for regulators.
The FDA has classified most microbiome-based therapies as biologics, which require a Biologics License Application (BLA) for approval. This process involves rigorous clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. For butyrate-related therapies, this means providing substantial evidence of its impact on chronic disease management through well-designed studies.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has also been developing guidelines for microbiome-based therapies. The EMA's approach emphasizes the importance of characterizing the microbiome components and their mechanisms of action. For butyrate therapies, this would involve detailed analysis of how butyrate interacts with the gut microbiome and affects chronic disease pathways.
Regulatory bodies are particularly concerned with the safety aspects of microbiome-based therapies. This includes potential risks of introducing live microorganisms into the human body and the long-term effects of altering the gut microbiome. For butyrate therapies, regulators may require extensive safety data, particularly regarding its impact on gut health and potential systemic effects.
Another key regulatory consideration is the standardization and quality control of microbiome-based products. Given the complexity of the microbiome, ensuring consistent composition and potency of these therapies is crucial. For butyrate-based treatments, this may involve developing standardized methods for measuring butyrate levels and its metabolic effects.
Regulatory agencies are also grappling with how to classify and regulate combination products that may include both microbiome components and traditional drug elements. This is particularly relevant for butyrate therapies that might be combined with other active ingredients or delivery systems.
As the field of microbiome research advances, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Both the FDA and EMA have shown a willingness to engage with researchers and industry to develop appropriate guidelines. This collaborative approach is crucial for fostering innovation while ensuring patient safety in the rapidly developing field of microbiome-based therapies, including those targeting butyrate's role in chronic disease management.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations for Butyrate Treatments
The safety and efficacy of butyrate treatments for chronic disease management are critical considerations that require thorough evaluation. Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut bacteria, has shown promising potential in various therapeutic applications. However, its use as a treatment modality necessitates careful assessment of both its beneficial effects and potential risks.
Safety considerations for butyrate treatments primarily focus on gastrointestinal tolerability and systemic effects. While butyrate is naturally present in the gut, exogenous administration may lead to dose-dependent side effects. Common adverse reactions include abdominal discomfort, bloating, and flatulence, particularly at higher doses. These effects are generally mild and transient but may impact patient compliance and quality of life.
Systemic safety concerns are relatively limited due to butyrate's rapid metabolism and the first-pass effect. However, long-term studies are needed to fully elucidate potential risks associated with prolonged use, especially in vulnerable populations such as pregnant women, children, and the elderly. Additionally, interactions with other medications and existing health conditions must be carefully evaluated to ensure overall safety.
Efficacy considerations for butyrate treatments span a range of chronic diseases, including inflammatory bowel diseases, metabolic disorders, and neurological conditions. In inflammatory bowel diseases, butyrate has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties and the ability to enhance intestinal barrier function. Clinical studies have shown promising results in reducing disease activity and improving symptoms in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease patients.
For metabolic disorders, butyrate's potential to modulate energy metabolism and improve insulin sensitivity has garnered significant interest. Preclinical and early clinical studies suggest that butyrate supplementation may help in managing obesity, type 2 diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. However, larger, well-designed clinical trials are necessary to establish optimal dosing regimens and long-term efficacy.
In neurological conditions, butyrate's neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing properties are being explored. Preliminary research indicates potential benefits in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, as well as in mood disorders. However, the efficacy of butyrate in these areas remains largely investigational, requiring further research to determine its clinical utility.
The route of administration plays a crucial role in both safety and efficacy considerations. Oral formulations, while convenient, face challenges related to stability and targeted delivery. Enteric-coated tablets and microencapsulation technologies are being developed to improve butyrate's bioavailability and reduce gastrointestinal side effects. Alternative delivery methods, such as rectal suppositories or enemas, may offer more direct effects in certain conditions but come with their own set of practical limitations and patient acceptability issues.