Butyrate’s Mechanisms in Appetite Regulation
Butyrate and Appetite Regulation: Background and Objectives
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut microbiota through fermentation of dietary fiber, has emerged as a key player in the complex interplay between the gut and the brain. This research aims to elucidate the mechanisms by which butyrate influences appetite regulation, a critical aspect of metabolic health and weight management.
The study of butyrate's role in appetite regulation has gained significant traction in recent years, driven by the growing recognition of the gut-brain axis in modulating various physiological processes. Historically, appetite regulation was primarily attributed to central nervous system mechanisms. However, the discovery of the gut microbiome's influence on host metabolism has revolutionized our understanding of energy homeostasis and eating behaviors.
Butyrate's potential in appetite regulation stems from its multifaceted effects on the gastrointestinal tract and systemic metabolism. It serves as an energy source for colonocytes, maintains intestinal barrier integrity, and modulates the production of gut hormones involved in satiety signaling. Furthermore, butyrate has been shown to influence the expression of neuropeptides in the hypothalamus, a key brain region for appetite control.
The objectives of this research are threefold. Firstly, to comprehensively map the pathways through which butyrate exerts its effects on appetite, from its production in the gut to its actions on central appetite-regulating circuits. Secondly, to investigate the dose-dependent effects of butyrate on various appetite-related parameters, including food intake, satiety hormones, and energy expenditure. Lastly, to explore the potential of butyrate as a therapeutic target for appetite modulation in the context of obesity and metabolic disorders.
This research is particularly timely given the global obesity epidemic and the urgent need for novel, effective strategies for weight management. By unraveling the mechanisms of butyrate's action on appetite regulation, we aim to pave the way for innovative dietary interventions and pharmacological approaches that harness the power of this gut-derived metabolite.
The study will employ a multidisciplinary approach, combining techniques from microbiology, endocrinology, neuroscience, and metabolomics. This comprehensive strategy will allow for a holistic understanding of butyrate's effects across different physiological systems involved in appetite control.
Understanding the intricate mechanisms by which butyrate influences appetite could lead to paradigm-shifting approaches in nutritional science and metabolic medicine. It may inform the development of prebiotic and probiotic strategies aimed at modulating gut microbiota composition to enhance butyrate production. Additionally, this research could provide insights into the design of butyrate-based therapeutics or dietary supplements for appetite management.
Market Analysis of Appetite Control Solutions
The appetite control solutions market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing global obesity rates and a growing awareness of the importance of weight management for overall health. This market encompasses a wide range of products and services, including dietary supplements, prescription medications, meal replacement products, and digital health applications.
The global market for appetite control solutions is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to exceed 5% over the next five years. This growth is fueled by several factors, including the rising prevalence of obesity-related health issues, changing dietary habits, and a growing emphasis on preventive healthcare.
North America currently dominates the market, accounting for the largest share of global revenue. This is primarily due to the high obesity rates in the region, coupled with greater consumer awareness and willingness to invest in weight management solutions. Europe follows closely behind, with Asia-Pacific emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by rapid urbanization, changing lifestyles, and increasing disposable incomes.
Within the appetite control solutions market, dietary supplements hold the largest market share. These products, which include natural ingredients like fiber, green tea extract, and garcinia cambogia, appeal to consumers seeking non-pharmaceutical options for weight management. The prescription medication segment, while smaller, is experiencing rapid growth, particularly with the introduction of new GLP-1 receptor agonists that have shown promising results in clinical trials.
The market is also witnessing a surge in demand for personalized nutrition solutions and digital health applications. These technologies leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to provide tailored dietary recommendations and track users' progress, catering to the growing consumer preference for customized health solutions.
Key market players include pharmaceutical companies like Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly, as well as nutraceutical firms such as Herbalife and GNC. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative appetite control solutions, with a particular focus on natural ingredients and advanced drug delivery systems.
The potential role of butyrate in appetite regulation represents an emerging area of interest within this market. As research on butyrate's mechanisms in appetite control progresses, it could open up new avenues for product development, potentially disrupting the current market landscape and offering novel solutions for weight management.
Current Understanding of Butyrate's Role in Appetite Regulation
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut microbiota through fermentation of dietary fiber, has emerged as a key player in appetite regulation. Recent research has shed light on its multifaceted role in modulating hunger and satiety signals, offering promising insights into potential therapeutic approaches for obesity and metabolic disorders.
At the molecular level, butyrate acts as a histone deacetylase inhibitor, influencing gene expression patterns related to appetite control. This epigenetic modulation affects the production and sensitivity of various appetite-regulating hormones, including leptin and ghrelin. Studies have shown that butyrate administration can increase circulating levels of peptide YY and glucagon-like peptide-1, both of which are known to promote satiety and reduce food intake.
Butyrate's effects extend beyond hormonal regulation to direct interactions with the central nervous system. It has been demonstrated to cross the blood-brain barrier and activate specific neurons in the hypothalamus, a region critical for appetite control. This activation leads to increased production of pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) and reduced expression of neuropeptide Y (NPY), resulting in decreased appetite and increased energy expenditure.
Furthermore, butyrate influences appetite through its impact on gut permeability and inflammation. By strengthening the intestinal barrier and reducing systemic inflammation, butyrate indirectly modulates appetite-regulating signals and improves overall metabolic health. This anti-inflammatory effect also contributes to enhanced insulin sensitivity, which is closely linked to appetite regulation and energy homeostasis.
Recent studies have explored the role of butyrate in modulating the gut-brain axis, revealing its potential to influence neural circuits involved in reward and motivation related to food intake. By altering the composition and activity of the gut microbiome, butyrate may indirectly affect neurotransmitter production and signaling pathways that govern eating behavior and food preferences.
While the current understanding of butyrate's mechanisms in appetite regulation is promising, several challenges remain. The optimal dosage, delivery methods, and long-term effects of butyrate supplementation in humans are still under investigation. Additionally, the complex interplay between butyrate, other short-chain fatty acids, and the diverse array of gut microbiota presents a challenge in isolating and fully elucidating butyrate's specific contributions to appetite control.
Existing Approaches to Butyrate-Mediated Appetite Regulation
01 Butyrate as an appetite suppressant
Butyrate and its derivatives can be used as appetite suppressants. These compounds affect the gut-brain axis, influencing hormones and neurotransmitters that regulate hunger and satiety. By modulating appetite, butyrate-based formulations may help in weight management and obesity treatment.- Butyrate as an appetite suppressant: Butyrate and its derivatives can be used as appetite suppressants. These compounds affect the gut-brain axis, influencing hormones and neurotransmitters that regulate hunger and satiety. By modulating appetite, butyrate-based formulations may help in weight management and obesity treatment.
- Butyrate in combination with other active ingredients: Combining butyrate with other active ingredients can enhance its appetite-regulating effects. These combinations may include probiotics, prebiotics, or other short-chain fatty acids. Such formulations can improve gut health, metabolism, and overall appetite control.
- Delivery systems for butyrate: Various delivery systems can be used to improve the efficacy and palatability of butyrate. These may include encapsulation techniques, controlled-release formulations, or novel dosage forms. Effective delivery systems can enhance butyrate's bioavailability and its impact on appetite regulation.
- Butyrate's effect on gut microbiome and metabolism: Butyrate influences the gut microbiome composition and metabolic processes, which in turn affects appetite regulation. By promoting beneficial bacteria growth and improving gut barrier function, butyrate can indirectly modulate appetite and energy homeostasis.
- Butyrate in medical applications for appetite control: Butyrate-based formulations can be used in medical applications for appetite control, particularly in conditions like obesity, diabetes, or eating disorders. These applications may involve specific dosing regimens, combination therapies, or targeted delivery methods to maximize the appetite-regulating effects of butyrate.
02 Butyrate in combination with other active ingredients
Combining butyrate with other active ingredients can enhance its appetite-regulating effects. These combinations may include probiotics, prebiotics, or other short-chain fatty acids. Such formulations can improve gut health, metabolism, and overall appetite control.Expand Specific Solutions03 Delivery methods for butyrate
Various delivery methods can be employed to administer butyrate for appetite control. These may include encapsulation techniques, controlled-release formulations, or targeted delivery systems. The goal is to ensure that butyrate reaches the intended site of action in the gastrointestinal tract.Expand Specific Solutions04 Butyrate's effect on gut microbiome and metabolism
Butyrate influences the gut microbiome composition and metabolic processes, which in turn affects appetite regulation. It can modulate the production of gut hormones and improve insulin sensitivity, contributing to better appetite control and metabolic health.Expand Specific Solutions05 Butyrate in medical applications for appetite-related disorders
Butyrate and its derivatives have potential applications in treating appetite-related disorders. These may include conditions such as obesity, anorexia, or appetite disturbances associated with other medical conditions. The use of butyrate in these contexts aims to normalize appetite and improve overall health outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Butyrate and Appetite Regulation Research
The research on butyrate's mechanisms in appetite regulation is in an emerging phase, with growing market potential as obesity and metabolic disorders become global health concerns. The market size is expanding, driven by increasing interest in gut microbiome-based therapies. Technologically, the field is still developing, with varying levels of maturity among key players. Companies like Nestlé, Baxter International, and Japan Tobacco are leveraging their resources to advance research, while academic institutions such as The University of Chicago and Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology contribute significant scientific insights. Pharmaceutical companies like Daiichi Sankyo and Janssen Pharmaceutica are also actively involved, indicating the potential for therapeutic applications. The diverse range of players, from food industry giants to biotech startups, suggests a multifaceted approach to understanding and harnessing butyrate's appetite-regulating properties.
Société des Produits Nestlé SA
Seed Health, Inc.
Core Mechanisms of Butyrate in Appetite Signaling Pathways
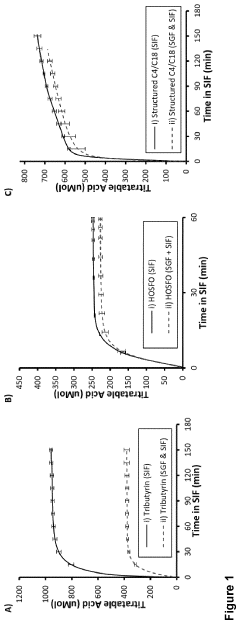
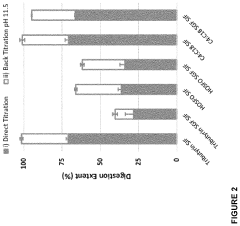
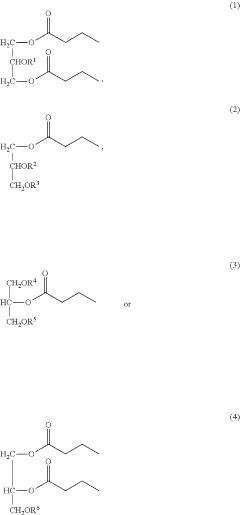
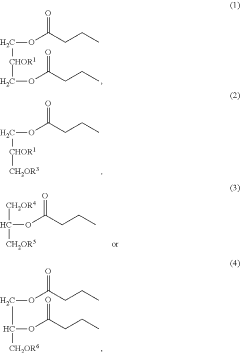
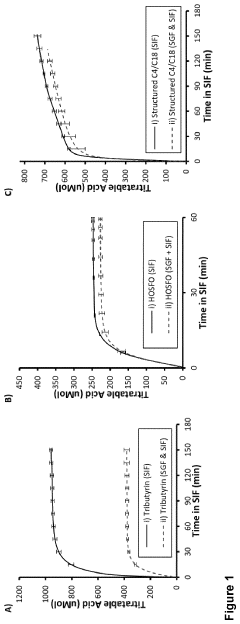
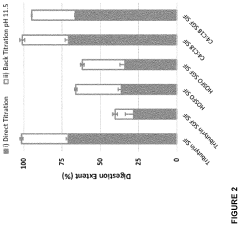
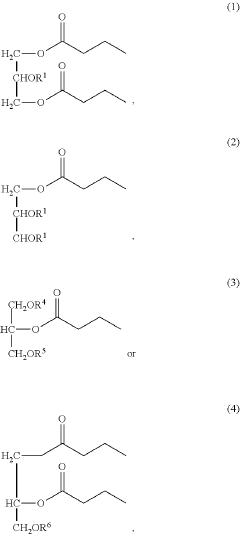
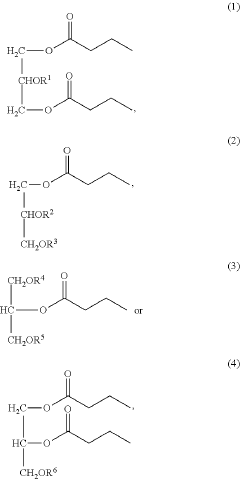
- Development of butyrate moiety containing triglycerides with improved organoleptic properties, such as 1,3-dibutyryl-2-palmitoylglycerol, which are synthesized through interesterification of tributyrin with high oleic sunflower oil, providing a dairy-free, cholesterol-free, and vegan alternative with reduced bitterness and odor, allowing effective delivery of butyric acid to the intestinal compartment.
- Development of butyrate moiety containing triglycerides with improved organoleptic properties, specifically designed to have reduced gastric lipolysis and enhanced delivery of butyric acid, using compounds like 1,3-dibutyryl-2-palmitoylglycerol and combinations thereof, for use in nutritional compositions and dietary supplements.
Regulatory Landscape for Microbiome-Based Therapeutics
The regulatory landscape for microbiome-based therapeutics is rapidly evolving as scientific understanding of the human microbiome and its impact on health continues to advance. Regulatory agencies worldwide are grappling with the unique challenges posed by these novel therapeutic approaches, which often blur the lines between traditional drug categories.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has taken steps to address the regulatory framework for microbiome-based therapeutics. The agency has issued guidance documents specifically tailored to live biotherapeutic products (LBPs), which include many microbiome-based interventions. These guidelines outline the requirements for chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) information, as well as preclinical and clinical study designs for LBPs.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has also recognized the potential of microbiome-based therapeutics and has been working on developing appropriate regulatory pathways. The EMA has established a dedicated working group to address the scientific and regulatory challenges associated with these products, focusing on issues such as product characterization, quality control, and safety assessment.
In Japan, the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has shown interest in microbiome-based therapeutics and is actively engaging with researchers and industry to develop suitable regulatory frameworks. The agency has emphasized the importance of product consistency and safety in its approach to regulating these novel therapies.
One of the key regulatory challenges in this field is the classification of microbiome-based products. Depending on their intended use and mechanism of action, these therapies may be regulated as drugs, biologics, medical devices, or even dietary supplements. This complexity requires regulatory agencies to adopt flexible approaches and collaborate closely with researchers and industry stakeholders.
Safety considerations are paramount in the regulatory landscape for microbiome-based therapeutics. Agencies are particularly concerned with the potential for unintended consequences, such as the transfer of antibiotic resistance genes or the overgrowth of opportunistic pathogens. As a result, regulatory requirements often include extensive safety testing and long-term follow-up studies.
As the field of microbiome research continues to advance, regulatory agencies are likely to refine and update their guidelines. This dynamic regulatory environment presents both opportunities and challenges for researchers and companies developing microbiome-based therapeutics, including those focused on butyrate's mechanisms in appetite regulation.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations for Butyrate Supplementation
When considering butyrate supplementation for appetite regulation, safety and efficacy are paramount concerns that require careful evaluation. The safety profile of butyrate supplementation is generally favorable, with most studies reporting minimal adverse effects. However, some individuals may experience gastrointestinal discomfort, such as bloating or flatulence, particularly during the initial stages of supplementation. These side effects are typically mild and transient, resolving as the body adapts to increased butyrate levels.
Dosage is a critical factor in both safety and efficacy. While optimal dosages may vary depending on individual factors, most studies have utilized doses ranging from 300 mg to 4 g per day. It is essential to start with lower doses and gradually increase to minimize potential side effects and allow for proper assessment of individual tolerance. Long-term safety data on butyrate supplementation is limited, necessitating ongoing monitoring and research to establish its safety profile for extended use.
Efficacy considerations for butyrate supplementation in appetite regulation are multifaceted. The form of butyrate used can significantly impact its effectiveness. Sodium butyrate and tributyrin are common forms, with tributyrin showing enhanced bioavailability due to its ability to bypass gastric degradation. The timing of supplementation may also influence efficacy, with some studies suggesting that pre-meal administration may yield optimal results for appetite control.
Individual variability in response to butyrate supplementation is an important factor to consider. Factors such as gut microbiome composition, diet, and overall health status can influence the efficacy of butyrate in regulating appetite. This variability underscores the need for personalized approaches and potentially combining butyrate supplementation with other strategies for optimal results.
Interactions with other dietary components and medications should be carefully evaluated. For instance, high-fiber diets may enhance the production of endogenous butyrate, potentially altering the effects of exogenous supplementation. Additionally, butyrate's potential to modulate gene expression and cellular processes necessitates caution when combined with certain medications, particularly those affecting metabolism or gut function.
In conclusion, while butyrate supplementation shows promise for appetite regulation, a balanced approach considering both safety and efficacy is crucial. Ongoing research is needed to refine dosing strategies, identify optimal formulations, and elucidate long-term effects. Healthcare providers should carefully weigh individual patient factors when considering butyrate supplementation as part of a comprehensive approach to appetite management.