Chiplet Designs Creating Next-Level Interactive Experiences
JUL 16, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Chiplet Evolution and Objectives
Chiplet technology has emerged as a revolutionary approach in semiconductor design, offering a paradigm shift in how we create and optimize integrated circuits. The evolution of chiplets can be traced back to the early 2010s when traditional monolithic chip designs began to face significant challenges in terms of scalability, performance, and cost-effectiveness. As Moore's Law slowed down, chiplets presented a viable solution to continue advancing computing capabilities.
The primary objective of chiplet designs is to disaggregate complex system-on-chip (SoC) architectures into smaller, more manageable components. These individual chiplets can be manufactured using different process nodes, optimized for specific functions, and then integrated onto a single package. This modular approach allows for greater flexibility, improved yield, and reduced costs compared to traditional monolithic designs.
In the context of creating next-level interactive experiences, chiplet designs aim to push the boundaries of performance, power efficiency, and functionality. The goal is to enable more immersive and responsive user interfaces, support advanced AI and machine learning capabilities, and facilitate seamless integration of various sensors and input/output devices. By leveraging chiplets, designers can create highly specialized components for tasks such as graphics processing, neural network acceleration, and high-speed communication interfaces.
The evolution of chiplet technology has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, the focus was on developing reliable interconnect technologies to enable high-bandwidth, low-latency communication between chiplets. This led to the development of advanced packaging solutions like Intel's EMIB (Embedded Multi-die Interconnect Bridge) and TSMC's CoWoS (Chip on Wafer on Substrate). Subsequently, industry standards such as UCIe (Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express) have emerged to promote interoperability and accelerate adoption.
Looking ahead, the objectives for chiplet designs in interactive experiences include further miniaturization, increased energy efficiency, and enhanced integration of heterogeneous components. There is a growing emphasis on developing chiplets that can support real-time ray tracing, advanced haptic feedback, and sophisticated natural language processing. Additionally, researchers are exploring ways to incorporate novel materials and 3D stacking techniques to push the boundaries of chiplet performance and functionality.
As the technology matures, we can expect to see chiplet designs enabling more lifelike virtual and augmented reality experiences, ultra-responsive gaming platforms, and intelligent user interfaces that can anticipate and adapt to user needs. The ultimate goal is to create seamless, intuitive, and immersive interactive experiences that blur the lines between the digital and physical worlds, opening up new possibilities for entertainment, education, and human-computer interaction.
The primary objective of chiplet designs is to disaggregate complex system-on-chip (SoC) architectures into smaller, more manageable components. These individual chiplets can be manufactured using different process nodes, optimized for specific functions, and then integrated onto a single package. This modular approach allows for greater flexibility, improved yield, and reduced costs compared to traditional monolithic designs.
In the context of creating next-level interactive experiences, chiplet designs aim to push the boundaries of performance, power efficiency, and functionality. The goal is to enable more immersive and responsive user interfaces, support advanced AI and machine learning capabilities, and facilitate seamless integration of various sensors and input/output devices. By leveraging chiplets, designers can create highly specialized components for tasks such as graphics processing, neural network acceleration, and high-speed communication interfaces.
The evolution of chiplet technology has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, the focus was on developing reliable interconnect technologies to enable high-bandwidth, low-latency communication between chiplets. This led to the development of advanced packaging solutions like Intel's EMIB (Embedded Multi-die Interconnect Bridge) and TSMC's CoWoS (Chip on Wafer on Substrate). Subsequently, industry standards such as UCIe (Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express) have emerged to promote interoperability and accelerate adoption.
Looking ahead, the objectives for chiplet designs in interactive experiences include further miniaturization, increased energy efficiency, and enhanced integration of heterogeneous components. There is a growing emphasis on developing chiplets that can support real-time ray tracing, advanced haptic feedback, and sophisticated natural language processing. Additionally, researchers are exploring ways to incorporate novel materials and 3D stacking techniques to push the boundaries of chiplet performance and functionality.
As the technology matures, we can expect to see chiplet designs enabling more lifelike virtual and augmented reality experiences, ultra-responsive gaming platforms, and intelligent user interfaces that can anticipate and adapt to user needs. The ultimate goal is to create seamless, intuitive, and immersive interactive experiences that blur the lines between the digital and physical worlds, opening up new possibilities for entertainment, education, and human-computer interaction.
Interactive Experience Market Analysis
The interactive experience market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and changing consumer preferences. This market encompasses a wide range of products and services, including virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR), and other immersive technologies. The demand for more engaging and realistic interactive experiences has been steadily increasing across various sectors, including gaming, entertainment, education, healthcare, and enterprise applications.
The global interactive experience market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with substantial growth projected over the next decade. This growth is fueled by several factors, including the increasing adoption of VR and AR technologies, the proliferation of smartphones and other mobile devices, and the growing demand for immersive content in both consumer and enterprise settings.
In the gaming sector, which represents a significant portion of the interactive experience market, there is a strong demand for more realistic and immersive gameplay. This has led to the development of advanced gaming consoles, VR headsets, and AR-enabled mobile games. The entertainment industry has also embraced interactive experiences, with theme parks, museums, and other attractions incorporating immersive technologies to enhance visitor engagement.
The education and training sector has shown increasing interest in interactive experiences, recognizing their potential to improve learning outcomes and provide more engaging and effective training solutions. Virtual simulations and interactive learning environments are being adopted in various fields, from medical training to industrial skills development.
In the enterprise sector, interactive experiences are being utilized for product design, virtual collaboration, and remote assistance. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of these technologies, as businesses seek ways to maintain productivity and connectivity in remote work environments.
The healthcare industry has also seen significant growth in the use of interactive experiences, particularly in areas such as surgical planning, patient education, and rehabilitation. VR and AR technologies are being used to enhance medical training, improve patient outcomes, and provide innovative therapeutic solutions.
As the demand for more immersive and realistic interactive experiences grows, there is an increasing need for advanced hardware and software solutions. This is where chiplet designs come into play, offering the potential to create more powerful and efficient systems capable of delivering next-level interactive experiences. The market analysis suggests that there is a significant opportunity for chiplet-based solutions to address the performance and power efficiency requirements of future interactive experience devices and platforms.
The global interactive experience market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with substantial growth projected over the next decade. This growth is fueled by several factors, including the increasing adoption of VR and AR technologies, the proliferation of smartphones and other mobile devices, and the growing demand for immersive content in both consumer and enterprise settings.
In the gaming sector, which represents a significant portion of the interactive experience market, there is a strong demand for more realistic and immersive gameplay. This has led to the development of advanced gaming consoles, VR headsets, and AR-enabled mobile games. The entertainment industry has also embraced interactive experiences, with theme parks, museums, and other attractions incorporating immersive technologies to enhance visitor engagement.
The education and training sector has shown increasing interest in interactive experiences, recognizing their potential to improve learning outcomes and provide more engaging and effective training solutions. Virtual simulations and interactive learning environments are being adopted in various fields, from medical training to industrial skills development.
In the enterprise sector, interactive experiences are being utilized for product design, virtual collaboration, and remote assistance. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of these technologies, as businesses seek ways to maintain productivity and connectivity in remote work environments.
The healthcare industry has also seen significant growth in the use of interactive experiences, particularly in areas such as surgical planning, patient education, and rehabilitation. VR and AR technologies are being used to enhance medical training, improve patient outcomes, and provide innovative therapeutic solutions.
As the demand for more immersive and realistic interactive experiences grows, there is an increasing need for advanced hardware and software solutions. This is where chiplet designs come into play, offering the potential to create more powerful and efficient systems capable of delivering next-level interactive experiences. The market analysis suggests that there is a significant opportunity for chiplet-based solutions to address the performance and power efficiency requirements of future interactive experience devices and platforms.
Chiplet Technology Landscape
Chiplet technology has emerged as a revolutionary approach in semiconductor design, offering a paradigm shift in how integrated circuits are conceived and manufactured. This landscape is characterized by the disaggregation of traditional monolithic chip designs into smaller, more specialized dies known as chiplets. These chiplets are then interconnected on a single package, allowing for greater flexibility, improved performance, and enhanced cost-effectiveness in chip production.
The chiplet landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by the increasing demand for more powerful and efficient computing solutions across various industries. Major semiconductor companies, including Intel, AMD, and TSMC, have embraced chiplet technology as a key strategy to overcome the limitations of traditional Moore's Law scaling. This approach enables the integration of heterogeneous components, each optimized for specific functions, resulting in superior overall system performance.
One of the primary drivers of chiplet adoption is the need for more advanced packaging technologies. As chiplets require high-bandwidth, low-latency connections between dies, innovations in packaging have become crucial. Advanced packaging solutions such as 2.5D and 3D integration, silicon interposers, and through-silicon vias (TSVs) are integral to the chiplet ecosystem, enabling seamless communication between different functional blocks.
The chiplet landscape is also characterized by a growing emphasis on standardization and interoperability. Initiatives like the Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe) consortium aim to establish common interfaces and protocols, facilitating the integration of chiplets from different vendors. This push towards standardization is expected to accelerate innovation and foster a more diverse and competitive chiplet marketplace.
In the context of creating next-level interactive experiences, chiplet designs offer significant advantages. They enable the integration of specialized processing units, such as high-performance GPUs, AI accelerators, and dedicated audio/video processors, alongside general-purpose CPUs. This heterogeneous integration allows for optimized performance in specific tasks critical to immersive and responsive user interfaces, virtual and augmented reality applications, and advanced gaming experiences.
The chiplet landscape is also witnessing advancements in die-to-die interconnect technologies, with companies exploring novel approaches to enhance bandwidth and reduce latency between chiplets. These developments are crucial for enabling seamless, real-time interactions in next-generation applications, where minimal latency and high data throughput are essential for creating truly immersive experiences.
As the chiplet technology landscape continues to mature, we can expect to see further innovations in areas such as thermal management, power distribution, and system-level integration. These advancements will be key to unlocking the full potential of chiplet designs in creating increasingly sophisticated and engaging interactive experiences across a wide range of devices and platforms.
The chiplet landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by the increasing demand for more powerful and efficient computing solutions across various industries. Major semiconductor companies, including Intel, AMD, and TSMC, have embraced chiplet technology as a key strategy to overcome the limitations of traditional Moore's Law scaling. This approach enables the integration of heterogeneous components, each optimized for specific functions, resulting in superior overall system performance.
One of the primary drivers of chiplet adoption is the need for more advanced packaging technologies. As chiplets require high-bandwidth, low-latency connections between dies, innovations in packaging have become crucial. Advanced packaging solutions such as 2.5D and 3D integration, silicon interposers, and through-silicon vias (TSVs) are integral to the chiplet ecosystem, enabling seamless communication between different functional blocks.
The chiplet landscape is also characterized by a growing emphasis on standardization and interoperability. Initiatives like the Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe) consortium aim to establish common interfaces and protocols, facilitating the integration of chiplets from different vendors. This push towards standardization is expected to accelerate innovation and foster a more diverse and competitive chiplet marketplace.
In the context of creating next-level interactive experiences, chiplet designs offer significant advantages. They enable the integration of specialized processing units, such as high-performance GPUs, AI accelerators, and dedicated audio/video processors, alongside general-purpose CPUs. This heterogeneous integration allows for optimized performance in specific tasks critical to immersive and responsive user interfaces, virtual and augmented reality applications, and advanced gaming experiences.
The chiplet landscape is also witnessing advancements in die-to-die interconnect technologies, with companies exploring novel approaches to enhance bandwidth and reduce latency between chiplets. These developments are crucial for enabling seamless, real-time interactions in next-generation applications, where minimal latency and high data throughput are essential for creating truly immersive experiences.
As the chiplet technology landscape continues to mature, we can expect to see further innovations in areas such as thermal management, power distribution, and system-level integration. These advancements will be key to unlocking the full potential of chiplet designs in creating increasingly sophisticated and engaging interactive experiences across a wide range of devices and platforms.
Current Chiplet Solutions
01 Chiplet-based interactive gaming experiences
Chiplet designs are utilized to create interactive gaming experiences, enhancing performance and user engagement. These designs allow for modular and scalable gaming systems, enabling more immersive and responsive gameplay. The chiplet architecture facilitates improved graphics processing, reduced latency, and more efficient power management in gaming devices.- Interactive chiplet-based system design: Chiplet designs are utilized to create interactive experiences by integrating multiple specialized chips on a single package. This approach allows for modular and flexible system designs, enabling customized user interactions and improved performance in various applications such as gaming, virtual reality, and interactive displays.
- User interface optimization for chiplet-based devices: Chiplet-based devices employ advanced user interface techniques to enhance interactive experiences. This includes optimizing touch controls, gesture recognition, and visual feedback mechanisms to create more intuitive and responsive interfaces for users across different device form factors and use cases.
- Chiplet integration for immersive multimedia experiences: Chiplets are leveraged to create immersive multimedia experiences by combining specialized processing units for graphics, audio, and haptics. This integration enables high-fidelity visual rendering, spatial audio processing, and advanced haptic feedback, resulting in more engaging and realistic interactive content.
- Adaptive chiplet configurations for personalized experiences: Chiplet designs allow for adaptive system configurations that can be tailored to individual user preferences and usage patterns. This flexibility enables personalized interactive experiences by dynamically allocating resources and adjusting performance based on user behavior and environmental factors.
- Chiplet-based AI acceleration for enhanced interactivity: Specialized AI acceleration chiplets are integrated into interactive systems to enhance user experiences through real-time data processing, predictive interactions, and intelligent content adaptation. This approach enables more natural and context-aware interactions in applications such as voice assistants, augmented reality, and smart home devices.
02 Chiplet integration for enhanced user interfaces
Chiplets are employed to improve user interface designs, offering more responsive and intuitive interactions. This approach allows for the integration of advanced touch sensors, haptic feedback systems, and high-resolution displays. The modular nature of chiplets enables customization of user interfaces for various devices and applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Chiplet-based augmented and virtual reality systems
Chiplet designs are implemented in augmented and virtual reality systems to create more immersive and interactive experiences. These designs allow for improved processing of complex 3D environments, real-time rendering, and seamless integration of virtual elements with the real world. The modular nature of chiplets enables scalable and upgradable AR/VR systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Chiplet architecture for interactive AI and machine learning applications
Chiplets are used to develop interactive AI and machine learning applications, enabling more sophisticated and responsive user experiences. This architecture allows for efficient processing of complex algorithms, real-time data analysis, and adaptive learning capabilities. The modular design facilitates the integration of specialized AI accelerators and neural processing units.Expand Specific Solutions05 Chiplet-enabled interactive IoT and smart device experiences
Chiplet designs are implemented in IoT and smart devices to create more interactive and personalized user experiences. This approach allows for efficient integration of various sensors, communication modules, and processing units. The modular nature of chiplets enables customization and upgradeability of smart devices, enhancing their interactive capabilities and user engagement.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Chiplet Industry Players
The chiplet design market is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across the semiconductor industry. The market size is expanding rapidly, driven by demand for more powerful and efficient computing solutions. Technologically, chiplet designs are maturing, with major players like Intel, AMD, and TSMC making significant advancements. Companies such as Micron Technology, Apple, and Qualcomm are also investing heavily in this area, developing innovative chiplet-based solutions for various applications. The competitive landscape is intensifying as more firms recognize the potential of chiplet technology to create next-level interactive experiences, particularly in areas like AI, gaming, and virtual reality.
Sony Group Corp.
Technical Solution: Sony's approach to Chiplet designs for interactive experiences is primarily focused on their gaming and entertainment systems, particularly the PlayStation platform. While Sony has not publicly announced specific chiplet-based designs, they have been exploring advanced packaging technologies and heterogeneous integration for their console hardware. The PlayStation 5, for example, uses a custom SoC that integrates CPU and GPU components[10]. Sony has also been investing in AI and sensor technologies, which could potentially benefit from chiplet-like designs in future iterations. The company's focus on creating immersive gaming and entertainment experiences drives their exploration of advanced chip architectures that can deliver high performance and sophisticated graphics capabilities.
Strengths: Strong focus on gaming and entertainment applications, experience with custom SoC designs, potential for innovative integration of sensors and AI. Weaknesses: Less public information on specific chiplet strategies, potential challenges in adapting to rapidly evolving chiplet ecosystem.
Apple, Inc.
Technical Solution: Apple's approach to Chiplet designs for interactive experiences centers around their custom Silicon, particularly the M-series chips. These chips utilize a system-on-chip (SoC) design that integrates various components, including CPU, GPU, Neural Engine, and memory, into a single package[4]. While not strictly using separate chiplets, Apple's design philosophy focuses on tight integration and customization. The company has been rumored to be exploring advanced packaging technologies, including fan-out wafer-level packaging (FOWLP) and integrated fan-out (InFO) technologies, which could enable more complex chiplet-like designs in the future[5].
Strengths: Highly integrated and optimized designs, excellent performance-per-watt, tight software-hardware integration. Weaknesses: Less flexibility compared to true chiplet designs, potential scalability limitations.
Innovative Chiplet Architectures
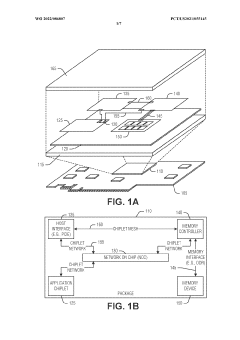
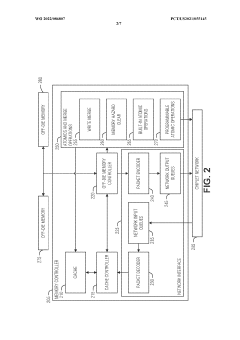
Edge interface placements to enable chiplet rotation into multi-chiplet cluster
PatentActiveUS20240170453A1
Innovation
- The implementation of a chiplet architecture that uses a network-on-chip (NOC) with a chiplet protocol interface (CPI) to facilitate high-speed, flexible inter-chiplet communication, combined with a tightly packed matrix arrangement of chiplets and I/O micro-bumps for close-coupled interconnects, to minimize latency and energy consumption.
On-demand programmable atomic kernel loading
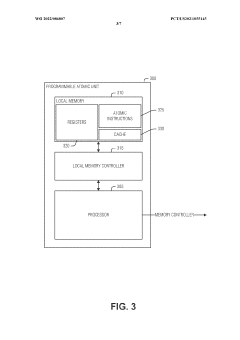
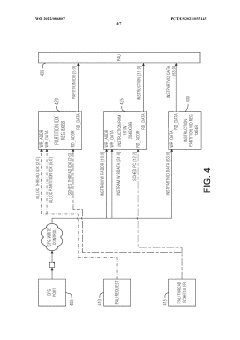
PatentWO2022086807A1
Innovation
- Implementing an on-demand mechanism for loading PAO kernels, where PAUs register for potential use and reserve space, loading the kernel only when requested, and signaling a trap to initiate kernel transfer when needed.
Thermal Management Strategies
Thermal management is a critical aspect of chiplet designs, especially when creating next-level interactive experiences. As chiplets become more prevalent in high-performance computing and consumer electronics, managing heat dissipation becomes increasingly challenging. The compact nature of chiplet designs, combined with the high processing power required for immersive interactive experiences, necessitates innovative thermal management strategies.
One key approach to thermal management in chiplet designs is the use of advanced packaging technologies. These include the implementation of through-silicon vias (TSVs) and interposers, which not only facilitate high-speed communication between chiplets but also aid in heat dissipation. By strategically placing TSVs, designers can create thermal pathways that efficiently channel heat away from critical components.
Another important strategy is the integration of advanced cooling solutions directly into the chiplet package. This may involve the use of micro-fluidic channels embedded within the interposer or substrate, allowing for more effective heat removal. Some designs incorporate phase-change materials or mini vapor chambers within the package to enhance thermal performance without significantly increasing the overall size of the device.
Active cooling techniques are also being adapted for chiplet designs. Miniaturized thermoelectric coolers (TECs) can be integrated at the package level to provide localized cooling for high-heat-generating components. These TECs can be dynamically controlled to optimize power consumption and cooling efficiency based on real-time thermal demands.
Software-based thermal management plays a crucial role in chiplet designs for interactive experiences. Advanced algorithms can dynamically adjust clock speeds, voltage levels, and workload distribution across different chiplets to maintain optimal thermal conditions. This approach allows for fine-grained control over heat generation and dissipation, ensuring consistent performance even under demanding interactive scenarios.
The development of new materials with superior thermal properties is also driving innovations in chiplet thermal management. High thermal conductivity materials, such as graphene-based composites or advanced ceramic substrates, are being explored to enhance heat spreading and dissipation within the package. These materials can significantly improve the overall thermal performance of chiplet-based systems without compromising electrical performance or reliability.
As interactive experiences become more sophisticated, requiring higher computational power and lower latency, the importance of effective thermal management in chiplet designs will continue to grow. Future developments may include the integration of AI-driven thermal management systems that can predict and preemptively address thermal issues, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of chiplet-based devices in interactive applications.
One key approach to thermal management in chiplet designs is the use of advanced packaging technologies. These include the implementation of through-silicon vias (TSVs) and interposers, which not only facilitate high-speed communication between chiplets but also aid in heat dissipation. By strategically placing TSVs, designers can create thermal pathways that efficiently channel heat away from critical components.
Another important strategy is the integration of advanced cooling solutions directly into the chiplet package. This may involve the use of micro-fluidic channels embedded within the interposer or substrate, allowing for more effective heat removal. Some designs incorporate phase-change materials or mini vapor chambers within the package to enhance thermal performance without significantly increasing the overall size of the device.
Active cooling techniques are also being adapted for chiplet designs. Miniaturized thermoelectric coolers (TECs) can be integrated at the package level to provide localized cooling for high-heat-generating components. These TECs can be dynamically controlled to optimize power consumption and cooling efficiency based on real-time thermal demands.
Software-based thermal management plays a crucial role in chiplet designs for interactive experiences. Advanced algorithms can dynamically adjust clock speeds, voltage levels, and workload distribution across different chiplets to maintain optimal thermal conditions. This approach allows for fine-grained control over heat generation and dissipation, ensuring consistent performance even under demanding interactive scenarios.
The development of new materials with superior thermal properties is also driving innovations in chiplet thermal management. High thermal conductivity materials, such as graphene-based composites or advanced ceramic substrates, are being explored to enhance heat spreading and dissipation within the package. These materials can significantly improve the overall thermal performance of chiplet-based systems without compromising electrical performance or reliability.
As interactive experiences become more sophisticated, requiring higher computational power and lower latency, the importance of effective thermal management in chiplet designs will continue to grow. Future developments may include the integration of AI-driven thermal management systems that can predict and preemptively address thermal issues, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of chiplet-based devices in interactive applications.
Chiplet Standardization Efforts
Chiplet standardization efforts have become increasingly crucial in the development of next-level interactive experiences. As the demand for more powerful and efficient computing solutions grows, the industry has recognized the need for a unified approach to chiplet design and integration.
The Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe) consortium, formed in 2022, has been at the forefront of these standardization efforts. UCIe aims to establish a common interconnect standard for chiplets, enabling seamless integration of diverse components from different manufacturers. This initiative has garnered support from major players in the semiconductor industry, including Intel, AMD, Arm, and TSMC.
One of the key focus areas of chiplet standardization is the development of common protocols for die-to-die communication. These protocols are essential for ensuring interoperability between chiplets from various vendors, allowing for more flexible and cost-effective system designs. The UCIe standard defines both the physical layer and protocol layer specifications, addressing critical aspects such as signal integrity, power efficiency, and data transfer rates.
Another important aspect of chiplet standardization is the establishment of common packaging and integration methodologies. This includes defining standard interfaces for chiplet-to-substrate connections, thermal management solutions, and power delivery systems. By standardizing these elements, manufacturers can reduce development costs and time-to-market for new products while improving overall system reliability.
Chiplet standardization efforts also extend to the development of design tools and methodologies. Industry collaborations are underway to create standardized design flows and verification processes for chiplet-based systems. These efforts aim to simplify the integration of chiplets from different sources and enable more efficient system-level optimization.
The impact of chiplet standardization on interactive experiences is significant. By enabling the integration of specialized processing units, high-bandwidth memory, and advanced I/O interfaces, chiplet-based designs can deliver unprecedented levels of performance and functionality. This is particularly relevant for applications such as virtual and augmented reality, AI-powered gaming, and immersive multimedia experiences.
As chiplet standardization efforts continue to mature, we can expect to see a proliferation of innovative system designs that leverage the flexibility and scalability of chiplet architectures. This will not only drive advancements in interactive experiences but also contribute to more sustainable and efficient computing solutions across various industries.
The Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe) consortium, formed in 2022, has been at the forefront of these standardization efforts. UCIe aims to establish a common interconnect standard for chiplets, enabling seamless integration of diverse components from different manufacturers. This initiative has garnered support from major players in the semiconductor industry, including Intel, AMD, Arm, and TSMC.
One of the key focus areas of chiplet standardization is the development of common protocols for die-to-die communication. These protocols are essential for ensuring interoperability between chiplets from various vendors, allowing for more flexible and cost-effective system designs. The UCIe standard defines both the physical layer and protocol layer specifications, addressing critical aspects such as signal integrity, power efficiency, and data transfer rates.
Another important aspect of chiplet standardization is the establishment of common packaging and integration methodologies. This includes defining standard interfaces for chiplet-to-substrate connections, thermal management solutions, and power delivery systems. By standardizing these elements, manufacturers can reduce development costs and time-to-market for new products while improving overall system reliability.
Chiplet standardization efforts also extend to the development of design tools and methodologies. Industry collaborations are underway to create standardized design flows and verification processes for chiplet-based systems. These efforts aim to simplify the integration of chiplets from different sources and enable more efficient system-level optimization.
The impact of chiplet standardization on interactive experiences is significant. By enabling the integration of specialized processing units, high-bandwidth memory, and advanced I/O interfaces, chiplet-based designs can deliver unprecedented levels of performance and functionality. This is particularly relevant for applications such as virtual and augmented reality, AI-powered gaming, and immersive multimedia experiences.
As chiplet standardization efforts continue to mature, we can expect to see a proliferation of innovative system designs that leverage the flexibility and scalability of chiplet architectures. This will not only drive advancements in interactive experiences but also contribute to more sustainable and efficient computing solutions across various industries.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!