How Chiplets Support Seamless Multilayer Network Operations?
JUL 16, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Chiplet Technology Evolution and Objectives
Chiplet technology has emerged as a revolutionary approach in the semiconductor industry, offering a paradigm shift in the design and manufacturing of integrated circuits. The evolution of chiplets can be traced back to the early 2010s when the limitations of traditional monolithic chip designs became increasingly apparent. As Moore's Law began to slow down, chiplets presented a viable solution to continue scaling performance and functionality while managing costs and manufacturing complexities.
The primary objective of chiplet technology is to disaggregate complex system-on-chip (SoC) designs into smaller, more manageable components that can be manufactured separately and then integrated into a single package. This approach allows for greater flexibility in design, improved yield, and the ability to mix and match different process nodes within a single product. In the context of supporting seamless multilayer network operations, chiplets offer several key advantages.
Firstly, chiplets enable the integration of specialized network processing units, each optimized for specific layers of the network stack. This modular approach allows for more efficient handling of diverse network protocols and functions, from physical layer processing to application-level operations. By dedicating specific chiplets to different network layers, manufacturers can achieve higher performance and lower latency in multilayer network operations.
Secondly, the chiplet architecture facilitates the incorporation of advanced packaging technologies, such as 2.5D and 3D integration. These packaging techniques support high-bandwidth, low-latency interconnects between chiplets, which is crucial for seamless communication across network layers. The ability to stack chiplets vertically or place them side by side on an interposer allows for more efficient use of silicon area and improved thermal management, both critical factors in high-performance network equipment.
The evolution of chiplet technology has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, the focus was on developing reliable interconnect technologies to enable chiplet-to-chiplet communication. This led to the development of standards like Advanced Interface Bus (AIB) and Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe), which have been instrumental in promoting interoperability between chiplets from different vendors.
Looking ahead, the objectives for chiplet technology in the context of multilayer network operations include further miniaturization, increased integration density, and improved energy efficiency. There is also a growing emphasis on developing chiplets with built-in security features to address the evolving threat landscape in network environments. Additionally, research is underway to explore the potential of photonic interconnects between chiplets, which could dramatically increase bandwidth and reduce power consumption in future network processing systems.
The primary objective of chiplet technology is to disaggregate complex system-on-chip (SoC) designs into smaller, more manageable components that can be manufactured separately and then integrated into a single package. This approach allows for greater flexibility in design, improved yield, and the ability to mix and match different process nodes within a single product. In the context of supporting seamless multilayer network operations, chiplets offer several key advantages.
Firstly, chiplets enable the integration of specialized network processing units, each optimized for specific layers of the network stack. This modular approach allows for more efficient handling of diverse network protocols and functions, from physical layer processing to application-level operations. By dedicating specific chiplets to different network layers, manufacturers can achieve higher performance and lower latency in multilayer network operations.
Secondly, the chiplet architecture facilitates the incorporation of advanced packaging technologies, such as 2.5D and 3D integration. These packaging techniques support high-bandwidth, low-latency interconnects between chiplets, which is crucial for seamless communication across network layers. The ability to stack chiplets vertically or place them side by side on an interposer allows for more efficient use of silicon area and improved thermal management, both critical factors in high-performance network equipment.
The evolution of chiplet technology has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, the focus was on developing reliable interconnect technologies to enable chiplet-to-chiplet communication. This led to the development of standards like Advanced Interface Bus (AIB) and Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe), which have been instrumental in promoting interoperability between chiplets from different vendors.
Looking ahead, the objectives for chiplet technology in the context of multilayer network operations include further miniaturization, increased integration density, and improved energy efficiency. There is also a growing emphasis on developing chiplets with built-in security features to address the evolving threat landscape in network environments. Additionally, research is underway to explore the potential of photonic interconnects between chiplets, which could dramatically increase bandwidth and reduce power consumption in future network processing systems.
Market Demand for Multilayer Network Solutions
The demand for multilayer network solutions has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by the growing complexity of modern network architectures and the need for more efficient data processing and transmission. As organizations continue to expand their digital infrastructure, the integration of various network layers has become crucial for seamless operations and improved performance.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the exponential growth in data traffic. With the proliferation of connected devices, cloud computing, and data-intensive applications, traditional network architectures are struggling to keep up with the volume and velocity of data. Multilayer network solutions offer a way to optimize data flow across different network layers, reducing latency and improving overall network efficiency.
The rise of 5G and edge computing has further fueled the demand for multilayer network solutions. These technologies require low-latency, high-bandwidth connections that can seamlessly integrate with existing network infrastructure. Multilayer solutions provide the flexibility and scalability needed to support these emerging technologies, enabling organizations to adapt to changing network requirements without significant overhauls.
In the enterprise sector, the adoption of software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV) has created a need for more sophisticated network management tools. Multilayer network solutions offer the ability to orchestrate and optimize network resources across multiple layers, providing greater visibility and control over complex network environments.
The telecommunications industry has been a significant driver of demand for multilayer network solutions. As telecom operators upgrade their networks to support 5G and beyond, they require solutions that can efficiently manage the increased complexity of their infrastructure. Multilayer solutions enable operators to optimize resource allocation, improve network reliability, and reduce operational costs.
Security concerns have also contributed to the growing demand for multilayer network solutions. With cyber threats becoming more sophisticated, organizations are looking for ways to implement security measures across all network layers. Multilayer solutions provide a comprehensive approach to security, allowing for the integration of various security protocols and technologies throughout the network stack.
The market for multilayer network solutions is expected to continue growing as organizations seek to improve network performance, reduce costs, and enhance security. The ability of chiplets to support seamless multilayer network operations aligns well with these market demands, offering a promising approach to addressing the complex networking challenges of the future.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the exponential growth in data traffic. With the proliferation of connected devices, cloud computing, and data-intensive applications, traditional network architectures are struggling to keep up with the volume and velocity of data. Multilayer network solutions offer a way to optimize data flow across different network layers, reducing latency and improving overall network efficiency.
The rise of 5G and edge computing has further fueled the demand for multilayer network solutions. These technologies require low-latency, high-bandwidth connections that can seamlessly integrate with existing network infrastructure. Multilayer solutions provide the flexibility and scalability needed to support these emerging technologies, enabling organizations to adapt to changing network requirements without significant overhauls.
In the enterprise sector, the adoption of software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV) has created a need for more sophisticated network management tools. Multilayer network solutions offer the ability to orchestrate and optimize network resources across multiple layers, providing greater visibility and control over complex network environments.
The telecommunications industry has been a significant driver of demand for multilayer network solutions. As telecom operators upgrade their networks to support 5G and beyond, they require solutions that can efficiently manage the increased complexity of their infrastructure. Multilayer solutions enable operators to optimize resource allocation, improve network reliability, and reduce operational costs.
Security concerns have also contributed to the growing demand for multilayer network solutions. With cyber threats becoming more sophisticated, organizations are looking for ways to implement security measures across all network layers. Multilayer solutions provide a comprehensive approach to security, allowing for the integration of various security protocols and technologies throughout the network stack.
The market for multilayer network solutions is expected to continue growing as organizations seek to improve network performance, reduce costs, and enhance security. The ability of chiplets to support seamless multilayer network operations aligns well with these market demands, offering a promising approach to addressing the complex networking challenges of the future.
Chiplet Integration Challenges in Networking
The integration of chiplets in networking devices presents several significant challenges that need to be addressed to ensure seamless multilayer network operations. One of the primary obstacles is the interconnection between different chiplets. As network devices require high-speed data transfer between various components, the interconnects must support extremely high bandwidth while maintaining low latency. This necessitates the development of advanced packaging technologies and high-speed interfaces that can handle the massive data flows typical in networking applications.
Another critical challenge lies in the thermal management of chiplet-based networking systems. As chiplets are densely packed and often operate at high frequencies, they generate substantial heat. Efficient heat dissipation becomes crucial to maintain optimal performance and prevent thermal-induced failures. This requires innovative cooling solutions and careful thermal design considerations, which can be particularly challenging in the compact form factors often required for networking equipment.
Power distribution and management across multiple chiplets also pose significant integration challenges. Ensuring stable and efficient power delivery to each chiplet while managing power consumption and optimizing energy efficiency is complex. This is especially true for networking devices that need to operate continuously and handle varying workloads. Implementing sophisticated power management techniques and designing effective power distribution networks become essential tasks in chiplet integration for networking applications.
Signal integrity and electromagnetic interference (EMI) management are additional hurdles in chiplet integration for networking. The high-speed signals traveling between chiplets can be susceptible to interference and signal degradation, potentially impacting network performance. Careful signal routing, shielding, and EMI mitigation techniques must be employed to maintain signal quality and prevent crosstalk between different chiplets and components.
Standardization and interoperability present yet another challenge in chiplet integration for networking. As chiplets may come from different vendors or use various technologies, ensuring seamless integration and compatibility becomes crucial. The development and adoption of industry standards for chiplet interfaces, protocols, and packaging are necessary to facilitate interoperability and reduce integration complexities.
Lastly, testing and validation of chiplet-based networking systems pose unique challenges. Traditional testing methodologies may not be sufficient to thoroughly evaluate the performance and reliability of integrated chiplet solutions. New testing strategies and tools need to be developed to assess the functionality, performance, and robustness of chiplet-based networking devices across various operating conditions and network scenarios.
Another critical challenge lies in the thermal management of chiplet-based networking systems. As chiplets are densely packed and often operate at high frequencies, they generate substantial heat. Efficient heat dissipation becomes crucial to maintain optimal performance and prevent thermal-induced failures. This requires innovative cooling solutions and careful thermal design considerations, which can be particularly challenging in the compact form factors often required for networking equipment.
Power distribution and management across multiple chiplets also pose significant integration challenges. Ensuring stable and efficient power delivery to each chiplet while managing power consumption and optimizing energy efficiency is complex. This is especially true for networking devices that need to operate continuously and handle varying workloads. Implementing sophisticated power management techniques and designing effective power distribution networks become essential tasks in chiplet integration for networking applications.
Signal integrity and electromagnetic interference (EMI) management are additional hurdles in chiplet integration for networking. The high-speed signals traveling between chiplets can be susceptible to interference and signal degradation, potentially impacting network performance. Careful signal routing, shielding, and EMI mitigation techniques must be employed to maintain signal quality and prevent crosstalk between different chiplets and components.
Standardization and interoperability present yet another challenge in chiplet integration for networking. As chiplets may come from different vendors or use various technologies, ensuring seamless integration and compatibility becomes crucial. The development and adoption of industry standards for chiplet interfaces, protocols, and packaging are necessary to facilitate interoperability and reduce integration complexities.
Lastly, testing and validation of chiplet-based networking systems pose unique challenges. Traditional testing methodologies may not be sufficient to thoroughly evaluate the performance and reliability of integrated chiplet solutions. New testing strategies and tools need to be developed to assess the functionality, performance, and robustness of chiplet-based networking devices across various operating conditions and network scenarios.
Current Chiplet Solutions for Network Operations
01 Chiplet-based network architecture
Implementing a seamless multilayer network operation using chiplet-based architecture. This approach involves designing interconnected chiplets that can perform various network functions across multiple layers, enabling efficient and scalable network operations.- Chiplet-based network architecture: This approach involves designing network operations using chiplet-based architectures. Chiplets are small, modular integrated circuits that can be combined to form larger systems. In the context of multilayer network operations, chiplets can be used to create scalable and flexible network processing units, allowing for seamless integration of various network functions across multiple layers.
- Inter-chiplet communication protocols: Efficient communication between chiplets is crucial for seamless multilayer network operations. This involves developing specialized protocols and interfaces that enable high-speed, low-latency data transfer between different chiplets. These protocols ensure coherent operation across the network layers and optimize overall system performance.
- Network function virtualization on chiplets: This approach focuses on implementing network function virtualization (NFV) techniques on chiplet-based systems. By virtualizing network functions across multiple chiplets, it becomes possible to create flexible and adaptable network architectures that can seamlessly operate across different layers of the network stack.
- Multilayer traffic management in chiplet systems: This involves developing sophisticated traffic management algorithms and mechanisms specifically designed for chiplet-based network systems. These solutions aim to efficiently handle and route network traffic across multiple layers, ensuring optimal utilization of chiplet resources and maintaining quality of service across the network.
- Power and thermal management for chiplet networks: Efficient power and thermal management is crucial for the seamless operation of multilayer chiplet-based networks. This involves developing advanced techniques to optimize power consumption and heat dissipation across the chiplet array, ensuring stable and reliable network operations across all layers.
02 Inter-chiplet communication protocols
Developing specialized communication protocols for seamless data transfer between chiplets in a multilayer network. These protocols ensure low-latency, high-bandwidth communication while maintaining coherence across different network layers.Expand Specific Solutions03 Network function virtualization on chiplets
Implementing network function virtualization (NFV) on chiplet-based systems to enable flexible and dynamic allocation of network resources across multiple layers. This approach allows for efficient utilization of chiplet resources and adaptable network configurations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Chiplet-based network processing acceleration
Utilizing specialized chiplets for accelerating specific network processing tasks across multiple layers. This includes dedicated chiplets for packet processing, encryption, and traffic management, enhancing overall network performance and efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Chiplet integration for seamless network scaling
Developing methods for seamless integration of additional chiplets to scale network operations across multiple layers. This includes hot-swapping capabilities, dynamic resource allocation, and adaptive routing techniques to ensure uninterrupted network performance during scaling operations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Chiplet-based Networking
The chiplet technology market is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across the semiconductor industry. The market size is expanding rapidly, driven by demand for more efficient and scalable chip designs. Technologically, chiplets are maturing but still evolving, with major players like Intel, AMD, and TSMC advancing interconnect standards and integration techniques. Companies such as Micron, Intel, and Huawei are actively developing chiplet-based solutions, while others like SMIC and Renesas are exploring implementation strategies. The competitive landscape is dynamic, with both established semiconductor giants and emerging players vying for market share in this transformative technology space.
Micron Technology, Inc.
Technical Solution: Micron's approach to chiplets in multilayer network operations focuses on advanced memory solutions. They are developing High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) and other 3D-stacked memory technologies that can be integrated as chiplets in complex system-on-chip (SoC) designs[7]. Micron's Hybrid Memory Cube (HMC) technology, for instance, uses through-silicon vias (TSVs) to stack multiple DRAM dies, providing high bandwidth and low latency for network processing applications. Additionally, Micron is exploring the use of compute-in-memory architectures, where memory chiplets can perform certain computations, potentially offloading tasks from the main processor in network devices[8].
Strengths: Expertise in memory technologies, potential for high-bandwidth and low-latency solutions in network devices. Weaknesses: Limited focus on logic and processing elements compared to more diversified semiconductor companies.
Intel Corp.
Technical Solution: Intel's approach to chiplets and seamless multilayer network operations involves their Embedded Multi-die Interconnect Bridge (EMIB) and Foveros 3D packaging technologies. EMIB allows for high-bandwidth connections between chiplets in a 2D arrangement, while Foveros enables true 3D chip stacking[1]. These technologies support heterogeneous integration, allowing different process nodes and IP blocks to be combined efficiently. Intel's Ponte Vecchio GPU, for instance, utilizes both EMIB and Foveros, incorporating over 40 tiles fabricated on multiple process nodes[2]. This approach enables Intel to optimize performance, power efficiency, and cost by selecting the most appropriate process node for each function.
Strengths: Flexibility in chip design, ability to mix and match different process nodes, and high-bandwidth die-to-die connections. Weaknesses: Complexity in manufacturing and potential thermal management challenges in 3D stacked designs.
Innovations in Chiplet Interconnect Technologies
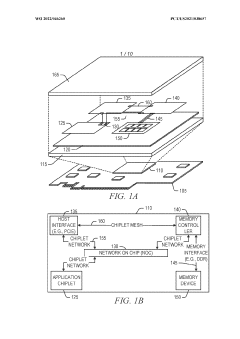
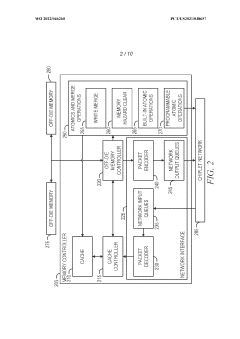
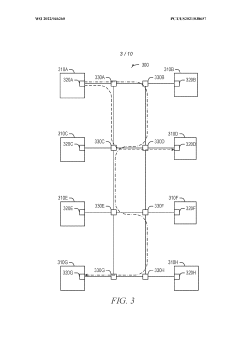
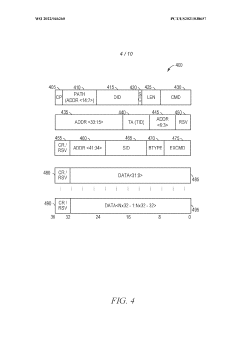
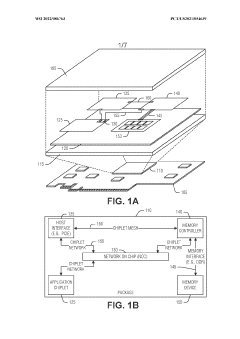
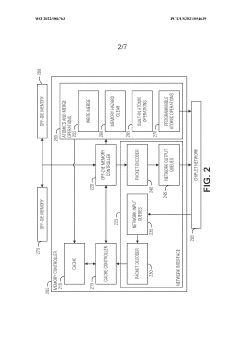
Mapping high-speed, point-to-point interface channels to packet virtual channels
PatentWO2022046260A1
Innovation
- Mapping AXI channels to packet virtual channels allows for independent flow control, enabling any AXI channel to be processed without blocking due to another channel's stall by converting data into a packet format and using virtual channels for transmission.
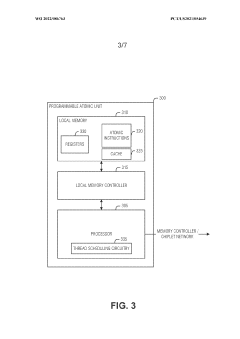
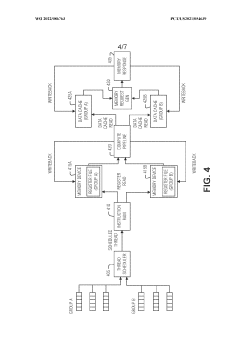
Thread scheduling control and memory splitting in a barrel processor
PatentWO2022086763A1
Innovation
- Implementing a thread scheduling control mechanism that organizes threads into separate groups, each with its own memory device, and alternates between groups for read and write access to reduce memory contention, allowing threads to progress through the pipeline more efficiently and reducing power draw.
Standardization Efforts in Chiplet Ecosystems
Standardization efforts in the chiplet ecosystem are crucial for enabling seamless multilayer network operations across diverse chiplet designs. These initiatives aim to establish common interfaces, protocols, and packaging standards that facilitate interoperability and integration of chiplets from different vendors.
One of the primary standardization efforts is the Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe), which defines a die-to-die interconnect standard for chiplets. UCIe provides a common physical and logical interface, allowing chiplets from various manufacturers to communicate effectively within a single package. This standardization is essential for creating a robust ecosystem where chiplets can be mixed and matched to build custom, high-performance systems.
Another significant standardization initiative is the Open Compute Project's Open Domain-Specific Architecture (ODSA) subproject. ODSA focuses on developing open architectures and standards for chiplet-based designs, including the Bunch of Wires (BoW) interface specification. BoW aims to standardize the physical layer interconnect between chiplets, promoting interoperability and reducing design complexity.
The JEDEC Solid State Technology Association has also been active in chiplet standardization, working on standards for chiplet interfaces and packaging technologies. Their efforts include developing specifications for high-bandwidth memory interfaces and 3D packaging standards, which are critical for enabling efficient multilayer network operations in chiplet-based systems.
Additionally, the IEEE is contributing to chiplet standardization through its P2851 standard for Exchangeable Chiplet Models. This standard aims to create a common language for describing chiplet functionality and interfaces, facilitating easier integration and verification of multi-vendor chiplet designs.
These standardization efforts collectively address various aspects of chiplet integration, from physical interconnects to logical interfaces and design methodologies. By establishing common standards, they enable seamless communication between chiplets, regardless of their origin or specific design. This interoperability is crucial for supporting multilayer network operations, as it allows different network layers to be implemented across multiple chiplets while maintaining efficient data flow and processing.
The success of these standardization initiatives is vital for the widespread adoption of chiplet technology in network systems. As these standards mature and gain industry acceptance, they will pave the way for more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective network architectures that can leverage the benefits of chiplet-based designs across multiple layers of network operations.
One of the primary standardization efforts is the Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe), which defines a die-to-die interconnect standard for chiplets. UCIe provides a common physical and logical interface, allowing chiplets from various manufacturers to communicate effectively within a single package. This standardization is essential for creating a robust ecosystem where chiplets can be mixed and matched to build custom, high-performance systems.
Another significant standardization initiative is the Open Compute Project's Open Domain-Specific Architecture (ODSA) subproject. ODSA focuses on developing open architectures and standards for chiplet-based designs, including the Bunch of Wires (BoW) interface specification. BoW aims to standardize the physical layer interconnect between chiplets, promoting interoperability and reducing design complexity.
The JEDEC Solid State Technology Association has also been active in chiplet standardization, working on standards for chiplet interfaces and packaging technologies. Their efforts include developing specifications for high-bandwidth memory interfaces and 3D packaging standards, which are critical for enabling efficient multilayer network operations in chiplet-based systems.
Additionally, the IEEE is contributing to chiplet standardization through its P2851 standard for Exchangeable Chiplet Models. This standard aims to create a common language for describing chiplet functionality and interfaces, facilitating easier integration and verification of multi-vendor chiplet designs.
These standardization efforts collectively address various aspects of chiplet integration, from physical interconnects to logical interfaces and design methodologies. By establishing common standards, they enable seamless communication between chiplets, regardless of their origin or specific design. This interoperability is crucial for supporting multilayer network operations, as it allows different network layers to be implemented across multiple chiplets while maintaining efficient data flow and processing.
The success of these standardization initiatives is vital for the widespread adoption of chiplet technology in network systems. As these standards mature and gain industry acceptance, they will pave the way for more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective network architectures that can leverage the benefits of chiplet-based designs across multiple layers of network operations.
Energy Efficiency of Chiplet-based Networks
Chiplet-based networks have emerged as a promising solution for addressing the energy efficiency challenges in modern computing systems. By disaggregating large monolithic chips into smaller, more specialized components, chiplets offer significant advantages in terms of power consumption and thermal management. The modular nature of chiplet designs allows for more efficient use of silicon area and enables the integration of heterogeneous components, each optimized for specific functions.
One of the key factors contributing to the energy efficiency of chiplet-based networks is the reduction in interconnect length. Traditional monolithic designs often require long interconnects to connect different functional units, resulting in increased power consumption due to signal propagation. In contrast, chiplet architectures allow for shorter interconnects between closely packed components, reducing signal loss and power requirements. This approach also enables the use of advanced packaging technologies, such as silicon interposers or organic substrates, which further optimize signal integrity and power delivery.
The ability to mix and match different process nodes within a single package is another significant advantage of chiplet-based networks in terms of energy efficiency. High-performance components can be manufactured using cutting-edge process nodes, while less critical components can utilize more mature and cost-effective nodes. This flexibility allows designers to optimize the power-performance trade-offs for each functional block, resulting in overall improved energy efficiency across the entire system.
Chiplet-based designs also facilitate better thermal management, which indirectly contributes to energy efficiency. By distributing heat-generating components across multiple smaller dies, chiplets allow for more effective heat dissipation compared to monolithic designs. This improved thermal performance enables higher clock speeds and better sustained performance without excessive power consumption or the need for aggressive cooling solutions.
Furthermore, the modularity of chiplet architectures supports more granular power management strategies. Individual chiplets can be selectively powered down or operated at lower frequencies when not in use, leading to significant power savings in dynamic workload scenarios. This fine-grained control over power states is particularly beneficial in multilayer network operations, where different components may have varying activity levels depending on network traffic patterns and processing requirements.
The energy efficiency benefits of chiplet-based networks extend beyond the chip level to the system and data center scale. By enabling more compact and power-efficient designs, chiplets contribute to reduced cooling requirements and improved rack density in data center environments. This cascading effect results in substantial energy savings across the entire computing infrastructure, aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainable and environmentally friendly IT solutions.
One of the key factors contributing to the energy efficiency of chiplet-based networks is the reduction in interconnect length. Traditional monolithic designs often require long interconnects to connect different functional units, resulting in increased power consumption due to signal propagation. In contrast, chiplet architectures allow for shorter interconnects between closely packed components, reducing signal loss and power requirements. This approach also enables the use of advanced packaging technologies, such as silicon interposers or organic substrates, which further optimize signal integrity and power delivery.
The ability to mix and match different process nodes within a single package is another significant advantage of chiplet-based networks in terms of energy efficiency. High-performance components can be manufactured using cutting-edge process nodes, while less critical components can utilize more mature and cost-effective nodes. This flexibility allows designers to optimize the power-performance trade-offs for each functional block, resulting in overall improved energy efficiency across the entire system.
Chiplet-based designs also facilitate better thermal management, which indirectly contributes to energy efficiency. By distributing heat-generating components across multiple smaller dies, chiplets allow for more effective heat dissipation compared to monolithic designs. This improved thermal performance enables higher clock speeds and better sustained performance without excessive power consumption or the need for aggressive cooling solutions.
Furthermore, the modularity of chiplet architectures supports more granular power management strategies. Individual chiplets can be selectively powered down or operated at lower frequencies when not in use, leading to significant power savings in dynamic workload scenarios. This fine-grained control over power states is particularly beneficial in multilayer network operations, where different components may have varying activity levels depending on network traffic patterns and processing requirements.
The energy efficiency benefits of chiplet-based networks extend beyond the chip level to the system and data center scale. By enabling more compact and power-efficient designs, chiplets contribute to reduced cooling requirements and improved rack density in data center environments. This cascading effect results in substantial energy savings across the entire computing infrastructure, aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainable and environmentally friendly IT solutions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!