Chiplet Systems in Adaptive Application Enhancement Processes
JUL 16, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Chiplet Systems Background and Objectives
Chiplet systems have emerged as a revolutionary approach in the semiconductor industry, addressing the challenges of traditional monolithic chip designs. This technology involves breaking down complex system-on-chip (SoC) designs into smaller, modular components called chiplets, which can be manufactured separately and then integrated onto a single package. The concept of chiplets has gained significant traction in recent years, driven by the need for improved performance, reduced costs, and enhanced scalability in semiconductor manufacturing.
The evolution of chiplet technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring the potential of multi-chip modules. However, it wasn't until the mid-2010s that chiplets gained widespread attention as a viable solution to overcome the limitations of Moore's Law. As transistor scaling became increasingly difficult and expensive, chiplets offered a way to continue improving performance and functionality without relying solely on process node advancements.
The primary objective of chiplet systems is to enable the creation of highly customizable and scalable semiconductor solutions. By leveraging a mix-and-match approach, chiplets allow designers to combine different functional blocks, potentially from various process nodes, onto a single package. This flexibility not only reduces development costs but also accelerates time-to-market for new products.
In the context of adaptive application enhancement processes, chiplet systems play a crucial role in enabling more efficient and flexible computing architectures. The modular nature of chiplets allows for the integration of specialized processing units, memory components, and I/O interfaces tailored to specific application requirements. This adaptability is particularly valuable in emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, edge computing, and 5G communications, where diverse and evolving workloads demand optimized hardware solutions.
The development of chiplet systems has been driven by several key technological advancements. These include improvements in packaging technologies, such as advanced 2.5D and 3D integration techniques, as well as the development of high-speed interconnect standards like Advanced Interface Bus (AIB) and Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe). These innovations have enabled seamless communication between chiplets and overcome many of the challenges associated with multi-chip integration.
As the semiconductor industry continues to evolve, chiplet systems are expected to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of computing. The technology promises to deliver higher performance, improved energy efficiency, and greater design flexibility compared to traditional monolithic approaches. Furthermore, chiplets have the potential to democratize chip design by lowering barriers to entry and fostering innovation across the semiconductor ecosystem.
The evolution of chiplet technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring the potential of multi-chip modules. However, it wasn't until the mid-2010s that chiplets gained widespread attention as a viable solution to overcome the limitations of Moore's Law. As transistor scaling became increasingly difficult and expensive, chiplets offered a way to continue improving performance and functionality without relying solely on process node advancements.
The primary objective of chiplet systems is to enable the creation of highly customizable and scalable semiconductor solutions. By leveraging a mix-and-match approach, chiplets allow designers to combine different functional blocks, potentially from various process nodes, onto a single package. This flexibility not only reduces development costs but also accelerates time-to-market for new products.
In the context of adaptive application enhancement processes, chiplet systems play a crucial role in enabling more efficient and flexible computing architectures. The modular nature of chiplets allows for the integration of specialized processing units, memory components, and I/O interfaces tailored to specific application requirements. This adaptability is particularly valuable in emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, edge computing, and 5G communications, where diverse and evolving workloads demand optimized hardware solutions.
The development of chiplet systems has been driven by several key technological advancements. These include improvements in packaging technologies, such as advanced 2.5D and 3D integration techniques, as well as the development of high-speed interconnect standards like Advanced Interface Bus (AIB) and Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe). These innovations have enabled seamless communication between chiplets and overcome many of the challenges associated with multi-chip integration.
As the semiconductor industry continues to evolve, chiplet systems are expected to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of computing. The technology promises to deliver higher performance, improved energy efficiency, and greater design flexibility compared to traditional monolithic approaches. Furthermore, chiplets have the potential to democratize chip design by lowering barriers to entry and fostering innovation across the semiconductor ecosystem.
Market Demand Analysis for Adaptive Applications
The market demand for adaptive applications in chiplet systems is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing complexity of modern computing tasks and the need for more flexible and efficient hardware solutions. As traditional monolithic chip designs reach their limits in terms of performance scaling and manufacturing efficiency, chiplet-based systems offer a promising alternative that can adapt to diverse application requirements.
In the data center and cloud computing sector, there is a strong demand for adaptive chiplet systems that can handle varying workloads, from general-purpose computing to specialized tasks like artificial intelligence and machine learning. These systems allow for the dynamic allocation of computing resources, optimizing performance and energy efficiency based on real-time application needs. This adaptability is particularly valuable for cloud service providers who need to cater to a wide range of customer requirements while maximizing resource utilization.
The telecommunications industry is another key driver of market demand for adaptive chiplet systems. With the ongoing rollout of 5G networks and the anticipated transition to 6G in the future, there is a growing need for flexible and scalable hardware solutions that can support diverse network configurations and evolving communication standards. Chiplet-based systems enable telecom equipment manufacturers to create modular designs that can be easily upgraded or reconfigured to meet changing network demands.
In the automotive sector, the shift towards autonomous vehicles and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) is creating a substantial market for adaptive chiplet systems. These systems must be capable of processing vast amounts of sensor data in real-time while adapting to various driving conditions and scenarios. The ability to integrate different types of chiplets, such as high-performance processors, AI accelerators, and sensor fusion units, allows automotive manufacturers to create flexible and scalable platforms that can evolve with advancing autonomous driving technologies.
The consumer electronics market is also showing increased interest in adaptive chiplet systems, particularly for high-end smartphones, tablets, and gaming devices. These systems can provide enhanced performance and power efficiency by dynamically adjusting to user behavior and application requirements. For example, a chiplet-based smartphone could allocate more resources to gaming or video processing when needed, while conserving energy during less demanding tasks.
In the industrial and manufacturing sector, there is growing demand for adaptive chiplet systems in edge computing applications. These systems can provide the necessary processing power and flexibility to handle complex industrial automation tasks, predictive maintenance, and real-time analytics at the edge of the network. The ability to customize and upgrade chiplet configurations allows industrial equipment manufacturers to create more versatile and future-proof solutions for their customers.
Overall, the market demand for adaptive applications in chiplet systems is driven by the need for more flexible, efficient, and scalable computing solutions across various industries. As technology continues to evolve and application requirements become more diverse, the adaptability offered by chiplet-based systems is likely to become increasingly valuable, fueling further market growth and innovation in this space.
In the data center and cloud computing sector, there is a strong demand for adaptive chiplet systems that can handle varying workloads, from general-purpose computing to specialized tasks like artificial intelligence and machine learning. These systems allow for the dynamic allocation of computing resources, optimizing performance and energy efficiency based on real-time application needs. This adaptability is particularly valuable for cloud service providers who need to cater to a wide range of customer requirements while maximizing resource utilization.
The telecommunications industry is another key driver of market demand for adaptive chiplet systems. With the ongoing rollout of 5G networks and the anticipated transition to 6G in the future, there is a growing need for flexible and scalable hardware solutions that can support diverse network configurations and evolving communication standards. Chiplet-based systems enable telecom equipment manufacturers to create modular designs that can be easily upgraded or reconfigured to meet changing network demands.
In the automotive sector, the shift towards autonomous vehicles and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) is creating a substantial market for adaptive chiplet systems. These systems must be capable of processing vast amounts of sensor data in real-time while adapting to various driving conditions and scenarios. The ability to integrate different types of chiplets, such as high-performance processors, AI accelerators, and sensor fusion units, allows automotive manufacturers to create flexible and scalable platforms that can evolve with advancing autonomous driving technologies.
The consumer electronics market is also showing increased interest in adaptive chiplet systems, particularly for high-end smartphones, tablets, and gaming devices. These systems can provide enhanced performance and power efficiency by dynamically adjusting to user behavior and application requirements. For example, a chiplet-based smartphone could allocate more resources to gaming or video processing when needed, while conserving energy during less demanding tasks.
In the industrial and manufacturing sector, there is growing demand for adaptive chiplet systems in edge computing applications. These systems can provide the necessary processing power and flexibility to handle complex industrial automation tasks, predictive maintenance, and real-time analytics at the edge of the network. The ability to customize and upgrade chiplet configurations allows industrial equipment manufacturers to create more versatile and future-proof solutions for their customers.
Overall, the market demand for adaptive applications in chiplet systems is driven by the need for more flexible, efficient, and scalable computing solutions across various industries. As technology continues to evolve and application requirements become more diverse, the adaptability offered by chiplet-based systems is likely to become increasingly valuable, fueling further market growth and innovation in this space.
Chiplet Technology Status and Challenges
Chiplet technology has emerged as a revolutionary approach in the semiconductor industry, offering a promising solution to the challenges faced in traditional monolithic chip designs. The current status of chiplet technology is characterized by rapid advancements and growing adoption across various sectors of the electronics industry.
One of the primary challenges in chiplet technology is achieving seamless integration between different chiplets. This includes addressing issues related to inter-chiplet communication, power management, and thermal dissipation. The industry is actively working on developing standardized interfaces and protocols to facilitate easier integration and interoperability between chiplets from different manufacturers.
Another significant challenge lies in the packaging and assembly of chiplets. As chiplets become smaller and more complex, traditional packaging techniques may not be sufficient to meet the demands of high-performance systems. Advanced packaging technologies, such as 2.5D and 3D integration, are being explored to overcome these limitations and enable more efficient chiplet-based designs.
The geographical distribution of chiplet technology development is primarily concentrated in regions with strong semiconductor industries. The United States, Taiwan, South Korea, and China are at the forefront of chiplet research and development. However, collaborative efforts across borders are becoming increasingly common as companies recognize the need for global expertise in addressing the complex challenges associated with chiplet technology.
In terms of technical constraints, one of the key issues is the need for high-bandwidth, low-latency interconnects between chiplets. Current solutions, such as silicon interposers and advanced packaging techniques, are continually being refined to improve performance and reduce costs. Additionally, the industry is grappling with challenges related to design complexity, as chiplet-based systems require sophisticated tools and methodologies for system-level optimization.
The adoption of chiplet technology in adaptive application enhancement processes presents unique challenges. These include ensuring seamless integration of chiplets with varying functionalities, managing power and thermal constraints in dynamic environments, and developing flexible architectures that can adapt to changing application requirements. Researchers are exploring novel approaches, such as reconfigurable interconnects and adaptive power management schemes, to address these challenges.
As the technology matures, standardization efforts are gaining momentum. Industry consortia and standards bodies are working towards establishing common specifications for chiplet interfaces, packaging, and testing. These efforts aim to create a more cohesive ecosystem that facilitates innovation and reduces barriers to entry for smaller players in the market.
One of the primary challenges in chiplet technology is achieving seamless integration between different chiplets. This includes addressing issues related to inter-chiplet communication, power management, and thermal dissipation. The industry is actively working on developing standardized interfaces and protocols to facilitate easier integration and interoperability between chiplets from different manufacturers.
Another significant challenge lies in the packaging and assembly of chiplets. As chiplets become smaller and more complex, traditional packaging techniques may not be sufficient to meet the demands of high-performance systems. Advanced packaging technologies, such as 2.5D and 3D integration, are being explored to overcome these limitations and enable more efficient chiplet-based designs.
The geographical distribution of chiplet technology development is primarily concentrated in regions with strong semiconductor industries. The United States, Taiwan, South Korea, and China are at the forefront of chiplet research and development. However, collaborative efforts across borders are becoming increasingly common as companies recognize the need for global expertise in addressing the complex challenges associated with chiplet technology.
In terms of technical constraints, one of the key issues is the need for high-bandwidth, low-latency interconnects between chiplets. Current solutions, such as silicon interposers and advanced packaging techniques, are continually being refined to improve performance and reduce costs. Additionally, the industry is grappling with challenges related to design complexity, as chiplet-based systems require sophisticated tools and methodologies for system-level optimization.
The adoption of chiplet technology in adaptive application enhancement processes presents unique challenges. These include ensuring seamless integration of chiplets with varying functionalities, managing power and thermal constraints in dynamic environments, and developing flexible architectures that can adapt to changing application requirements. Researchers are exploring novel approaches, such as reconfigurable interconnects and adaptive power management schemes, to address these challenges.
As the technology matures, standardization efforts are gaining momentum. Industry consortia and standards bodies are working towards establishing common specifications for chiplet interfaces, packaging, and testing. These efforts aim to create a more cohesive ecosystem that facilitates innovation and reduces barriers to entry for smaller players in the market.
Current Chiplet Integration Solutions
01 Adaptive chiplet interconnection and configuration
Chiplet systems can be enhanced through adaptive interconnection and configuration techniques. This involves dynamically adjusting the connections between chiplets and optimizing their arrangement based on application requirements. Such adaptability allows for improved performance, power efficiency, and resource utilization in multi-chiplet systems.- Adaptive chiplet interconnection: Chiplet systems employ adaptive interconnection techniques to enhance application performance. This involves dynamically adjusting communication pathways between chiplets based on application requirements, workload characteristics, and system conditions. The adaptive interconnection allows for optimized data transfer, reduced latency, and improved overall system efficiency.
- Dynamic resource allocation in chiplet systems: Chiplet-based architectures implement dynamic resource allocation mechanisms to enhance application performance. This approach involves real-time monitoring of application demands and system resources, allowing for intelligent distribution of computing, memory, and I/O resources across chiplets. The dynamic allocation enables efficient utilization of system capabilities and adapts to varying workload requirements.
- Application-specific chiplet configuration: Chiplet systems support application-specific configurations to optimize performance for particular use cases. This involves selecting and arranging chiplets with specialized functionalities tailored to specific application domains. The ability to customize chiplet configurations allows for enhanced performance in targeted applications while maintaining system flexibility.
- AI-driven chiplet optimization: Artificial intelligence techniques are employed in chiplet systems to continuously optimize application performance. Machine learning algorithms analyze application behavior, system metrics, and historical data to make intelligent decisions on chiplet configuration, resource allocation, and interconnect optimization. This AI-driven approach enables adaptive enhancement of application performance over time.
- Power-aware chiplet management: Chiplet systems incorporate power-aware management techniques to balance performance enhancement with energy efficiency. This involves dynamically adjusting power consumption across chiplets based on application requirements and thermal constraints. Power-aware management enables optimal performance within given power envelopes, enhancing overall system efficiency and reliability.
02 Application-specific chiplet optimization
Chiplet systems can be tailored to specific applications by optimizing individual chiplets or combinations thereof. This may involve customizing chiplet designs, selecting appropriate chiplet types, and fine-tuning their parameters to meet the unique demands of different applications, resulting in enhanced overall system performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Dynamic resource allocation in chiplet systems
Adaptive application enhancement in chiplet systems can be achieved through dynamic resource allocation. This involves real-time monitoring of application requirements and system performance, followed by intelligent redistribution of computing resources across chiplets to optimize execution efficiency and power consumption.Expand Specific Solutions04 AI-driven chiplet system optimization
Artificial intelligence techniques can be employed to enhance chiplet system performance adaptively. Machine learning algorithms can analyze application behavior, predict resource requirements, and make intelligent decisions on chiplet configuration and task distribution, leading to improved system efficiency and adaptability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Heterogeneous chiplet integration for application-specific acceleration
Chiplet systems can be enhanced by integrating heterogeneous chiplets with specialized functionalities. This approach allows for the combination of different types of processing units, memory modules, and accelerators tailored to specific application requirements, resulting in improved performance and energy efficiency for diverse workloads.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Chiplet Industry
The research on Chiplet Systems in Adaptive Application Enhancement Processes is in an emerging stage, with significant potential for growth. The market is expanding rapidly as chiplet technology offers solutions to scaling challenges in traditional monolithic chip designs. Companies like Intel, Micron, and Xilinx are at the forefront, leveraging their expertise in semiconductor manufacturing and FPGA technologies. Startups such as D-Matrix and MemryX are introducing innovative approaches, focusing on AI and edge computing applications. The technology's maturity varies across players, with established firms having a head start but newer entrants bringing fresh perspectives to chiplet integration and system-level optimization.
Intel Corp.
Technical Solution: Intel's approach to Chiplet Systems in Adaptive Application Enhancement Processes focuses on their innovative Foveros 3D packaging technology. This technology allows for the vertical stacking of multiple chiplets, enabling higher performance and lower power consumption[1]. Intel's Ponte Vecchio GPU, built using Foveros, incorporates over 40 chiplets in a single package, demonstrating the scalability of their approach[2]. The company has also developed the Advanced Interface Bus (AIB) for high-bandwidth, low-power die-to-die communication between chiplets[3]. Intel's EMIB (Embedded Multi-die Interconnect Bridge) technology complements Foveros by providing high-density interconnects for 2.5D packaging, allowing for the integration of heterogeneous chiplets[4].
Strengths: Advanced 3D packaging capabilities, high-performance interconnect technologies, and a proven track record in heterogeneous integration. Weaknesses: Potential complexity in manufacturing and thermal management challenges in densely packed 3D structures.
Xilinx, Inc.
Technical Solution: Xilinx, now part of AMD, has been at the forefront of chiplet technology with their Adaptive Compute Acceleration Platform (ACAP) architecture. Their Versal ACAP combines FPGA fabric, CPUs, and AI engines in a modular chiplet-based design[9]. The company's Stacked Silicon Interconnect (SSI) technology allows for the integration of multiple FPGA dies, creating larger, more powerful devices[10]. Xilinx has also developed the Network-on-Chip (NoC) architecture for efficient communication between different chiplets and IP blocks within their devices[11]. Their adaptive applications enhancement processes leverage the reconfigurable nature of FPGAs, allowing for real-time optimization of hardware accelerators based on changing workload requirements[12].
Strengths: Leader in FPGA technology, advanced chiplet integration capabilities, and flexible, reconfigurable architectures. Weaknesses: Potential complexity in programming and optimizing heterogeneous systems for specific applications.
Core Chiplet Innovations for Adaptive Applications
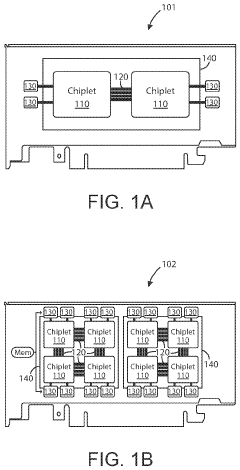
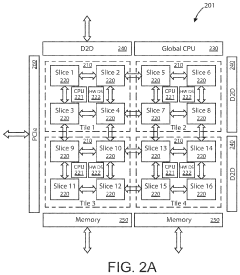
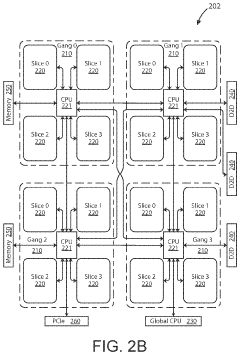
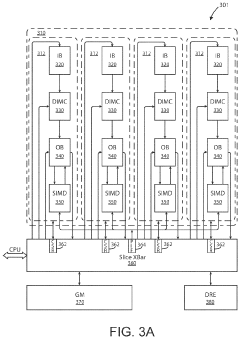
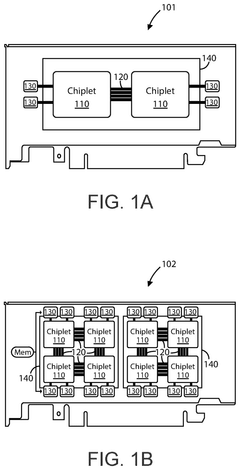
Generative ai accelerator apparatus using in-memory compute chiplet devices for transformer workloads
PatentActiveUS20230168899A1
Innovation
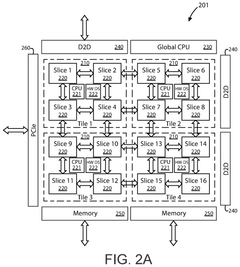
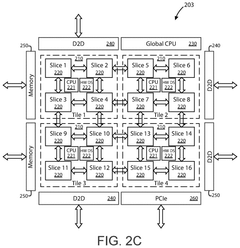
- The implementation of AI accelerator apparatuses using chiplet devices with digital in-memory compute functionality, which includes multiple slices with CPUs and hardware dispatch devices, along with die-to-die interconnects and PCIe buses, to accelerate transformer computations by integrating computational functions and memory fabric, enabling efficient processing and reducing power consumption.
Ai accelerator apparatus using full mesh connectivity chiplet devices for transformer workloads
PatentPendingUS20250123984A1
Innovation
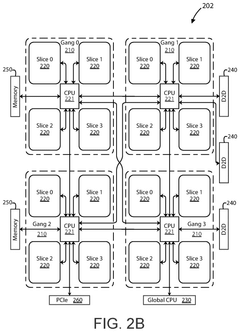
- The development of an AI accelerator apparatus with a modular chiplet architecture, featuring in-memory compute and full mesh connectivity, which includes multiple chiplets coupled in a full mesh configuration, each with tiles and slices that integrate CPU, DIMC, and hardware dispatch devices, optimizing computational performance and reducing power consumption.
Standardization Efforts in Chiplet Technology
Standardization efforts in chiplet technology have become increasingly crucial as the industry moves towards more modular and heterogeneous chip designs. These efforts aim to establish common interfaces, protocols, and design methodologies that enable seamless integration of diverse chiplets from different vendors.
One of the most prominent standardization initiatives is the Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe), which was introduced in 2022. UCIe focuses on defining a die-to-die interconnect standard that allows chiplets from various manufacturers to communicate effectively. This standard encompasses both the physical layer and the protocol layer, ensuring compatibility across different chiplet designs.
Another significant standardization effort is the Open Compute Project's (OCP) Chiplet Design Exchange (CDX) format. CDX aims to create a common language for describing chiplet designs, facilitating easier exchange of information between different tools and design teams. This standardization helps streamline the chiplet design process and promotes interoperability.
The CHIPS Alliance, an open-source hardware organization, has also been actively working on chiplet standardization. Their efforts include developing open-source tools and methodologies for chiplet-based designs, as well as promoting the adoption of open standards in the industry.
In the realm of packaging technologies, the Joint Electron Device Engineering Council (JEDEC) has been instrumental in standardizing advanced packaging solutions that support chiplet integration. Their work includes standards for 2.5D and 3D packaging technologies, which are crucial for enabling high-performance chiplet-based systems.
The IEEE has also contributed to chiplet standardization through its P2851 standard for 3D Stacked Die Interface. This standard focuses on the electrical and mechanical specifications for die-to-die interfaces in 3D integrated circuits, which is directly applicable to chiplet technology.
These standardization efforts are essential for the widespread adoption of chiplet technology in adaptive application enhancement processes. By establishing common standards, the industry can reduce design complexity, improve interoperability, and accelerate time-to-market for chiplet-based systems. Furthermore, standardization promotes innovation by allowing companies to focus on their core competencies while leveraging standardized interfaces for integration.
As chiplet technology continues to evolve, ongoing collaboration between industry leaders, research institutions, and standards organizations will be crucial to refine and expand these standards. This collaborative approach will ensure that chiplet technology can meet the diverse and changing needs of adaptive applications across various domains.
One of the most prominent standardization initiatives is the Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe), which was introduced in 2022. UCIe focuses on defining a die-to-die interconnect standard that allows chiplets from various manufacturers to communicate effectively. This standard encompasses both the physical layer and the protocol layer, ensuring compatibility across different chiplet designs.
Another significant standardization effort is the Open Compute Project's (OCP) Chiplet Design Exchange (CDX) format. CDX aims to create a common language for describing chiplet designs, facilitating easier exchange of information between different tools and design teams. This standardization helps streamline the chiplet design process and promotes interoperability.
The CHIPS Alliance, an open-source hardware organization, has also been actively working on chiplet standardization. Their efforts include developing open-source tools and methodologies for chiplet-based designs, as well as promoting the adoption of open standards in the industry.
In the realm of packaging technologies, the Joint Electron Device Engineering Council (JEDEC) has been instrumental in standardizing advanced packaging solutions that support chiplet integration. Their work includes standards for 2.5D and 3D packaging technologies, which are crucial for enabling high-performance chiplet-based systems.
The IEEE has also contributed to chiplet standardization through its P2851 standard for 3D Stacked Die Interface. This standard focuses on the electrical and mechanical specifications for die-to-die interfaces in 3D integrated circuits, which is directly applicable to chiplet technology.
These standardization efforts are essential for the widespread adoption of chiplet technology in adaptive application enhancement processes. By establishing common standards, the industry can reduce design complexity, improve interoperability, and accelerate time-to-market for chiplet-based systems. Furthermore, standardization promotes innovation by allowing companies to focus on their core competencies while leveraging standardized interfaces for integration.
As chiplet technology continues to evolve, ongoing collaboration between industry leaders, research institutions, and standards organizations will be crucial to refine and expand these standards. This collaborative approach will ensure that chiplet technology can meet the diverse and changing needs of adaptive applications across various domains.
Energy Efficiency in Chiplet-based Systems
Energy efficiency has become a critical concern in the development of chiplet-based systems, particularly in the context of adaptive application enhancement processes. As the demand for more powerful and versatile computing systems continues to grow, chiplet technology offers a promising solution to address both performance and energy consumption challenges.
Chiplet-based systems leverage modular design principles, allowing for the integration of multiple smaller silicon dies (chiplets) into a single package. This approach enables the combination of different process technologies and specialized functionalities, potentially leading to significant improvements in energy efficiency. By optimizing the design and interconnection of chiplets, manufacturers can reduce power consumption while maintaining or even enhancing overall system performance.
One of the key factors contributing to energy efficiency in chiplet-based systems is the ability to selectively power on or off specific chiplets based on workload requirements. This granular power management approach allows for more efficient resource utilization, as unused components can be temporarily disabled to conserve energy. Additionally, the modular nature of chiplets enables the integration of specialized accelerators optimized for specific tasks, further improving energy efficiency for targeted applications.
The interconnect technology used to link chiplets plays a crucial role in determining the overall energy efficiency of the system. Advanced packaging technologies, such as silicon interposers and through-silicon vias (TSVs), facilitate high-bandwidth, low-latency communication between chiplets while minimizing power consumption. These interconnect solutions help reduce the energy overhead associated with data transfer between different components of the system.
Thermal management is another critical aspect of energy efficiency in chiplet-based systems. The modular design allows for more effective heat dissipation strategies, as thermal solutions can be tailored to the specific requirements of each chiplet. This approach helps maintain optimal operating temperatures, preventing performance throttling and reducing the need for energy-intensive cooling mechanisms.
As chiplet technology continues to evolve, researchers are exploring novel approaches to further enhance energy efficiency. These include the development of advanced power gating techniques, the integration of on-chip voltage regulators, and the implementation of AI-driven power management algorithms. These innovations aim to optimize power consumption dynamically, adapting to changing workload conditions and environmental factors in real-time.
In conclusion, energy efficiency remains a paramount consideration in the development of chiplet-based systems for adaptive application enhancement processes. By leveraging modular design principles, advanced interconnect technologies, and innovative power management strategies, chiplet-based systems offer significant potential for improving energy efficiency in next-generation computing platforms.
Chiplet-based systems leverage modular design principles, allowing for the integration of multiple smaller silicon dies (chiplets) into a single package. This approach enables the combination of different process technologies and specialized functionalities, potentially leading to significant improvements in energy efficiency. By optimizing the design and interconnection of chiplets, manufacturers can reduce power consumption while maintaining or even enhancing overall system performance.
One of the key factors contributing to energy efficiency in chiplet-based systems is the ability to selectively power on or off specific chiplets based on workload requirements. This granular power management approach allows for more efficient resource utilization, as unused components can be temporarily disabled to conserve energy. Additionally, the modular nature of chiplets enables the integration of specialized accelerators optimized for specific tasks, further improving energy efficiency for targeted applications.
The interconnect technology used to link chiplets plays a crucial role in determining the overall energy efficiency of the system. Advanced packaging technologies, such as silicon interposers and through-silicon vias (TSVs), facilitate high-bandwidth, low-latency communication between chiplets while minimizing power consumption. These interconnect solutions help reduce the energy overhead associated with data transfer between different components of the system.
Thermal management is another critical aspect of energy efficiency in chiplet-based systems. The modular design allows for more effective heat dissipation strategies, as thermal solutions can be tailored to the specific requirements of each chiplet. This approach helps maintain optimal operating temperatures, preventing performance throttling and reducing the need for energy-intensive cooling mechanisms.
As chiplet technology continues to evolve, researchers are exploring novel approaches to further enhance energy efficiency. These include the development of advanced power gating techniques, the integration of on-chip voltage regulators, and the implementation of AI-driven power management algorithms. These innovations aim to optimize power consumption dynamically, adapting to changing workload conditions and environmental factors in real-time.
In conclusion, energy efficiency remains a paramount consideration in the development of chiplet-based systems for adaptive application enhancement processes. By leveraging modular design principles, advanced interconnect technologies, and innovative power management strategies, chiplet-based systems offer significant potential for improving energy efficiency in next-generation computing platforms.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!