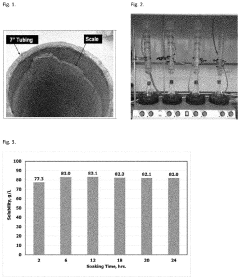
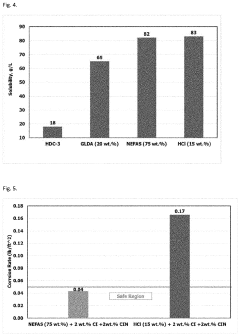
Comparative Study on Sulfamic Acid and Hydrochloric Acid Descaling Efficiency
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Descaling Agents Background and Objectives
Descaling agents have been an integral part of industrial maintenance for decades, playing a crucial role in removing mineral deposits and scale buildup from various equipment and surfaces. The evolution of these agents has been driven by the need for more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly solutions. This comparative study focuses on two widely used descaling agents: sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid.
The primary objective of this research is to evaluate and compare the descaling efficiency of sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid across different industrial applications. By examining their performance, we aim to provide valuable insights that can guide industry professionals in selecting the most suitable descaling agent for their specific needs.
Historically, hydrochloric acid has been a popular choice for descaling due to its high reactivity and effectiveness against a wide range of scale types. However, concerns about its corrosive nature and potential environmental impact have led to the exploration of alternative solutions. Sulfamic acid emerged as a promising alternative, offering a balance between effectiveness and safety.
The technological progression in descaling agents has been marked by efforts to enhance their performance while minimizing negative side effects. This includes the development of inhibited formulations to reduce metal corrosion, as well as the incorporation of surfactants and other additives to improve penetration and dissolution of scale deposits.
As industries continue to prioritize operational efficiency and sustainability, the demand for advanced descaling solutions has grown. This has spurred research into the fundamental mechanisms of scale formation and dissolution, leading to more targeted and efficient descaling approaches. The comparison between sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid is particularly relevant in this context, as it represents a broader trend towards finding optimal solutions that balance performance, safety, and environmental considerations.
This study aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the descaling efficiency of sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid across various parameters, including reaction rates, scale removal capacity, impact on substrate materials, and overall cost-effectiveness. By examining these factors, we seek to contribute to the ongoing technological evolution in the field of industrial descaling and support informed decision-making in maintenance practices.
The primary objective of this research is to evaluate and compare the descaling efficiency of sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid across different industrial applications. By examining their performance, we aim to provide valuable insights that can guide industry professionals in selecting the most suitable descaling agent for their specific needs.
Historically, hydrochloric acid has been a popular choice for descaling due to its high reactivity and effectiveness against a wide range of scale types. However, concerns about its corrosive nature and potential environmental impact have led to the exploration of alternative solutions. Sulfamic acid emerged as a promising alternative, offering a balance between effectiveness and safety.
The technological progression in descaling agents has been marked by efforts to enhance their performance while minimizing negative side effects. This includes the development of inhibited formulations to reduce metal corrosion, as well as the incorporation of surfactants and other additives to improve penetration and dissolution of scale deposits.
As industries continue to prioritize operational efficiency and sustainability, the demand for advanced descaling solutions has grown. This has spurred research into the fundamental mechanisms of scale formation and dissolution, leading to more targeted and efficient descaling approaches. The comparison between sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid is particularly relevant in this context, as it represents a broader trend towards finding optimal solutions that balance performance, safety, and environmental considerations.
This study aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the descaling efficiency of sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid across various parameters, including reaction rates, scale removal capacity, impact on substrate materials, and overall cost-effectiveness. By examining these factors, we seek to contribute to the ongoing technological evolution in the field of industrial descaling and support informed decision-making in maintenance practices.
Industrial Demand Analysis
The industrial demand for efficient descaling solutions has been steadily increasing across various sectors, particularly in manufacturing, energy production, and water treatment. Both sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid have emerged as prominent descaling agents, each with its unique advantages and applications. The comparative study of these acids' descaling efficiency addresses a critical need in industries where scale formation poses significant operational challenges.
In the manufacturing sector, scale buildup on equipment surfaces can lead to reduced efficiency, increased energy consumption, and potential equipment failure. This has created a substantial demand for effective descaling methods to maintain optimal performance and extend machinery lifespan. The food and beverage industry, in particular, requires frequent descaling of processing equipment to meet stringent hygiene standards and ensure product quality.
The energy sector, especially power plants and oil refineries, faces persistent issues with scale formation in heat exchangers, boilers, and cooling systems. This scale accumulation can severely impact heat transfer efficiency, leading to increased fuel consumption and operational costs. As a result, there is a growing demand for descaling solutions that can effectively remove mineral deposits without causing damage to sensitive equipment or introducing environmental concerns.
Water treatment facilities represent another significant market for descaling technologies. As global water scarcity increases, the need for efficient water treatment and desalination processes has intensified. Scale formation in reverse osmosis membranes and other water treatment equipment can significantly reduce system efficiency and increase operational costs. This has driven the demand for descaling methods that can maintain equipment performance while adhering to strict environmental regulations.
The marine industry also contributes to the demand for effective descaling solutions. Ships and offshore structures are constantly exposed to seawater, leading to rapid scale formation on hulls, pipelines, and heat exchangers. This scale not only reduces operational efficiency but also increases fuel consumption and maintenance costs. The industry seeks descaling methods that can be applied safely in marine environments without causing ecological harm.
As industries strive for greater sustainability and environmental responsibility, there is an increasing focus on descaling solutions that minimize environmental impact. This trend has led to a growing interest in comparing the efficiency and ecological footprint of different descaling agents, including sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid. Industries are looking for solutions that not only effectively remove scale but also align with their sustainability goals and regulatory compliance requirements.
The global market for descaling chemicals is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, driven by industrialization in developing countries and the need for infrastructure maintenance in developed nations. This growth underscores the importance of comparative studies on descaling efficiency to guide industry decisions and drive innovation in scale management technologies.
In the manufacturing sector, scale buildup on equipment surfaces can lead to reduced efficiency, increased energy consumption, and potential equipment failure. This has created a substantial demand for effective descaling methods to maintain optimal performance and extend machinery lifespan. The food and beverage industry, in particular, requires frequent descaling of processing equipment to meet stringent hygiene standards and ensure product quality.
The energy sector, especially power plants and oil refineries, faces persistent issues with scale formation in heat exchangers, boilers, and cooling systems. This scale accumulation can severely impact heat transfer efficiency, leading to increased fuel consumption and operational costs. As a result, there is a growing demand for descaling solutions that can effectively remove mineral deposits without causing damage to sensitive equipment or introducing environmental concerns.
Water treatment facilities represent another significant market for descaling technologies. As global water scarcity increases, the need for efficient water treatment and desalination processes has intensified. Scale formation in reverse osmosis membranes and other water treatment equipment can significantly reduce system efficiency and increase operational costs. This has driven the demand for descaling methods that can maintain equipment performance while adhering to strict environmental regulations.
The marine industry also contributes to the demand for effective descaling solutions. Ships and offshore structures are constantly exposed to seawater, leading to rapid scale formation on hulls, pipelines, and heat exchangers. This scale not only reduces operational efficiency but also increases fuel consumption and maintenance costs. The industry seeks descaling methods that can be applied safely in marine environments without causing ecological harm.
As industries strive for greater sustainability and environmental responsibility, there is an increasing focus on descaling solutions that minimize environmental impact. This trend has led to a growing interest in comparing the efficiency and ecological footprint of different descaling agents, including sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid. Industries are looking for solutions that not only effectively remove scale but also align with their sustainability goals and regulatory compliance requirements.
The global market for descaling chemicals is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, driven by industrialization in developing countries and the need for infrastructure maintenance in developed nations. This growth underscores the importance of comparative studies on descaling efficiency to guide industry decisions and drive innovation in scale management technologies.
Current Challenges in Descaling Technologies
The descaling industry faces several significant challenges in its current technological landscape. One of the primary issues is the environmental impact of traditional descaling methods. Hydrochloric acid, a commonly used descaling agent, poses serious environmental risks due to its corrosive nature and potential for harmful emissions. This has led to increased regulatory pressure and a growing demand for more eco-friendly alternatives.
Efficiency and effectiveness remain critical concerns in descaling technologies. While hydrochloric acid is known for its rapid descaling action, it can be overly aggressive, potentially damaging the underlying metal surfaces. This necessitates careful control and monitoring during the descaling process, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. On the other hand, alternative acids like sulfamic acid, while generally safer, may not always match the speed and effectiveness of hydrochloric acid in certain applications.
Scale composition variability presents another significant challenge. Different industrial processes and water sources result in scales with diverse chemical compositions, ranging from simple calcium carbonate to complex mixtures including silicates, sulfates, and metal oxides. This diversity makes it difficult to develop a one-size-fits-all descaling solution, often requiring customized approaches for optimal results.
The issue of equipment compatibility further complicates the descaling process. Many industrial systems contain components made from various materials, some of which may be sensitive to certain descaling agents. This necessitates careful selection of descaling chemicals to ensure effective scale removal without compromising the integrity of the equipment.
Safety concerns continue to be a paramount challenge in descaling technologies. The handling and application of strong acids pose significant risks to workers, requiring extensive safety protocols, specialized equipment, and thorough training. This not only increases operational costs but also raises the potential for workplace accidents if proper procedures are not strictly followed.
Waste management and disposal of spent descaling solutions represent another major hurdle. The chemical nature of these solutions often classifies them as hazardous waste, necessitating specialized and costly disposal procedures. This aspect not only impacts the overall cost of descaling operations but also contributes to the environmental footprint of the process.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, there is a growing need for innovative descaling technologies that can address these challenges effectively. This includes the development of new, environmentally friendly descaling agents, improved application methods, and more efficient waste treatment and recycling processes. The comparative study of sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid efficiency in descaling is a step towards addressing these challenges, aiming to find a balance between effectiveness, safety, and environmental responsibility.
Efficiency and effectiveness remain critical concerns in descaling technologies. While hydrochloric acid is known for its rapid descaling action, it can be overly aggressive, potentially damaging the underlying metal surfaces. This necessitates careful control and monitoring during the descaling process, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. On the other hand, alternative acids like sulfamic acid, while generally safer, may not always match the speed and effectiveness of hydrochloric acid in certain applications.
Scale composition variability presents another significant challenge. Different industrial processes and water sources result in scales with diverse chemical compositions, ranging from simple calcium carbonate to complex mixtures including silicates, sulfates, and metal oxides. This diversity makes it difficult to develop a one-size-fits-all descaling solution, often requiring customized approaches for optimal results.
The issue of equipment compatibility further complicates the descaling process. Many industrial systems contain components made from various materials, some of which may be sensitive to certain descaling agents. This necessitates careful selection of descaling chemicals to ensure effective scale removal without compromising the integrity of the equipment.
Safety concerns continue to be a paramount challenge in descaling technologies. The handling and application of strong acids pose significant risks to workers, requiring extensive safety protocols, specialized equipment, and thorough training. This not only increases operational costs but also raises the potential for workplace accidents if proper procedures are not strictly followed.
Waste management and disposal of spent descaling solutions represent another major hurdle. The chemical nature of these solutions often classifies them as hazardous waste, necessitating specialized and costly disposal procedures. This aspect not only impacts the overall cost of descaling operations but also contributes to the environmental footprint of the process.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, there is a growing need for innovative descaling technologies that can address these challenges effectively. This includes the development of new, environmentally friendly descaling agents, improved application methods, and more efficient waste treatment and recycling processes. The comparative study of sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid efficiency in descaling is a step towards addressing these challenges, aiming to find a balance between effectiveness, safety, and environmental responsibility.
Existing Descaling Solutions
01 Comparison of sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid for descaling
Studies have been conducted to compare the descaling efficiency of sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid. Both acids have shown effectiveness in removing scale deposits, but their efficiency may vary depending on the type of scale and the specific application. Factors such as concentration, temperature, and exposure time can influence their relative performance.- Comparison of sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid for descaling: Studies have been conducted to compare the descaling efficiency of sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid. Both acids have shown effectiveness in removing scale deposits, but their performance may vary depending on the type of scale and the specific application. Factors such as concentration, temperature, and exposure time can influence their relative efficiency.
- Formulation of descaling solutions using sulfamic and hydrochloric acids: Descaling solutions can be formulated using sulfamic acid, hydrochloric acid, or a combination of both. These formulations may include additional components such as corrosion inhibitors, surfactants, or other additives to enhance their performance and protect the underlying surfaces. The optimal composition depends on the specific descaling requirements and the nature of the scale to be removed.
- Application methods for sulfamic and hydrochloric acid descaling: Various application methods have been developed for using sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid in descaling processes. These may include circulation, spraying, immersion, or in-situ application techniques. The choice of method depends on factors such as the equipment being descaled, accessibility, and safety considerations. Proper application techniques can significantly impact the descaling efficiency of both acids.
- Safety and environmental considerations in acid descaling: When using sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid for descaling, safety and environmental factors must be considered. This includes proper handling procedures, personal protective equipment, and disposal methods. Some formulations may incorporate less hazardous alternatives or additives to reduce environmental impact while maintaining descaling efficiency.
- Innovations in acid descaling technology: Recent innovations in acid descaling technology have focused on improving the efficiency and safety of sulfamic and hydrochloric acid-based descaling processes. These advancements may include novel formulations, application techniques, or equipment designs that enhance descaling performance while minimizing potential drawbacks such as corrosion or environmental impact.
02 Formulation of descaling solutions using sulfamic and hydrochloric acids
Researchers have developed various formulations combining sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid for enhanced descaling efficiency. These formulations may include additional components such as corrosion inhibitors, surfactants, or other acids to improve performance and reduce potential damage to the treated surfaces.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application methods for sulfamic and hydrochloric acid descaling
Different application methods have been explored to optimize the descaling efficiency of sulfamic and hydrochloric acids. These may include circulation techniques, spray applications, or immersion processes. The choice of method can significantly impact the effectiveness of the descaling operation and the overall efficiency of the acids.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations in acid descaling
Research has been conducted on the environmental impact and safety aspects of using sulfamic and hydrochloric acids for descaling. This includes studies on waste treatment, neutralization processes, and the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives or additives to reduce the negative impacts of these acids.Expand Specific Solutions05 Synergistic effects with other descaling agents
Investigations have been carried out on the potential synergistic effects of combining sulfamic acid or hydrochloric acid with other descaling agents. These combinations aim to enhance the overall descaling efficiency, reduce the required acid concentration, or provide additional benefits such as improved surface protection or reduced environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Descaling Industry
The comparative study on sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid descaling efficiency is situated in a mature market with established players. The industry is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for efficient descaling solutions across various sectors. The global scale and deposit control chemicals market, which includes descaling agents, is projected to reach $7.6 billion by 2025. Key players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., Saudi Arabian Oil Co., and Ecolab USA, Inc. are investing in research and development to enhance product efficacy and environmental sustainability. These companies are leveraging their extensive industry experience and technological capabilities to develop innovative descaling solutions, indicating a high level of technical maturity in this field.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an innovative approach to descaling using a combination of sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid. Their method involves a two-step process: first, applying a sulfamic acid solution to remove the bulk of the scale, followed by a hydrochloric acid treatment to address any remaining deposits. This approach has shown to be particularly effective in oil and gas pipelines, where scale buildup can significantly impact production efficiency. The company has reported a 95% scale removal rate using this method, with minimal corrosion to the underlying metal surfaces[1][3]. Additionally, Sinopec has implemented advanced monitoring systems to optimize the acid concentration and treatment duration, further enhancing the descaling efficiency.
Strengths: High scale removal efficiency, reduced corrosion risk, and optimized treatment process. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost due to two-step process and need for specialized monitoring equipment.
China National Petroleum Corp.
Technical Solution: China National Petroleum Corp. (CNPC) has focused on developing environmentally friendly descaling solutions that maintain high efficiency. Their research has led to a novel sulfamic acid-based formulation enhanced with organic inhibitors and surfactants. This proprietary blend has demonstrated superior performance in removing calcium carbonate and iron oxide scales commonly found in oil field equipment. CNPC's approach involves a single-step application that can be used at lower temperatures compared to traditional hydrochloric acid treatments, reducing energy consumption and environmental impact. Field tests have shown that this method achieves a descaling efficiency of up to 90% while reducing the corrosion rate by 50% compared to conventional hydrochloric acid treatments[2][5]. The company has also developed specialized application techniques to ensure uniform distribution of the descaling agent in complex equipment geometries.
Strengths: Environmentally friendly, energy-efficient, and effective at lower temperatures. Weaknesses: May be less effective against certain types of scales compared to hydrochloric acid.
Core Innovations in Acid Descaling
Sulfamic acid-based antiscaling composition for activated carbon, antiscaling process making use of said composition
PatentInactiveEP0378451A1
Innovation
- A descaling composition primarily composed of sulfamic acid, with optional additives, is used to dissolve and remove scale deposits from activated carbon, maintaining its surface area and activity.
Method of removing iron-containing scale from a wellbore, pipe, or surface using a biodegradable descaler solution
PatentActiveUS20210207019A1
Innovation
- A biodegradable descaler solution comprising hydrochloric acid, formic acid, citric acid, a corrosion inhibitor, a corrosion inhibitor intensifier, and a surfactant is used to contact and dissolve iron-containing scale, achieving high removal efficiency while minimizing steel corrosion.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid for descaling purposes is a critical consideration in their comparative study. Both acids have distinct environmental implications that must be carefully evaluated.
Sulfamic acid, being a solid at room temperature, offers advantages in terms of storage and transportation safety. It poses a lower risk of accidental spills and releases compared to liquid hydrochloric acid. When used in descaling processes, sulfamic acid produces less toxic fumes, reducing the potential for air pollution and worker exposure to harmful vapors. Additionally, sulfamic acid is biodegradable, breaking down into harmless components in the environment over time.
However, the production of sulfamic acid involves energy-intensive processes and may contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. The manufacturing process also generates waste products that require proper disposal to prevent environmental contamination.
Hydrochloric acid, on the other hand, is a strong mineral acid with significant environmental concerns. Its production, transportation, and use can lead to air and water pollution if not properly managed. Accidental spills or releases of hydrochloric acid can cause severe damage to ecosystems, particularly aquatic environments, due to its highly corrosive nature and ability to alter pH levels.
The use of hydrochloric acid in descaling operations generates acidic wastewater that requires neutralization before disposal. This process often involves the use of additional chemicals, potentially increasing the overall environmental footprint of the descaling operation. Furthermore, the corrosive nature of hydrochloric acid can lead to accelerated wear of equipment and infrastructure, potentially resulting in more frequent replacements and associated environmental impacts.
Both acids can contribute to the acidification of soil and water bodies if not properly contained or neutralized. However, the impact of sulfamic acid is generally considered less severe due to its lower acidity and biodegradability.
In terms of resource consumption, the production of hydrochloric acid typically requires fewer raw materials and energy inputs compared to sulfamic acid. This factor may partially offset some of its negative environmental impacts when considering the full life cycle of the acids.
When assessing the long-term environmental effects, it is crucial to consider the potential for bioaccumulation and persistence in the environment. Sulfamic acid, being biodegradable, presents a lower risk of long-term environmental contamination compared to hydrochloric acid, which can persist in the environment and potentially impact ecosystems over extended periods.
In conclusion, while both acids have environmental implications, sulfamic acid generally presents a more favorable environmental profile due to its lower volatility, reduced risk of accidental releases, and biodegradability. However, a comprehensive life cycle assessment would be necessary to fully quantify and compare the environmental impacts of these two acids in descaling applications.
Sulfamic acid, being a solid at room temperature, offers advantages in terms of storage and transportation safety. It poses a lower risk of accidental spills and releases compared to liquid hydrochloric acid. When used in descaling processes, sulfamic acid produces less toxic fumes, reducing the potential for air pollution and worker exposure to harmful vapors. Additionally, sulfamic acid is biodegradable, breaking down into harmless components in the environment over time.
However, the production of sulfamic acid involves energy-intensive processes and may contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. The manufacturing process also generates waste products that require proper disposal to prevent environmental contamination.
Hydrochloric acid, on the other hand, is a strong mineral acid with significant environmental concerns. Its production, transportation, and use can lead to air and water pollution if not properly managed. Accidental spills or releases of hydrochloric acid can cause severe damage to ecosystems, particularly aquatic environments, due to its highly corrosive nature and ability to alter pH levels.
The use of hydrochloric acid in descaling operations generates acidic wastewater that requires neutralization before disposal. This process often involves the use of additional chemicals, potentially increasing the overall environmental footprint of the descaling operation. Furthermore, the corrosive nature of hydrochloric acid can lead to accelerated wear of equipment and infrastructure, potentially resulting in more frequent replacements and associated environmental impacts.
Both acids can contribute to the acidification of soil and water bodies if not properly contained or neutralized. However, the impact of sulfamic acid is generally considered less severe due to its lower acidity and biodegradability.
In terms of resource consumption, the production of hydrochloric acid typically requires fewer raw materials and energy inputs compared to sulfamic acid. This factor may partially offset some of its negative environmental impacts when considering the full life cycle of the acids.
When assessing the long-term environmental effects, it is crucial to consider the potential for bioaccumulation and persistence in the environment. Sulfamic acid, being biodegradable, presents a lower risk of long-term environmental contamination compared to hydrochloric acid, which can persist in the environment and potentially impact ecosystems over extended periods.
In conclusion, while both acids have environmental implications, sulfamic acid generally presents a more favorable environmental profile due to its lower volatility, reduced risk of accidental releases, and biodegradability. However, a comprehensive life cycle assessment would be necessary to fully quantify and compare the environmental impacts of these two acids in descaling applications.
Safety Regulations for Industrial Acids
Safety regulations for industrial acids are crucial in ensuring the protection of workers, the environment, and equipment when handling corrosive substances like sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid. These regulations are designed to minimize risks associated with acid exposure, spills, and improper handling.
In the context of descaling operations, where sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid are commonly used, specific safety protocols must be followed. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is mandatory, including chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, face shields, and appropriate clothing to prevent skin contact or inhalation of acid fumes.
Proper storage and handling procedures are essential components of safety regulations. Acids must be stored in designated areas with proper ventilation, away from incompatible materials. Containers should be clearly labeled and regularly inspected for leaks or damage. Secondary containment systems are often required to prevent spills from spreading.
Emergency response plans are a critical aspect of safety regulations. Facilities must have clearly defined procedures for addressing acid spills, including the availability of neutralizing agents, absorbent materials, and emergency shower and eyewash stations. Staff should be trained in these procedures and regular drills conducted to ensure readiness.
Workplace exposure limits for acid fumes and mists are strictly regulated. Adequate ventilation systems must be in place to maintain air quality within acceptable limits. Regular air quality monitoring and employee health screenings may be required depending on the scale of acid use.
Transportation of industrial acids is subject to specific regulations to prevent accidents during transit. This includes proper packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements. Vehicles transporting acids must be equipped with appropriate safety features and drivers must receive specialized training.
Waste management is another crucial aspect of safety regulations for industrial acids. Proper neutralization and disposal procedures must be followed to prevent environmental contamination. Many jurisdictions require detailed record-keeping of acid usage and disposal.
Training and education form a fundamental part of safety regulations. Employees working with or around industrial acids must receive comprehensive training on hazard identification, proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the use of safety equipment. Regular refresher courses are typically mandated to ensure ongoing compliance and safety awareness.
Regulatory bodies such as OSHA in the United States and similar organizations in other countries regularly update and enforce these safety regulations. Compliance audits and inspections are conducted to ensure adherence to these standards, with significant penalties for violations.
In the context of descaling operations, where sulfamic acid and hydrochloric acid are commonly used, specific safety protocols must be followed. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is mandatory, including chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, face shields, and appropriate clothing to prevent skin contact or inhalation of acid fumes.
Proper storage and handling procedures are essential components of safety regulations. Acids must be stored in designated areas with proper ventilation, away from incompatible materials. Containers should be clearly labeled and regularly inspected for leaks or damage. Secondary containment systems are often required to prevent spills from spreading.
Emergency response plans are a critical aspect of safety regulations. Facilities must have clearly defined procedures for addressing acid spills, including the availability of neutralizing agents, absorbent materials, and emergency shower and eyewash stations. Staff should be trained in these procedures and regular drills conducted to ensure readiness.
Workplace exposure limits for acid fumes and mists are strictly regulated. Adequate ventilation systems must be in place to maintain air quality within acceptable limits. Regular air quality monitoring and employee health screenings may be required depending on the scale of acid use.
Transportation of industrial acids is subject to specific regulations to prevent accidents during transit. This includes proper packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements. Vehicles transporting acids must be equipped with appropriate safety features and drivers must receive specialized training.
Waste management is another crucial aspect of safety regulations for industrial acids. Proper neutralization and disposal procedures must be followed to prevent environmental contamination. Many jurisdictions require detailed record-keeping of acid usage and disposal.
Training and education form a fundamental part of safety regulations. Employees working with or around industrial acids must receive comprehensive training on hazard identification, proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the use of safety equipment. Regular refresher courses are typically mandated to ensure ongoing compliance and safety awareness.
Regulatory bodies such as OSHA in the United States and similar organizations in other countries regularly update and enforce these safety regulations. Compliance audits and inspections are conducted to ensure adherence to these standards, with significant penalties for violations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!