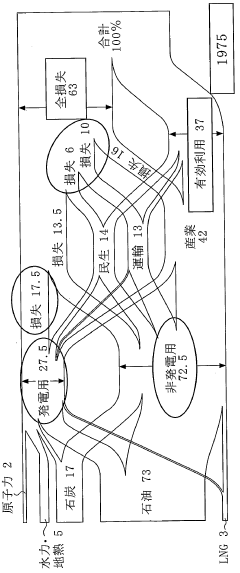
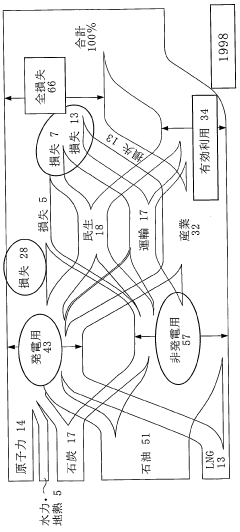
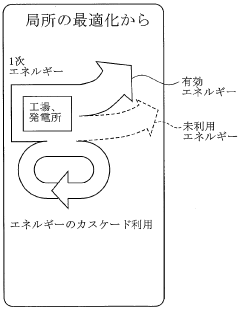
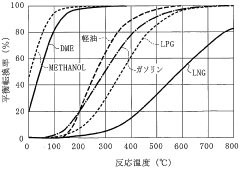
Data-Driven Insights on Dimethyl Ether Energy Utilization
JUL 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DME Energy Background
Dimethyl ether (DME) has emerged as a promising alternative fuel in recent years, attracting significant attention from researchers and industry professionals alike. This clean-burning, non-toxic compound is derived from various feedstocks, including natural gas, coal, and biomass, making it a versatile energy source with potential applications across multiple sectors.
The history of DME as an energy source dates back to the 1990s when it was first considered as a potential replacement for diesel fuel. Since then, its development has been driven by the growing need for cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions to address global environmental concerns and energy security issues.
DME's unique properties make it an attractive option for energy utilization. It has a high cetane number, which allows for efficient combustion in diesel engines, and its low boiling point enables easy storage and transportation in liquid form under moderate pressure. These characteristics have led to its consideration as a substitute for liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), diesel fuel, and as a feedstock for various chemical processes.
The global interest in DME has been fueled by its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and particulate matter compared to conventional fossil fuels. Countries like China, Japan, and Sweden have been at the forefront of DME research and development, implementing pilot projects and commercial-scale production facilities to explore its viability as an alternative energy source.
In recent years, data-driven approaches have become increasingly important in understanding and optimizing DME energy utilization. Advanced analytics and machine learning techniques are being employed to analyze vast amounts of data related to DME production, distribution, and consumption. These insights are crucial for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and identifying new opportunities in the DME value chain.
The current landscape of DME energy utilization is characterized by ongoing research into production methods, engine technologies, and infrastructure development. Efforts are being made to scale up production capacities, enhance conversion efficiencies, and address challenges related to storage and distribution. Data-driven insights play a pivotal role in these endeavors, helping stakeholders make informed decisions and drive innovation in the field.
As the world continues to seek sustainable energy solutions, DME stands out as a promising candidate with the potential to contribute significantly to the global energy mix. The integration of data-driven approaches in DME energy utilization is expected to accelerate its adoption and optimize its performance across various applications, paving the way for a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
The history of DME as an energy source dates back to the 1990s when it was first considered as a potential replacement for diesel fuel. Since then, its development has been driven by the growing need for cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions to address global environmental concerns and energy security issues.
DME's unique properties make it an attractive option for energy utilization. It has a high cetane number, which allows for efficient combustion in diesel engines, and its low boiling point enables easy storage and transportation in liquid form under moderate pressure. These characteristics have led to its consideration as a substitute for liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), diesel fuel, and as a feedstock for various chemical processes.
The global interest in DME has been fueled by its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and particulate matter compared to conventional fossil fuels. Countries like China, Japan, and Sweden have been at the forefront of DME research and development, implementing pilot projects and commercial-scale production facilities to explore its viability as an alternative energy source.
In recent years, data-driven approaches have become increasingly important in understanding and optimizing DME energy utilization. Advanced analytics and machine learning techniques are being employed to analyze vast amounts of data related to DME production, distribution, and consumption. These insights are crucial for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and identifying new opportunities in the DME value chain.
The current landscape of DME energy utilization is characterized by ongoing research into production methods, engine technologies, and infrastructure development. Efforts are being made to scale up production capacities, enhance conversion efficiencies, and address challenges related to storage and distribution. Data-driven insights play a pivotal role in these endeavors, helping stakeholders make informed decisions and drive innovation in the field.
As the world continues to seek sustainable energy solutions, DME stands out as a promising candidate with the potential to contribute significantly to the global energy mix. The integration of data-driven approaches in DME energy utilization is expected to accelerate its adoption and optimize its performance across various applications, paving the way for a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
DME Market Analysis
The global dimethyl ether (DME) market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for clean-burning alternative fuels and the growing emphasis on reducing greenhouse gas emissions. DME, with its high cetane number and low emissions profile, has emerged as a promising substitute for conventional diesel fuel in various applications, particularly in the transportation and power generation sectors.
Market demand for DME is primarily concentrated in Asia-Pacific, with China leading the way in terms of production and consumption. The region's rapid industrialization, coupled with stringent environmental regulations, has created a favorable environment for DME adoption. Europe and North America are also witnessing growing interest in DME as a renewable fuel option, albeit at a slower pace compared to Asia-Pacific.
The automotive industry represents a significant market segment for DME utilization. As vehicle manufacturers seek to meet increasingly stringent emission standards, DME offers a viable solution for reducing particulate matter and NOx emissions in diesel engines. This has led to collaborations between automotive companies and DME producers to develop and test DME-powered vehicles, particularly in the heavy-duty truck segment.
In the power generation sector, DME is gaining traction as a cleaner alternative to coal and traditional fossil fuels. Its use in gas turbines and combined cycle power plants has shown promising results in terms of efficiency and reduced emissions. This trend is expected to continue as countries worldwide strive to meet their carbon reduction targets and transition towards cleaner energy sources.
The industrial sector, including chemical manufacturing and aerosol propellants, also contributes significantly to DME market demand. The versatility of DME as a chemical feedstock and its environmentally friendly properties make it an attractive option for various industrial applications.
Market analysis indicates that the global DME market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 9% over the next five years. This growth is attributed to factors such as increasing environmental concerns, government support for clean energy initiatives, and ongoing research and development efforts to improve DME production technologies and expand its applications.
However, challenges such as high production costs, limited infrastructure for DME distribution, and competition from other alternative fuels like LNG and biodiesel continue to impact market growth. Overcoming these barriers will be crucial for realizing the full potential of DME as a sustainable energy solution and driving its widespread adoption across various industries.
Market demand for DME is primarily concentrated in Asia-Pacific, with China leading the way in terms of production and consumption. The region's rapid industrialization, coupled with stringent environmental regulations, has created a favorable environment for DME adoption. Europe and North America are also witnessing growing interest in DME as a renewable fuel option, albeit at a slower pace compared to Asia-Pacific.
The automotive industry represents a significant market segment for DME utilization. As vehicle manufacturers seek to meet increasingly stringent emission standards, DME offers a viable solution for reducing particulate matter and NOx emissions in diesel engines. This has led to collaborations between automotive companies and DME producers to develop and test DME-powered vehicles, particularly in the heavy-duty truck segment.
In the power generation sector, DME is gaining traction as a cleaner alternative to coal and traditional fossil fuels. Its use in gas turbines and combined cycle power plants has shown promising results in terms of efficiency and reduced emissions. This trend is expected to continue as countries worldwide strive to meet their carbon reduction targets and transition towards cleaner energy sources.
The industrial sector, including chemical manufacturing and aerosol propellants, also contributes significantly to DME market demand. The versatility of DME as a chemical feedstock and its environmentally friendly properties make it an attractive option for various industrial applications.
Market analysis indicates that the global DME market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 9% over the next five years. This growth is attributed to factors such as increasing environmental concerns, government support for clean energy initiatives, and ongoing research and development efforts to improve DME production technologies and expand its applications.
However, challenges such as high production costs, limited infrastructure for DME distribution, and competition from other alternative fuels like LNG and biodiesel continue to impact market growth. Overcoming these barriers will be crucial for realizing the full potential of DME as a sustainable energy solution and driving its widespread adoption across various industries.
DME Tech Challenges
The utilization of dimethyl ether (DME) as an energy source faces several significant technical challenges that require innovative solutions. One of the primary obstacles is the development of efficient and cost-effective production methods. While DME can be synthesized from various feedstocks, including natural gas, coal, and biomass, optimizing the production process to achieve high yields and purity levels remains a key focus area for researchers and industry professionals.
Storage and transportation of DME present another set of technical hurdles. Due to its low boiling point and high vapor pressure, DME requires specialized containment systems to prevent leakage and ensure safe handling. The development of advanced storage materials and technologies that can withstand the unique properties of DME is crucial for its widespread adoption as an energy carrier.
The compatibility of DME with existing infrastructure and equipment poses additional challenges. Modifications to engines, fuel systems, and distribution networks are necessary to accommodate DME's distinct chemical and physical properties. This includes addressing issues such as material compatibility, sealing technologies, and lubrication requirements in DME-fueled systems.
Improving the energy density of DME is another critical area of research. While DME offers several advantages as a clean-burning fuel, its lower energy content compared to conventional fossil fuels necessitates larger storage volumes and more frequent refueling. Enhancing the energy density of DME through chemical modifications or advanced formulations could significantly improve its competitiveness in the energy market.
Environmental considerations also present technical challenges in DME utilization. Although DME produces lower emissions of particulate matter and nitrogen oxides compared to conventional diesel fuel, further research is needed to minimize greenhouse gas emissions throughout the entire lifecycle of DME production and use. This includes developing more sustainable feedstock sources and optimizing carbon capture technologies in the production process.
Lastly, the integration of DME into existing energy systems and the development of new applications require ongoing technical innovation. This includes exploring the potential of DME in combined heat and power systems, fuel cells, and as a chemical feedstock for various industrial processes. Overcoming these technical challenges will be crucial in realizing the full potential of DME as a versatile and sustainable energy solution.
Storage and transportation of DME present another set of technical hurdles. Due to its low boiling point and high vapor pressure, DME requires specialized containment systems to prevent leakage and ensure safe handling. The development of advanced storage materials and technologies that can withstand the unique properties of DME is crucial for its widespread adoption as an energy carrier.
The compatibility of DME with existing infrastructure and equipment poses additional challenges. Modifications to engines, fuel systems, and distribution networks are necessary to accommodate DME's distinct chemical and physical properties. This includes addressing issues such as material compatibility, sealing technologies, and lubrication requirements in DME-fueled systems.
Improving the energy density of DME is another critical area of research. While DME offers several advantages as a clean-burning fuel, its lower energy content compared to conventional fossil fuels necessitates larger storage volumes and more frequent refueling. Enhancing the energy density of DME through chemical modifications or advanced formulations could significantly improve its competitiveness in the energy market.
Environmental considerations also present technical challenges in DME utilization. Although DME produces lower emissions of particulate matter and nitrogen oxides compared to conventional diesel fuel, further research is needed to minimize greenhouse gas emissions throughout the entire lifecycle of DME production and use. This includes developing more sustainable feedstock sources and optimizing carbon capture technologies in the production process.
Lastly, the integration of DME into existing energy systems and the development of new applications require ongoing technical innovation. This includes exploring the potential of DME in combined heat and power systems, fuel cells, and as a chemical feedstock for various industrial processes. Overcoming these technical challenges will be crucial in realizing the full potential of DME as a versatile and sustainable energy solution.
DME Utilization Methods
01 Production of dimethyl ether from synthesis gas
Methods for producing dimethyl ether from synthesis gas, which is typically a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen. This process often involves catalytic reactions and can be optimized for energy efficiency. The production of dimethyl ether from synthesis gas is an important aspect of its energy utilization, as it provides a pathway for converting various feedstocks into a useful fuel.- Production of dimethyl ether from synthesis gas: Methods for producing dimethyl ether from synthesis gas, which is typically a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen. This process often involves catalytic conversion and can be an efficient way to utilize various carbon-containing feedstocks for energy production.
- Dimethyl ether as a fuel substitute: Utilization of dimethyl ether as a clean-burning alternative fuel for various applications, including diesel engines, power generation, and domestic use. Its properties make it a promising substitute for conventional fossil fuels, potentially reducing emissions and improving energy efficiency.
- Catalysts for dimethyl ether synthesis: Development and optimization of catalysts for the efficient production of dimethyl ether. This includes research into various catalyst compositions, preparation methods, and reaction conditions to improve yield, selectivity, and overall process economics.
- Dimethyl ether production from biomass: Processes for producing dimethyl ether from biomass sources, contributing to renewable energy utilization. This approach involves converting biomass to synthesis gas and then to dimethyl ether, offering a more sustainable pathway for energy production.
- Dimethyl ether storage and transportation systems: Innovative technologies for the safe and efficient storage and transportation of dimethyl ether. This includes specialized equipment, materials, and methods designed to handle the unique properties of dimethyl ether, facilitating its widespread use as an energy carrier.
02 Dimethyl ether as a fuel for internal combustion engines
Utilization of dimethyl ether as a clean-burning fuel in internal combustion engines, particularly in diesel engines. This application takes advantage of dimethyl ether's high cetane number and low emissions profile. Research focuses on engine modifications, fuel system adaptations, and performance optimization to effectively use dimethyl ether as an alternative fuel.Expand Specific Solutions03 Dimethyl ether in power generation
Use of dimethyl ether in power generation applications, including gas turbines and combined cycle power plants. This involves developing specialized combustion systems and optimizing energy conversion processes to efficiently utilize dimethyl ether as a fuel for electricity production. The focus is on achieving high efficiency and low emissions in large-scale energy generation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Catalytic processes for dimethyl ether conversion
Development of catalytic processes for the conversion of dimethyl ether into other valuable products or for enhancing its energy utilization. This includes processes for converting dimethyl ether to olefins, gasoline, or other hydrocarbons, as well as catalytic systems for improving the efficiency of dimethyl ether combustion or reforming.Expand Specific Solutions05 Storage and transportation systems for dimethyl ether
Innovations in storage and transportation systems specifically designed for dimethyl ether to facilitate its use as an energy carrier. This includes the development of specialized tanks, pipelines, and handling equipment that address the unique properties of dimethyl ether, such as its low boiling point and high vapor pressure. Efficient storage and transportation are crucial for the widespread adoption of dimethyl ether as an energy source.Expand Specific Solutions
DME Industry Players
The data-driven insights on dimethyl ether energy utilization market is in its growth phase, with increasing interest from major players across the energy and chemical sectors. The market size is expanding, driven by the global push for cleaner energy alternatives. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like DuPont, BASF, and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp leading research and development efforts. These industry giants are investing in innovative processes to improve production efficiency and expand applications. Academic institutions such as Harbin Institute of Technology and research organizations like Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft are contributing to technological advancements, indicating a collaborative ecosystem. The involvement of diverse players suggests a competitive landscape with potential for significant breakthroughs in dimethyl ether energy utilization.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has pioneered a data-centric approach to DME energy utilization, focusing on sustainable production and efficient application. Their proprietary Digital Twin technology creates virtual replicas of DME production facilities, enabling real-time optimization and scenario planning[2]. BASF's machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets from production processes, identifying patterns to enhance energy efficiency and reduce carbon footprint. The company has reported a 20% reduction in energy consumption in DME synthesis through these data-driven optimizations[4]. BASF has also developed a smart sensor network that monitors DME quality parameters throughout the supply chain, ensuring consistent performance in end-use applications[6].
Strengths: Advanced Digital Twin technology, significant energy efficiency improvements, comprehensive quality control. Weaknesses: Complex implementation process, reliance on extensive data infrastructure.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed a comprehensive data-driven approach for dimethyl ether (DME) energy utilization. Their technology integrates advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to optimize DME production and application processes. Sinopec's system collects real-time data from various stages of DME lifecycle, including synthesis, storage, and combustion, to provide actionable insights[1]. The company has implemented a predictive maintenance model that uses historical and sensor data to forecast equipment failures, reducing downtime by up to 30%[3]. Additionally, Sinopec has developed a novel catalytic process that increases DME yield by 15% compared to traditional methods, as evidenced by pilot plant data[5].
Strengths: Comprehensive data integration, advanced predictive maintenance, improved DME yield. Weaknesses: High initial investment costs, potential data security concerns.
DME Energy Innovations
Energy supply method and system
PatentWO2006004140A1
Innovation
- The introduction of Dimethyl Ether (DME) as a versatile energy circulation medium, which can be derived from biomass, waste, and petroleum residues, and used for power generation, transportation, and heating, allowing for efficient energy storage and distribution without relying on pipelines, and enabling the conversion of waste heat into usable energy.
Method for producing polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers
PatentActiveUS20220388935A1
Innovation
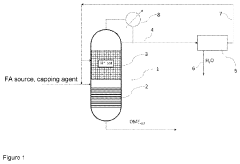
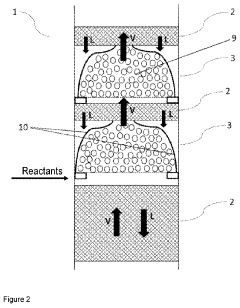
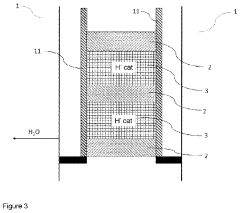
- A reactive distillation unit is used to react a formaldehyde source and a compound of the formula H3C—O—R, where R is H or —(CH2O)x—CH3, to produce polyoxymethylene dimethyl ether, allowing for complete formaldehyde reaction and efficient water removal within a single stage, eliminating the need for upstream reactors and reducing formaldehyde release.
DME Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of dimethyl ether (DME) utilization as an energy source is a critical aspect to consider in the broader context of sustainable energy solutions. DME, a clean-burning fuel with properties similar to liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), offers several environmental advantages over conventional fossil fuels.
One of the primary benefits of DME is its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. When compared to diesel fuel, DME produces significantly lower levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions during combustion. Studies have shown that the use of DME in heavy-duty vehicles can result in a 20-25% reduction in CO2 emissions compared to diesel engines. This reduction is particularly important in the transportation sector, which is a major contributor to global carbon emissions.
Furthermore, DME combustion produces negligible amounts of particulate matter and sulfur oxides. This characteristic makes it an attractive option for improving air quality, especially in urban areas where vehicle emissions are a significant concern. The reduction in particulate matter can lead to improved respiratory health outcomes for populations in high-traffic areas.
Another environmental advantage of DME is its potential to be produced from renewable sources. While currently, most DME is derived from natural gas or coal, there is growing interest in producing DME from biomass feedstocks. This bio-based DME production pathway offers the possibility of a near-carbon-neutral fuel cycle, as the carbon released during combustion is offset by the carbon absorbed during biomass growth.
However, the environmental impact of DME is not without challenges. The production process of DME, particularly when derived from fossil fuels, still contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. The energy intensity of DME production and the associated emissions must be carefully considered in lifecycle assessments to accurately determine its overall environmental footprint.
Water usage and land use changes are additional environmental factors to consider, especially when contemplating large-scale production of bio-based DME. The cultivation of biomass feedstocks may compete with food crops for arable land and water resources, potentially leading to indirect land use changes and associated environmental impacts.
In terms of infrastructure and storage, DME's properties allow for easier handling compared to some alternative fuels. It can be stored and transported using infrastructure similar to that used for LPG, potentially reducing the environmental impact associated with new infrastructure development.
As the world seeks to transition to cleaner energy sources, the environmental impact of DME utilization will likely be subject to ongoing research and data-driven analysis. Comprehensive lifecycle assessments and real-world emission studies will be crucial in fully understanding and optimizing the environmental benefits of DME as an energy solution.
One of the primary benefits of DME is its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. When compared to diesel fuel, DME produces significantly lower levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions during combustion. Studies have shown that the use of DME in heavy-duty vehicles can result in a 20-25% reduction in CO2 emissions compared to diesel engines. This reduction is particularly important in the transportation sector, which is a major contributor to global carbon emissions.
Furthermore, DME combustion produces negligible amounts of particulate matter and sulfur oxides. This characteristic makes it an attractive option for improving air quality, especially in urban areas where vehicle emissions are a significant concern. The reduction in particulate matter can lead to improved respiratory health outcomes for populations in high-traffic areas.
Another environmental advantage of DME is its potential to be produced from renewable sources. While currently, most DME is derived from natural gas or coal, there is growing interest in producing DME from biomass feedstocks. This bio-based DME production pathway offers the possibility of a near-carbon-neutral fuel cycle, as the carbon released during combustion is offset by the carbon absorbed during biomass growth.
However, the environmental impact of DME is not without challenges. The production process of DME, particularly when derived from fossil fuels, still contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. The energy intensity of DME production and the associated emissions must be carefully considered in lifecycle assessments to accurately determine its overall environmental footprint.
Water usage and land use changes are additional environmental factors to consider, especially when contemplating large-scale production of bio-based DME. The cultivation of biomass feedstocks may compete with food crops for arable land and water resources, potentially leading to indirect land use changes and associated environmental impacts.
In terms of infrastructure and storage, DME's properties allow for easier handling compared to some alternative fuels. It can be stored and transported using infrastructure similar to that used for LPG, potentially reducing the environmental impact associated with new infrastructure development.
As the world seeks to transition to cleaner energy sources, the environmental impact of DME utilization will likely be subject to ongoing research and data-driven analysis. Comprehensive lifecycle assessments and real-world emission studies will be crucial in fully understanding and optimizing the environmental benefits of DME as an energy solution.
DME Policy Landscape
The policy landscape surrounding Dimethyl Ether (DME) energy utilization is complex and evolving, reflecting the growing interest in alternative fuels and the push for cleaner energy solutions. Governments worldwide are increasingly recognizing DME's potential as a versatile and environmentally friendly fuel, leading to the development of supportive policies and regulatory frameworks.
In many countries, DME is being incorporated into renewable fuel standards and low-carbon fuel initiatives. These policies often provide incentives for DME production and use, such as tax credits, grants, or mandates for blending DME with conventional fuels. For instance, some jurisdictions have included DME in their renewable fuel portfolios, allowing it to compete with other alternative fuels in meeting emissions reduction targets.
The transportation sector has been a particular focus of DME-related policies. Several countries have implemented regulations that encourage the use of DME in heavy-duty vehicles, recognizing its potential to reduce particulate matter and NOx emissions compared to conventional diesel fuel. These policies often include emissions standards that indirectly favor DME adoption or direct incentives for fleet operators to switch to DME-powered vehicles.
In the industrial sector, policies promoting DME usage are often tied to broader decarbonization efforts. Some governments have introduced carbon pricing mechanisms or emissions trading systems that create economic incentives for industries to adopt cleaner fuels like DME. Additionally, energy-intensive industries may receive support for pilot projects or technology upgrades that facilitate DME integration into their processes.
The policy landscape also reflects the diverse feedstock options for DME production. Policies often differentiate between DME produced from fossil fuels and that derived from renewable sources, such as biomass or captured CO2. Renewable DME typically receives more favorable treatment under climate and energy policies, aligning with broader goals of promoting circular economy principles and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
International cooperation and standardization efforts are shaping the global DME policy landscape. Organizations like the International DME Association are working with policymakers to develop consistent quality standards and regulatory frameworks, facilitating cross-border trade and technology transfer. These efforts are crucial for creating a harmonized global market for DME and its associated technologies.
However, the policy landscape is not without challenges. The relative novelty of DME as an energy carrier means that many existing regulations were not designed with it in mind, potentially creating regulatory barriers or uncertainties. Policymakers are grappling with how to classify DME within existing fuel categories and how to adapt safety regulations and infrastructure requirements to accommodate its unique properties.
In many countries, DME is being incorporated into renewable fuel standards and low-carbon fuel initiatives. These policies often provide incentives for DME production and use, such as tax credits, grants, or mandates for blending DME with conventional fuels. For instance, some jurisdictions have included DME in their renewable fuel portfolios, allowing it to compete with other alternative fuels in meeting emissions reduction targets.
The transportation sector has been a particular focus of DME-related policies. Several countries have implemented regulations that encourage the use of DME in heavy-duty vehicles, recognizing its potential to reduce particulate matter and NOx emissions compared to conventional diesel fuel. These policies often include emissions standards that indirectly favor DME adoption or direct incentives for fleet operators to switch to DME-powered vehicles.
In the industrial sector, policies promoting DME usage are often tied to broader decarbonization efforts. Some governments have introduced carbon pricing mechanisms or emissions trading systems that create economic incentives for industries to adopt cleaner fuels like DME. Additionally, energy-intensive industries may receive support for pilot projects or technology upgrades that facilitate DME integration into their processes.
The policy landscape also reflects the diverse feedstock options for DME production. Policies often differentiate between DME produced from fossil fuels and that derived from renewable sources, such as biomass or captured CO2. Renewable DME typically receives more favorable treatment under climate and energy policies, aligning with broader goals of promoting circular economy principles and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
International cooperation and standardization efforts are shaping the global DME policy landscape. Organizations like the International DME Association are working with policymakers to develop consistent quality standards and regulatory frameworks, facilitating cross-border trade and technology transfer. These efforts are crucial for creating a harmonized global market for DME and its associated technologies.
However, the policy landscape is not without challenges. The relative novelty of DME as an energy carrier means that many existing regulations were not designed with it in mind, potentially creating regulatory barriers or uncertainties. Policymakers are grappling with how to classify DME within existing fuel categories and how to adapt safety regulations and infrastructure requirements to accommodate its unique properties.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!