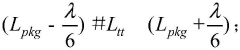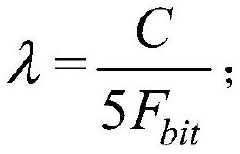DDR5 Signal Integrity in High-Speed Communication Boards
SEP 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DDR5 Evolution and Performance Targets
DDR5 memory technology represents a significant evolution in the DRAM landscape, building upon its predecessor DDR4 with substantial improvements in performance, power efficiency, and signal integrity. The development of DDR5 began in 2016, with JEDEC finalizing the standard in July 2020. This fifth generation of double data rate synchronous dynamic random-access memory aims to address the growing demands of data-intensive applications across enterprise servers, high-performance computing systems, and advanced consumer devices.
The evolution from DDR4 to DDR5 has been driven by the exponential growth in data processing requirements and the need for higher bandwidth memory solutions. DDR4, which reached market maturity around 2014, typically operates at speeds between 1600-3200 MT/s (million transfers per second). In contrast, DDR5 starts at 4800 MT/s and has a roadmap extending to 8400 MT/s and beyond, effectively doubling the data rate of its predecessor.
A key architectural change in DDR5 is the transition from a single 72-bit channel to dual 40-bit channels per DIMM, enabling higher efficiency in multi-core processing environments. This design modification allows for improved channel utilization and reduced latency in memory-intensive workloads. Additionally, DDR5 introduces on-die ECC (Error Correction Code), decision feedback equalization, and improved refresh schemes to enhance data integrity at higher speeds.
The performance targets for DDR5 extend beyond raw speed improvements. Power efficiency has been significantly enhanced through the reduction of operating voltage from 1.2V in DDR4 to 1.1V in DDR5. This voltage reduction, combined with more efficient power delivery architecture including on-module voltage regulation, results in approximately 20% lower power consumption despite the substantial increase in data rates.
Signal integrity challenges have grown exponentially with the speed increases in DDR5. At 4800 MT/s and above, the electrical signals traveling through PCB traces experience severe degradation due to factors such as dielectric loss, skin effect, and impedance discontinuities. The industry has responded with advanced PCB materials, refined transmission line designs, and sophisticated equalization techniques to maintain signal quality at these unprecedented speeds.
Capacity scaling represents another critical aspect of DDR5 evolution. The standard supports significantly higher density memory chips, with single DIMMs capable of reaching 128GB compared to DDR4's typical maximum of 64GB. This capacity expansion is achieved through advancements in manufacturing processes and chip stacking technologies, enabling more memory cells per die and more dies per package.
The performance trajectory of DDR5 is expected to continue through multiple generations, with industry roadmaps projecting speeds reaching 10,000 MT/s by 2025. These advancements will be crucial for supporting next-generation computing applications including artificial intelligence, real-time analytics, and high-resolution content creation that demand ever-increasing memory bandwidth and capacity.
The evolution from DDR4 to DDR5 has been driven by the exponential growth in data processing requirements and the need for higher bandwidth memory solutions. DDR4, which reached market maturity around 2014, typically operates at speeds between 1600-3200 MT/s (million transfers per second). In contrast, DDR5 starts at 4800 MT/s and has a roadmap extending to 8400 MT/s and beyond, effectively doubling the data rate of its predecessor.
A key architectural change in DDR5 is the transition from a single 72-bit channel to dual 40-bit channels per DIMM, enabling higher efficiency in multi-core processing environments. This design modification allows for improved channel utilization and reduced latency in memory-intensive workloads. Additionally, DDR5 introduces on-die ECC (Error Correction Code), decision feedback equalization, and improved refresh schemes to enhance data integrity at higher speeds.
The performance targets for DDR5 extend beyond raw speed improvements. Power efficiency has been significantly enhanced through the reduction of operating voltage from 1.2V in DDR4 to 1.1V in DDR5. This voltage reduction, combined with more efficient power delivery architecture including on-module voltage regulation, results in approximately 20% lower power consumption despite the substantial increase in data rates.
Signal integrity challenges have grown exponentially with the speed increases in DDR5. At 4800 MT/s and above, the electrical signals traveling through PCB traces experience severe degradation due to factors such as dielectric loss, skin effect, and impedance discontinuities. The industry has responded with advanced PCB materials, refined transmission line designs, and sophisticated equalization techniques to maintain signal quality at these unprecedented speeds.
Capacity scaling represents another critical aspect of DDR5 evolution. The standard supports significantly higher density memory chips, with single DIMMs capable of reaching 128GB compared to DDR4's typical maximum of 64GB. This capacity expansion is achieved through advancements in manufacturing processes and chip stacking technologies, enabling more memory cells per die and more dies per package.
The performance trajectory of DDR5 is expected to continue through multiple generations, with industry roadmaps projecting speeds reaching 10,000 MT/s by 2025. These advancements will be crucial for supporting next-generation computing applications including artificial intelligence, real-time analytics, and high-resolution content creation that demand ever-increasing memory bandwidth and capacity.
Market Demand for High-Speed Memory Solutions
The global market for high-speed memory solutions has experienced unprecedented growth in recent years, driven primarily by the increasing demands of data-intensive applications across multiple sectors. The transition from DDR4 to DDR5 represents a significant leap in memory technology, with DDR5 offering substantially higher data rates, improved power efficiency, and enhanced signal integrity capabilities essential for modern computing environments.
Data center expansion remains the primary driver for high-speed memory adoption, with the market expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 26% through 2026. This growth is fueled by the explosive increase in cloud computing services, which require massive memory bandwidth to support simultaneous user requests and complex computational tasks. Enterprise servers utilizing DDR5 technology can achieve memory speeds exceeding 4800 MT/s, representing a 50% improvement over previous generation solutions.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning applications have emerged as critical consumers of high-speed memory, with training complex neural networks demanding unprecedented memory bandwidth and capacity. Research indicates that AI workloads benefit significantly from DDR5's improved channel efficiency and reduced latency, with performance gains of 18-35% observed in large language model training scenarios compared to equivalent DDR4 systems.
The gaming and high-performance computing segments also demonstrate strong demand for advanced memory solutions. Gaming PCs and next-generation consoles increasingly leverage high-bandwidth memory to support real-time ray tracing and complex physics simulations. Market research shows that premium gaming systems with DDR5 memory command a 22% price premium, indicating consumer willingness to invest in superior memory performance.
Edge computing represents an emerging frontier for high-speed memory applications, with distributed processing nodes requiring efficient memory solutions to handle local data processing tasks. The reduced power consumption of DDR5 (approximately 20% lower than DDR4) makes it particularly suitable for edge deployments where energy efficiency is paramount.
Signal integrity challenges in high-speed communication boards have become a limiting factor in memory performance scaling. Industry surveys reveal that 78% of hardware engineers consider signal integrity as the primary technical challenge when implementing DDR5 designs. This has created a specialized market for advanced PCB materials, simulation software, and testing equipment specifically designed to address signal integrity issues in high-speed memory implementations.
The automotive sector presents a growing opportunity for high-speed memory solutions, particularly with the advancement of autonomous driving technologies. Advanced driver assistance systems require substantial memory bandwidth to process sensor data in real-time, with automotive-grade DDR5 solutions beginning to enter production to meet these specialized requirements.
Data center expansion remains the primary driver for high-speed memory adoption, with the market expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 26% through 2026. This growth is fueled by the explosive increase in cloud computing services, which require massive memory bandwidth to support simultaneous user requests and complex computational tasks. Enterprise servers utilizing DDR5 technology can achieve memory speeds exceeding 4800 MT/s, representing a 50% improvement over previous generation solutions.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning applications have emerged as critical consumers of high-speed memory, with training complex neural networks demanding unprecedented memory bandwidth and capacity. Research indicates that AI workloads benefit significantly from DDR5's improved channel efficiency and reduced latency, with performance gains of 18-35% observed in large language model training scenarios compared to equivalent DDR4 systems.
The gaming and high-performance computing segments also demonstrate strong demand for advanced memory solutions. Gaming PCs and next-generation consoles increasingly leverage high-bandwidth memory to support real-time ray tracing and complex physics simulations. Market research shows that premium gaming systems with DDR5 memory command a 22% price premium, indicating consumer willingness to invest in superior memory performance.
Edge computing represents an emerging frontier for high-speed memory applications, with distributed processing nodes requiring efficient memory solutions to handle local data processing tasks. The reduced power consumption of DDR5 (approximately 20% lower than DDR4) makes it particularly suitable for edge deployments where energy efficiency is paramount.
Signal integrity challenges in high-speed communication boards have become a limiting factor in memory performance scaling. Industry surveys reveal that 78% of hardware engineers consider signal integrity as the primary technical challenge when implementing DDR5 designs. This has created a specialized market for advanced PCB materials, simulation software, and testing equipment specifically designed to address signal integrity issues in high-speed memory implementations.
The automotive sector presents a growing opportunity for high-speed memory solutions, particularly with the advancement of autonomous driving technologies. Advanced driver assistance systems require substantial memory bandwidth to process sensor data in real-time, with automotive-grade DDR5 solutions beginning to enter production to meet these specialized requirements.
Signal Integrity Challenges in DDR5 Implementation
DDR5 memory technology represents a significant advancement in high-speed memory interfaces, operating at speeds exceeding 6400 MT/s compared to DDR4's typical 3200 MT/s. This substantial increase in data rates introduces unprecedented signal integrity challenges that must be addressed through innovative design approaches and advanced materials.
The primary signal integrity challenges in DDR5 implementation stem from the reduced timing margins and voltage swings. With data rates doubling from previous generations, the timing budget has shrunk dramatically, leaving minimal margin for signal distortions. The reduced operating voltage of 1.1V (down from DDR4's 1.2V) further complicates matters by decreasing noise immunity and signal-to-noise ratios.
Impedance matching becomes increasingly critical in DDR5 designs. The faster edge rates create more pronounced reflections when impedance discontinuities exist, potentially causing data errors. Maintaining consistent 50-ohm impedance across the entire signal path requires precise PCB stackup design and manufacturing tolerances tighter than ±10%.
Crosstalk emerges as a dominant concern due to the densely packed routing channels. Adjacent signals operating at multi-gigahertz frequencies induce significant electromagnetic coupling, corrupting data integrity. This necessitates sophisticated routing strategies including optimized trace spacing, strategic use of ground planes, and potentially specialized shielding techniques.
Power delivery network (PDN) design faces unprecedented challenges with DDR5. The simultaneous switching noise (SSN) generated by multiple data lines transitioning simultaneously creates substantial ground bounce and power supply fluctuations. DDR5's on-die power management further complicates PDN design, requiring careful decoupling capacitor selection and placement.
Signal attenuation through PCB materials becomes more pronounced at DDR5 frequencies. Standard FR-4 materials exhibit significant dielectric losses above 3 GHz, necessitating the adoption of high-performance laminates with controlled dielectric constants and loss tangents. These specialized materials add cost but are essential for maintaining signal integrity.
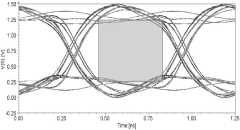
Equalization techniques have become mandatory rather than optional in DDR5 designs. Both transmitter-side (Tx) and receiver-side (Rx) equalization must be carefully tuned to compensate for channel losses and maintain open eye diagrams. Decision feedback equalization (DFE) and feed-forward equalization (FFE) techniques require sophisticated simulation and validation methodologies.
The verification of DDR5 signal integrity demands advanced measurement techniques. Traditional time-domain reflectometry (TDR) must be complemented with vector network analysis (VNA) and high-bandwidth oscilloscopes capable of accurately capturing multi-gigahertz signals. Eye diagram analysis with statistical methods has become essential for validating design margins.
The primary signal integrity challenges in DDR5 implementation stem from the reduced timing margins and voltage swings. With data rates doubling from previous generations, the timing budget has shrunk dramatically, leaving minimal margin for signal distortions. The reduced operating voltage of 1.1V (down from DDR4's 1.2V) further complicates matters by decreasing noise immunity and signal-to-noise ratios.
Impedance matching becomes increasingly critical in DDR5 designs. The faster edge rates create more pronounced reflections when impedance discontinuities exist, potentially causing data errors. Maintaining consistent 50-ohm impedance across the entire signal path requires precise PCB stackup design and manufacturing tolerances tighter than ±10%.
Crosstalk emerges as a dominant concern due to the densely packed routing channels. Adjacent signals operating at multi-gigahertz frequencies induce significant electromagnetic coupling, corrupting data integrity. This necessitates sophisticated routing strategies including optimized trace spacing, strategic use of ground planes, and potentially specialized shielding techniques.
Power delivery network (PDN) design faces unprecedented challenges with DDR5. The simultaneous switching noise (SSN) generated by multiple data lines transitioning simultaneously creates substantial ground bounce and power supply fluctuations. DDR5's on-die power management further complicates PDN design, requiring careful decoupling capacitor selection and placement.
Signal attenuation through PCB materials becomes more pronounced at DDR5 frequencies. Standard FR-4 materials exhibit significant dielectric losses above 3 GHz, necessitating the adoption of high-performance laminates with controlled dielectric constants and loss tangents. These specialized materials add cost but are essential for maintaining signal integrity.
Equalization techniques have become mandatory rather than optional in DDR5 designs. Both transmitter-side (Tx) and receiver-side (Rx) equalization must be carefully tuned to compensate for channel losses and maintain open eye diagrams. Decision feedback equalization (DFE) and feed-forward equalization (FFE) techniques require sophisticated simulation and validation methodologies.
The verification of DDR5 signal integrity demands advanced measurement techniques. Traditional time-domain reflectometry (TDR) must be complemented with vector network analysis (VNA) and high-bandwidth oscilloscopes capable of accurately capturing multi-gigahertz signals. Eye diagram analysis with statistical methods has become essential for validating design margins.
Current Signal Integrity Solutions for DDR5
01 Signal integrity testing and measurement for DDR5 memory
Various methods and systems for testing and measuring signal integrity in DDR5 memory interfaces. These include specialized test equipment, simulation tools, and measurement techniques that help identify and quantify signal degradation, jitter, noise, and other factors affecting high-speed DDR5 data transmission. Advanced testing methodologies enable engineers to validate designs against specifications and ensure reliable operation at the increased data rates of DDR5 memory systems.- Signal integrity testing and measurement for DDR5 memory: Various methods and systems for testing and measuring signal integrity in DDR5 memory interfaces. These include specialized test equipment, measurement techniques, and analysis tools that help identify and quantify signal integrity issues such as noise, jitter, and crosstalk. Advanced testing methodologies enable accurate characterization of high-speed DDR5 signals to ensure reliable operation at increased data rates.
- DDR5 signal routing and layout optimization: Techniques for optimizing signal routing and PCB layout for DDR5 memory interfaces to maintain signal integrity. This includes controlled impedance routing, length matching, via optimization, and proper layer stackup design. Advanced routing methodologies help minimize signal reflections, crosstalk, and electromagnetic interference, which are critical for maintaining signal integrity at the higher frequencies used in DDR5 systems.
- DDR5 termination and impedance matching techniques: Implementation of proper termination schemes and impedance matching techniques for DDR5 interfaces to maintain signal integrity. This includes on-die termination, series termination, parallel termination, and dynamic impedance matching. These techniques help reduce signal reflections, ringing, and other transmission line effects that can degrade signal quality in high-speed DDR5 memory systems.
- DDR5 equalization and signal conditioning: Advanced equalization and signal conditioning techniques for DDR5 interfaces to compensate for channel losses and improve signal integrity. This includes transmitter pre-emphasis, receiver equalization, decision feedback equalization, and adaptive equalization algorithms. These techniques help overcome signal degradation caused by PCB traces, connectors, and other channel components, enabling reliable data transmission at higher DDR5 speeds.
- DDR5 signal integrity simulation and modeling: Simulation and modeling approaches for predicting and analyzing signal integrity issues in DDR5 memory systems before physical implementation. This includes channel modeling, S-parameter analysis, time-domain simulation, and statistical analysis techniques. Advanced simulation tools help designers identify potential signal integrity problems early in the design process, reducing development time and improving DDR5 system reliability.
02 DDR5 signal routing and layout optimization
Techniques for optimizing signal routing and PCB layout for DDR5 memory interfaces to maintain signal integrity. This includes controlled impedance routing, length matching, minimizing crosstalk, and proper layer stackup design. Advanced routing methodologies address the challenges of higher frequencies in DDR5, including considerations for vias, trace geometry, and reference planes to ensure clean signal transmission and reception between memory components and controllers.Expand Specific Solutions03 Equalization and termination techniques for DDR5
Implementation of equalization and termination techniques specifically designed for DDR5 interfaces to compensate for channel losses and reflections. These include decision feedback equalization (DFE), feed-forward equalization (FFE), and various termination schemes that help maintain signal integrity at higher data rates. Proper termination resistors and on-die termination configurations are crucial for reducing reflections and ensuring clean signal transitions in the high-frequency DDR5 environment.Expand Specific Solutions04 DDR5 power integrity and noise reduction
Methods for maintaining power integrity and reducing noise in DDR5 memory systems, which is critical for signal integrity. This includes power delivery network (PDN) design, decoupling capacitor placement strategies, and ground plane optimization. Techniques for mitigating simultaneous switching noise (SSN) and power supply induced jitter help ensure stable voltage references for high-speed signaling, contributing to overall signal integrity in DDR5 interfaces.Expand Specific Solutions05 Simulation and modeling for DDR5 signal integrity
Advanced simulation and modeling approaches for predicting and optimizing DDR5 signal integrity before physical implementation. These include channel modeling, S-parameter analysis, time-domain reflectometry (TDR) simulation, and eye diagram prediction. Computational methods help engineers identify potential signal integrity issues early in the design process, allowing for optimization of trace geometries, via structures, and component placement to ensure reliable operation at DDR5 speeds.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in DDR5 Ecosystem
The DDR5 Signal Integrity market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across high-speed communication boards as data transfer demands escalate. The market is projected to expand significantly as next-generation computing platforms emerge, with an estimated value exceeding $5 billion by 2025. Technologically, the landscape shows varying maturity levels, with established semiconductor leaders like Samsung Electronics, SK hynix, and Micron Technology demonstrating advanced capabilities in DDR5 implementation. Intel, Qualcomm, and IBM are focusing on system-level integration challenges, while companies like Renesas and Infineon are developing specialized signal integrity solutions. Chinese players including Huawei, ChangXin Memory, and Inspur are rapidly advancing their technologies to reduce dependency on foreign suppliers, though they still lag behind global leaders in high-performance DDR5 applications.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung's DDR5 signal integrity solution employs a multi-layered approach combining hardware and algorithmic innovations. Their technology features an advanced on-die termination (ODT) system with calibrated impedance matching that dynamically adjusts to varying operating conditions. Samsung has implemented proprietary Through-Silicon Via (TSV) technology in their DDR5 modules, reducing signal path lengths by approximately 30% compared to traditional wire bonding methods. This significantly improves signal quality at high frequencies. Their solution also incorporates a novel equalization scheme that combines feed-forward equalization (FFE) with decision feedback equalization (DFE), enabling reliable operation at speeds up to 7200MT/s while maintaining signal integrity across complex server and workstation motherboards with multiple DIMM configurations.
Strengths: Exceptional signal quality at high data rates; reduced power consumption through optimized signal paths; compatibility with a wide range of motherboard designs. Weaknesses: Higher manufacturing costs; requires specialized PCB design considerations; more complex qualification process for system integrators.
QUALCOMM, Inc.
Technical Solution: Qualcomm's DDR5 signal integrity solution for mobile and edge computing platforms features their proprietary Smart Signal Conditioning (SSC) technology, which implements adaptive equalization techniques optimized for compact PCB layouts. Their approach includes a novel hybrid termination scheme that dynamically switches between different termination modes based on operating conditions, reducing power consumption while maintaining signal integrity. Qualcomm has developed specialized SerDes circuits with decision feedback equalization (DFE) that compensate for channel losses at frequencies above 3.5GHz, enabling reliable operation in space-constrained designs. Their solution also incorporates advanced power delivery network (PDN) designs with integrated voltage regulation that reduces noise coupling by approximately 18% compared to conventional approaches, resulting in cleaner signal transmission even in dense mobile device layouts.
Strengths: Excellent power efficiency optimized for mobile applications; compact implementation suitable for space-constrained designs; adaptive equalization that handles varying environmental conditions. Weaknesses: Lower maximum data rates compared to server-focused solutions; more limited memory capacity support; requires specialized design expertise for optimal implementation.
Advanced PCB Design Techniques for DDR5
Memory signal transmission system, signal line arrangement method, product, equipment and medium
PatentActiveCN118711625A
Innovation
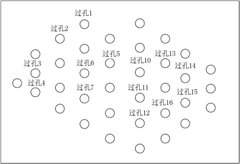
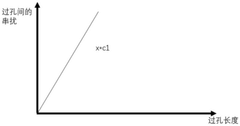
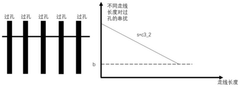
- By optimizing the length of the signal line and the length of the via in the inner layer of the circuit board, using the principle of matching short holes with long signal lines and long holes with short signal lines, a link model is established for crosstalk analysis and adjustment, and the signal lines are optimized. Arranged to reduce crosstalk values.
A DDR signal Rtt termination PCB board-level layout and wiring constraint method and electronic device
PatentActiveCN117408219B
Innovation
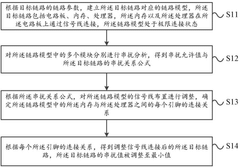
- By determining the wiring length between the bare chip in the control chip and the circuit packaging substrate, calculating the transmission delay and signal transmission rate, combined with the lumped parameter method and the preset data frequency of the DDR signal, the constraints on the wiring length and The optimal constraints of the location are elicited to ensure the integrity of the signal in the transmission link.
Thermal Management in High-Speed DDR5 Designs
Thermal management has become a critical challenge in high-speed DDR5 designs due to the significant increase in operating frequencies and data rates. With DDR5 memory modules operating at speeds of up to 6400 MT/s and beyond, power consumption and heat generation have increased substantially compared to previous generations. This thermal challenge is further exacerbated by the higher density of components on modern communication boards, limiting natural heat dissipation pathways.
The thermal characteristics of DDR5 memory present unique challenges for signal integrity. As temperatures rise, resistance in conductive pathways increases, leading to greater signal attenuation and potential timing violations. Research indicates that for every 10°C increase in operating temperature, signal integrity metrics can degrade by approximately 5-8%, potentially pushing high-speed designs beyond their operating margins.
Advanced thermal management solutions for DDR5 implementations include active and passive cooling strategies. Passive solutions involve optimized PCB designs with enhanced copper spreading layers and strategic component placement to facilitate heat dissipation. Some manufacturers have implemented thermal pads between memory modules and heat sinks to improve thermal conductivity, reducing hotspots that can affect signal performance.
Active cooling solutions include dedicated airflow channels, micro-fans, and even liquid cooling systems for extreme performance applications. These solutions must be carefully designed to avoid introducing electromagnetic interference that could further compromise signal integrity. Recent innovations include phase-change materials embedded in PCB substrates that absorb heat during peak operations and release it during idle periods, helping to stabilize operating temperatures.
Thermal simulation has become an essential part of the DDR5 design process. Advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) models now integrate with signal integrity simulators to provide comprehensive analysis of the thermal-electrical interaction. These tools enable designers to identify potential thermal issues early in the design cycle and implement mitigation strategies before physical prototyping.
The relationship between power delivery networks (PDN) and thermal management is particularly important in DDR5 designs. Voltage regulators integrated directly onto DDR5 DIMMs generate additional heat sources that must be managed. Thermal vias, strategically placed throughout the PCB design, help channel heat away from critical signal paths and sensitive components, maintaining signal integrity under various operating conditions.
The thermal characteristics of DDR5 memory present unique challenges for signal integrity. As temperatures rise, resistance in conductive pathways increases, leading to greater signal attenuation and potential timing violations. Research indicates that for every 10°C increase in operating temperature, signal integrity metrics can degrade by approximately 5-8%, potentially pushing high-speed designs beyond their operating margins.
Advanced thermal management solutions for DDR5 implementations include active and passive cooling strategies. Passive solutions involve optimized PCB designs with enhanced copper spreading layers and strategic component placement to facilitate heat dissipation. Some manufacturers have implemented thermal pads between memory modules and heat sinks to improve thermal conductivity, reducing hotspots that can affect signal performance.
Active cooling solutions include dedicated airflow channels, micro-fans, and even liquid cooling systems for extreme performance applications. These solutions must be carefully designed to avoid introducing electromagnetic interference that could further compromise signal integrity. Recent innovations include phase-change materials embedded in PCB substrates that absorb heat during peak operations and release it during idle periods, helping to stabilize operating temperatures.
Thermal simulation has become an essential part of the DDR5 design process. Advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) models now integrate with signal integrity simulators to provide comprehensive analysis of the thermal-electrical interaction. These tools enable designers to identify potential thermal issues early in the design cycle and implement mitigation strategies before physical prototyping.
The relationship between power delivery networks (PDN) and thermal management is particularly important in DDR5 designs. Voltage regulators integrated directly onto DDR5 DIMMs generate additional heat sources that must be managed. Thermal vias, strategically placed throughout the PCB design, help channel heat away from critical signal paths and sensitive components, maintaining signal integrity under various operating conditions.
EMI/EMC Considerations for DDR5 Systems
The electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) challenges in DDR5 systems have become increasingly critical as data rates exceed 6400 MT/s. DDR5 memory interfaces generate significant electromagnetic emissions due to their high-frequency switching and fast edge rates, potentially causing interference with nearby components and violating regulatory standards.
Signal integrity issues in DDR5 systems are closely linked to EMI/EMC performance. The faster edge rates that improve signal integrity simultaneously create broader spectral content, increasing radiated emissions. This fundamental trade-off requires careful system design considerations to balance performance with compliance requirements.
DDR5 introduces several architectural changes that impact EMI/EMC characteristics. The transition to on-die termination (ODT) and decision feedback equalization (DFE) helps improve signal quality but creates new EMI challenges. Additionally, the voltage reduction from 1.2V in DDR4 to 1.1V in DDR5 decreases noise margins, making systems more susceptible to external interference.
Board-level mitigation strategies have evolved significantly for DDR5 implementations. Advanced stackup designs incorporating embedded capacitance materials and optimized reference planes help contain electromagnetic fields. Strategic via placement and antipads sizing minimize return path discontinuities that could otherwise act as unintentional antennas.
Shielding techniques have become more sophisticated for DDR5 systems. Localized shield cans, guard traces, and stitching vias are increasingly employed to contain emissions from high-speed memory channels. Some advanced designs incorporate partial Faraday cage structures around critical DDR5 routing areas.
Power delivery network (PDN) design significantly impacts EMI/EMC performance in DDR5 systems. The increased switching currents and tighter voltage regulation requirements necessitate more robust decoupling strategies. Multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) with low equivalent series inductance (ESL) are strategically placed to suppress power rail noise that could couple into signal paths.
Regulatory compliance presents new challenges for DDR5 implementations. Systems must meet FCC Class B and CISPR 22 requirements despite higher operating frequencies. Pre-compliance testing during development has become essential, with near-field scanning techniques helping identify emission hotspots before formal certification testing.
Signal integrity issues in DDR5 systems are closely linked to EMI/EMC performance. The faster edge rates that improve signal integrity simultaneously create broader spectral content, increasing radiated emissions. This fundamental trade-off requires careful system design considerations to balance performance with compliance requirements.
DDR5 introduces several architectural changes that impact EMI/EMC characteristics. The transition to on-die termination (ODT) and decision feedback equalization (DFE) helps improve signal quality but creates new EMI challenges. Additionally, the voltage reduction from 1.2V in DDR4 to 1.1V in DDR5 decreases noise margins, making systems more susceptible to external interference.
Board-level mitigation strategies have evolved significantly for DDR5 implementations. Advanced stackup designs incorporating embedded capacitance materials and optimized reference planes help contain electromagnetic fields. Strategic via placement and antipads sizing minimize return path discontinuities that could otherwise act as unintentional antennas.
Shielding techniques have become more sophisticated for DDR5 systems. Localized shield cans, guard traces, and stitching vias are increasingly employed to contain emissions from high-speed memory channels. Some advanced designs incorporate partial Faraday cage structures around critical DDR5 routing areas.
Power delivery network (PDN) design significantly impacts EMI/EMC performance in DDR5 systems. The increased switching currents and tighter voltage regulation requirements necessitate more robust decoupling strategies. Multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) with low equivalent series inductance (ESL) are strategically placed to suppress power rail noise that could couple into signal paths.
Regulatory compliance presents new challenges for DDR5 implementations. Systems must meet FCC Class B and CISPR 22 requirements despite higher operating frequencies. Pre-compliance testing during development has become essential, with near-field scanning techniques helping identify emission hotspots before formal certification testing.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!