Designing Muscimol-Based Combination Therapies
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol Research Background and Objectives
Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has been the subject of extensive research in neuropharmacology for decades. Originally isolated from the Amanita muscaria mushroom, this compound has garnered significant attention due to its potential therapeutic applications in various neurological and psychiatric disorders. The evolution of muscimol research has been marked by a progressive understanding of its mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, and potential clinical uses.
The primary objective of current muscimol research is to explore its efficacy in combination therapies for complex neurological conditions. This approach stems from the recognition that many disorders of the central nervous system involve multiple neurotransmitter systems and pathways. By combining muscimol with other pharmacological agents, researchers aim to achieve synergistic effects that could potentially enhance therapeutic outcomes while minimizing side effects.
One of the key trends in muscimol research is the development of novel delivery methods to overcome its poor blood-brain barrier penetration and short half-life. This includes the exploration of nanoparticle-based delivery systems, prodrug formulations, and targeted delivery techniques. These advancements are crucial for realizing the full therapeutic potential of muscimol in clinical settings.
Another significant focus is the investigation of muscimol's role in modulating neuroplasticity and neuroprotection. Recent studies have suggested that muscimol may have broader effects beyond its well-known GABAergic activity, potentially influencing neuronal survival and regeneration pathways. This has opened up new avenues for research into its application in neurodegenerative disorders and brain injury recovery.
The design of muscimol-based combination therapies represents a convergence of these research trends. By leveraging muscimol's GABAergic properties in conjunction with other neuroactive compounds, researchers aim to develop more effective treatments for conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and chronic pain syndromes. This approach necessitates a deep understanding of drug interactions, receptor pharmacology, and the complex interplay of neurotransmitter systems in the brain.
As the field progresses, there is an increasing emphasis on personalized medicine approaches in muscimol-based therapies. This involves tailoring combination treatments to individual patient profiles based on genetic, metabolic, and neurophysiological factors. The goal is to optimize therapeutic outcomes while minimizing adverse effects through precise, patient-specific drug combinations and dosing regimens.
The primary objective of current muscimol research is to explore its efficacy in combination therapies for complex neurological conditions. This approach stems from the recognition that many disorders of the central nervous system involve multiple neurotransmitter systems and pathways. By combining muscimol with other pharmacological agents, researchers aim to achieve synergistic effects that could potentially enhance therapeutic outcomes while minimizing side effects.
One of the key trends in muscimol research is the development of novel delivery methods to overcome its poor blood-brain barrier penetration and short half-life. This includes the exploration of nanoparticle-based delivery systems, prodrug formulations, and targeted delivery techniques. These advancements are crucial for realizing the full therapeutic potential of muscimol in clinical settings.
Another significant focus is the investigation of muscimol's role in modulating neuroplasticity and neuroprotection. Recent studies have suggested that muscimol may have broader effects beyond its well-known GABAergic activity, potentially influencing neuronal survival and regeneration pathways. This has opened up new avenues for research into its application in neurodegenerative disorders and brain injury recovery.
The design of muscimol-based combination therapies represents a convergence of these research trends. By leveraging muscimol's GABAergic properties in conjunction with other neuroactive compounds, researchers aim to develop more effective treatments for conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and chronic pain syndromes. This approach necessitates a deep understanding of drug interactions, receptor pharmacology, and the complex interplay of neurotransmitter systems in the brain.
As the field progresses, there is an increasing emphasis on personalized medicine approaches in muscimol-based therapies. This involves tailoring combination treatments to individual patient profiles based on genetic, metabolic, and neurophysiological factors. The goal is to optimize therapeutic outcomes while minimizing adverse effects through precise, patient-specific drug combinations and dosing regimens.
Market Analysis for Muscimol-Based Therapies
The market for muscimol-based therapies is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing research into novel applications of this GABA receptor agonist. Muscimol, traditionally known for its psychoactive properties, is now being explored for its potential in treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders. This shift in focus has opened up new market opportunities in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors.
The global neurology drugs market, which encompasses muscimol-based therapies, is projected to expand substantially in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the rising prevalence of neurological disorders, an aging population, and advancements in drug delivery technologies. Muscimol's unique pharmacological profile positions it as a promising candidate for combination therapies, particularly in areas where traditional treatments have shown limitations.
In the realm of psychiatric disorders, muscimol-based therapies are gaining traction. The global market for anxiety disorders and depression treatments, where muscimol shows potential, is expected to see robust growth. This is partly due to the increasing recognition of mental health issues and the need for more effective, targeted treatments with fewer side effects.
The market for epilepsy treatments, another area where muscimol-based therapies are being researched, is also expanding. The potential of muscimol to modulate neuronal excitability makes it an attractive option for combination therapies in this field. As drug-resistant epilepsy remains a significant challenge, novel approaches involving muscimol are likely to attract considerable interest from both researchers and pharmaceutical companies.
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America present substantial growth opportunities for muscimol-based therapies. These regions are experiencing rapid economic development, improved healthcare infrastructure, and increasing healthcare expenditure, all of which contribute to a growing demand for advanced neurological and psychiatric treatments.
However, the market for muscimol-based therapies faces challenges. Regulatory hurdles, particularly given muscimol's psychoactive properties, may slow down market penetration in some regions. Additionally, competition from established treatments and other emerging therapies could impact market share.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for muscimol-based combination therapies remains positive. The increasing focus on personalized medicine and the need for more effective treatments for complex neurological and psychiatric disorders are likely to drive continued research and development in this field. As clinical trials progress and more data becomes available, the market potential for muscimol-based therapies is expected to become more clearly defined, potentially leading to significant market opportunities in the coming years.
The global neurology drugs market, which encompasses muscimol-based therapies, is projected to expand substantially in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the rising prevalence of neurological disorders, an aging population, and advancements in drug delivery technologies. Muscimol's unique pharmacological profile positions it as a promising candidate for combination therapies, particularly in areas where traditional treatments have shown limitations.
In the realm of psychiatric disorders, muscimol-based therapies are gaining traction. The global market for anxiety disorders and depression treatments, where muscimol shows potential, is expected to see robust growth. This is partly due to the increasing recognition of mental health issues and the need for more effective, targeted treatments with fewer side effects.
The market for epilepsy treatments, another area where muscimol-based therapies are being researched, is also expanding. The potential of muscimol to modulate neuronal excitability makes it an attractive option for combination therapies in this field. As drug-resistant epilepsy remains a significant challenge, novel approaches involving muscimol are likely to attract considerable interest from both researchers and pharmaceutical companies.
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America present substantial growth opportunities for muscimol-based therapies. These regions are experiencing rapid economic development, improved healthcare infrastructure, and increasing healthcare expenditure, all of which contribute to a growing demand for advanced neurological and psychiatric treatments.
However, the market for muscimol-based therapies faces challenges. Regulatory hurdles, particularly given muscimol's psychoactive properties, may slow down market penetration in some regions. Additionally, competition from established treatments and other emerging therapies could impact market share.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for muscimol-based combination therapies remains positive. The increasing focus on personalized medicine and the need for more effective treatments for complex neurological and psychiatric disorders are likely to drive continued research and development in this field. As clinical trials progress and more data becomes available, the market potential for muscimol-based therapies is expected to become more clearly defined, potentially leading to significant market opportunities in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Muscimol Drug Development
Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has shown promise in various therapeutic applications. However, its development as a standalone drug faces several significant challenges. One of the primary obstacles is its poor blood-brain barrier (BBB) penetration, which limits its effectiveness in treating central nervous system disorders. This necessitates the exploration of novel delivery methods or chemical modifications to enhance its bioavailability in the brain.
Another major challenge is the potential for off-target effects due to the widespread distribution of GABA-A receptors throughout the body. This can lead to unwanted side effects, including sedation, muscle relaxation, and cognitive impairment. Developing strategies to improve the selectivity of muscimol for specific GABA-A receptor subtypes or brain regions is crucial for minimizing these adverse effects.
The short half-life of muscimol in the body presents another hurdle in drug development. This rapid elimination necessitates frequent dosing, which can be impractical for patients and may lead to compliance issues. Researchers are exploring various formulations and delivery systems to extend the drug's duration of action and improve its pharmacokinetic profile.
Muscimol's potent activity at GABA-A receptors also raises concerns about tolerance and dependence with long-term use. This is particularly problematic for chronic conditions that may require extended treatment periods. Developing strategies to mitigate these risks, such as intermittent dosing regimens or combination therapies, is essential for the successful clinical application of muscimol-based drugs.
The synthesis and large-scale production of high-purity muscimol present additional challenges. Current methods often involve complex extraction processes from natural sources or multi-step chemical syntheses, which can be costly and time-consuming. Improving the efficiency and scalability of muscimol production is crucial for its commercial viability as a pharmaceutical agent.
Regulatory hurdles also pose significant challenges in muscimol drug development. As a compound with psychoactive properties, muscimol faces stringent regulatory scrutiny. Demonstrating its safety and efficacy in clinical trials, while addressing concerns about potential abuse or misuse, is critical for gaining regulatory approval.
Lastly, the development of appropriate formulations and delivery systems for muscimol-based therapies presents technical challenges. Ensuring stability, bioavailability, and targeted delivery of the drug requires innovative approaches in pharmaceutical technology. This may involve the development of novel drug carriers, controlled-release formulations, or combination with other therapeutic agents to enhance efficacy and reduce side effects.
Another major challenge is the potential for off-target effects due to the widespread distribution of GABA-A receptors throughout the body. This can lead to unwanted side effects, including sedation, muscle relaxation, and cognitive impairment. Developing strategies to improve the selectivity of muscimol for specific GABA-A receptor subtypes or brain regions is crucial for minimizing these adverse effects.
The short half-life of muscimol in the body presents another hurdle in drug development. This rapid elimination necessitates frequent dosing, which can be impractical for patients and may lead to compliance issues. Researchers are exploring various formulations and delivery systems to extend the drug's duration of action and improve its pharmacokinetic profile.
Muscimol's potent activity at GABA-A receptors also raises concerns about tolerance and dependence with long-term use. This is particularly problematic for chronic conditions that may require extended treatment periods. Developing strategies to mitigate these risks, such as intermittent dosing regimens or combination therapies, is essential for the successful clinical application of muscimol-based drugs.
The synthesis and large-scale production of high-purity muscimol present additional challenges. Current methods often involve complex extraction processes from natural sources or multi-step chemical syntheses, which can be costly and time-consuming. Improving the efficiency and scalability of muscimol production is crucial for its commercial viability as a pharmaceutical agent.
Regulatory hurdles also pose significant challenges in muscimol drug development. As a compound with psychoactive properties, muscimol faces stringent regulatory scrutiny. Demonstrating its safety and efficacy in clinical trials, while addressing concerns about potential abuse or misuse, is critical for gaining regulatory approval.
Lastly, the development of appropriate formulations and delivery systems for muscimol-based therapies presents technical challenges. Ensuring stability, bioavailability, and targeted delivery of the drug requires innovative approaches in pharmaceutical technology. This may involve the development of novel drug carriers, controlled-release formulations, or combination with other therapeutic agents to enhance efficacy and reduce side effects.
Existing Muscimol Combination Therapy Approaches
01 Muscimol-based therapies for neurological disorders
Combination therapies involving muscimol are being developed for various neurological disorders. These therapies leverage muscimol's GABA-A receptor agonist properties to modulate neural activity and potentially treat conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety, and sleep disorders. The combination approach may enhance efficacy and reduce side effects compared to monotherapies.- Muscimol-based therapies for neurological disorders: Combination therapies involving muscimol are being developed for treating various neurological disorders. These therapies may include muscimol in combination with other active ingredients to enhance efficacy and reduce side effects in treating conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety, and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Muscimol delivery systems and formulations: Novel delivery systems and formulations are being developed to improve the efficacy and bioavailability of muscimol-based therapies. These may include controlled-release formulations, transdermal patches, or nanoparticle-based delivery systems to optimize the therapeutic effects of muscimol and its combinations.
- Muscimol in combination with psychedelic compounds: Research is exploring the potential synergistic effects of combining muscimol with psychedelic compounds for treating mental health disorders. These combination therapies may offer new approaches to addressing conditions such as depression, PTSD, and addiction.
- Muscimol-based therapies for pain management: Combination therapies involving muscimol are being investigated for pain management applications. These therapies may combine muscimol with other analgesics or pain modulators to provide more effective and potentially safer alternatives to current pain treatments.
- Muscimol in cognitive enhancement and neuroprotection: Research is exploring the potential of muscimol-based combination therapies for cognitive enhancement and neuroprotection. These therapies may combine muscimol with other compounds to improve memory, learning, and overall brain health, potentially offering new approaches to treating age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders.
02 Muscimol in pain management
Muscimol is being explored in combination therapies for pain management. Its ability to enhance inhibitory neurotransmission may help alleviate various types of pain, including neuropathic and chronic pain. These combinations aim to provide more effective pain relief with potentially fewer side effects than traditional analgesics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Muscimol combinations for psychiatric disorders
Combination therapies incorporating muscimol are being investigated for psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety, and PTSD. These approaches aim to modulate GABA signaling in conjunction with other neurotransmitter systems to achieve improved therapeutic outcomes in mental health treatment.Expand Specific Solutions04 Muscimol in neurodegenerative disease treatment
Muscimol-based combination therapies are being explored for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. These approaches aim to leverage muscimol's neuroprotective properties in conjunction with other agents to slow disease progression and alleviate symptoms associated with neurodegeneration.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel delivery methods for muscimol combinations
Innovative delivery methods are being developed for muscimol-based combination therapies to enhance their efficacy and safety. These may include targeted delivery systems, controlled-release formulations, and novel routes of administration to optimize the therapeutic effects of muscimol and its combination partners.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Muscimol Research and Development
The development of muscimol-based combination therapies is in an early stage, with significant potential for growth. The market size is currently modest but expected to expand as research progresses. Technologically, the field is still maturing, with various companies and institutions exploring different approaches. Key players like Takeda Pharmaceutical, Genentech, and Janssen Pharmaceutica are leveraging their expertise in drug development to advance muscimol-based therapies. Academic institutions such as the University of California and University of Michigan are contributing valuable research. Smaller biotechnology firms like Galecto Biotech and Izun Pharmaceuticals are also making strides in this area, potentially offering innovative solutions.
Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. has developed a comprehensive approach to muscimol-based combination therapies, focusing on gastrointestinal and central nervous system disorders. Their strategy involves combining muscimol with selective gut-brain axis modulators to address both peripheral and central GABAergic signaling. Takeda's research has shown promising results in preclinical models of irritable bowel syndrome and functional dyspepsia, demonstrating synergistic effects between muscimol and their proprietary compounds targeting enteric nervous system receptors[1]. The company has also explored the use of pH-sensitive polymer-based delivery systems to target muscimol release to specific regions of the gastrointestinal tract, potentially enhancing local effects while minimizing systemic exposure[3]. Additionally, Takeda has investigated the potential of combining muscimol with microbiome-modulating agents to create novel therapies for gut-brain axis disorders, leveraging the emerging understanding of the microbiota's role in neurotransmitter signaling[5].
Strengths: Strong expertise in gastrointestinal and CNS drug development, innovative approach to gut-brain axis modulation, and a diverse portfolio of potential combination agents. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in demonstrating efficacy across both peripheral and central nervous system endpoints and the need for extensive clinical trials to establish the safety of novel gut-brain axis therapies.
Merck & Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: Merck & Co., Inc. has developed a multifaceted approach to muscimol-based combination therapies, leveraging their expertise in neuroscience and drug development. Their strategy involves combining muscimol with proprietary small molecule GABA receptor modulators to enhance therapeutic efficacy while minimizing side effects. Merck's research has shown promising results in animal models of anxiety and sleep disorders[2]. The company has also explored the use of controlled-release formulations to optimize the pharmacokinetics of muscimol, potentially allowing for once-daily dosing and improved patient compliance[4]. Furthermore, Merck has investigated the potential of combining muscimol with other neurotransmitter-targeting compounds, such as serotonin reuptake inhibitors, to create novel treatments for mood disorders and other neuropsychiatric conditions[6].
Strengths: Strong R&D capabilities, extensive experience in bringing CNS drugs to market, and a diverse portfolio of potential combination agents. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in differentiating their products in a competitive market and the need for long-term safety data on novel combinations.
Innovative Muscimol Delivery Systems
Combinations comprising antimuscarinic agents and corticosteroids
PatentInactiveEP1765405A1
Innovation
- Combining a corticosteroid with an antagonist of M3 muscarinic receptors of a specific formula, which allows for reduced dosages while maintaining therapeutic effectiveness in the respiratory tract, thereby minimizing side effects.
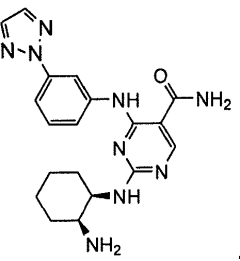
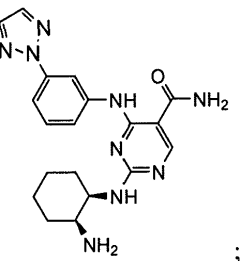
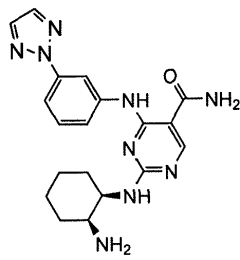
Combination therapy with 4-(3-(2h-1,2,3-triazol-2-yl)phenylamino)-2-((1r,2s)-2-aminocyclohexylamino)pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
PatentWO2012044936A1
Innovation
- A combination therapy using the SYK inhibitor 4-(3-(2H-1,2,3-triazol-2-yl)phenylamino)-2-((1R,2S)-2-aminocyclohexylamino)pyrimidine-5-carboxamide, referred to as Compound 1, in conjunction with antineoplastic or anti-inflammatory agents to treat inflammatory, autoimmune, and cell proliferative diseases, including leukemia and lymphoma, by administering a therapeutically effective amount of Compound 1 and an antineoplastic or anti-inflammatory agent, such as methotrexate, dexamethasone, or rituximab, to enhance therapeutic effects while reducing side effects.
Regulatory Pathway for Muscimol Therapies
The regulatory pathway for muscimol-based combination therapies involves a complex process of approval and oversight by regulatory agencies, primarily the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States. Given the novel nature of muscimol as a therapeutic agent, developers must navigate carefully through various stages of regulatory review and compliance.
Initially, preclinical studies must be conducted to establish the safety profile and potential efficacy of muscimol-based therapies. These studies typically involve in vitro and animal testing to assess toxicity, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. The data from these studies form the basis for an Investigational New Drug (IND) application, which must be submitted to the FDA before clinical trials can begin.
Once the IND is approved, clinical trials can commence, progressing through Phase I, II, and III studies. Phase I trials focus on safety and dosing in healthy volunteers, while Phase II and III trials assess efficacy and further safety in larger patient populations. For combination therapies, additional complexities arise as the interaction between muscimol and other active ingredients must be thoroughly evaluated.
Throughout the clinical trial process, sponsors must adhere to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines and maintain open communication with the FDA through regular meetings and submissions. The FDA may require additional studies or modifications to the trial design based on emerging data or concerns.
Upon successful completion of clinical trials, sponsors must compile and submit a New Drug Application (NDA) or Biologics License Application (BLA), depending on the nature of the therapy. This comprehensive application includes all data from preclinical and clinical studies, proposed labeling, and manufacturing information.
The FDA review process typically takes 6-10 months, during which time the agency may request additional information or clarifications. If approved, the sponsor must comply with post-marketing surveillance requirements and may need to conduct Phase IV studies to gather long-term safety data.
For muscimol-based combination therapies, special considerations may apply due to the compound's psychoactive properties. The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) may need to be involved in scheduling decisions, which could impact prescribing and distribution regulations.
Internationally, developers must navigate similar but distinct regulatory pathways in other jurisdictions, such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in the European Union or the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) in Japan. Harmonization efforts, such as the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), aim to streamline these processes globally, but regional differences in requirements and timelines persist.
Initially, preclinical studies must be conducted to establish the safety profile and potential efficacy of muscimol-based therapies. These studies typically involve in vitro and animal testing to assess toxicity, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. The data from these studies form the basis for an Investigational New Drug (IND) application, which must be submitted to the FDA before clinical trials can begin.
Once the IND is approved, clinical trials can commence, progressing through Phase I, II, and III studies. Phase I trials focus on safety and dosing in healthy volunteers, while Phase II and III trials assess efficacy and further safety in larger patient populations. For combination therapies, additional complexities arise as the interaction between muscimol and other active ingredients must be thoroughly evaluated.
Throughout the clinical trial process, sponsors must adhere to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines and maintain open communication with the FDA through regular meetings and submissions. The FDA may require additional studies or modifications to the trial design based on emerging data or concerns.
Upon successful completion of clinical trials, sponsors must compile and submit a New Drug Application (NDA) or Biologics License Application (BLA), depending on the nature of the therapy. This comprehensive application includes all data from preclinical and clinical studies, proposed labeling, and manufacturing information.
The FDA review process typically takes 6-10 months, during which time the agency may request additional information or clarifications. If approved, the sponsor must comply with post-marketing surveillance requirements and may need to conduct Phase IV studies to gather long-term safety data.
For muscimol-based combination therapies, special considerations may apply due to the compound's psychoactive properties. The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) may need to be involved in scheduling decisions, which could impact prescribing and distribution regulations.
Internationally, developers must navigate similar but distinct regulatory pathways in other jurisdictions, such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in the European Union or the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) in Japan. Harmonization efforts, such as the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), aim to streamline these processes globally, but regional differences in requirements and timelines persist.
Safety and Toxicology Considerations
Safety and toxicology considerations are paramount when designing muscimol-based combination therapies. Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has a complex pharmacological profile that necessitates careful evaluation of its safety profile, especially when combined with other therapeutic agents.
The primary concern with muscimol is its potential for central nervous system (CNS) depression. As a GABA-A receptor agonist, it can cause sedation, dizziness, and impaired cognitive function. When designing combination therapies, it is crucial to assess the potential for additive or synergistic CNS depressant effects with other drugs, particularly those that also act on the GABAergic system or have sedative properties.
Hepatotoxicity is another important consideration. While muscimol itself has not been extensively studied for liver toxicity, some GABAergic drugs have been associated with rare cases of liver injury. Combination therapies should be carefully evaluated for potential hepatotoxic interactions, especially when combined with drugs known to affect liver function.
Renal clearance of muscimol and its metabolites must be taken into account, particularly in patients with impaired kidney function. The potential for drug-drug interactions affecting renal excretion should be thoroughly investigated to prevent accumulation and toxicity.
Muscimol's effects on the cardiovascular system, although generally mild, should not be overlooked. Monitoring for potential hypotensive effects, especially when combined with antihypertensive medications, is essential. Additionally, the impact on heart rate and cardiac conduction should be evaluated, particularly in combination with drugs that affect these parameters.
Long-term safety and the potential for tolerance or dependence are critical aspects to consider. While muscimol is not typically associated with addiction, its chronic use in combination therapies may lead to adaptive changes in GABA-A receptor function. This could potentially result in withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation or reduced efficacy over time.
Neurodevelopmental toxicity is a concern, especially if muscimol-based therapies are considered for use in pediatric populations or pregnant women. Preclinical studies should thoroughly assess the impact on neural development and potential teratogenic effects.
Finally, the potential for immunotoxicity should be evaluated. While muscimol itself is not known to have significant immunomodulatory effects, its combination with other drugs may alter immune function. This is particularly important for therapies targeting conditions with an immunological component.
The primary concern with muscimol is its potential for central nervous system (CNS) depression. As a GABA-A receptor agonist, it can cause sedation, dizziness, and impaired cognitive function. When designing combination therapies, it is crucial to assess the potential for additive or synergistic CNS depressant effects with other drugs, particularly those that also act on the GABAergic system or have sedative properties.
Hepatotoxicity is another important consideration. While muscimol itself has not been extensively studied for liver toxicity, some GABAergic drugs have been associated with rare cases of liver injury. Combination therapies should be carefully evaluated for potential hepatotoxic interactions, especially when combined with drugs known to affect liver function.
Renal clearance of muscimol and its metabolites must be taken into account, particularly in patients with impaired kidney function. The potential for drug-drug interactions affecting renal excretion should be thoroughly investigated to prevent accumulation and toxicity.
Muscimol's effects on the cardiovascular system, although generally mild, should not be overlooked. Monitoring for potential hypotensive effects, especially when combined with antihypertensive medications, is essential. Additionally, the impact on heart rate and cardiac conduction should be evaluated, particularly in combination with drugs that affect these parameters.
Long-term safety and the potential for tolerance or dependence are critical aspects to consider. While muscimol is not typically associated with addiction, its chronic use in combination therapies may lead to adaptive changes in GABA-A receptor function. This could potentially result in withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation or reduced efficacy over time.
Neurodevelopmental toxicity is a concern, especially if muscimol-based therapies are considered for use in pediatric populations or pregnant women. Preclinical studies should thoroughly assess the impact on neural development and potential teratogenic effects.
Finally, the potential for immunotoxicity should be evaluated. While muscimol itself is not known to have significant immunomodulatory effects, its combination with other drugs may alter immune function. This is particularly important for therapies targeting conditions with an immunological component.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!