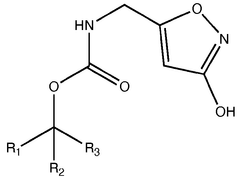
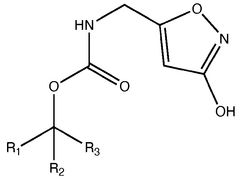
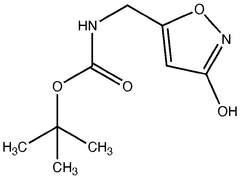
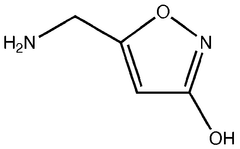
Trend Analysis of Muscimol in Clinical Research
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol Research Background and Objectives
Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has been the subject of increasing interest in clinical research over the past few decades. This naturally occurring psychoactive compound, found in various species of mushrooms, particularly Amanita muscaria, has a rich history in traditional medicine and shamanic practices.
The evolution of muscimol research can be traced back to the mid-20th century when its chemical structure was first elucidated. Since then, scientific understanding of its pharmacological properties and potential therapeutic applications has grown significantly. The primary focus of muscimol research has shifted from its psychoactive effects to its potential as a therapeutic agent for various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Recent advancements in neuroscience and pharmacology have led to a resurgence of interest in muscimol's clinical potential. The compound's ability to modulate GABAergic neurotransmission has positioned it as a promising candidate for treating conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and sleep disturbances. Additionally, its neuroprotective properties have sparked investigations into its potential role in managing neurodegenerative diseases.
The current trend in muscimol research is characterized by a multidisciplinary approach, combining molecular biology, neuropharmacology, and clinical studies. Researchers are exploring novel delivery methods, including nanoparticle-based systems and targeted drug delivery, to enhance muscimol's efficacy and minimize potential side effects.
One of the key objectives in contemporary muscimol research is to develop a comprehensive understanding of its mechanism of action at the molecular and cellular levels. This includes investigating its interactions with various GABA receptor subtypes and its effects on neural circuits implicated in different neurological and psychiatric conditions.
Another important goal is to establish the safety profile and optimal dosing regimens for muscimol in clinical applications. This involves conducting rigorous preclinical and clinical trials to assess its efficacy, tolerability, and potential long-term effects. Researchers are also exploring the possibility of developing synthetic analogues of muscimol with improved pharmacokinetic properties and reduced psychoactive effects.
The trend analysis of muscimol in clinical research aims to identify emerging patterns and future directions in this field. This includes evaluating the growing body of literature, analyzing ongoing clinical trials, and assessing the potential impact of muscimol-based therapies on current treatment paradigms for various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
The evolution of muscimol research can be traced back to the mid-20th century when its chemical structure was first elucidated. Since then, scientific understanding of its pharmacological properties and potential therapeutic applications has grown significantly. The primary focus of muscimol research has shifted from its psychoactive effects to its potential as a therapeutic agent for various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Recent advancements in neuroscience and pharmacology have led to a resurgence of interest in muscimol's clinical potential. The compound's ability to modulate GABAergic neurotransmission has positioned it as a promising candidate for treating conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and sleep disturbances. Additionally, its neuroprotective properties have sparked investigations into its potential role in managing neurodegenerative diseases.
The current trend in muscimol research is characterized by a multidisciplinary approach, combining molecular biology, neuropharmacology, and clinical studies. Researchers are exploring novel delivery methods, including nanoparticle-based systems and targeted drug delivery, to enhance muscimol's efficacy and minimize potential side effects.
One of the key objectives in contemporary muscimol research is to develop a comprehensive understanding of its mechanism of action at the molecular and cellular levels. This includes investigating its interactions with various GABA receptor subtypes and its effects on neural circuits implicated in different neurological and psychiatric conditions.
Another important goal is to establish the safety profile and optimal dosing regimens for muscimol in clinical applications. This involves conducting rigorous preclinical and clinical trials to assess its efficacy, tolerability, and potential long-term effects. Researchers are also exploring the possibility of developing synthetic analogues of muscimol with improved pharmacokinetic properties and reduced psychoactive effects.
The trend analysis of muscimol in clinical research aims to identify emerging patterns and future directions in this field. This includes evaluating the growing body of literature, analyzing ongoing clinical trials, and assessing the potential impact of muscimol-based therapies on current treatment paradigms for various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Clinical Applications and Market Potential
Muscimol, a potent GABA receptor agonist, has been gaining significant attention in clinical research due to its potential therapeutic applications. The market for muscimol-based treatments is expected to grow substantially in the coming years, driven by increasing research into neurological and psychiatric disorders.
In the field of neurology, muscimol shows promise for treating epilepsy, a condition affecting millions worldwide. Clinical trials have demonstrated its ability to reduce seizure frequency and severity in some patients resistant to conventional anticonvulsants. This opens up a potentially lucrative market segment, as there is a constant demand for more effective epilepsy treatments.
Psychiatric applications of muscimol are also being extensively explored. Research indicates its potential in treating anxiety disorders, particularly generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and social anxiety disorder. The global anxiety disorder market is projected to expand significantly, and muscimol-based therapies could capture a substantial portion of this growth.
Another promising area for muscimol is in the treatment of sleep disorders. Preliminary studies suggest that muscimol may help improve sleep quality and duration in patients with insomnia. Given the prevalence of sleep disorders and the limitations of current treatments, this represents a substantial market opportunity.
In the realm of pain management, muscimol is being investigated for its analgesic properties. Early research indicates potential efficacy in treating chronic pain conditions, including neuropathic pain. The chronic pain market is large and growing, offering significant potential for muscimol-based treatments.
The potential applications of muscimol in addiction treatment are also garnering attention. Preclinical studies suggest it may help reduce drug-seeking behavior and withdrawal symptoms in various substance use disorders. This could open up new avenues for treating addiction, a persistent and costly global health issue.
As research progresses, the market potential for muscimol-based therapies is expected to expand. Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly investing in muscimol research, recognizing its diverse clinical applications. However, the path to market will require extensive clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy profiles for specific indications.
The growing interest in muscimol also presents opportunities for drug delivery innovations. Researchers are exploring novel formulations and delivery methods to optimize muscimol's therapeutic effects while minimizing potential side effects. This could lead to the development of patentable drug delivery technologies, further enhancing the market value of muscimol-based treatments.
In the field of neurology, muscimol shows promise for treating epilepsy, a condition affecting millions worldwide. Clinical trials have demonstrated its ability to reduce seizure frequency and severity in some patients resistant to conventional anticonvulsants. This opens up a potentially lucrative market segment, as there is a constant demand for more effective epilepsy treatments.
Psychiatric applications of muscimol are also being extensively explored. Research indicates its potential in treating anxiety disorders, particularly generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and social anxiety disorder. The global anxiety disorder market is projected to expand significantly, and muscimol-based therapies could capture a substantial portion of this growth.
Another promising area for muscimol is in the treatment of sleep disorders. Preliminary studies suggest that muscimol may help improve sleep quality and duration in patients with insomnia. Given the prevalence of sleep disorders and the limitations of current treatments, this represents a substantial market opportunity.
In the realm of pain management, muscimol is being investigated for its analgesic properties. Early research indicates potential efficacy in treating chronic pain conditions, including neuropathic pain. The chronic pain market is large and growing, offering significant potential for muscimol-based treatments.
The potential applications of muscimol in addiction treatment are also garnering attention. Preclinical studies suggest it may help reduce drug-seeking behavior and withdrawal symptoms in various substance use disorders. This could open up new avenues for treating addiction, a persistent and costly global health issue.
As research progresses, the market potential for muscimol-based therapies is expected to expand. Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly investing in muscimol research, recognizing its diverse clinical applications. However, the path to market will require extensive clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy profiles for specific indications.
The growing interest in muscimol also presents opportunities for drug delivery innovations. Researchers are exploring novel formulations and delivery methods to optimize muscimol's therapeutic effects while minimizing potential side effects. This could lead to the development of patentable drug delivery technologies, further enhancing the market value of muscimol-based treatments.
Current Challenges in Muscimol Research
Despite the promising potential of muscimol in clinical research, several significant challenges currently hinder its widespread application and development. These challenges span across various domains, including pharmacological, methodological, and regulatory aspects.
One of the primary obstacles in muscimol research is its limited bioavailability when administered orally. Muscimol, being a polar molecule, struggles to cross the blood-brain barrier efficiently, which restricts its therapeutic potential. This necessitates the exploration of alternative delivery methods or the development of novel formulations to enhance its bioavailability and efficacy.
Another challenge lies in the precise dosing of muscimol. Given its potent GABA-A receptor agonist properties, even slight variations in dosage can lead to significant differences in effects. This sensitivity makes it difficult to establish standardized dosing protocols across diverse patient populations and conditions, potentially limiting its clinical applicability.
The short half-life of muscimol presents another hurdle in its clinical application. The rapid metabolism and elimination of the compound from the body necessitate frequent dosing, which can be impractical for long-term treatments and may lead to compliance issues among patients. Developing sustained-release formulations or discovering ways to prolong muscimol's activity in the body remains a critical challenge.
Furthermore, the potential for side effects and adverse reactions poses a significant concern in muscimol research. As a GABA-A receptor agonist, muscimol can cause sedation, cognitive impairment, and motor incoordination. Balancing its therapeutic benefits with these potential side effects is crucial for its successful clinical application.
From a methodological standpoint, the lack of standardized protocols for muscimol administration and assessment of its effects complicates the comparison and interpretation of research findings across different studies. This inconsistency hampers the ability to draw robust conclusions and slows down the progress of muscimol research.
Regulatory challenges also play a significant role in the current landscape of muscimol research. As a compound derived from the Amanita muscaria mushroom, which has psychoactive properties, muscimol faces stringent regulatory scrutiny. Navigating the complex regulatory framework for clinical trials and potential therapeutic applications presents a considerable obstacle for researchers and pharmaceutical companies.
Lastly, the limited understanding of muscimol's long-term effects on brain function and potential interactions with other medications poses another challenge. More extensive longitudinal studies are needed to elucidate the safety profile of muscimol, particularly in chronic use scenarios.
One of the primary obstacles in muscimol research is its limited bioavailability when administered orally. Muscimol, being a polar molecule, struggles to cross the blood-brain barrier efficiently, which restricts its therapeutic potential. This necessitates the exploration of alternative delivery methods or the development of novel formulations to enhance its bioavailability and efficacy.
Another challenge lies in the precise dosing of muscimol. Given its potent GABA-A receptor agonist properties, even slight variations in dosage can lead to significant differences in effects. This sensitivity makes it difficult to establish standardized dosing protocols across diverse patient populations and conditions, potentially limiting its clinical applicability.
The short half-life of muscimol presents another hurdle in its clinical application. The rapid metabolism and elimination of the compound from the body necessitate frequent dosing, which can be impractical for long-term treatments and may lead to compliance issues among patients. Developing sustained-release formulations or discovering ways to prolong muscimol's activity in the body remains a critical challenge.
Furthermore, the potential for side effects and adverse reactions poses a significant concern in muscimol research. As a GABA-A receptor agonist, muscimol can cause sedation, cognitive impairment, and motor incoordination. Balancing its therapeutic benefits with these potential side effects is crucial for its successful clinical application.
From a methodological standpoint, the lack of standardized protocols for muscimol administration and assessment of its effects complicates the comparison and interpretation of research findings across different studies. This inconsistency hampers the ability to draw robust conclusions and slows down the progress of muscimol research.
Regulatory challenges also play a significant role in the current landscape of muscimol research. As a compound derived from the Amanita muscaria mushroom, which has psychoactive properties, muscimol faces stringent regulatory scrutiny. Navigating the complex regulatory framework for clinical trials and potential therapeutic applications presents a considerable obstacle for researchers and pharmaceutical companies.
Lastly, the limited understanding of muscimol's long-term effects on brain function and potential interactions with other medications poses another challenge. More extensive longitudinal studies are needed to elucidate the safety profile of muscimol, particularly in chronic use scenarios.
Current Muscimol Research Methodologies
01 Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol
Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include different formulations and delivery methods to enhance the efficacy and bioavailability of muscimol. The compositions can be designed for treating neurological disorders, anxiety, or other conditions affected by GABA receptor modulation.- Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol: Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include formulations for treating neurological disorders, anxiety, or sleep-related issues. The compound is often combined with other active ingredients or delivery systems to enhance its efficacy and bioavailability.
- Muscimol as a GABA receptor agonist: Muscimol acts as a potent GABA receptor agonist, particularly at GABA-A receptors. This property makes it useful in research and potential therapeutic applications related to the GABAergic system, including the treatment of epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and other neurological conditions.
- Novel delivery methods for muscimol: Researchers are developing innovative delivery methods for muscimol to improve its therapeutic potential. These may include transdermal patches, nanoparticle formulations, or controlled-release systems designed to enhance the compound's bioavailability and reduce side effects.
- Muscimol in combination therapies: Muscimol is being studied in combination with other compounds for synergistic effects in treating various conditions. These combinations may target multiple pathways or receptors simultaneously, potentially leading to more effective treatments for complex disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases or psychiatric conditions.
- Muscimol analogues and derivatives: Research is ongoing to develop and study muscimol analogues and derivatives. These modified compounds aim to retain or enhance the beneficial properties of muscimol while potentially reducing unwanted side effects or improving pharmacokinetic profiles. Such analogues may offer new therapeutic opportunities in various fields of medicine.
02 Muscimol analogs and derivatives
Research focuses on developing and synthesizing muscimol analogs and derivatives. These modified compounds aim to improve upon the properties of muscimol, such as increased potency, selectivity, or reduced side effects. The analogs may be designed to target specific GABA receptor subtypes or to have improved pharmacokinetic profiles.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of muscimol in neurostimulation therapies
Muscimol is explored in combination with neurostimulation techniques for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders. This approach may involve the use of muscimol to enhance or modulate the effects of electrical or magnetic stimulation of the brain, potentially improving outcomes in conditions such as depression or epilepsy.Expand Specific Solutions04 Muscimol in combination therapies
Muscimol is investigated as part of combination therapies with other active compounds. These combinations may target multiple pathways or receptors simultaneously, potentially leading to synergistic effects in treating various disorders. The combinations could include other GABA modulators, antidepressants, or anxiolytics.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel delivery systems for muscimol
Innovative delivery systems are being developed to improve the administration and efficacy of muscimol. These may include nanoparticle formulations, transdermal patches, or controlled-release mechanisms. The goal is to enhance the bioavailability of muscimol, reduce dosing frequency, or target specific areas of the body or brain.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Institutions in Muscimol Studies
The trend analysis of muscimol in clinical research reveals a competitive landscape in an emerging field. The market is in its early growth stage, with increasing interest from both academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies. While the market size is still relatively small, it shows potential for significant expansion as research progresses. The technology is in the early stages of maturity, with key players like The University of Michigan, Dynavax Technologies, and Taisho Pharmaceutical leading research efforts. Companies such as Bayer HealthCare and Novartis AG are also exploring muscimol's potential, indicating growing industry interest. As the field develops, collaboration between academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies is likely to drive innovation and market growth.
The Regents of the University of Michigan
Technical Solution: The University of Michigan has been conducting groundbreaking research on muscimol's potential in treating neurological disorders. Their approach involves using advanced neuroimaging techniques to study the effects of muscimol on brain activity. They have developed novel methods for targeted delivery of muscimol to specific brain regions using nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems[12]. Their research has shown promising results in using muscimol for the treatment of tinnitus and certain types of chronic pain. The university has also been exploring the use of muscimol in combination with non-invasive brain stimulation techniques to enhance its therapeutic effects[13]. Additionally, they have conducted several pilot clinical studies investigating the potential of muscimol in treating sleep disorders and anxiety in patients with neurodegenerative diseases[14].
Strengths: Advanced neuroimaging techniques, innovative drug delivery methods, exploration of combination therapies with non-invasive brain stimulation. Weaknesses: Limited large-scale clinical trial experience, potential challenges in translating academic research to commercial applications.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis AG has been actively involved in the clinical research of muscimol and its derivatives. Their approach focuses on developing muscimol-based therapies for neurological disorders. They have conducted several phase II clinical trials exploring the use of muscimol in treating epilepsy and anxiety disorders[4]. Novartis has also invested in developing advanced drug delivery systems to enhance the bioavailability and targeted delivery of muscimol to the central nervous system. Their research has shown promising results in reducing seizure frequency in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy[5]. Additionally, Novartis has been exploring the potential of muscimol in combination therapies, particularly for treatment-resistant depression and post-traumatic stress disorder[6].
Strengths: Extensive clinical trial experience, advanced drug delivery systems, exploration of combination therapies. Weaknesses: High development costs, potential market competition from established anti-epileptic drugs.
Breakthrough Studies in Muscimol Research
Pharmaceutical intermediates and methods for preparing the same in the synthesis of muscimol and congeners and derivatives thereof
PatentWO2025128106A1
Innovation
- A novel method for preparing muscimol mono-BOC and muscimol hydrochloride that avoids the use of ion exchange chromatography by modifying the original synthetic route to include a flow reactor for the cyclization step and using BOC anhydride to purify the muscimol, thereby stabilizing the product and improving yields.
Mascarinic receptor antagonists
PatentInactiveIN1557DEL2006A
Innovation
- Development of novel muscarinic receptor antagonists with target organ selectivity, specifically compounds of Formula I and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, enantiomers, diastereomers, and polymorphs, which are synthesized using reaction sequences and administered to treat diseases mediated through muscarinic receptors.
Regulatory Framework for Muscimol Use
The regulatory framework for muscimol use in clinical research is complex and evolving, reflecting the compound's status as a psychoactive substance derived from mushrooms. Muscimol, primarily found in Amanita muscaria, is classified as a GABA receptor agonist with potential therapeutic applications. However, its regulatory status varies significantly across jurisdictions.
In the United States, muscimol is not specifically scheduled under the Controlled Substances Act, but it falls under the Federal Analogue Act due to its structural similarity to other controlled substances. This classification imposes strict controls on its research use, requiring extensive documentation and approval processes for clinical trials. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of muscimol in clinical research, mandating rigorous safety and efficacy studies before any potential therapeutic use can be approved.
European regulations on muscimol research are generally more permissive but still maintain strict oversight. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides guidelines for the conduct of clinical trials involving novel psychoactive substances, including muscimol. These guidelines emphasize the importance of comprehensive preclinical data and robust risk management strategies in clinical study designs.
In Japan, the Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has established specific protocols for researching compounds like muscimol, focusing on their potential applications in neurological disorders. The Japanese regulatory framework places a strong emphasis on long-term safety data and the development of precise dosing regimens.
International collaboration in muscimol research is governed by the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). The ICH guidelines provide a unified approach to the quality, safety, and efficacy aspects of clinical trials involving novel compounds like muscimol, facilitating cross-border research initiatives.
Recent trends in regulatory approaches to muscimol research include an increased focus on personalized medicine applications and the development of targeted delivery systems to minimize systemic effects. Regulatory bodies are also showing growing interest in the potential of muscimol as a treatment for neuropsychiatric disorders, leading to more streamlined approval processes for clinical trials in these areas.
As research into muscimol's therapeutic potential expands, regulatory frameworks are adapting to balance the need for scientific progress with patient safety concerns. This evolving landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for researchers and pharmaceutical companies interested in exploring muscimol's clinical applications.
In the United States, muscimol is not specifically scheduled under the Controlled Substances Act, but it falls under the Federal Analogue Act due to its structural similarity to other controlled substances. This classification imposes strict controls on its research use, requiring extensive documentation and approval processes for clinical trials. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of muscimol in clinical research, mandating rigorous safety and efficacy studies before any potential therapeutic use can be approved.
European regulations on muscimol research are generally more permissive but still maintain strict oversight. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides guidelines for the conduct of clinical trials involving novel psychoactive substances, including muscimol. These guidelines emphasize the importance of comprehensive preclinical data and robust risk management strategies in clinical study designs.
In Japan, the Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has established specific protocols for researching compounds like muscimol, focusing on their potential applications in neurological disorders. The Japanese regulatory framework places a strong emphasis on long-term safety data and the development of precise dosing regimens.
International collaboration in muscimol research is governed by the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). The ICH guidelines provide a unified approach to the quality, safety, and efficacy aspects of clinical trials involving novel compounds like muscimol, facilitating cross-border research initiatives.
Recent trends in regulatory approaches to muscimol research include an increased focus on personalized medicine applications and the development of targeted delivery systems to minimize systemic effects. Regulatory bodies are also showing growing interest in the potential of muscimol as a treatment for neuropsychiatric disorders, leading to more streamlined approval processes for clinical trials in these areas.
As research into muscimol's therapeutic potential expands, regulatory frameworks are adapting to balance the need for scientific progress with patient safety concerns. This evolving landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for researchers and pharmaceutical companies interested in exploring muscimol's clinical applications.
Ethical Considerations in Muscimol Research
The ethical considerations in muscimol research are paramount, given the compound's potent psychoactive effects and potential for misuse. As clinical trials involving muscimol expand, researchers must prioritize participant safety and well-being. This includes rigorous screening processes to exclude individuals with a history of substance abuse or mental health disorders that could be exacerbated by muscimol exposure.
Informed consent is a critical ethical requirement in muscimol studies. Participants must be fully aware of the potential risks and side effects associated with the compound, including its hallucinogenic properties and possible cognitive impairments. Researchers should provide clear, comprehensive information about the study's objectives, procedures, and potential outcomes, ensuring that participants can make an informed decision about their involvement.
The long-term effects of muscimol use are not yet fully understood, necessitating careful monitoring of participants during and after clinical trials. Follow-up assessments should be conducted to identify any delayed or persistent effects on cognitive function, mood, or behavior. Ethical protocols must include provisions for addressing adverse reactions and providing appropriate medical care if needed.
Privacy and confidentiality are crucial ethical considerations in muscimol research. Given the sensitive nature of psychoactive substance studies, researchers must implement robust data protection measures to safeguard participants' personal information and study results. This includes anonymizing data and restricting access to identifiable information.
The potential for muscimol to induce altered states of consciousness raises ethical questions about the validity of consent during the active phase of the compound's effects. Researchers must carefully consider the timing of any decision-making processes required of participants and ensure that they are not unduly influenced by the drug's psychoactive properties.
As muscimol research progresses, there is an ethical obligation to consider the broader societal implications of its potential therapeutic applications. This includes addressing concerns about addiction potential, off-label use, and the impact on public health policies. Researchers should engage with regulatory bodies, ethics committees, and community stakeholders to ensure that the development of muscimol-based therapies aligns with societal values and healthcare priorities.
Lastly, the ethical conduct of muscimol research demands transparency in reporting results, including negative findings or unexpected outcomes. This commitment to open science is essential for building trust within the scientific community and the public, and for advancing our understanding of muscimol's potential benefits and risks in clinical applications.
Informed consent is a critical ethical requirement in muscimol studies. Participants must be fully aware of the potential risks and side effects associated with the compound, including its hallucinogenic properties and possible cognitive impairments. Researchers should provide clear, comprehensive information about the study's objectives, procedures, and potential outcomes, ensuring that participants can make an informed decision about their involvement.
The long-term effects of muscimol use are not yet fully understood, necessitating careful monitoring of participants during and after clinical trials. Follow-up assessments should be conducted to identify any delayed or persistent effects on cognitive function, mood, or behavior. Ethical protocols must include provisions for addressing adverse reactions and providing appropriate medical care if needed.
Privacy and confidentiality are crucial ethical considerations in muscimol research. Given the sensitive nature of psychoactive substance studies, researchers must implement robust data protection measures to safeguard participants' personal information and study results. This includes anonymizing data and restricting access to identifiable information.
The potential for muscimol to induce altered states of consciousness raises ethical questions about the validity of consent during the active phase of the compound's effects. Researchers must carefully consider the timing of any decision-making processes required of participants and ensure that they are not unduly influenced by the drug's psychoactive properties.
As muscimol research progresses, there is an ethical obligation to consider the broader societal implications of its potential therapeutic applications. This includes addressing concerns about addiction potential, off-label use, and the impact on public health policies. Researchers should engage with regulatory bodies, ethics committees, and community stakeholders to ensure that the development of muscimol-based therapies aligns with societal values and healthcare priorities.
Lastly, the ethical conduct of muscimol research demands transparency in reporting results, including negative findings or unexpected outcomes. This commitment to open science is essential for building trust within the scientific community and the public, and for advancing our understanding of muscimol's potential benefits and risks in clinical applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!