Muscimol's Therapeutic Influence on Autoimmune Encephalopathies
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol Background and Objectives
Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has emerged as a promising therapeutic agent in the treatment of autoimmune encephalopathies. This class of neurological disorders, characterized by inflammation of the brain due to autoimmune responses, presents significant challenges in diagnosis and management. The exploration of muscimol's potential in this field marks a pivotal development in neuropharmacology and immunology.
The journey of muscimol from a naturally occurring psychoactive compound to a potential therapeutic agent spans several decades. Initially identified in the Amanita muscaria mushroom, muscimol's GABA-mimetic properties have long intrigued researchers. Recent advancements in understanding the role of GABAergic signaling in neuroinflammation and autoimmune processes have reignited interest in muscimol's therapeutic applications.
The primary objective of investigating muscimol in the context of autoimmune encephalopathies is to harness its potent GABA-A receptor activation properties to modulate neuroinflammation and autoimmune responses. This approach aims to address the limitations of current treatments, which often rely heavily on broad-spectrum immunosuppression with significant side effects.
Autoimmune encephalopathies encompass a diverse group of disorders, including anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis, limbic encephalitis, and Hashimoto's encephalopathy. These conditions share common features of cognitive dysfunction, seizures, and psychiatric symptoms, often resulting from antibody-mediated attacks on neuronal structures. The complexity and heterogeneity of these disorders underscore the need for novel, targeted therapeutic approaches.
Muscimol's potential in this field stems from its ability to enhance inhibitory neurotransmission through GABA-A receptor activation. This mechanism is hypothesized to counteract the excitotoxicity and neuronal hyperactivity often observed in autoimmune encephalopathies. Additionally, emerging evidence suggests that GABAergic signaling plays a crucial role in modulating immune responses, offering a dual mechanism of action for muscimol in treating these disorders.
The technological evolution in drug delivery systems and the growing understanding of the blood-brain barrier present new opportunities for optimizing muscimol's therapeutic efficacy. Innovations in nanoparticle-based delivery and targeted drug release systems are being explored to enhance muscimol's bioavailability and specificity in the central nervous system.
As research progresses, the objectives extend beyond symptom management to exploring muscimol's potential in halting disease progression and promoting neuronal repair. This ambitious goal aligns with the broader trend in neurology towards developing disease-modifying therapies for autoimmune and neurodegenerative disorders.
The journey of muscimol from a naturally occurring psychoactive compound to a potential therapeutic agent spans several decades. Initially identified in the Amanita muscaria mushroom, muscimol's GABA-mimetic properties have long intrigued researchers. Recent advancements in understanding the role of GABAergic signaling in neuroinflammation and autoimmune processes have reignited interest in muscimol's therapeutic applications.
The primary objective of investigating muscimol in the context of autoimmune encephalopathies is to harness its potent GABA-A receptor activation properties to modulate neuroinflammation and autoimmune responses. This approach aims to address the limitations of current treatments, which often rely heavily on broad-spectrum immunosuppression with significant side effects.
Autoimmune encephalopathies encompass a diverse group of disorders, including anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis, limbic encephalitis, and Hashimoto's encephalopathy. These conditions share common features of cognitive dysfunction, seizures, and psychiatric symptoms, often resulting from antibody-mediated attacks on neuronal structures. The complexity and heterogeneity of these disorders underscore the need for novel, targeted therapeutic approaches.
Muscimol's potential in this field stems from its ability to enhance inhibitory neurotransmission through GABA-A receptor activation. This mechanism is hypothesized to counteract the excitotoxicity and neuronal hyperactivity often observed in autoimmune encephalopathies. Additionally, emerging evidence suggests that GABAergic signaling plays a crucial role in modulating immune responses, offering a dual mechanism of action for muscimol in treating these disorders.
The technological evolution in drug delivery systems and the growing understanding of the blood-brain barrier present new opportunities for optimizing muscimol's therapeutic efficacy. Innovations in nanoparticle-based delivery and targeted drug release systems are being explored to enhance muscimol's bioavailability and specificity in the central nervous system.
As research progresses, the objectives extend beyond symptom management to exploring muscimol's potential in halting disease progression and promoting neuronal repair. This ambitious goal aligns with the broader trend in neurology towards developing disease-modifying therapies for autoimmune and neurodegenerative disorders.
Market Analysis for Autoimmune Encephalopathy Treatments
The market for autoimmune encephalopathy treatments is experiencing significant growth due to increasing awareness, improved diagnostic techniques, and a rising prevalence of autoimmune disorders. Autoimmune encephalopathies, including conditions like anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis and limbic encephalitis, represent a subset of neurological disorders with substantial unmet medical needs.
The global market for autoimmune encephalopathy treatments is primarily driven by the pharmaceutical sector, with a focus on immunomodulatory therapies and symptomatic management. Current treatment options include corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), plasma exchange, and various immunosuppressants. However, these treatments often have limited efficacy and significant side effects, creating a demand for novel, targeted therapies.
Market growth is further propelled by ongoing research into the pathophysiology of autoimmune encephalopathies, leading to the development of more specific and effective treatments. The potential of Muscimol as a therapeutic agent for these conditions represents an exciting avenue for market expansion, as it offers a unique mechanism of action that could address some of the limitations of current therapies.
Key market players in this space include large pharmaceutical companies with established neurology portfolios, as well as smaller biotechnology firms focusing on innovative approaches to autoimmune disorders. The market is characterized by a high level of research and development activity, with numerous clinical trials exploring novel treatment modalities.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the market due to advanced healthcare infrastructure, higher diagnosis rates, and greater access to specialized care. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show rapid growth as awareness increases and healthcare systems improve.
The market for autoimmune encephalopathy treatments faces challenges such as the rarity of these conditions, which can limit patient populations for clinical trials and commercial viability. Additionally, the complexity of diagnosing these disorders and the need for long-term management contribute to the overall market dynamics.
Despite these challenges, the market outlook remains positive. The potential for personalized medicine approaches, coupled with advancements in biomarker discovery and diagnostic technologies, is expected to drive market growth. The introduction of novel therapies like Muscimol could potentially reshape the treatment landscape, offering new hope for patients and creating significant market opportunities for innovative pharmaceutical companies.
The global market for autoimmune encephalopathy treatments is primarily driven by the pharmaceutical sector, with a focus on immunomodulatory therapies and symptomatic management. Current treatment options include corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), plasma exchange, and various immunosuppressants. However, these treatments often have limited efficacy and significant side effects, creating a demand for novel, targeted therapies.
Market growth is further propelled by ongoing research into the pathophysiology of autoimmune encephalopathies, leading to the development of more specific and effective treatments. The potential of Muscimol as a therapeutic agent for these conditions represents an exciting avenue for market expansion, as it offers a unique mechanism of action that could address some of the limitations of current therapies.
Key market players in this space include large pharmaceutical companies with established neurology portfolios, as well as smaller biotechnology firms focusing on innovative approaches to autoimmune disorders. The market is characterized by a high level of research and development activity, with numerous clinical trials exploring novel treatment modalities.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the market due to advanced healthcare infrastructure, higher diagnosis rates, and greater access to specialized care. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show rapid growth as awareness increases and healthcare systems improve.
The market for autoimmune encephalopathy treatments faces challenges such as the rarity of these conditions, which can limit patient populations for clinical trials and commercial viability. Additionally, the complexity of diagnosing these disorders and the need for long-term management contribute to the overall market dynamics.
Despite these challenges, the market outlook remains positive. The potential for personalized medicine approaches, coupled with advancements in biomarker discovery and diagnostic technologies, is expected to drive market growth. The introduction of novel therapies like Muscimol could potentially reshape the treatment landscape, offering new hope for patients and creating significant market opportunities for innovative pharmaceutical companies.
Current Challenges in Muscimol Research
Despite the promising potential of muscimol in treating autoimmune encephalopathies, several significant challenges currently hinder its research and clinical application. One of the primary obstacles is the limited understanding of muscimol's precise mechanisms of action in the context of autoimmune encephalopathies. While its GABA-A receptor agonist properties are well-established, the intricate interplay between GABAergic modulation and autoimmune processes in the brain remains unclear.
Another major challenge lies in the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of muscimol. Its short half-life and rapid metabolism in the body pose difficulties in maintaining therapeutic concentrations over extended periods. This necessitates frequent dosing or advanced drug delivery systems, which can complicate treatment regimens and patient compliance.
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) presents a formidable obstacle in muscimol research. Ensuring sufficient penetration of the compound into the central nervous system while minimizing systemic effects is crucial for effective treatment of autoimmune encephalopathies. Developing strategies to enhance BBB permeability or utilizing targeted delivery methods remains an active area of investigation.
Safety concerns also pose significant challenges in muscimol research. As a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, muscimol can induce sedation, cognitive impairment, and other CNS-related side effects. Striking a balance between therapeutic efficacy and acceptable safety profiles is essential for its clinical application in autoimmune encephalopathies.
The heterogeneity of autoimmune encephalopathies further complicates muscimol research. Different subtypes of the disease may respond variably to GABAergic modulation, necessitating a more nuanced approach to treatment strategies. Identifying biomarkers or patient subgroups that are most likely to benefit from muscimol therapy remains a critical challenge.
Regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials also impede the progress of muscimol research. As a compound with psychoactive properties, muscimol faces stringent regulatory scrutiny, requiring robust evidence of safety and efficacy before approval for clinical use in autoimmune encephalopathies.
Lastly, funding and resource allocation for muscimol research in the context of autoimmune encephalopathies present ongoing challenges. Competing priorities in neuroscience research and the relatively niche nature of this application may limit the availability of resources for comprehensive studies and clinical trials.
Another major challenge lies in the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of muscimol. Its short half-life and rapid metabolism in the body pose difficulties in maintaining therapeutic concentrations over extended periods. This necessitates frequent dosing or advanced drug delivery systems, which can complicate treatment regimens and patient compliance.
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) presents a formidable obstacle in muscimol research. Ensuring sufficient penetration of the compound into the central nervous system while minimizing systemic effects is crucial for effective treatment of autoimmune encephalopathies. Developing strategies to enhance BBB permeability or utilizing targeted delivery methods remains an active area of investigation.
Safety concerns also pose significant challenges in muscimol research. As a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, muscimol can induce sedation, cognitive impairment, and other CNS-related side effects. Striking a balance between therapeutic efficacy and acceptable safety profiles is essential for its clinical application in autoimmune encephalopathies.
The heterogeneity of autoimmune encephalopathies further complicates muscimol research. Different subtypes of the disease may respond variably to GABAergic modulation, necessitating a more nuanced approach to treatment strategies. Identifying biomarkers or patient subgroups that are most likely to benefit from muscimol therapy remains a critical challenge.
Regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials also impede the progress of muscimol research. As a compound with psychoactive properties, muscimol faces stringent regulatory scrutiny, requiring robust evidence of safety and efficacy before approval for clinical use in autoimmune encephalopathies.
Lastly, funding and resource allocation for muscimol research in the context of autoimmune encephalopathies present ongoing challenges. Competing priorities in neuroscience research and the relatively niche nature of this application may limit the availability of resources for comprehensive studies and clinical trials.
Current Muscimol Therapeutic Approaches
01 Muscimol as a therapeutic agent for neurological disorders
Muscimol, a GABA receptor agonist, shows potential in treating various neurological disorders. Its ability to modulate neurotransmitter activity makes it a promising candidate for conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety, and sleep disorders. Research indicates that controlled administration of muscimol may help alleviate symptoms and improve patient outcomes in these areas.- Muscimol as a therapeutic agent for neurological disorders: Muscimol, a GABA receptor agonist, shows potential in treating various neurological disorders. Its ability to modulate neurotransmitter activity makes it a promising candidate for conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety, and sleep disorders. Research indicates that muscimol's therapeutic effects may be due to its inhibitory action on overactive neural circuits.
- Muscimol in pain management: Studies suggest that muscimol may have analgesic properties, making it potentially useful in pain management. Its mechanism of action involves modulating pain signals in the central nervous system. This could lead to new therapeutic approaches for chronic pain conditions, potentially offering an alternative to traditional pain medications.
- Muscimol's influence on cognitive function: Research explores muscimol's effects on cognitive processes, including memory and learning. While high doses may impair cognitive function, controlled administration shows potential benefits in certain cognitive disorders. Studies investigate its role in enhancing neuroplasticity and potentially aiding in cognitive rehabilitation therapies.
- Muscimol in addiction treatment: Emerging research examines muscimol's potential in treating addiction disorders. Its ability to modulate GABA receptors may help in reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms associated with substance abuse. Studies are exploring its use in combination with other therapies for more effective addiction treatment protocols.
- Muscimol's neuroprotective properties: Investigations into muscimol's neuroprotective effects show promise for treating neurodegenerative diseases. Its ability to reduce excitotoxicity and oxidative stress in neural tissues may help slow the progression of conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Research focuses on optimizing delivery methods and dosages for maximum neuroprotective benefits.
02 Muscimol's impact on cognitive function and memory
Studies suggest that muscimol may have both positive and negative effects on cognitive function and memory, depending on dosage and administration method. While it can potentially enhance certain aspects of memory formation, high doses may lead to temporary cognitive impairment. Ongoing research aims to optimize its use for cognitive enhancement while minimizing adverse effects.Expand Specific Solutions03 Muscimol in pain management and anesthesia
Muscimol's analgesic properties make it a subject of interest in pain management research. Its ability to modulate pain perception through GABA receptor activation suggests potential applications in both acute and chronic pain conditions. Additionally, some studies explore its use as an adjunct in anesthesia protocols to enhance pain control and reduce opioid requirements.Expand Specific Solutions04 Muscimol's role in addiction treatment
Research indicates that muscimol may have therapeutic potential in addiction treatment. Its ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems involved in reward and craving behaviors suggests possible applications in managing substance use disorders. Studies are exploring its efficacy in reducing drug-seeking behavior and preventing relapse in various addiction models.Expand Specific Solutions05 Muscimol's influence on mood disorders and psychiatric conditions
Emerging evidence suggests that muscimol may have therapeutic effects in mood disorders and certain psychiatric conditions. Its action on GABA receptors could potentially modulate neurotransmitter imbalances associated with depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders. Ongoing research aims to elucidate its mechanisms of action and optimize its use in psychiatric treatment protocols.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Muscimol Research
The therapeutic potential of muscimol in autoimmune encephalopathies represents an emerging field with growing interest from both academic and pharmaceutical sectors. The market is in its early stages, with research primarily conducted by universities and research institutions like Johns Hopkins University and The Regents of the University of California. Pharmaceutical companies such as ACADIA Pharmaceuticals, Janssen Pharmaceutica, and Merck & Co. are exploring this area, indicating its potential for future growth. The technology is still in the preclinical or early clinical stages, with companies like Compugen Ltd. and Suven Life Sciences Ltd. contributing to the development of novel therapeutic approaches. As the field progresses, collaborations between academia and industry are likely to accelerate the translation of research findings into potential treatments.
ACADIA Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Technical Solution: ACADIA Pharmaceuticals has been exploring the potential of muscimol, a GABA-A receptor agonist, in treating autoimmune encephalopathies. Their approach involves developing a proprietary formulation of muscimol that can cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively. This formulation is designed to modulate GABAergic signaling in the central nervous system, potentially reducing neuroinflammation and autoimmune responses in the brain[1]. The company has conducted preclinical studies demonstrating that their muscimol formulation can reduce inflammatory markers and improve cognitive function in animal models of autoimmune encephalopathy[3]. ACADIA is currently in the early stages of clinical trials to assess the safety and efficacy of this treatment in humans with autoimmune encephalopathies[5].
Strengths: Innovative drug delivery system for improved brain penetration, strong preclinical data supporting efficacy. Weaknesses: Early stage of clinical development, potential for off-target effects due to widespread GABA-A receptor distribution.
Janssen Pharmaceutica NV
Technical Solution: Janssen Pharmaceutica has been investigating the use of muscimol as a potential treatment for autoimmune encephalopathies through its immunomodulatory effects. Their approach focuses on developing a long-acting muscimol analog that can provide sustained activation of GABA-A receptors in the central nervous system. This sustained activation is hypothesized to dampen excessive immune responses and reduce neuroinflammation in autoimmune encephalopathies[2]. Janssen's research has shown that their muscimol analog can reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and promote the differentiation of regulatory T cells in preclinical models[4]. The company is currently optimizing the pharmacokinetic profile of their compound to ensure an appropriate balance between efficacy and safety[6].
Strengths: Expertise in drug development and clinical trials, focus on long-acting formulations for improved patient compliance. Weaknesses: Potential for developing tolerance to long-term GABA-A receptor activation, need for extensive safety studies due to novel analog.
Key Muscimol Mechanisms in Autoimmune Encephalopathies
Treatment of diseases by expression of an enzyme which has a deoxyribonuclease (DNASE) activity
PatentWO2021011365A1
Innovation
- A recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) expression vector with a liver-specific, nervous system-specific, or intestine-specific promoter is used to deliver a deoxyribonuclease (DNase) enzyme, enhancing its expression in these tissues to clear cfDNA.
Treatment of macrophage-related disorders
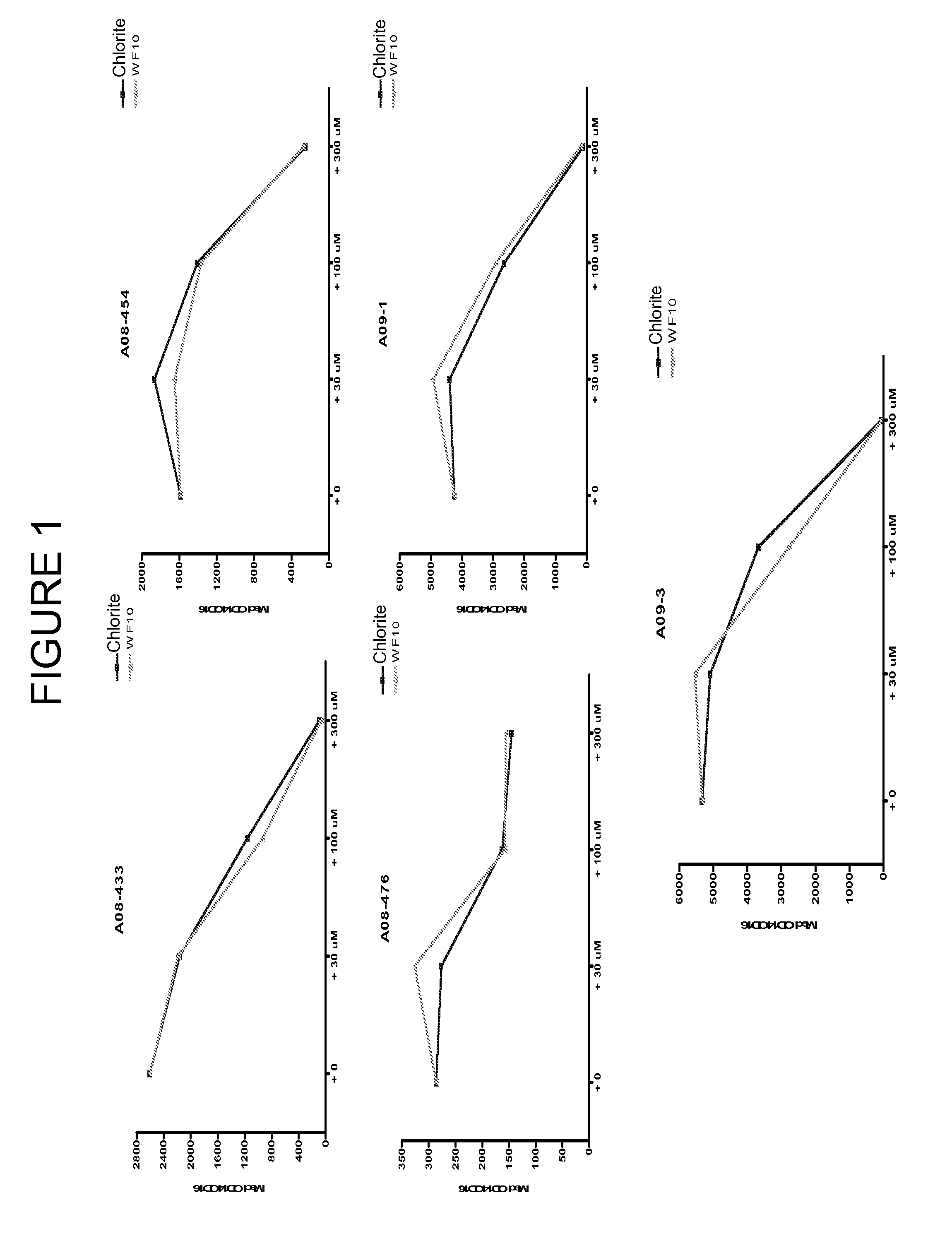
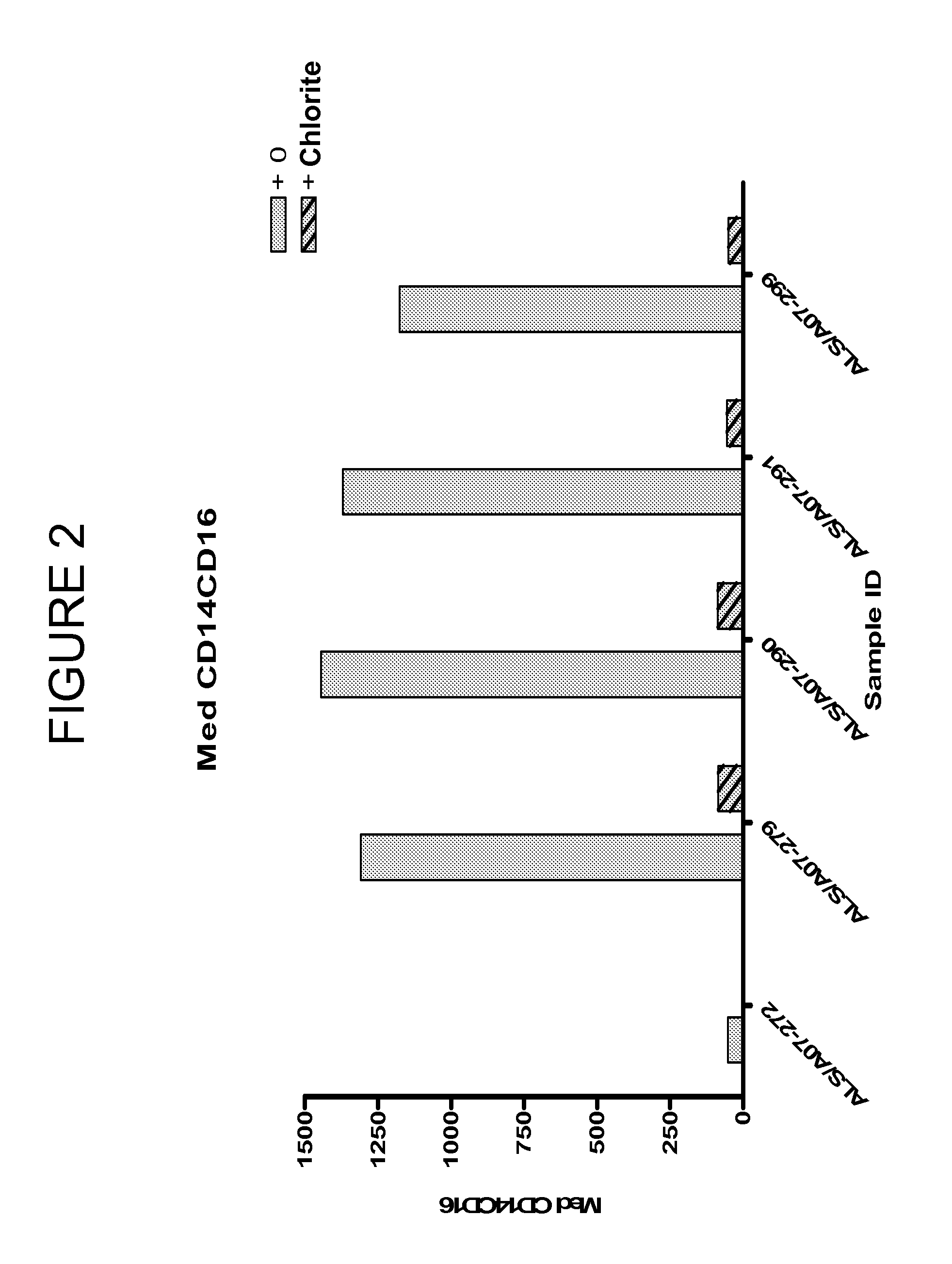
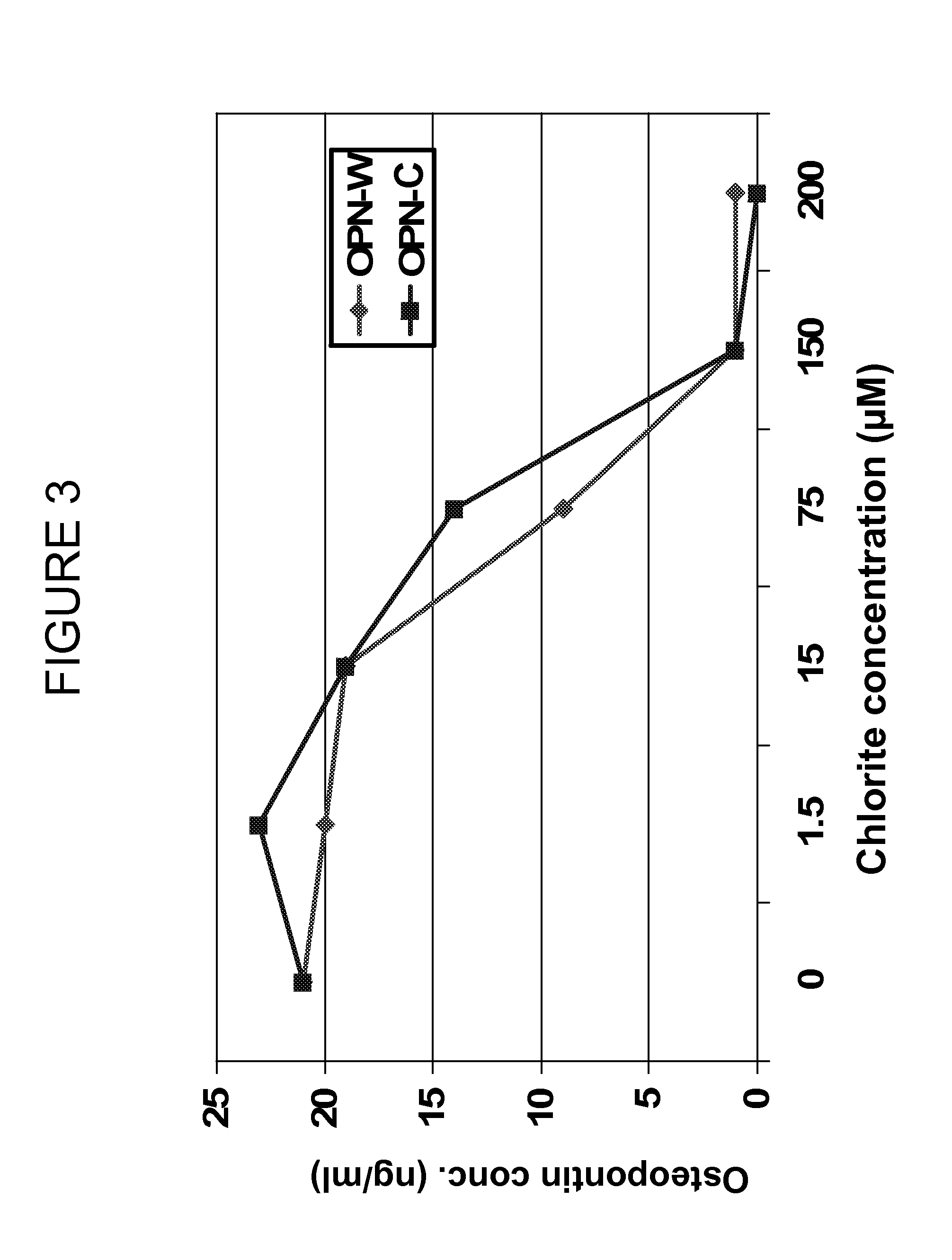
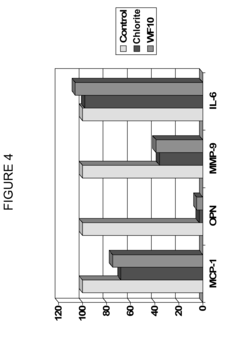
PatentInactiveUS20120134929A1
Innovation
- Administration of pharmaceutical compositions containing oxidative agents like chlorite, pH adjusting agents, and pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, or immunomodulatory agents to treat macrophage-related diseases by modulating macrophage activation or accumulation.
Regulatory Landscape for Muscimol-Based Therapies
The regulatory landscape for muscimol-based therapies is complex and evolving, reflecting the unique challenges associated with developing treatments for autoimmune encephalopathies. As a GABA receptor agonist, muscimol falls under the purview of several regulatory bodies, primarily the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe.
In the United States, muscimol-based therapies would likely be classified as new molecular entities (NMEs) and subject to the rigorous approval process outlined in the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. This process includes extensive preclinical studies, Investigational New Drug (IND) application, and multiple phases of clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy. Given the potential neurological effects of muscimol, additional scrutiny may be applied to assess long-term safety and potential for abuse.
The FDA's Orphan Drug Designation program may be applicable for muscimol-based therapies targeting rare autoimmune encephalopathies, potentially offering incentives such as tax credits for clinical research and extended market exclusivity. However, this designation would require demonstrating that the condition affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States.
In Europe, the EMA's regulatory framework for novel therapies includes similar requirements for clinical trials and safety assessments. The agency's Priority Medicines (PRIME) scheme could potentially accelerate the development of muscimol-based therapies if they demonstrate the potential to address unmet medical needs in autoimmune encephalopathies.
Both the FDA and EMA have established guidelines for the development of drugs targeting central nervous system disorders, which would be applicable to muscimol-based therapies. These guidelines emphasize the need for robust pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies, as well as careful assessment of potential cognitive and behavioral effects.
Regulatory considerations also extend to manufacturing processes and quality control. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations would apply to the production of muscimol-based therapies, ensuring consistent quality and purity of the final product. Given muscimol's psychoactive properties, additional controls may be necessary to prevent diversion and misuse.
As research progresses, regulatory agencies may need to develop specific guidance for muscimol and related compounds, particularly if their therapeutic potential in autoimmune encephalopathies is substantiated. This could involve the creation of new regulatory pathways or the adaptation of existing frameworks to address the unique characteristics of these therapies.
In the United States, muscimol-based therapies would likely be classified as new molecular entities (NMEs) and subject to the rigorous approval process outlined in the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. This process includes extensive preclinical studies, Investigational New Drug (IND) application, and multiple phases of clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy. Given the potential neurological effects of muscimol, additional scrutiny may be applied to assess long-term safety and potential for abuse.
The FDA's Orphan Drug Designation program may be applicable for muscimol-based therapies targeting rare autoimmune encephalopathies, potentially offering incentives such as tax credits for clinical research and extended market exclusivity. However, this designation would require demonstrating that the condition affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States.
In Europe, the EMA's regulatory framework for novel therapies includes similar requirements for clinical trials and safety assessments. The agency's Priority Medicines (PRIME) scheme could potentially accelerate the development of muscimol-based therapies if they demonstrate the potential to address unmet medical needs in autoimmune encephalopathies.
Both the FDA and EMA have established guidelines for the development of drugs targeting central nervous system disorders, which would be applicable to muscimol-based therapies. These guidelines emphasize the need for robust pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies, as well as careful assessment of potential cognitive and behavioral effects.
Regulatory considerations also extend to manufacturing processes and quality control. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations would apply to the production of muscimol-based therapies, ensuring consistent quality and purity of the final product. Given muscimol's psychoactive properties, additional controls may be necessary to prevent diversion and misuse.
As research progresses, regulatory agencies may need to develop specific guidance for muscimol and related compounds, particularly if their therapeutic potential in autoimmune encephalopathies is substantiated. This could involve the creation of new regulatory pathways or the adaptation of existing frameworks to address the unique characteristics of these therapies.
Safety and Toxicology Profile of Muscimol
The safety and toxicology profile of muscimol is a critical aspect to consider when evaluating its potential therapeutic use in autoimmune encephalopathies. Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has been the subject of extensive research to determine its safety parameters and potential adverse effects.
Acute toxicity studies in animal models have shown that muscimol has a relatively low toxicity profile when administered in controlled doses. The LD50 (median lethal dose) for muscimol in mice is reported to be around 3.8 mg/kg when administered intraperitoneally, indicating a moderate level of acute toxicity. However, it is important to note that the therapeutic window for muscimol is relatively narrow, necessitating careful dosage control in clinical applications.
Chronic toxicity studies have revealed that prolonged exposure to muscimol can lead to tolerance and dependence, similar to other GABA-A receptor agonists. This highlights the need for careful monitoring and potential dose adjustments in long-term treatment regimens. Additionally, withdrawal symptoms have been observed in animal studies following abrupt discontinuation of muscimol administration, suggesting the importance of gradual tapering when ceasing treatment.
Neurotoxicity is a primary concern with muscimol due to its potent effects on the central nervous system. While therapeutic doses are generally well-tolerated, excessive activation of GABA-A receptors can lead to sedation, cognitive impairment, and in severe cases, respiratory depression. Preclinical studies have shown that muscimol can induce neuronal cell death at high concentrations, emphasizing the importance of maintaining appropriate dosage levels.
Pharmacokinetic studies have demonstrated that muscimol readily crosses the blood-brain barrier, allowing for efficient central nervous system penetration. This property, while beneficial for its therapeutic effects, also contributes to its potential for adverse neurological effects. The half-life of muscimol in humans is relatively short, typically ranging from 1 to 3 hours, which may necessitate frequent dosing to maintain therapeutic levels.
Reproductive toxicity studies in animal models have shown mixed results. While some studies have reported no significant teratogenic effects, others have suggested potential risks during pregnancy. As a result, the use of muscimol in pregnant women or those of childbearing age should be approached with caution, and further research is needed to fully elucidate its effects on fetal development.
Drug interaction studies have revealed that muscimol can potentiate the effects of other CNS depressants, including alcohol and benzodiazepines. This synergistic effect increases the risk of excessive sedation and respiratory depression, highlighting the need for careful consideration of concomitant medications in patients receiving muscimol-based therapies.
In conclusion, while muscimol shows promise as a therapeutic agent for autoimmune encephalopathies, its safety and toxicology profile underscores the need for careful dosing, monitoring, and patient selection. Further clinical studies are warranted to fully characterize its long-term safety profile and optimize its therapeutic potential while minimizing adverse effects.
Acute toxicity studies in animal models have shown that muscimol has a relatively low toxicity profile when administered in controlled doses. The LD50 (median lethal dose) for muscimol in mice is reported to be around 3.8 mg/kg when administered intraperitoneally, indicating a moderate level of acute toxicity. However, it is important to note that the therapeutic window for muscimol is relatively narrow, necessitating careful dosage control in clinical applications.
Chronic toxicity studies have revealed that prolonged exposure to muscimol can lead to tolerance and dependence, similar to other GABA-A receptor agonists. This highlights the need for careful monitoring and potential dose adjustments in long-term treatment regimens. Additionally, withdrawal symptoms have been observed in animal studies following abrupt discontinuation of muscimol administration, suggesting the importance of gradual tapering when ceasing treatment.
Neurotoxicity is a primary concern with muscimol due to its potent effects on the central nervous system. While therapeutic doses are generally well-tolerated, excessive activation of GABA-A receptors can lead to sedation, cognitive impairment, and in severe cases, respiratory depression. Preclinical studies have shown that muscimol can induce neuronal cell death at high concentrations, emphasizing the importance of maintaining appropriate dosage levels.
Pharmacokinetic studies have demonstrated that muscimol readily crosses the blood-brain barrier, allowing for efficient central nervous system penetration. This property, while beneficial for its therapeutic effects, also contributes to its potential for adverse neurological effects. The half-life of muscimol in humans is relatively short, typically ranging from 1 to 3 hours, which may necessitate frequent dosing to maintain therapeutic levels.
Reproductive toxicity studies in animal models have shown mixed results. While some studies have reported no significant teratogenic effects, others have suggested potential risks during pregnancy. As a result, the use of muscimol in pregnant women or those of childbearing age should be approached with caution, and further research is needed to fully elucidate its effects on fetal development.
Drug interaction studies have revealed that muscimol can potentiate the effects of other CNS depressants, including alcohol and benzodiazepines. This synergistic effect increases the risk of excessive sedation and respiratory depression, highlighting the need for careful consideration of concomitant medications in patients receiving muscimol-based therapies.
In conclusion, while muscimol shows promise as a therapeutic agent for autoimmune encephalopathies, its safety and toxicology profile underscores the need for careful dosing, monitoring, and patient selection. Further clinical studies are warranted to fully characterize its long-term safety profile and optimize its therapeutic potential while minimizing adverse effects.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!