Traditional Usage of Muscimol in Indigenous Cultures
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol History and Research Objectives
Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in various species of mushrooms, particularly those belonging to the Amanita genus, has a rich history of traditional use in indigenous cultures spanning thousands of years. The exploration of muscimol's history and its research objectives provides a fascinating glimpse into the intersection of ethnobotany, neuroscience, and cultural practices.
The use of muscimol-containing mushrooms can be traced back to ancient shamanic practices in Siberia and other parts of Northern Europe. These cultures, particularly the Koryak people of Kamchatka, have long utilized Amanita muscaria mushrooms in religious and medicinal contexts. The mushrooms were often dried and consumed directly or used to create psychoactive beverages, playing a crucial role in spiritual ceremonies and healing rituals.
As Western explorers and researchers encountered these practices, interest in muscimol and its effects on the human mind and body began to grow. The 20th century saw a surge in scientific curiosity about the compound, with researchers seeking to understand its chemical structure, pharmacological properties, and potential therapeutic applications.
The primary research objectives surrounding muscimol have evolved significantly over time. Initially, studies focused on identifying and isolating the active compounds in Amanita mushrooms. This led to the discovery of muscimol and its precursor, ibotenic acid, in the 1960s. Subsequent research aimed to elucidate the mechanism of action of muscimol in the brain, revealing its role as a potent GABA receptor agonist.
In recent decades, research objectives have expanded to explore the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol. Scientists are investigating its use in treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders, including epilepsy, anxiety, and sleep disorders. Additionally, there is growing interest in understanding the neuroprotective properties of muscimol and its potential role in combating neurodegenerative diseases.
Another key research objective is to develop safer and more controlled methods of administering muscimol. This includes exploring synthetic analogues and novel delivery systems that could harness the compound's beneficial effects while minimizing risks associated with traditional consumption methods.
Furthermore, researchers are increasingly focusing on the cultural and anthropological aspects of muscimol use. This includes documenting and preserving traditional knowledge about Amanita mushrooms and their applications in indigenous medicine. Such studies aim to bridge the gap between traditional wisdom and modern scientific understanding, potentially uncovering valuable insights for future medical applications.
As we move forward, the research objectives surrounding muscimol continue to evolve. There is a growing emphasis on interdisciplinary approaches, combining insights from neuroscience, pharmacology, anthropology, and indigenous knowledge systems. This holistic approach aims to fully unlock the potential of this fascinating compound while respecting its cultural significance and traditional uses.
The use of muscimol-containing mushrooms can be traced back to ancient shamanic practices in Siberia and other parts of Northern Europe. These cultures, particularly the Koryak people of Kamchatka, have long utilized Amanita muscaria mushrooms in religious and medicinal contexts. The mushrooms were often dried and consumed directly or used to create psychoactive beverages, playing a crucial role in spiritual ceremonies and healing rituals.
As Western explorers and researchers encountered these practices, interest in muscimol and its effects on the human mind and body began to grow. The 20th century saw a surge in scientific curiosity about the compound, with researchers seeking to understand its chemical structure, pharmacological properties, and potential therapeutic applications.
The primary research objectives surrounding muscimol have evolved significantly over time. Initially, studies focused on identifying and isolating the active compounds in Amanita mushrooms. This led to the discovery of muscimol and its precursor, ibotenic acid, in the 1960s. Subsequent research aimed to elucidate the mechanism of action of muscimol in the brain, revealing its role as a potent GABA receptor agonist.
In recent decades, research objectives have expanded to explore the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol. Scientists are investigating its use in treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders, including epilepsy, anxiety, and sleep disorders. Additionally, there is growing interest in understanding the neuroprotective properties of muscimol and its potential role in combating neurodegenerative diseases.
Another key research objective is to develop safer and more controlled methods of administering muscimol. This includes exploring synthetic analogues and novel delivery systems that could harness the compound's beneficial effects while minimizing risks associated with traditional consumption methods.
Furthermore, researchers are increasingly focusing on the cultural and anthropological aspects of muscimol use. This includes documenting and preserving traditional knowledge about Amanita mushrooms and their applications in indigenous medicine. Such studies aim to bridge the gap between traditional wisdom and modern scientific understanding, potentially uncovering valuable insights for future medical applications.
As we move forward, the research objectives surrounding muscimol continue to evolve. There is a growing emphasis on interdisciplinary approaches, combining insights from neuroscience, pharmacology, anthropology, and indigenous knowledge systems. This holistic approach aims to fully unlock the potential of this fascinating compound while respecting its cultural significance and traditional uses.
Ethnobotanical Market Analysis
The ethnobotanical market for muscimol-containing plants, particularly Amanita muscaria mushrooms, has shown significant growth in recent years. This trend is driven by increasing interest in traditional indigenous practices and the exploration of alternative natural remedies. The global market for ethnobotanical products is estimated to reach several billion dollars annually, with muscimol-containing products representing a small but growing segment.
Demand for muscimol-related products stems from various sectors, including alternative medicine, spiritual practices, and research institutions. Traditional indigenous communities have long used Amanita muscaria for ceremonial and medicinal purposes, creating a niche market for authentic, sustainably sourced products. This has led to the development of specialized suppliers and distributors catering to this demand.
The market for muscimol-containing products faces several challenges, including regulatory restrictions in many countries due to the psychoactive properties of muscimol. This has resulted in a fragmented market landscape, with varying levels of legality and accessibility across different regions. Despite these challenges, there is a growing consumer base seeking natural alternatives to conventional pharmaceuticals, driving demand for muscimol-derived products.
In recent years, there has been an increase in research and development activities focused on muscimol and its potential applications. This has led to the emergence of new product categories, such as muscimol-based supplements and extracts, which are marketed for their potential cognitive and mood-enhancing effects. The expanding body of scientific literature on muscimol's pharmacological properties has also contributed to growing consumer awareness and interest.
The supply chain for muscimol-containing products remains largely informal, with many suppliers operating in gray markets or relying on wild-harvested sources. This presents both opportunities and challenges for market growth, as there is potential for the development of more formalized and sustainable supply chains. Some companies have begun exploring cultivation methods for Amanita muscaria and other muscimol-rich species to meet increasing demand while ensuring product consistency and quality.
Market trends indicate a shift towards more refined and standardized muscimol products, moving away from raw plant materials. This evolution is driven by consumer demand for safer, more reliable dosing options and the need to comply with evolving regulatory frameworks. As a result, there is growing investment in extraction technologies and quality control measures within the industry.
The future growth potential of the muscimol market is closely tied to ongoing research into its therapeutic applications and the development of novel delivery methods. As scientific understanding of muscimol's effects on the human body expands, new market opportunities are likely to emerge, potentially leading to the development of pharmaceutical-grade products and expanding the overall market size.
Demand for muscimol-related products stems from various sectors, including alternative medicine, spiritual practices, and research institutions. Traditional indigenous communities have long used Amanita muscaria for ceremonial and medicinal purposes, creating a niche market for authentic, sustainably sourced products. This has led to the development of specialized suppliers and distributors catering to this demand.
The market for muscimol-containing products faces several challenges, including regulatory restrictions in many countries due to the psychoactive properties of muscimol. This has resulted in a fragmented market landscape, with varying levels of legality and accessibility across different regions. Despite these challenges, there is a growing consumer base seeking natural alternatives to conventional pharmaceuticals, driving demand for muscimol-derived products.
In recent years, there has been an increase in research and development activities focused on muscimol and its potential applications. This has led to the emergence of new product categories, such as muscimol-based supplements and extracts, which are marketed for their potential cognitive and mood-enhancing effects. The expanding body of scientific literature on muscimol's pharmacological properties has also contributed to growing consumer awareness and interest.
The supply chain for muscimol-containing products remains largely informal, with many suppliers operating in gray markets or relying on wild-harvested sources. This presents both opportunities and challenges for market growth, as there is potential for the development of more formalized and sustainable supply chains. Some companies have begun exploring cultivation methods for Amanita muscaria and other muscimol-rich species to meet increasing demand while ensuring product consistency and quality.
Market trends indicate a shift towards more refined and standardized muscimol products, moving away from raw plant materials. This evolution is driven by consumer demand for safer, more reliable dosing options and the need to comply with evolving regulatory frameworks. As a result, there is growing investment in extraction technologies and quality control measures within the industry.
The future growth potential of the muscimol market is closely tied to ongoing research into its therapeutic applications and the development of novel delivery methods. As scientific understanding of muscimol's effects on the human body expands, new market opportunities are likely to emerge, potentially leading to the development of pharmaceutical-grade products and expanding the overall market size.
Current Challenges in Muscimol Research
Despite the long history of muscimol use in indigenous cultures, modern research on this compound faces several significant challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the limited availability of pure, natural muscimol. The Amanita muscaria mushroom, the primary source of muscimol, contains varying concentrations of the compound, making it difficult to obtain consistent samples for research purposes.
The legal status of muscimol and its source mushrooms presents another hurdle. In many countries, Amanita muscaria is classified as a controlled substance, restricting access for scientific study. This legal ambiguity hampers large-scale clinical trials and comprehensive research efforts, slowing the progress of understanding muscimol's potential therapeutic applications.
Ethical considerations also pose challenges in muscimol research. Given its psychoactive properties and traditional use in spiritual practices, researchers must navigate complex cultural sensitivities when studying the compound. Balancing scientific inquiry with respect for indigenous knowledge and practices requires careful consideration and collaboration with affected communities.
The pharmacological complexity of muscimol presents additional research challenges. As a GABA receptor agonist, muscimol interacts with multiple neural pathways, making it difficult to isolate its specific effects and potential side effects. This complexity necessitates extensive preclinical studies to understand its mechanisms of action fully.
Moreover, the lack of standardized protocols for muscimol extraction, purification, and administration hinders comparative studies and reproducibility of results. Developing consistent methodologies across research institutions is crucial for advancing the field and ensuring the validity of findings.
Funding limitations also impact muscimol research. Given its niche status and association with traditional practices, securing substantial grants for comprehensive studies can be challenging. This financial constraint often leads to smaller-scale investigations that may not fully capture the compound's potential or address all safety concerns.
Lastly, the interdisciplinary nature of muscimol research presents coordination challenges. Effective study of this compound requires collaboration among chemists, pharmacologists, neuroscientists, anthropologists, and indigenous knowledge holders. Bridging these diverse fields and perspectives to create cohesive research programs remains an ongoing challenge in the field.
The legal status of muscimol and its source mushrooms presents another hurdle. In many countries, Amanita muscaria is classified as a controlled substance, restricting access for scientific study. This legal ambiguity hampers large-scale clinical trials and comprehensive research efforts, slowing the progress of understanding muscimol's potential therapeutic applications.
Ethical considerations also pose challenges in muscimol research. Given its psychoactive properties and traditional use in spiritual practices, researchers must navigate complex cultural sensitivities when studying the compound. Balancing scientific inquiry with respect for indigenous knowledge and practices requires careful consideration and collaboration with affected communities.
The pharmacological complexity of muscimol presents additional research challenges. As a GABA receptor agonist, muscimol interacts with multiple neural pathways, making it difficult to isolate its specific effects and potential side effects. This complexity necessitates extensive preclinical studies to understand its mechanisms of action fully.
Moreover, the lack of standardized protocols for muscimol extraction, purification, and administration hinders comparative studies and reproducibility of results. Developing consistent methodologies across research institutions is crucial for advancing the field and ensuring the validity of findings.
Funding limitations also impact muscimol research. Given its niche status and association with traditional practices, securing substantial grants for comprehensive studies can be challenging. This financial constraint often leads to smaller-scale investigations that may not fully capture the compound's potential or address all safety concerns.
Lastly, the interdisciplinary nature of muscimol research presents coordination challenges. Effective study of this compound requires collaboration among chemists, pharmacologists, neuroscientists, anthropologists, and indigenous knowledge holders. Bridging these diverse fields and perspectives to create cohesive research programs remains an ongoing challenge in the field.
Traditional Preparation Methods
01 Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol
Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include muscimol as an active ingredient, often in combination with other compounds or excipients. The formulations are designed to treat neurological disorders, anxiety, or other conditions affected by GABA receptor modulation.- Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol: Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include muscimol as an active ingredient, often in combination with other compounds or excipients. The formulations are designed to treat neurological disorders, anxiety, or other conditions affected by GABA receptor modulation.
- Methods of administering muscimol: Various methods for administering muscimol have been developed, including oral, topical, and parenteral routes. Some approaches focus on targeted delivery to specific areas of the body, such as the central nervous system. Novel delivery systems may be employed to enhance bioavailability or control release rates of muscimol.
- Synthesis and production of muscimol: Techniques for synthesizing and producing muscimol have been developed and improved. These methods may involve chemical synthesis routes, biotechnological approaches, or extraction from natural sources. The focus is often on increasing yield, purity, and cost-effectiveness of muscimol production.
- Use of muscimol in combination therapies: Muscimol is explored in combination with other therapeutic agents for synergistic effects. These combinations may target multiple pathways or receptors simultaneously, potentially enhancing efficacy or reducing side effects. Such approaches are investigated for various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
- Muscimol analogs and derivatives: Research into muscimol analogs and derivatives aims to develop compounds with improved pharmacological profiles. These modified versions of muscimol may offer enhanced potency, selectivity, or reduced side effects. Structure-activity relationship studies guide the design of these novel compounds for potential therapeutic applications.
02 Methods of administering muscimol
Various methods for administering muscimol have been developed, including oral, topical, and parenteral routes. Some approaches focus on targeted delivery to specific areas of the body, such as the central nervous system. Novel delivery systems may be employed to enhance bioavailability or control release rates of muscimol.Expand Specific Solutions03 Muscimol analogs and derivatives
Research has been conducted on muscimol analogs and derivatives to enhance its therapeutic properties or reduce side effects. These modified compounds may have improved pharmacokinetics, increased potency, or altered selectivity for specific GABA receptor subtypes. Some analogs are designed to cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use of muscimol in combination therapies
Muscimol is often used in combination with other active ingredients to create synergistic effects or address multiple aspects of a condition. These combination therapies may target various neurotransmitter systems or incorporate muscimol with other GABA receptor modulators for enhanced therapeutic outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Muscimol in diagnostic and research applications
Beyond its therapeutic uses, muscimol is employed in diagnostic tools and research applications. It serves as a valuable compound for studying GABA receptor function, neurotransmitter systems, and brain activity. Some applications involve using muscimol as a probe or marker in neuroimaging studies or electrophysiological experiments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Institutions in Ethnopharmacology
The traditional usage of muscimol in indigenous cultures represents an emerging field of research at the intersection of ethnobotany, pharmacology, and cultural anthropology. The market is in its early stages, with limited commercial applications but growing scientific interest. Key players like Psyched Wellness Ltd. and Kadence Bio Ltd. are exploring muscimol's potential in health supplements and novel medicines, respectively. Established companies such as Colgate-Palmolive Co. and Unilever Plc may also be monitoring developments for potential applications in personal care products. Academic institutions like Northwest A&F University and Shanghai Normal University are contributing to the fundamental research. While the technology is still maturing, increasing interest in traditional plant-based remedies is driving exploration of muscimol's properties and potential modern applications.
Psyched Wellness Ltd.
Technical Solution: Psyched Wellness Ltd. has developed a proprietary extraction and purification process for muscimol from Amanita muscaria mushrooms. Their approach focuses on creating standardized, safe dosages of muscimol for potential therapeutic applications. The company has conducted extensive research on the traditional uses of muscimol in indigenous cultures, particularly in Siberian shamanic practices[1]. They are working on formulating muscimol-based products that could potentially address anxiety, stress, and sleep disorders, drawing inspiration from traditional applications while adhering to modern scientific standards[2][3].
Strengths: Specialized focus on muscimol, leveraging traditional knowledge with modern scientific methods. Weaknesses: Limited clinical data on efficacy and safety for modern applications, regulatory challenges in many jurisdictions.
CaaMTech LLC
Technical Solution: CaaMTech LLC is pioneering research into the pharmacology of muscimol and other compounds found in Amanita muscaria. They are developing novel formulations that combine muscimol with other natural or synthetic compounds to enhance its therapeutic potential. The company has filed several patents related to muscimol derivatives and their potential applications in treating neurological disorders[4]. CaaMTech's approach includes studying the synergistic effects of muscimol with other psychoactive compounds, aiming to create more effective and targeted therapies inspired by traditional uses[5].
Strengths: Innovative approach to muscimol research, potential for novel drug discoveries. Weaknesses: Early-stage research, long pathway to regulatory approval and commercialization.
Muscimol Pharmacology Insights
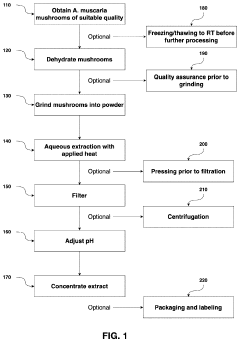
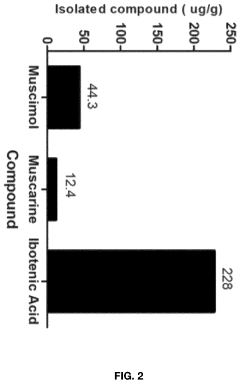
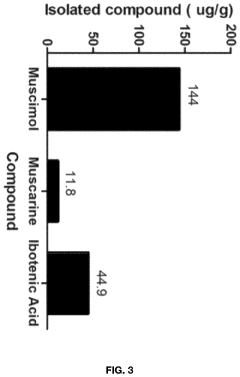
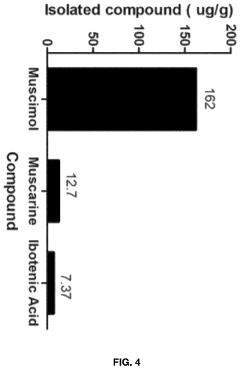
Processes for Extracting Muscimol from Amanita Muscaria
PatentPendingUS20240165180A1
Innovation
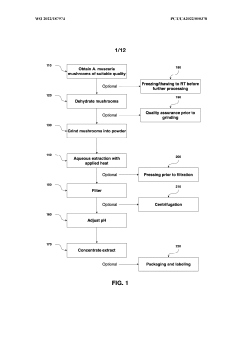
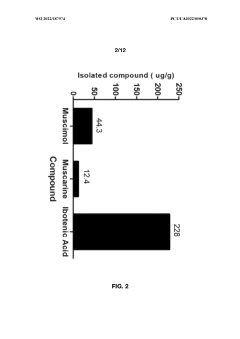
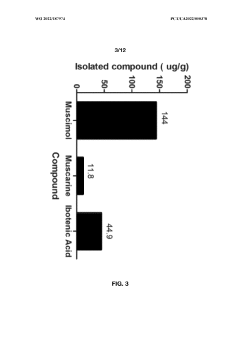
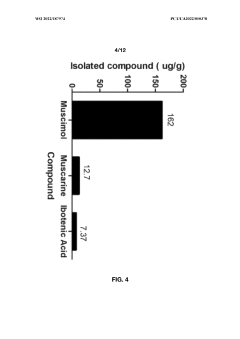
- Aqueous extraction of Amanita muscaria biomass is performed with heat, followed by pH reduction between 2.0 to 4.0 and concentration through distillation or refluxing, which decreases ibotenic acid content and increases muscimol content, resulting in a muscimol-rich extract with enhanced purity.
Processes for extracting muscimol from amanita muscaria
PatentWO2022187974A1
Innovation
- Aqueous extraction methods involving heat, pH reduction, and concentration techniques such as distillation and refluxing are employed to decrease ibotenic acid content and increase muscimol content in the extract, including steps like grinding the mushroom biomass, filtering, and acidification to facilitate decarboxylation of ibotenic acid to muscimol.
Legal Status of Muscimol
The legal status of muscimol varies significantly across different jurisdictions worldwide. In many countries, muscimol is not specifically regulated, falling into a legal gray area. However, its presence in Amanita mushrooms, particularly Amanita muscaria, often leads to indirect regulation through laws governing these fungi.
In the United States, muscimol is not listed as a controlled substance under federal law. However, the Amanita muscaria mushroom, which contains muscimol, is considered illegal to sell for human consumption in Louisiana, and its possession is restricted in some other states. The ambiguity in federal law has led to a complex patchwork of state and local regulations.
In Europe, the legal landscape is equally diverse. The United Kingdom does not classify muscimol or Amanita muscaria as controlled substances, making their possession and sale legal. However, prepared extracts or products intended for human consumption may fall under the Psychoactive Substances Act of 2016. In contrast, countries like the Netherlands have explicitly banned the sale and possession of Amanita muscaria mushrooms.
Australia maintains a more restrictive approach, with muscimol listed as a Schedule 9 prohibited substance in the Poisons Standard. This classification places it alongside substances like heroin and LSD, making its possession, sale, and use illegal without appropriate licenses.
In Canada, muscimol is not explicitly scheduled, but Amanita muscaria is regulated under the Natural Health Products Regulations when used for medicinal purposes. This creates a situation where the mushroom's legal status depends on its intended use and marketing.
Japan has taken a unique approach by specifically banning muscimol and ibotenic acid (another compound found in Amanita muscaria) under the Narcotics and Psychotropics Control Law. This makes Japan one of the few countries to directly regulate muscimol as a controlled substance.
The international legal status of muscimol is further complicated by its traditional use in indigenous cultures. Many countries have provisions protecting indigenous practices, which may provide exemptions for the traditional use of Amanita muscaria and, by extension, muscimol. However, these protections are often limited and do not extend to non-indigenous populations or commercial applications.
As research into the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol progresses, there is growing pressure for clearer regulations. Some advocates argue for a more nuanced approach that distinguishes between natural sources like Amanita mushrooms and synthetic muscimol, potentially leading to different legal classifications based on origin and intended use.
In the United States, muscimol is not listed as a controlled substance under federal law. However, the Amanita muscaria mushroom, which contains muscimol, is considered illegal to sell for human consumption in Louisiana, and its possession is restricted in some other states. The ambiguity in federal law has led to a complex patchwork of state and local regulations.
In Europe, the legal landscape is equally diverse. The United Kingdom does not classify muscimol or Amanita muscaria as controlled substances, making their possession and sale legal. However, prepared extracts or products intended for human consumption may fall under the Psychoactive Substances Act of 2016. In contrast, countries like the Netherlands have explicitly banned the sale and possession of Amanita muscaria mushrooms.
Australia maintains a more restrictive approach, with muscimol listed as a Schedule 9 prohibited substance in the Poisons Standard. This classification places it alongside substances like heroin and LSD, making its possession, sale, and use illegal without appropriate licenses.
In Canada, muscimol is not explicitly scheduled, but Amanita muscaria is regulated under the Natural Health Products Regulations when used for medicinal purposes. This creates a situation where the mushroom's legal status depends on its intended use and marketing.
Japan has taken a unique approach by specifically banning muscimol and ibotenic acid (another compound found in Amanita muscaria) under the Narcotics and Psychotropics Control Law. This makes Japan one of the few countries to directly regulate muscimol as a controlled substance.
The international legal status of muscimol is further complicated by its traditional use in indigenous cultures. Many countries have provisions protecting indigenous practices, which may provide exemptions for the traditional use of Amanita muscaria and, by extension, muscimol. However, these protections are often limited and do not extend to non-indigenous populations or commercial applications.
As research into the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol progresses, there is growing pressure for clearer regulations. Some advocates argue for a more nuanced approach that distinguishes between natural sources like Amanita mushrooms and synthetic muscimol, potentially leading to different legal classifications based on origin and intended use.
Cultural Preservation Aspects
The preservation of cultural heritage associated with the traditional usage of muscimol in indigenous cultures is a critical aspect of maintaining the rich tapestry of human knowledge and practices. Indigenous communities have long utilized muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushroom species, for various cultural and spiritual purposes. These practices often form an integral part of their identity, rituals, and traditional medicine systems.
Efforts to preserve these cultural practices face numerous challenges in the modern world. Urbanization, globalization, and the erosion of traditional lifestyles have led to a decline in the transmission of knowledge about muscimol usage from one generation to the next. This loss of cultural continuity threatens the survival of age-old wisdom and practices that have been refined over centuries.
Conservation initiatives aimed at protecting the natural habitats where muscimol-containing mushrooms grow are crucial for ensuring the continued availability of these resources to indigenous communities. Sustainable harvesting practices and the cultivation of these mushrooms can help maintain a balance between cultural needs and ecological preservation.
Documentation of traditional knowledge related to muscimol usage is another vital aspect of cultural preservation. Ethnobotanical studies, oral history projects, and collaborative research efforts between indigenous communities and academic institutions can help capture and preserve this valuable information for future generations.
Legal frameworks and policies that recognize and protect indigenous rights to their traditional knowledge and practices are essential. These measures can help safeguard against biopiracy and ensure that indigenous communities maintain control over their cultural heritage related to muscimol usage.
Education and awareness programs within indigenous communities can play a significant role in revitalizing interest in traditional practices among younger generations. These initiatives can help bridge the generational gap and ensure the continuity of cultural knowledge.
The ethical considerations surrounding the preservation of muscimol-related practices are complex. Balancing the need for cultural preservation with concerns about potential health risks and legal issues requires careful navigation and respect for indigenous autonomy in decision-making processes.
International cooperation and support for indigenous communities in their efforts to preserve their cultural heritage are crucial. This can include funding for research, conservation projects, and community-led initiatives that aim to maintain and revitalize traditional practices involving muscimol.
Efforts to preserve these cultural practices face numerous challenges in the modern world. Urbanization, globalization, and the erosion of traditional lifestyles have led to a decline in the transmission of knowledge about muscimol usage from one generation to the next. This loss of cultural continuity threatens the survival of age-old wisdom and practices that have been refined over centuries.
Conservation initiatives aimed at protecting the natural habitats where muscimol-containing mushrooms grow are crucial for ensuring the continued availability of these resources to indigenous communities. Sustainable harvesting practices and the cultivation of these mushrooms can help maintain a balance between cultural needs and ecological preservation.
Documentation of traditional knowledge related to muscimol usage is another vital aspect of cultural preservation. Ethnobotanical studies, oral history projects, and collaborative research efforts between indigenous communities and academic institutions can help capture and preserve this valuable information for future generations.
Legal frameworks and policies that recognize and protect indigenous rights to their traditional knowledge and practices are essential. These measures can help safeguard against biopiracy and ensure that indigenous communities maintain control over their cultural heritage related to muscimol usage.
Education and awareness programs within indigenous communities can play a significant role in revitalizing interest in traditional practices among younger generations. These initiatives can help bridge the generational gap and ensure the continuity of cultural knowledge.
The ethical considerations surrounding the preservation of muscimol-related practices are complex. Balancing the need for cultural preservation with concerns about potential health risks and legal issues requires careful navigation and respect for indigenous autonomy in decision-making processes.
International cooperation and support for indigenous communities in their efforts to preserve their cultural heritage are crucial. This can include funding for research, conservation projects, and community-led initiatives that aim to maintain and revitalize traditional practices involving muscimol.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!