Efficacy of Bioresonance in Managing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Bioresonance and PCOS: Background and Objectives
Bioresonance therapy, a form of alternative medicine, has gained attention in recent years for its potential application in managing various health conditions, including Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). This complex endocrine disorder affects millions of women worldwide, causing hormonal imbalances, metabolic disturbances, and reproductive challenges. As conventional treatments often yield limited success, there is a growing interest in exploring complementary approaches like bioresonance.
The concept of bioresonance is rooted in the belief that all cells and organs in the human body emit unique electromagnetic frequencies. Proponents of this therapy argue that these frequencies can be detected, analyzed, and manipulated to restore balance and promote healing. In the context of PCOS, bioresonance aims to address the underlying hormonal and metabolic imbalances that characterize the condition.
The evolution of bioresonance technology can be traced back to the mid-20th century, with significant advancements in recent decades. Early devices were rudimentary, focusing on basic frequency detection. However, modern bioresonance machines incorporate sophisticated software and algorithms, claiming to offer more precise diagnosis and targeted treatment protocols.
As we delve into the potential efficacy of bioresonance in managing PCOS, it is crucial to understand the multifaceted nature of this syndrome. PCOS is characterized by a triad of symptoms: irregular menstrual cycles, excess androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries. These manifestations can lead to a range of complications, including infertility, insulin resistance, and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to critically evaluate the current evidence supporting the use of bioresonance therapy in PCOS management. We aim to explore the proposed mechanisms of action, assess the quality and reliability of existing studies, and identify potential areas for further research and development.
Furthermore, this report seeks to contextualize bioresonance within the broader landscape of PCOS treatments, comparing its purported benefits and limitations to established medical interventions. By examining the technological aspects of bioresonance devices and their application in PCOS, we hope to provide insights into the feasibility and potential integration of this therapy into comprehensive PCOS management strategies.
As we progress through this analysis, it is essential to maintain a balanced perspective, acknowledging both the promising aspects of bioresonance and the skepticism it faces within the mainstream medical community. This report aims to bridge the gap between alternative and conventional approaches, fostering a more nuanced understanding of bioresonance's potential role in addressing the complex challenges posed by PCOS.
The concept of bioresonance is rooted in the belief that all cells and organs in the human body emit unique electromagnetic frequencies. Proponents of this therapy argue that these frequencies can be detected, analyzed, and manipulated to restore balance and promote healing. In the context of PCOS, bioresonance aims to address the underlying hormonal and metabolic imbalances that characterize the condition.
The evolution of bioresonance technology can be traced back to the mid-20th century, with significant advancements in recent decades. Early devices were rudimentary, focusing on basic frequency detection. However, modern bioresonance machines incorporate sophisticated software and algorithms, claiming to offer more precise diagnosis and targeted treatment protocols.
As we delve into the potential efficacy of bioresonance in managing PCOS, it is crucial to understand the multifaceted nature of this syndrome. PCOS is characterized by a triad of symptoms: irregular menstrual cycles, excess androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries. These manifestations can lead to a range of complications, including infertility, insulin resistance, and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to critically evaluate the current evidence supporting the use of bioresonance therapy in PCOS management. We aim to explore the proposed mechanisms of action, assess the quality and reliability of existing studies, and identify potential areas for further research and development.
Furthermore, this report seeks to contextualize bioresonance within the broader landscape of PCOS treatments, comparing its purported benefits and limitations to established medical interventions. By examining the technological aspects of bioresonance devices and their application in PCOS, we hope to provide insights into the feasibility and potential integration of this therapy into comprehensive PCOS management strategies.
As we progress through this analysis, it is essential to maintain a balanced perspective, acknowledging both the promising aspects of bioresonance and the skepticism it faces within the mainstream medical community. This report aims to bridge the gap between alternative and conventional approaches, fostering a more nuanced understanding of bioresonance's potential role in addressing the complex challenges posed by PCOS.
Market Analysis for PCOS Management Solutions
The market for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) management solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing prevalence of PCOS among women of reproductive age. PCOS affects approximately 6-12% of women worldwide, with variations across different populations and ethnicities. This widespread occurrence has created a substantial demand for effective treatment options and management strategies.
The global PCOS treatment market is segmented into various categories, including medications, devices, and lifestyle interventions. Traditional pharmaceutical approaches, such as oral contraceptives and anti-androgen medications, currently dominate the market. However, there is a growing interest in alternative and complementary therapies, including bioresonance, as patients seek non-invasive and holistic treatment options.
Bioresonance therapy, as a potential management solution for PCOS, is gaining attention in the alternative medicine sector. While still considered controversial in mainstream medical circles, the market for bioresonance devices and treatments is expanding. This growth is partly fueled by patient demand for non-pharmacological interventions and the increasing focus on personalized medicine approaches.
The market for PCOS management solutions is influenced by several factors, including the rising awareness of PCOS among both patients and healthcare providers, advancements in diagnostic technologies, and the growing emphasis on women's health issues. Additionally, the increasing adoption of telemedicine and digital health platforms is creating new opportunities for remote monitoring and management of PCOS symptoms.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the PCOS treatment market, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher awareness levels. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising disposable incomes.
The competitive landscape of the PCOS management market is diverse, with pharmaceutical companies, medical device manufacturers, and alternative therapy providers vying for market share. As research into bioresonance and other novel therapies progresses, new entrants are likely to disrupt the traditional market dynamics, potentially leading to a shift in treatment paradigms for PCOS.
Looking ahead, the market for PCOS management solutions, including bioresonance therapy, is projected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as the increasing prevalence of PCOS, growing patient preference for non-invasive treatments, and ongoing research into novel therapies are expected to drive market expansion. However, the acceptance and integration of alternative therapies like bioresonance into mainstream PCOS management will depend on robust clinical evidence and regulatory approvals.
The global PCOS treatment market is segmented into various categories, including medications, devices, and lifestyle interventions. Traditional pharmaceutical approaches, such as oral contraceptives and anti-androgen medications, currently dominate the market. However, there is a growing interest in alternative and complementary therapies, including bioresonance, as patients seek non-invasive and holistic treatment options.
Bioresonance therapy, as a potential management solution for PCOS, is gaining attention in the alternative medicine sector. While still considered controversial in mainstream medical circles, the market for bioresonance devices and treatments is expanding. This growth is partly fueled by patient demand for non-pharmacological interventions and the increasing focus on personalized medicine approaches.
The market for PCOS management solutions is influenced by several factors, including the rising awareness of PCOS among both patients and healthcare providers, advancements in diagnostic technologies, and the growing emphasis on women's health issues. Additionally, the increasing adoption of telemedicine and digital health platforms is creating new opportunities for remote monitoring and management of PCOS symptoms.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the PCOS treatment market, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher awareness levels. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising disposable incomes.
The competitive landscape of the PCOS management market is diverse, with pharmaceutical companies, medical device manufacturers, and alternative therapy providers vying for market share. As research into bioresonance and other novel therapies progresses, new entrants are likely to disrupt the traditional market dynamics, potentially leading to a shift in treatment paradigms for PCOS.
Looking ahead, the market for PCOS management solutions, including bioresonance therapy, is projected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as the increasing prevalence of PCOS, growing patient preference for non-invasive treatments, and ongoing research into novel therapies are expected to drive market expansion. However, the acceptance and integration of alternative therapies like bioresonance into mainstream PCOS management will depend on robust clinical evidence and regulatory approvals.
Current State of Bioresonance in PCOS Treatment
Bioresonance therapy has gained attention in recent years as a potential complementary treatment for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Currently, the application of bioresonance in PCOS management is still in its early stages, with limited clinical evidence supporting its efficacy. However, several practitioners and clinics worldwide have begun incorporating this approach into their treatment protocols.
The principle behind bioresonance therapy in PCOS treatment is based on the concept that electromagnetic waves can be used to detect and correct imbalances in the body's energy fields. In the context of PCOS, proponents argue that bioresonance can help regulate hormonal imbalances, reduce inflammation, and improve overall metabolic function.
Some clinics offering bioresonance for PCOS claim to address various aspects of the syndrome, including insulin resistance, androgen excess, and ovarian dysfunction. The treatment typically involves placing electrodes on specific points of the body to measure electromagnetic frequencies and then using a device to emit corrective frequencies aimed at restoring balance.
While anecdotal reports suggest positive outcomes for some patients, the scientific community remains skeptical due to the lack of large-scale, randomized controlled trials. Most studies on bioresonance for PCOS have been small-scale and observational, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about its effectiveness.
Current research efforts are focused on understanding the potential mechanisms by which bioresonance might influence PCOS symptoms. Some theories propose that the therapy may modulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis, influence cellular metabolism, or affect the autonomic nervous system. However, these hypotheses require further investigation and validation.
The integration of bioresonance into conventional PCOS treatment plans varies widely among healthcare providers. Some practitioners use it as a standalone therapy, while others incorporate it as part of a holistic approach alongside dietary changes, exercise, and traditional medications. This lack of standardization in treatment protocols contributes to the challenges in assessing its overall efficacy.
Regulatory bodies in most countries have not yet approved bioresonance as a recognized treatment for PCOS, citing insufficient evidence of its safety and effectiveness. This has led to variations in the availability and quality of bioresonance treatments across different regions, with some countries imposing stricter regulations on its use in clinical settings.
As research in this field continues to evolve, there is a growing interest in conducting more rigorous clinical trials to evaluate the potential benefits and limitations of bioresonance in PCOS management. Future studies aim to establish standardized protocols, determine optimal treatment frequencies and durations, and identify specific subgroups of PCOS patients who may benefit most from this approach.
The principle behind bioresonance therapy in PCOS treatment is based on the concept that electromagnetic waves can be used to detect and correct imbalances in the body's energy fields. In the context of PCOS, proponents argue that bioresonance can help regulate hormonal imbalances, reduce inflammation, and improve overall metabolic function.
Some clinics offering bioresonance for PCOS claim to address various aspects of the syndrome, including insulin resistance, androgen excess, and ovarian dysfunction. The treatment typically involves placing electrodes on specific points of the body to measure electromagnetic frequencies and then using a device to emit corrective frequencies aimed at restoring balance.
While anecdotal reports suggest positive outcomes for some patients, the scientific community remains skeptical due to the lack of large-scale, randomized controlled trials. Most studies on bioresonance for PCOS have been small-scale and observational, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about its effectiveness.
Current research efforts are focused on understanding the potential mechanisms by which bioresonance might influence PCOS symptoms. Some theories propose that the therapy may modulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis, influence cellular metabolism, or affect the autonomic nervous system. However, these hypotheses require further investigation and validation.
The integration of bioresonance into conventional PCOS treatment plans varies widely among healthcare providers. Some practitioners use it as a standalone therapy, while others incorporate it as part of a holistic approach alongside dietary changes, exercise, and traditional medications. This lack of standardization in treatment protocols contributes to the challenges in assessing its overall efficacy.
Regulatory bodies in most countries have not yet approved bioresonance as a recognized treatment for PCOS, citing insufficient evidence of its safety and effectiveness. This has led to variations in the availability and quality of bioresonance treatments across different regions, with some countries imposing stricter regulations on its use in clinical settings.
As research in this field continues to evolve, there is a growing interest in conducting more rigorous clinical trials to evaluate the potential benefits and limitations of bioresonance in PCOS management. Future studies aim to establish standardized protocols, determine optimal treatment frequencies and durations, and identify specific subgroups of PCOS patients who may benefit most from this approach.
Existing Bioresonance Protocols for PCOS
01 Bioresonance therapy devices and methods
Various devices and methods for bioresonance therapy have been developed. These systems typically involve measuring electromagnetic signals from the body, processing them, and applying modified signals back to the body. The aim is to detect and correct energetic imbalances that may be associated with health issues.- Bioresonance devices for diagnosis and therapy: Bioresonance devices are used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. These devices measure electromagnetic frequencies emitted by the body and can be used to detect imbalances or health issues. They can also emit specific frequencies for therapeutic purposes, aiming to restore balance and promote healing.
- Integration of bioresonance with other therapeutic methods: Bioresonance therapy is often combined with other therapeutic approaches to enhance overall treatment efficacy. This integration may include combining bioresonance with traditional medicine, acupuncture, or other alternative therapies to provide a more comprehensive approach to health and wellness.
- Bioresonance for specific health conditions: Research and development in bioresonance therapy has focused on its application for specific health conditions. Studies have explored its potential efficacy in treating allergies, chronic pain, digestive disorders, and other health issues. The therapy aims to address these conditions by identifying and correcting frequency imbalances associated with them.
- Technological advancements in bioresonance equipment: Ongoing technological advancements have led to improvements in bioresonance equipment. These innovations include more sensitive frequency detection, enhanced data processing capabilities, and user-friendly interfaces. Such advancements aim to increase the accuracy and reliability of bioresonance diagnostics and treatments.
- Evaluation and standardization of bioresonance efficacy: Efforts are being made to evaluate and standardize the efficacy of bioresonance therapy. This includes developing protocols for clinical trials, establishing quality control measures for bioresonance devices, and creating standardized treatment procedures. These efforts aim to provide more concrete evidence of bioresonance efficacy and improve its acceptance in mainstream healthcare.
02 Bioresonance for specific health conditions
Research has explored the application of bioresonance therapy for specific health conditions. This includes studies on its potential efficacy for allergies, pain management, and stress reduction. While some positive results have been reported, the scientific evidence remains limited and controversial.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration with other therapeutic approaches
Some researchers and practitioners have explored combining bioresonance therapy with other therapeutic approaches. This includes integration with traditional medicine, acupuncture, or other complementary therapies. The goal is to potentially enhance overall treatment efficacy through a holistic approach.Expand Specific Solutions04 Technological advancements in bioresonance devices
Ongoing technological advancements have led to the development of more sophisticated bioresonance devices. These improvements include better signal processing, enhanced user interfaces, and integration with digital health platforms. Some devices now incorporate artificial intelligence to analyze and interpret bioresonance data.Expand Specific Solutions05 Evaluation and standardization efforts
There have been efforts to evaluate the efficacy of bioresonance therapy more rigorously and to establish standardized protocols. This includes attempts to develop quality control measures, conduct controlled clinical trials, and create guidelines for the use of bioresonance in various settings. However, challenges remain in achieving scientific consensus on its effectiveness.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Bioresonance and PCOS Research
The bioresonance market for managing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is in its early development stage, with limited market size and technological maturity. The field is characterized by ongoing research and clinical trials, primarily conducted by academic institutions such as Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine and the University of Nottingham. While established healthcare companies like Bayer AG and Medtronic have shown interest, specialized firms like Galvani Bioelectronics are at the forefront of bioelectronic medicine development. The technology's efficacy for PCOS management remains under investigation, with research institutions like INSERM and Centre Hospitalier Regional Universitaire de Lille contributing to the growing body of knowledge in this emerging field.
Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale
Technical Solution: The Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM) is conducting research into novel approaches for managing PCOS, including the potential application of bioresonance therapy. Their studies focus on understanding the complex interplay between hormonal imbalances, metabolic dysfunction, and ovarian physiology in PCOS. INSERM researchers are investigating how bioresonance techniques might be used to modulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis, potentially improving hormonal regulation in PCOS patients[5]. They are also exploring the use of non-invasive bioresonance devices to enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce androgen levels, two key factors in PCOS pathophysiology. INSERM's approach combines basic scientific research with clinical studies to evaluate the efficacy and safety of bioresonance in PCOS management.
Strengths: Strong scientific research capabilities, access to diverse patient populations for clinical studies, and collaboration with multiple healthcare institutions. Weaknesses: As a research institution, may face challenges in translating findings into commercially viable treatments, and potential limitations in funding for large-scale clinical trials.
The University of Nottingham
Technical Solution: The University of Nottingham is at the forefront of research into novel treatments for PCOS, including the potential application of bioresonance therapy. Their approach combines cutting-edge biomedical research with clinical studies to explore non-invasive treatments for PCOS. The university's researchers are investigating how bioresonance technology can be used to modulate the endocrine system and improve metabolic function in PCOS patients. They are developing protocols that use specific electromagnetic frequencies to target ovarian tissue and potentially restore normal hormonal balance[6]. Additionally, the university is conducting studies on the effects of bioresonance on insulin sensitivity and androgen production, two key factors in PCOS pathophysiology. Their research also includes the development of personalized bioresonance treatment plans based on individual patient profiles.
Strengths: Strong academic research capabilities, multidisciplinary approach combining endocrinology and bioengineering, and access to advanced laboratory facilities. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in securing funding for large-scale clinical trials, and the need to navigate regulatory pathways for new medical technologies.
Core Studies on Bioresonance Efficacy in PCOS
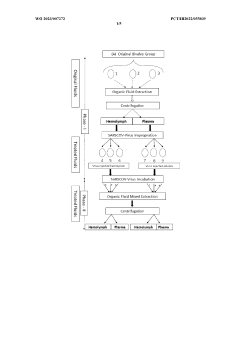
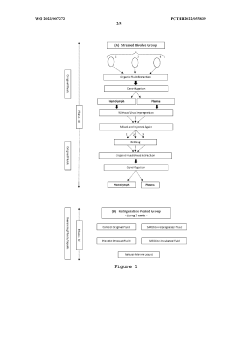
Method of obtaining electromagnetic frequencies from aquatic organisms bioactivated fluids for bioresonance therapy against a disease and/or pathogen
PatentWO2023007272A1
Innovation
- A method involving bioresonance therapy using electromagnetic frequencies obtained from aquatic non-human organisms, specifically bioactivated fluids from bivalves like Anodonta cygnea, to induce an immune response and treat diseases and pathogens in humans, utilizing a bioresonance device to transfer and record these frequencies for therapeutic applications.
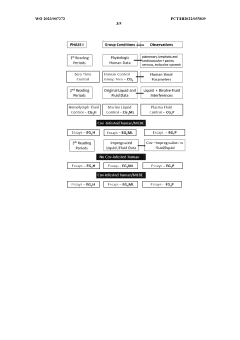
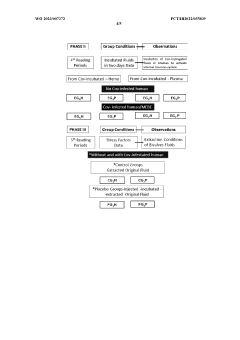
System and method for diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome
PatentWO2022246882A1
Innovation
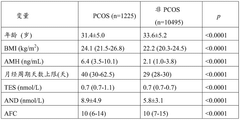
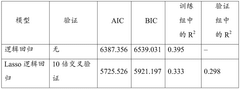
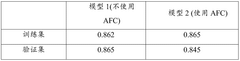
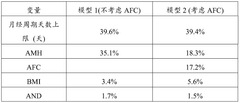
- By establishing a multi-categorical variable model based on anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) levels, upper limit of menstrual cycle days, BMI and androstenedione levels, logistic regression analysis was used to calculate the probability of subjects suffering from PCOS, and based on the calculation results Assess risks in groups.
Regulatory Framework for Bioresonance Devices
The regulatory framework for bioresonance devices varies significantly across different countries and regions, reflecting the diverse approaches to alternative and complementary medicine worldwide. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies bioresonance devices as Class II medical devices, requiring premarket notification (510(k)) before they can be legally marketed. However, the FDA has not approved any bioresonance devices for diagnostic or therapeutic use in managing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) or any other medical condition.
In the European Union, bioresonance devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with safety and performance requirements, including clinical evaluation and risk management. The devices are typically classified as Class IIa or IIb, depending on their intended use and potential risks. However, the regulatory landscape for bioresonance in PCOS management remains ambiguous, as there is limited scientific evidence supporting its efficacy.
Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) regulates bioresonance devices as therapeutic goods. Manufacturers must register their devices on the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG) before they can be legally supplied. The TGA has issued warnings about the lack of scientific evidence supporting bioresonance therapy, particularly for complex conditions like PCOS.
In Canada, bioresonance devices are regulated by Health Canada as Class II medical devices. Manufacturers must obtain a Medical Device License before marketing their products. However, Health Canada has not approved any bioresonance devices for PCOS management, citing insufficient evidence of safety and efficacy.
Many countries, including China, Russia, and several Eastern European nations, have more lenient regulations for bioresonance devices. In these regions, bioresonance therapy is often considered a form of traditional or alternative medicine, subject to less stringent regulatory oversight. This regulatory disparity has led to a global market where the availability and use of bioresonance devices for PCOS management vary widely.
The lack of harmonized international standards for bioresonance devices poses challenges for manufacturers, healthcare providers, and patients. As research into the efficacy of bioresonance for PCOS continues, regulatory bodies may need to reassess their approaches to ensure patient safety while allowing for potential innovation in this field. Future regulatory frameworks may need to balance the need for scientific evidence with the growing interest in complementary therapies for managing complex conditions like PCOS.
In the European Union, bioresonance devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with safety and performance requirements, including clinical evaluation and risk management. The devices are typically classified as Class IIa or IIb, depending on their intended use and potential risks. However, the regulatory landscape for bioresonance in PCOS management remains ambiguous, as there is limited scientific evidence supporting its efficacy.
Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) regulates bioresonance devices as therapeutic goods. Manufacturers must register their devices on the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG) before they can be legally supplied. The TGA has issued warnings about the lack of scientific evidence supporting bioresonance therapy, particularly for complex conditions like PCOS.
In Canada, bioresonance devices are regulated by Health Canada as Class II medical devices. Manufacturers must obtain a Medical Device License before marketing their products. However, Health Canada has not approved any bioresonance devices for PCOS management, citing insufficient evidence of safety and efficacy.
Many countries, including China, Russia, and several Eastern European nations, have more lenient regulations for bioresonance devices. In these regions, bioresonance therapy is often considered a form of traditional or alternative medicine, subject to less stringent regulatory oversight. This regulatory disparity has led to a global market where the availability and use of bioresonance devices for PCOS management vary widely.
The lack of harmonized international standards for bioresonance devices poses challenges for manufacturers, healthcare providers, and patients. As research into the efficacy of bioresonance for PCOS continues, regulatory bodies may need to reassess their approaches to ensure patient safety while allowing for potential innovation in this field. Future regulatory frameworks may need to balance the need for scientific evidence with the growing interest in complementary therapies for managing complex conditions like PCOS.
Patient Perspectives on Bioresonance for PCOS
Patient perspectives on bioresonance for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) offer valuable insights into the perceived efficacy and overall experience of this alternative treatment approach. Many patients report feeling drawn to bioresonance therapy due to its non-invasive nature and the promise of a holistic approach to managing their PCOS symptoms.
A significant number of women with PCOS express frustration with conventional treatments, citing limited success or undesirable side effects. This dissatisfaction often leads them to explore complementary and alternative medicine options, including bioresonance. Patients frequently mention the appeal of a treatment that purportedly addresses the root causes of their condition rather than merely managing symptoms.
Anecdotal evidence from patient testimonials suggests that some women experience improvements in various PCOS symptoms after undergoing bioresonance therapy. These reported benefits include regularization of menstrual cycles, reduction in acne and hirsutism, improved mood, and in some cases, enhanced fertility. However, it is important to note that these experiences vary widely among individuals, and not all patients report positive outcomes.
Many patients appreciate the personalized approach of bioresonance therapy, feeling that practitioners take the time to understand their unique health profiles and tailor treatments accordingly. This individualized attention often contrasts with their experiences in conventional medical settings, where they may feel rushed or not fully heard.
Despite positive experiences reported by some, a considerable number of patients express skepticism about the scientific basis of bioresonance therapy. They often struggle to reconcile the lack of robust clinical evidence with their personal experiences or the anecdotal success stories they encounter. This cognitive dissonance can lead to mixed feelings about the treatment's efficacy and value.
Cost is another significant factor in patient perspectives, as bioresonance therapy is typically not covered by health insurance. Some patients view the out-of-pocket expense as a worthwhile investment in their health, while others find it prohibitively expensive, especially given the uncertain outcomes.
Patient opinions on the duration and frequency of bioresonance sessions vary. Some find the treatment regimen manageable and integrate it easily into their lives, while others struggle with the time commitment required for multiple sessions. The lack of immediate results can also be a source of frustration for some patients, who may abandon the treatment before experiencing any perceived benefits.
Overall, patient perspectives on bioresonance for PCOS reflect a complex interplay of hope, skepticism, personal experiences, and practical considerations. While some patients advocate strongly for the therapy based on their positive outcomes, others remain cautious or unconvinced. These diverse viewpoints underscore the need for more comprehensive research to better understand the potential role of bioresonance in PCOS management.
A significant number of women with PCOS express frustration with conventional treatments, citing limited success or undesirable side effects. This dissatisfaction often leads them to explore complementary and alternative medicine options, including bioresonance. Patients frequently mention the appeal of a treatment that purportedly addresses the root causes of their condition rather than merely managing symptoms.
Anecdotal evidence from patient testimonials suggests that some women experience improvements in various PCOS symptoms after undergoing bioresonance therapy. These reported benefits include regularization of menstrual cycles, reduction in acne and hirsutism, improved mood, and in some cases, enhanced fertility. However, it is important to note that these experiences vary widely among individuals, and not all patients report positive outcomes.
Many patients appreciate the personalized approach of bioresonance therapy, feeling that practitioners take the time to understand their unique health profiles and tailor treatments accordingly. This individualized attention often contrasts with their experiences in conventional medical settings, where they may feel rushed or not fully heard.
Despite positive experiences reported by some, a considerable number of patients express skepticism about the scientific basis of bioresonance therapy. They often struggle to reconcile the lack of robust clinical evidence with their personal experiences or the anecdotal success stories they encounter. This cognitive dissonance can lead to mixed feelings about the treatment's efficacy and value.
Cost is another significant factor in patient perspectives, as bioresonance therapy is typically not covered by health insurance. Some patients view the out-of-pocket expense as a worthwhile investment in their health, while others find it prohibitively expensive, especially given the uncertain outcomes.
Patient opinions on the duration and frequency of bioresonance sessions vary. Some find the treatment regimen manageable and integrate it easily into their lives, while others struggle with the time commitment required for multiple sessions. The lack of immediate results can also be a source of frustration for some patients, who may abandon the treatment before experiencing any perceived benefits.
Overall, patient perspectives on bioresonance for PCOS reflect a complex interplay of hope, skepticism, personal experiences, and practical considerations. While some patients advocate strongly for the therapy based on their positive outcomes, others remain cautious or unconvinced. These diverse viewpoints underscore the need for more comprehensive research to better understand the potential role of bioresonance in PCOS management.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!