Enhancing Acrylic Resin’s UV Absorption with Stabilizers
OCT 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
UV Stabilization Technology Background and Objectives
Ultraviolet (UV) stabilization technology has evolved significantly over the past decades, driven by the increasing demand for durable materials in outdoor applications. The journey began in the 1950s with the introduction of basic UV absorbers, progressing through various generations of stabilizers with enhanced performance characteristics. Initially focused on preventing yellowing and physical degradation, the technology has expanded to address comprehensive protection against multiple degradation mechanisms while maintaining aesthetic and functional properties of materials.
The evolution of UV stabilization for acrylic resins specifically has been marked by several key milestones. Early stabilizers offered limited protection and often compromised the optical clarity that makes acrylic desirable. The 1980s saw the development of more compatible stabilizers that preserved transparency while extending service life. Recent advancements have focused on nano-scale additives and chemically bonded stabilizers that provide superior protection without migration or leaching issues.
Current technological trends in UV stabilization for acrylic resins include the development of multifunctional additives that simultaneously address UV protection, thermal stability, and processing improvements. There is also significant movement toward environmentally friendly stabilizers that avoid harmful substances while maintaining high performance standards. The integration of computational modeling to predict degradation patterns and optimize stabilizer formulations represents another frontier in this field.
The primary objective of enhancing acrylic resin's UV absorption with stabilizers is to significantly extend the service life of acrylic products exposed to outdoor conditions without compromising their inherent properties. This includes maintaining optical clarity, preventing yellowing, and preserving mechanical strength under prolonged UV exposure. Additionally, there is a focus on developing cost-effective solutions that can be easily incorporated into existing manufacturing processes.
Secondary objectives include reducing the environmental impact of stabilizers through the development of non-toxic, biodegradable alternatives to traditional additives. There is also emphasis on creating stabilization systems that can withstand extreme weather conditions, addressing the challenges posed by climate change and expanding applications in harsh environments. The technology aims to enable acrylic materials to compete effectively with more expensive engineering plastics in demanding outdoor applications.
The intersection of UV stabilization technology with other emerging fields, such as smart materials and self-healing polymers, presents exciting opportunities for innovation. Research is increasingly focused on responsive stabilization systems that can adapt to changing environmental conditions, providing optimal protection across diverse exposure scenarios while minimizing the overall additive load in the polymer matrix.
The evolution of UV stabilization for acrylic resins specifically has been marked by several key milestones. Early stabilizers offered limited protection and often compromised the optical clarity that makes acrylic desirable. The 1980s saw the development of more compatible stabilizers that preserved transparency while extending service life. Recent advancements have focused on nano-scale additives and chemically bonded stabilizers that provide superior protection without migration or leaching issues.
Current technological trends in UV stabilization for acrylic resins include the development of multifunctional additives that simultaneously address UV protection, thermal stability, and processing improvements. There is also significant movement toward environmentally friendly stabilizers that avoid harmful substances while maintaining high performance standards. The integration of computational modeling to predict degradation patterns and optimize stabilizer formulations represents another frontier in this field.
The primary objective of enhancing acrylic resin's UV absorption with stabilizers is to significantly extend the service life of acrylic products exposed to outdoor conditions without compromising their inherent properties. This includes maintaining optical clarity, preventing yellowing, and preserving mechanical strength under prolonged UV exposure. Additionally, there is a focus on developing cost-effective solutions that can be easily incorporated into existing manufacturing processes.
Secondary objectives include reducing the environmental impact of stabilizers through the development of non-toxic, biodegradable alternatives to traditional additives. There is also emphasis on creating stabilization systems that can withstand extreme weather conditions, addressing the challenges posed by climate change and expanding applications in harsh environments. The technology aims to enable acrylic materials to compete effectively with more expensive engineering plastics in demanding outdoor applications.
The intersection of UV stabilization technology with other emerging fields, such as smart materials and self-healing polymers, presents exciting opportunities for innovation. Research is increasingly focused on responsive stabilization systems that can adapt to changing environmental conditions, providing optimal protection across diverse exposure scenarios while minimizing the overall additive load in the polymer matrix.
Market Analysis for UV-Resistant Acrylic Products
The global market for UV-resistant acrylic products has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven primarily by increasing applications in automotive, construction, electronics, and outdoor signage industries. Current market valuation stands at approximately 12.5 billion USD, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 6.8% through 2028, according to recent industry analyses.
Consumer demand for durable outdoor materials has created substantial market opportunities for UV-stabilized acrylic products. The construction sector represents the largest market segment, accounting for roughly 35% of total consumption, followed by automotive applications at 28%. This demand is particularly pronounced in regions with high UV exposure, including the Middle East, Australia, and parts of North America and Southern Europe.
Regional market distribution shows Asia-Pacific leading with 42% market share, attributed to rapid industrialization and construction activities in China and India. North America follows at 27%, with Europe at 23%. Emerging markets in Latin America and Africa are showing accelerated adoption rates, albeit from smaller baseline volumes.
Price sensitivity varies significantly across application segments. High-performance UV-resistant acrylics command premium pricing in specialized applications such as aerospace and medical devices, while construction and general consumer products remain highly price-competitive. The average price premium for UV-stabilized acrylic versus standard formulations ranges between 18-25%.
Market research indicates shifting consumer preferences toward environmentally sustainable UV stabilizers, creating new market opportunities for bio-based and non-toxic formulations. This trend is particularly strong in European markets where regulatory frameworks increasingly restrict certain traditional UV stabilizer compounds.
Industry surveys reveal that product longevity and color retention under UV exposure represent the two most critical performance attributes valued by end-users, with 87% of industrial buyers citing these as primary purchase considerations. This underscores the market potential for advanced UV absorption technologies that can extend product lifespans.
Competition in this market segment is intensifying, with approximately 65% of market share controlled by major chemical corporations. However, specialized medium-sized enterprises focusing exclusively on high-performance UV-resistant formulations have gained market traction through innovation and customized solutions. The remaining market share is fragmented among numerous smaller regional producers.
Future market growth is expected to be driven by technological advancements in UV stabilizer efficiency, increasing outdoor applications of acrylic materials, and growing consumer awareness regarding UV degradation. Particular growth potential exists in developing economies where infrastructure development and increasing disposable income are creating new market opportunities for UV-resistant acrylic products.
Consumer demand for durable outdoor materials has created substantial market opportunities for UV-stabilized acrylic products. The construction sector represents the largest market segment, accounting for roughly 35% of total consumption, followed by automotive applications at 28%. This demand is particularly pronounced in regions with high UV exposure, including the Middle East, Australia, and parts of North America and Southern Europe.
Regional market distribution shows Asia-Pacific leading with 42% market share, attributed to rapid industrialization and construction activities in China and India. North America follows at 27%, with Europe at 23%. Emerging markets in Latin America and Africa are showing accelerated adoption rates, albeit from smaller baseline volumes.
Price sensitivity varies significantly across application segments. High-performance UV-resistant acrylics command premium pricing in specialized applications such as aerospace and medical devices, while construction and general consumer products remain highly price-competitive. The average price premium for UV-stabilized acrylic versus standard formulations ranges between 18-25%.
Market research indicates shifting consumer preferences toward environmentally sustainable UV stabilizers, creating new market opportunities for bio-based and non-toxic formulations. This trend is particularly strong in European markets where regulatory frameworks increasingly restrict certain traditional UV stabilizer compounds.
Industry surveys reveal that product longevity and color retention under UV exposure represent the two most critical performance attributes valued by end-users, with 87% of industrial buyers citing these as primary purchase considerations. This underscores the market potential for advanced UV absorption technologies that can extend product lifespans.
Competition in this market segment is intensifying, with approximately 65% of market share controlled by major chemical corporations. However, specialized medium-sized enterprises focusing exclusively on high-performance UV-resistant formulations have gained market traction through innovation and customized solutions. The remaining market share is fragmented among numerous smaller regional producers.
Future market growth is expected to be driven by technological advancements in UV stabilizer efficiency, increasing outdoor applications of acrylic materials, and growing consumer awareness regarding UV degradation. Particular growth potential exists in developing economies where infrastructure development and increasing disposable income are creating new market opportunities for UV-resistant acrylic products.
Current Challenges in Acrylic UV Protection
Despite significant advancements in acrylic resin technology, several critical challenges persist in achieving optimal UV protection. The primary issue lies in the inherent photochemical degradation of acrylic polymers when exposed to ultraviolet radiation, particularly in the UVA (315-400 nm) and UVB (280-315 nm) ranges. This degradation manifests as yellowing, surface crazing, and mechanical property deterioration, significantly reducing product lifespan and aesthetic appeal.
Current UV stabilizers demonstrate limited long-term effectiveness, with performance typically declining after 2-3 years of outdoor exposure. This degradation timeline falls short of industry requirements, particularly in architectural, automotive, and outdoor signage applications where 5-10 year performance guarantees are standard. The trade-off between UV protection and optical clarity presents another significant challenge, as higher concentrations of traditional UV absorbers often impart undesirable yellow tinting.
Compatibility issues between acrylic matrices and UV stabilizers represent another major hurdle. Many effective UV absorbers exhibit poor solubility in acrylic systems, leading to migration, blooming, and eventual performance loss. This incompatibility is particularly problematic in thin-film applications where stabilizer loading must be carefully balanced against physical property requirements.
The environmental persistence of certain UV stabilizers, particularly benzotriazoles and benzophenones, has raised regulatory concerns globally. Several jurisdictions have implemented or proposed restrictions on these compounds due to their potential environmental accumulation and ecotoxicity. This regulatory landscape creates uncertainty for manufacturers and necessitates the development of more environmentally benign alternatives.
Cost-effectiveness remains a significant barrier to widespread implementation of advanced UV protection systems. High-performance stabilizers can increase raw material costs by 15-30%, creating market resistance particularly in price-sensitive segments. The complex processing requirements of some stabilizer systems further increase manufacturing complexity and cost.
Synergistic effects between different UV stabilizer classes (absorbers, quenchers, and hindered amine light stabilizers) are poorly understood and often unpredictable in acrylic systems. This knowledge gap hampers the development of optimized stabilizer packages tailored to specific application requirements and exposure conditions.
Accelerated weathering tests frequently fail to accurately predict real-world performance, creating uncertainty in product development and qualification. The correlation between laboratory testing and actual field performance varies significantly depending on geographic location, orientation, and local environmental factors, complicating the validation of new stabilizer technologies.
Current UV stabilizers demonstrate limited long-term effectiveness, with performance typically declining after 2-3 years of outdoor exposure. This degradation timeline falls short of industry requirements, particularly in architectural, automotive, and outdoor signage applications where 5-10 year performance guarantees are standard. The trade-off between UV protection and optical clarity presents another significant challenge, as higher concentrations of traditional UV absorbers often impart undesirable yellow tinting.
Compatibility issues between acrylic matrices and UV stabilizers represent another major hurdle. Many effective UV absorbers exhibit poor solubility in acrylic systems, leading to migration, blooming, and eventual performance loss. This incompatibility is particularly problematic in thin-film applications where stabilizer loading must be carefully balanced against physical property requirements.
The environmental persistence of certain UV stabilizers, particularly benzotriazoles and benzophenones, has raised regulatory concerns globally. Several jurisdictions have implemented or proposed restrictions on these compounds due to their potential environmental accumulation and ecotoxicity. This regulatory landscape creates uncertainty for manufacturers and necessitates the development of more environmentally benign alternatives.
Cost-effectiveness remains a significant barrier to widespread implementation of advanced UV protection systems. High-performance stabilizers can increase raw material costs by 15-30%, creating market resistance particularly in price-sensitive segments. The complex processing requirements of some stabilizer systems further increase manufacturing complexity and cost.
Synergistic effects between different UV stabilizer classes (absorbers, quenchers, and hindered amine light stabilizers) are poorly understood and often unpredictable in acrylic systems. This knowledge gap hampers the development of optimized stabilizer packages tailored to specific application requirements and exposure conditions.
Accelerated weathering tests frequently fail to accurately predict real-world performance, creating uncertainty in product development and qualification. The correlation between laboratory testing and actual field performance varies significantly depending on geographic location, orientation, and local environmental factors, complicating the validation of new stabilizer technologies.
Current UV Stabilizer Integration Methods
01 UV stabilizers in acrylic resin compositions
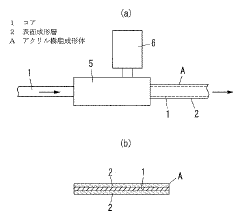
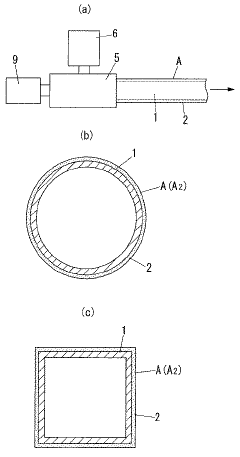
Various UV stabilizers can be incorporated into acrylic resin compositions to enhance their resistance to UV degradation. These stabilizers work by absorbing harmful UV radiation and converting it into less damaging forms of energy. Common UV stabilizers used in acrylic resins include benzotriazoles, benzophenones, and hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS). These additives help maintain the physical properties and appearance of acrylic materials exposed to outdoor conditions.- UV stabilizers in acrylic resin compositions: Various UV stabilizers can be incorporated into acrylic resin compositions to enhance their resistance to UV degradation. These stabilizers work by absorbing harmful UV radiation and dissipating it as heat or lower energy radiation, thereby protecting the polymer matrix. Common UV stabilizers used in acrylic resins include benzotriazoles, benzophenones, and hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS). These additives can significantly extend the service life of acrylic resin products exposed to outdoor conditions.
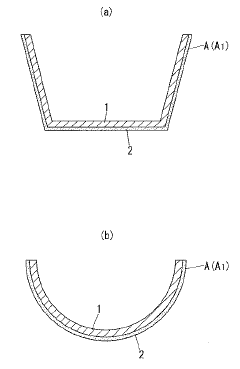
- Acrylic resin formulations with enhanced UV absorption properties: Specialized acrylic resin formulations can be developed with inherently improved UV absorption capabilities. These formulations may include modified acrylic monomers or copolymers with UV-absorbing functional groups chemically bonded to the polymer backbone. This approach provides more permanent UV protection compared to additive-based methods, as the UV-absorbing functionality becomes an integral part of the polymer structure and cannot migrate or leach out over time.
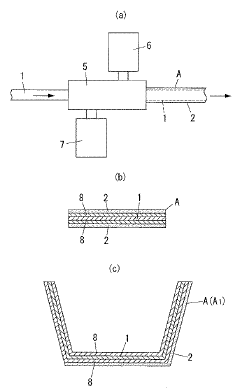
- Synergistic combinations of UV stabilizers for acrylic resins: Combining different types of UV stabilizers can create synergistic effects that provide superior protection compared to single-component systems. For example, using UV absorbers together with hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) can address different degradation mechanisms simultaneously. The UV absorbers prevent initial photodegradation by absorbing harmful radiation, while HALS act as radical scavengers to interrupt the degradation process. This multi-mechanism approach results in more comprehensive protection for acrylic resin systems.
- Nanoparticle-based UV protection for acrylic resins: Incorporating inorganic nanoparticles such as zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, or cerium oxide into acrylic resins can provide effective UV protection. These nanoparticles can absorb and scatter UV radiation while maintaining the transparency of the acrylic material due to their small size. The nanoscale dimensions also allow for better dispersion throughout the polymer matrix, resulting in more uniform protection. Additionally, surface-modified nanoparticles can improve compatibility with the acrylic resin and prevent agglomeration.
- Weatherable acrylic resin coatings with UV protection: Specialized acrylic resin coatings can be formulated with UV stabilizers to provide protection for underlying substrates. These coatings combine the inherent properties of acrylic resins (such as clarity, adhesion, and flexibility) with enhanced UV resistance. The coatings can be applied to various substrates including plastics, metals, and wood to extend their outdoor durability. Advanced formulations may include additional components such as antioxidants and thermal stabilizers to provide comprehensive protection against environmental degradation factors.
02 Acrylic resin formulations with enhanced UV protection
Specialized acrylic resin formulations can be developed with enhanced UV protection properties. These formulations often combine multiple types of UV absorbers and stabilizers to provide broad-spectrum protection. The acrylic matrix can be modified to improve compatibility with UV stabilizers, ensuring uniform distribution and long-term effectiveness. These enhanced formulations are particularly useful for applications requiring extended outdoor exposure or protection of sensitive substrates.Expand Specific Solutions03 Nanoparticle-enhanced UV absorption in acrylic systems
Incorporating nanoparticles such as zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, or cerium oxide into acrylic resin systems can significantly enhance UV absorption capabilities. These nanoparticles provide efficient UV blocking while maintaining transparency in the visible light spectrum. Surface modification of nanoparticles improves their dispersion in the acrylic matrix and prevents agglomeration, resulting in more effective UV protection and improved mechanical properties of the final product.Expand Specific Solutions04 Weatherable acrylic coating systems with UV stabilizers
Weatherable acrylic coating systems incorporate specialized UV stabilizers to provide long-term protection against environmental degradation. These coatings often feature synergistic combinations of UV absorbers, radical scavengers, and antioxidants to prevent yellowing, cracking, and loss of gloss. The stabilizers are carefully selected to be compatible with the acrylic resin system and to maintain their effectiveness throughout the service life of the coating, even under harsh outdoor conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Multi-functional acrylic additives with UV absorption properties
Multi-functional additives can be incorporated into acrylic resins to provide UV absorption along with other beneficial properties. These additives may combine UV protection with features such as thermal stability, flame retardancy, or antimicrobial activity. Some additives are designed to chemically bond with the acrylic polymer chains, preventing migration and leaching over time. This approach results in more durable UV protection and extended service life for acrylic products exposed to sunlight.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions
The UV stabilization market for acrylic resins is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by expanding applications in automotive, construction, and electronics sectors. The global market size is estimated to reach $1.2 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 5.8%. Technology maturity varies across different stabilization approaches, with companies demonstrating diverse capabilities. Industry leaders like BASF SE, LG Chem, and Arkema France have established advanced UV stabilizer portfolios, while Kaneka Corp., Sumitomo Chemical, and Toray Industries focus on specialized high-performance solutions. Japanese firms including Nippon Shokubai and Adeka Corp. have developed proprietary technologies for enhanced durability, while Chinese manufacturers like Wanhua Chemical are rapidly advancing their technical capabilities to compete in this increasingly sophisticated market.
LG Chem Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Chem has developed a comprehensive UV stabilization technology for acrylic resins marketed under their LUCIDA® series. Their approach combines benzophenone and benzotriazole-based UV absorbers with specialized antioxidants to create multi-functional protection systems. LG Chem's proprietary technology involves molecular encapsulation of UV absorbers within cyclodextrin structures, significantly improving their compatibility with acrylic matrices while reducing blooming effects. Their research has led to the development of oligomeric UV stabilizers with high molecular weights that resist migration and extraction, providing extended service life. LG Chem has also pioneered the use of reactive UV stabilizers that can chemically bond to acrylic polymer chains during polymerization, creating inherently UV-resistant materials. Their testing protocols have demonstrated that these systems can maintain optical clarity and mechanical properties after exposure to over 10,000 hours of accelerated weathering conditions, representing a significant advancement over conventional technologies.
Strengths: Excellent retention of optical properties; superior resistance to extraction and migration; comprehensive protection against multiple degradation mechanisms. Weaknesses: Higher processing complexity; potential color shifts in some formulations; requires careful control of polymerization conditions when using reactive stabilizers.
SABIC Global Technologies BV
Technical Solution: SABIC has developed innovative UV stabilization technologies for acrylic resins through their CYASORB® and LEXAN® product lines. Their approach integrates UV absorbers with specialized light stabilizers in carefully engineered ratios to provide comprehensive protection. SABIC's technology employs hydroxyphenyl triazine (HPT) UV absorbers that offer superior photostability compared to traditional benzotriazoles, particularly in high-temperature applications. Their proprietary manufacturing process creates stabilizer packages with controlled particle size distribution, ensuring optimal dispersion throughout acrylic matrices. SABIC has pioneered the development of red-shifted UV absorbers that provide protection further into the visible spectrum without compromising transparency. Their research has also led to the creation of synergistic stabilizer blends that can maintain mechanical properties after exposure to over 8,000 hours of accelerated weathering conditions. SABIC's latest innovation includes UV stabilizers with enhanced compatibility with various acrylic copolymers, addressing formulation challenges in specialized applications like automotive glazing and architectural panels.
Strengths: Excellent thermal stability of stabilizer packages; superior protection in high-intensity UV environments; good compatibility with various acrylic processing methods. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to conventional systems; some formulations may require additional processing steps; performance can vary with different acrylic copolymer compositions.
Key Patents in UV Absorption Enhancement
Acrylic resin molding
PatentInactiveJP2009173864A
Innovation
- An acrylic resin molding composition containing 0.1 to 1.0 parts by mass of an ultraviolet absorber, 0 to 0.5 parts by mass of a high molecular weight hindered amine light stabilizer, and 10 to 60 parts by mass of rubber, with a silicone-coated surface, improves impact resistance and weather resistance without surface bleeding.
Enhanced weather-ability acrylate based thermoplastic formulations incorporating synergistic UV photo-protective system
PatentInactiveMYPI2018701203A0
Innovation
- Incorporation of a synergistic UV photoprotective system combining dimeric benzotriazole UV absorber, hindered amine light stabilizers, antioxidants, and light screening agents to enhance weather resistance of acrylate-based thermoplastic resins.
- Achieving balanced performance between weather resistance, melt flowability, impact resistance, and aesthetic appearance through the specific combination of UV protective components.
- Development of a highly versatile and durable thermoplastic resin composition specifically designed for high-performance outdoor applications in construction, electronics, and automotive sectors.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental implications of enhancing acrylic resin with UV stabilizers extend beyond product performance to ecological considerations. The manufacturing processes for UV stabilizers often involve energy-intensive procedures and potentially hazardous chemicals, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. Traditional benzotriazole and benzophenone stabilizers, while effective, may contain compounds that persist in the environment and bioaccumulate in aquatic ecosystems when products eventually degrade or are disposed of improperly.
Recent lifecycle assessments indicate that certain UV stabilizers can leach from acrylic products during their service life, particularly when exposed to weathering conditions or acidic environments. Studies conducted by the Environmental Protection Agency have detected trace amounts of these compounds in surface waters, raising concerns about their long-term ecological impact. The environmental persistence of these compounds varies significantly, with half-lives ranging from several months to multiple years depending on environmental conditions.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly addressing these concerns. The European Union's REACH regulation has placed restrictions on several UV stabilizers due to environmental persistence concerns, while similar regulatory trends are emerging in North America and Asia-Pacific regions. This evolving regulatory landscape necessitates the development of more environmentally benign alternatives that maintain performance standards while reducing ecological footprint.
Promising developments in green chemistry approaches are yielding more sustainable UV stabilizer options. Bio-based stabilizers derived from natural phenolic compounds show potential for biodegradability while maintaining acceptable performance profiles. Additionally, encapsulation technologies that prevent leaching and controlled-release mechanisms are reducing the environmental mobility of these compounds when incorporated into acrylic resins.
Waste management considerations also factor significantly into environmental impact assessments. End-of-life scenarios for acrylic products containing UV stabilizers present challenges for recycling streams, as these additives can complicate material recovery processes. Advanced sorting technologies and chemical recycling methods are being developed to address these challenges, potentially enabling closed-loop systems for acrylic materials with specialized additives.
Water consumption and pollution metrics associated with UV stabilizer production reveal opportunities for process optimization. Manufacturers implementing green chemistry principles have reported reductions in water usage by up to 40% and hazardous waste generation by 35% compared to conventional production methods. These improvements demonstrate the feasibility of more sustainable manufacturing approaches without compromising product quality or economic viability.
Recent lifecycle assessments indicate that certain UV stabilizers can leach from acrylic products during their service life, particularly when exposed to weathering conditions or acidic environments. Studies conducted by the Environmental Protection Agency have detected trace amounts of these compounds in surface waters, raising concerns about their long-term ecological impact. The environmental persistence of these compounds varies significantly, with half-lives ranging from several months to multiple years depending on environmental conditions.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly addressing these concerns. The European Union's REACH regulation has placed restrictions on several UV stabilizers due to environmental persistence concerns, while similar regulatory trends are emerging in North America and Asia-Pacific regions. This evolving regulatory landscape necessitates the development of more environmentally benign alternatives that maintain performance standards while reducing ecological footprint.
Promising developments in green chemistry approaches are yielding more sustainable UV stabilizer options. Bio-based stabilizers derived from natural phenolic compounds show potential for biodegradability while maintaining acceptable performance profiles. Additionally, encapsulation technologies that prevent leaching and controlled-release mechanisms are reducing the environmental mobility of these compounds when incorporated into acrylic resins.
Waste management considerations also factor significantly into environmental impact assessments. End-of-life scenarios for acrylic products containing UV stabilizers present challenges for recycling streams, as these additives can complicate material recovery processes. Advanced sorting technologies and chemical recycling methods are being developed to address these challenges, potentially enabling closed-loop systems for acrylic materials with specialized additives.
Water consumption and pollution metrics associated with UV stabilizer production reveal opportunities for process optimization. Manufacturers implementing green chemistry principles have reported reductions in water usage by up to 40% and hazardous waste generation by 35% compared to conventional production methods. These improvements demonstrate the feasibility of more sustainable manufacturing approaches without compromising product quality or economic viability.
Durability Testing Protocols
Durability testing protocols for acrylic resins enhanced with UV stabilizers require systematic and comprehensive methodologies to evaluate long-term performance under various environmental conditions. Standard accelerated weathering tests form the foundation of these protocols, including QUV exposure (ASTM G154), which alternates UV light and moisture at controlled temperatures to simulate outdoor weathering conditions. Xenon arc testing (ASTM G155) provides a fuller spectrum simulation that more closely resembles natural sunlight, making it particularly valuable for evaluating the effectiveness of UV stabilizers in acrylic formulations.
Weather-Ometer testing represents another critical protocol, exposing samples to controlled cycles of light, temperature, and humidity to predict material degradation over time. These tests typically run for 1,000 to 5,000 hours, with periodic measurements of key performance indicators such as yellowness index, light transmission, and mechanical properties to track degradation patterns.
Real-time outdoor exposure testing complements accelerated methods, with samples placed in diverse geographic locations representing different climate conditions. Florida and Arizona exposures are industry standards due to their high UV intensity, while additional sites in humid tropical environments and industrial areas provide data on performance under varied environmental stressors. These tests typically run for 1-5 years, establishing correlation factors between accelerated and real-world performance.
Specialized protocols for acrylic resins with UV stabilizers include thermal cycling tests that evaluate material performance through temperature extremes (-40°C to 80°C), simulating seasonal variations. Chemical resistance testing exposes samples to common environmental contaminants including acid rain, cleaning agents, and pollutants to assess the stabilizers' effectiveness under chemical stress.
Mechanical property retention testing measures changes in tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexural properties after UV exposure, providing critical data on structural integrity maintenance. Optical property measurements track changes in light transmission, haze, and color shift using spectrophotometric analysis according to ASTM D1003 standards.
Advanced analytical techniques supplement these protocols, including FTIR spectroscopy to monitor chemical changes in the polymer structure and GPC (Gel Permeation Chromatography) to detect changes in molecular weight distribution resulting from UV-induced degradation. Cross-section analysis using microscopy techniques helps evaluate the depth of UV protection and degradation patterns throughout the material thickness.
Standardized reporting frameworks ensure consistency across testing programs, with results typically presented as percentage retention of key properties compared to unexposed controls, along with statistical analysis of variability and confidence intervals. These comprehensive protocols enable reliable prediction of service life and performance characteristics for UV-stabilized acrylic resin systems in various application environments.
Weather-Ometer testing represents another critical protocol, exposing samples to controlled cycles of light, temperature, and humidity to predict material degradation over time. These tests typically run for 1,000 to 5,000 hours, with periodic measurements of key performance indicators such as yellowness index, light transmission, and mechanical properties to track degradation patterns.
Real-time outdoor exposure testing complements accelerated methods, with samples placed in diverse geographic locations representing different climate conditions. Florida and Arizona exposures are industry standards due to their high UV intensity, while additional sites in humid tropical environments and industrial areas provide data on performance under varied environmental stressors. These tests typically run for 1-5 years, establishing correlation factors between accelerated and real-world performance.
Specialized protocols for acrylic resins with UV stabilizers include thermal cycling tests that evaluate material performance through temperature extremes (-40°C to 80°C), simulating seasonal variations. Chemical resistance testing exposes samples to common environmental contaminants including acid rain, cleaning agents, and pollutants to assess the stabilizers' effectiveness under chemical stress.
Mechanical property retention testing measures changes in tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexural properties after UV exposure, providing critical data on structural integrity maintenance. Optical property measurements track changes in light transmission, haze, and color shift using spectrophotometric analysis according to ASTM D1003 standards.
Advanced analytical techniques supplement these protocols, including FTIR spectroscopy to monitor chemical changes in the polymer structure and GPC (Gel Permeation Chromatography) to detect changes in molecular weight distribution resulting from UV-induced degradation. Cross-section analysis using microscopy techniques helps evaluate the depth of UV protection and degradation patterns throughout the material thickness.
Standardized reporting frameworks ensure consistency across testing programs, with results typically presented as percentage retention of key properties compared to unexposed controls, along with statistical analysis of variability and confidence intervals. These comprehensive protocols enable reliable prediction of service life and performance characteristics for UV-stabilized acrylic resin systems in various application environments.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!