Environmental Monitoring of Glacial Acetic Acid Emissions
AUG 5, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Glacial Acetic Acid Monitoring Background and Objectives
Glacial acetic acid, a concentrated form of acetic acid, has become a subject of increasing environmental concern due to its potential impact on ecosystems and human health. The monitoring of glacial acetic acid emissions has gained prominence in recent years as industrial processes and chemical manufacturing have expanded globally. This technological field has evolved from rudimentary detection methods to sophisticated real-time monitoring systems, reflecting the growing awareness of environmental protection and regulatory compliance.
The historical development of glacial acetic acid monitoring techniques can be traced back to the early 20th century when basic chemical analysis methods were employed. As industrial production of acetic acid increased, so did the need for more accurate and efficient monitoring solutions. The 1970s and 1980s saw significant advancements in analytical instrumentation, paving the way for more precise detection of acetic acid in various environmental matrices.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards continuous emission monitoring systems (CEMS) capable of providing real-time data on glacial acetic acid releases. This transition has been driven by stricter environmental regulations, increased public awareness, and the chemical industry's commitment to sustainable practices. The development of sensor technologies, coupled with advances in data processing and communication, has revolutionized the field of environmental monitoring for glacial acetic acid.
The primary objectives of current glacial acetic acid monitoring efforts are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a pressing need to accurately quantify emissions from industrial sources to ensure compliance with environmental standards and regulations. This involves developing robust monitoring systems that can operate reliably in diverse industrial settings and under varying environmental conditions.
Secondly, researchers and environmental agencies aim to enhance our understanding of the fate and transport of glacial acetic acid in the environment. This includes studying its atmospheric chemistry, deposition patterns, and potential impacts on ecosystems. Such knowledge is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies and assessing long-term environmental risks.
Another key objective is to improve the sensitivity and selectivity of detection methods. As regulatory thresholds become more stringent, there is a growing demand for monitoring technologies capable of detecting trace amounts of glacial acetic acid with high precision. This challenge is driving innovation in sensor design, sample collection techniques, and data analysis algorithms.
Furthermore, the integration of glacial acetic acid monitoring into broader environmental management systems is an emerging goal. This involves developing interoperable platforms that can combine acetic acid emission data with other environmental parameters to provide a comprehensive view of industrial impacts on local and regional scales.
The historical development of glacial acetic acid monitoring techniques can be traced back to the early 20th century when basic chemical analysis methods were employed. As industrial production of acetic acid increased, so did the need for more accurate and efficient monitoring solutions. The 1970s and 1980s saw significant advancements in analytical instrumentation, paving the way for more precise detection of acetic acid in various environmental matrices.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards continuous emission monitoring systems (CEMS) capable of providing real-time data on glacial acetic acid releases. This transition has been driven by stricter environmental regulations, increased public awareness, and the chemical industry's commitment to sustainable practices. The development of sensor technologies, coupled with advances in data processing and communication, has revolutionized the field of environmental monitoring for glacial acetic acid.
The primary objectives of current glacial acetic acid monitoring efforts are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a pressing need to accurately quantify emissions from industrial sources to ensure compliance with environmental standards and regulations. This involves developing robust monitoring systems that can operate reliably in diverse industrial settings and under varying environmental conditions.
Secondly, researchers and environmental agencies aim to enhance our understanding of the fate and transport of glacial acetic acid in the environment. This includes studying its atmospheric chemistry, deposition patterns, and potential impacts on ecosystems. Such knowledge is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies and assessing long-term environmental risks.
Another key objective is to improve the sensitivity and selectivity of detection methods. As regulatory thresholds become more stringent, there is a growing demand for monitoring technologies capable of detecting trace amounts of glacial acetic acid with high precision. This challenge is driving innovation in sensor design, sample collection techniques, and data analysis algorithms.
Furthermore, the integration of glacial acetic acid monitoring into broader environmental management systems is an emerging goal. This involves developing interoperable platforms that can combine acetic acid emission data with other environmental parameters to provide a comprehensive view of industrial impacts on local and regional scales.
Market Demand for Emission Monitoring Solutions
The market demand for emission monitoring solutions, particularly for glacial acetic acid, has been steadily increasing due to growing environmental concerns and stricter regulatory requirements. Industries such as chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, which utilize glacial acetic acid in their processes, are facing mounting pressure to monitor and control their emissions effectively.
Environmental agencies worldwide have been implementing more stringent regulations on industrial emissions, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs) like glacial acetic acid. This regulatory landscape has created a significant market opportunity for advanced monitoring solutions. Companies are now required to invest in sophisticated monitoring systems to ensure compliance and avoid hefty fines or operational shutdowns.
The global market for environmental monitoring equipment is projected to experience substantial growth in the coming years. This growth is driven by factors such as increasing awareness of environmental issues, technological advancements in monitoring devices, and the need for real-time data to support decision-making processes in industrial operations.
Specifically, for glacial acetic acid emissions monitoring, there is a rising demand for solutions that offer high accuracy, reliability, and continuous monitoring capabilities. Industries are seeking systems that can detect even trace amounts of acetic acid in the air, as prolonged exposure can have detrimental effects on human health and the environment.
The market is also witnessing a shift towards integrated monitoring systems that can simultaneously track multiple pollutants, including glacial acetic acid. This trend is driven by the desire for comprehensive environmental management and the need to optimize operational costs by consolidating monitoring equipment.
Another key factor influencing market demand is the growing adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud-based monitoring solutions. These technologies enable remote monitoring, real-time alerts, and data analytics, which are highly valued by industries looking to improve their environmental performance and operational efficiency.
Emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, are expected to present significant growth opportunities for emission monitoring solutions. As these regions industrialize rapidly, there is an increasing focus on environmental protection and sustainable development, driving the adoption of advanced monitoring technologies.
In conclusion, the market demand for emission monitoring solutions, especially for glacial acetic acid, is robust and expected to grow. This demand is fueled by regulatory pressures, technological advancements, and a growing emphasis on environmental stewardship across industries worldwide.
Environmental agencies worldwide have been implementing more stringent regulations on industrial emissions, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs) like glacial acetic acid. This regulatory landscape has created a significant market opportunity for advanced monitoring solutions. Companies are now required to invest in sophisticated monitoring systems to ensure compliance and avoid hefty fines or operational shutdowns.
The global market for environmental monitoring equipment is projected to experience substantial growth in the coming years. This growth is driven by factors such as increasing awareness of environmental issues, technological advancements in monitoring devices, and the need for real-time data to support decision-making processes in industrial operations.
Specifically, for glacial acetic acid emissions monitoring, there is a rising demand for solutions that offer high accuracy, reliability, and continuous monitoring capabilities. Industries are seeking systems that can detect even trace amounts of acetic acid in the air, as prolonged exposure can have detrimental effects on human health and the environment.
The market is also witnessing a shift towards integrated monitoring systems that can simultaneously track multiple pollutants, including glacial acetic acid. This trend is driven by the desire for comprehensive environmental management and the need to optimize operational costs by consolidating monitoring equipment.
Another key factor influencing market demand is the growing adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud-based monitoring solutions. These technologies enable remote monitoring, real-time alerts, and data analytics, which are highly valued by industries looking to improve their environmental performance and operational efficiency.
Emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, are expected to present significant growth opportunities for emission monitoring solutions. As these regions industrialize rapidly, there is an increasing focus on environmental protection and sustainable development, driving the adoption of advanced monitoring technologies.
In conclusion, the market demand for emission monitoring solutions, especially for glacial acetic acid, is robust and expected to grow. This demand is fueled by regulatory pressures, technological advancements, and a growing emphasis on environmental stewardship across industries worldwide.
Current Challenges in Acetic Acid Detection
The detection of glacial acetic acid emissions presents several significant challenges in environmental monitoring. One of the primary difficulties lies in the development of sensitive and selective sensors capable of accurately measuring acetic acid concentrations in complex atmospheric mixtures. Current detection methods often struggle to differentiate between acetic acid and other volatile organic compounds, leading to potential false positives or inaccurate measurements.
Another major challenge is the need for real-time monitoring capabilities. Many existing detection systems require sample collection and laboratory analysis, resulting in delays between emission events and data acquisition. This time lag can hinder rapid response to environmental changes or potential hazards associated with acetic acid emissions.
The harsh environmental conditions typically found in glacial regions pose additional obstacles for detection equipment. Extreme temperatures, high humidity, and the presence of ice and snow can interfere with sensor performance and durability. Developing robust, weather-resistant monitoring systems that can withstand these conditions while maintaining accuracy and reliability remains a significant technical hurdle.
Furthermore, the spatial variability of acetic acid emissions from glacial sources complicates the design of effective monitoring networks. Determining optimal sensor placement to capture representative data across diverse glacial landscapes requires advanced modeling and data analysis techniques, which are still evolving in this field.
Calibration and standardization of acetic acid detection methods across different monitoring sites and studies also present ongoing challenges. The lack of universally accepted protocols for measurement and data reporting can hinder comparisons between different research efforts and limit the broader applicability of collected data.
Additionally, the low concentrations of acetic acid typically found in glacial environments push the limits of current detection technologies. Improving the sensitivity of sensors while maintaining their specificity and reducing interference from other atmospheric components remains an active area of research and development.
Lastly, the integration of acetic acid detection systems with other environmental monitoring parameters, such as temperature, humidity, and other trace gas measurements, presents both technical and data management challenges. Creating comprehensive, multi-parameter monitoring platforms that can provide a holistic view of glacial environments and their emissions is a complex undertaking that requires interdisciplinary collaboration and innovative approaches to data integration and analysis.
Another major challenge is the need for real-time monitoring capabilities. Many existing detection systems require sample collection and laboratory analysis, resulting in delays between emission events and data acquisition. This time lag can hinder rapid response to environmental changes or potential hazards associated with acetic acid emissions.
The harsh environmental conditions typically found in glacial regions pose additional obstacles for detection equipment. Extreme temperatures, high humidity, and the presence of ice and snow can interfere with sensor performance and durability. Developing robust, weather-resistant monitoring systems that can withstand these conditions while maintaining accuracy and reliability remains a significant technical hurdle.
Furthermore, the spatial variability of acetic acid emissions from glacial sources complicates the design of effective monitoring networks. Determining optimal sensor placement to capture representative data across diverse glacial landscapes requires advanced modeling and data analysis techniques, which are still evolving in this field.
Calibration and standardization of acetic acid detection methods across different monitoring sites and studies also present ongoing challenges. The lack of universally accepted protocols for measurement and data reporting can hinder comparisons between different research efforts and limit the broader applicability of collected data.
Additionally, the low concentrations of acetic acid typically found in glacial environments push the limits of current detection technologies. Improving the sensitivity of sensors while maintaining their specificity and reducing interference from other atmospheric components remains an active area of research and development.
Lastly, the integration of acetic acid detection systems with other environmental monitoring parameters, such as temperature, humidity, and other trace gas measurements, presents both technical and data management challenges. Creating comprehensive, multi-parameter monitoring platforms that can provide a holistic view of glacial environments and their emissions is a complex undertaking that requires interdisciplinary collaboration and innovative approaches to data integration and analysis.
Existing Acetic Acid Detection Methods
01 Production process optimization
Optimizing the production process of glacial acetic acid to reduce emissions. This includes improving reaction conditions, enhancing catalysts, and implementing more efficient separation techniques. These improvements can lead to higher yields and reduced waste, thereby minimizing overall emissions.- Process improvements for reducing glacial acetic acid emissions: Various process improvements have been developed to reduce glacial acetic acid emissions in industrial settings. These include optimizing reaction conditions, implementing closed-loop systems, and using more efficient catalysts. Such improvements can significantly decrease the amount of acetic acid released into the environment during production processes.
- Emission control technologies for glacial acetic acid: Specialized emission control technologies have been designed to capture and treat glacial acetic acid emissions. These may include scrubbers, adsorption systems, and thermal oxidizers. These technologies can effectively remove acetic acid from exhaust gases before they are released into the atmosphere, reducing environmental impact.
- Recovery and recycling of glacial acetic acid: Systems and methods for recovering and recycling glacial acetic acid from process streams and emissions have been developed. These techniques can involve distillation, membrane separation, or other purification processes to reclaim acetic acid for reuse in production, thereby reducing overall emissions and improving resource efficiency.
- Monitoring and detection systems for glacial acetic acid emissions: Advanced monitoring and detection systems have been created to accurately measure and track glacial acetic acid emissions in real-time. These systems can use various sensors and analytical techniques to provide early warning of potential leaks or excessive emissions, allowing for prompt corrective action.
- Alternative production methods to reduce glacial acetic acid use: Research has been conducted into alternative production methods that reduce or eliminate the use of glacial acetic acid in various industrial processes. These may include the use of different solvents, catalysts, or reaction pathways that produce less acetic acid as a byproduct or emission, thereby minimizing environmental impact.
02 Emission control systems
Implementing advanced emission control systems specifically designed for glacial acetic acid production. These systems may include scrubbers, condensers, and absorption units to capture and treat vapors and gases before they are released into the environment. Such systems can significantly reduce the amount of acetic acid emissions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Closed-loop systems and recycling
Developing closed-loop systems and recycling processes to minimize glacial acetic acid emissions. This approach involves capturing and reusing acetic acid vapors within the production process, reducing the need for fresh raw materials and decreasing overall emissions. It may also include the recovery and purification of acetic acid from waste streams.Expand Specific Solutions04 Alternative production methods
Exploring alternative production methods for glacial acetic acid that inherently produce fewer emissions. This may involve using different raw materials, developing new catalysts, or employing novel reaction pathways that result in reduced byproducts and emissions. These methods aim to address the emission issue at its source.Expand Specific Solutions05 Monitoring and control technologies
Implementing advanced monitoring and control technologies to detect and manage glacial acetic acid emissions in real-time. This includes the use of sensors, automated control systems, and data analytics to optimize production parameters, identify potential emission sources, and enable rapid response to any deviations. These technologies can help maintain emissions within acceptable limits and improve overall process efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Emission Monitoring Industry
The environmental monitoring of glacial acetic acid emissions is an emerging field within the broader context of industrial emissions control and environmental protection. The market is in its early growth stage, with increasing regulatory focus driving demand. While the exact market size is not specified, it is likely to expand as industries face stricter emissions standards. Technologically, the field is evolving rapidly, with companies like Aclima, Inc. and Project Canary PBC leading in innovative sensor technologies and data analytics for emissions monitoring. Established players such as General Electric Company and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. are also contributing their expertise in environmental monitoring solutions, indicating a growing maturity in the sector.
Aclima, Inc.
Technical Solution: Aclima specializes in environmental intelligence through a network of air quality sensors. For monitoring glacial acetic acid emissions, they employ a distributed sensor network combined with advanced data analytics. Their system uses high-precision electrochemical sensors capable of detecting ppb-level concentrations of acetic acid[1]. The data is collected in real-time and processed using machine learning algorithms to identify emission patterns and sources. Aclima's platform integrates meteorological data to account for atmospheric conditions affecting dispersion[2]. They also utilize mobile sensing units mounted on vehicles to create high-resolution pollution maps, allowing for comprehensive coverage of glacial areas[3].
Strengths: High-resolution spatial and temporal data, real-time monitoring capabilities, and advanced analytics for source identification. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in sensor deployment and maintenance in remote glacial environments.
SICK AG
Technical Solution: SICK AG has developed a laser-based monitoring system for detecting glacial acetic acid emissions. Their approach uses Quantum Cascade Laser (QCL) technology, which allows for highly selective and sensitive measurements of acetic acid in the atmosphere[10]. The system can detect concentrations as low as parts per billion (ppb) levels with minimal interference from other gases. SICK's monitoring stations are designed for long-term, unattended operation in harsh glacial environments, featuring robust enclosures and automated calibration routines. The data is transmitted in real-time to a central monitoring platform, where advanced algorithms process the information to create emission maps and trend analyses[11].
Strengths: High sensitivity and selectivity for acetic acid detection, robust design for long-term deployment in harsh conditions, and real-time data transmission capabilities. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to some other technologies, potential complexity in system maintenance and calibration in remote locations.
Innovative Sensor Technologies for Acetic Acid
Measurement of contaminant components in exhaust gas and reduction of excessive contaminant emissions during cold starts and while driving
PatentInactiveEP1002186A2
Innovation
- A system that measures pollutant concentrations in the exhaust gas path using a modular monitoring system capable of recording high and low concentrations, with an adsorption system that can be switched into the exhaust path to reduce emissions during cold starts and faults, and an on-board monitoring system that adjusts the starting process based on external conditions, along with data transmission and evaluation for various modes of transport.
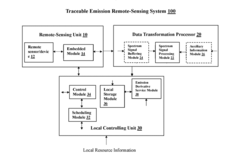
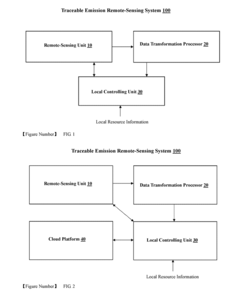
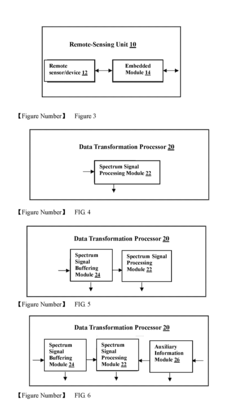
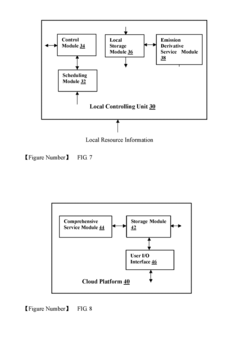
Traceable emission remote monitoring system and method
PatentInactiveUS20170350795A1
Innovation
- A traceable emission remote monitoring system that uses remote sensing units, transformation data processors, and cloud platforms to collect, analyze, and share emission data in real-time, enabling continuous, simultaneous detection across multiple locations without disrupting operations, and providing comprehensive analysis reports for regulatory purposes.
Regulatory Framework for Industrial Emissions
The regulatory framework for industrial emissions concerning glacial acetic acid is a complex and evolving landscape. At the international level, the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) provides overarching guidelines for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, which indirectly impacts acetic acid production and monitoring. The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015, further strengthens global efforts to limit industrial emissions and encourages nations to implement stricter regulations.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating industrial emissions, including those from glacial acetic acid production. The Clean Air Act (CAA) serves as the primary federal law governing air emissions from stationary and mobile sources. Under the CAA, the EPA has established National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP), which include specific regulations for acetic acid manufacturing facilities.
The European Union has implemented the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) to control emissions from various industrial activities. This directive sets out the main principles for permitting and controlling industrial installations, including those producing glacial acetic acid. The IED requires the use of Best Available Techniques (BAT) to prevent or minimize emissions and their impact on the environment.
In China, the Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE) oversees industrial emissions regulations. The Law on the Prevention and Control of Atmospheric Pollution provides the legal framework for managing air pollutants, including those from acetic acid production. The MEE has also issued specific emission standards for the chemical industry, which apply to glacial acetic acid manufacturers.
Many countries have implemented their own national regulations and standards for industrial emissions. These often include permitting systems, emission limits, monitoring requirements, and reporting obligations. For instance, Japan's Air Pollution Control Act sets emission standards for various pollutants and requires continuous monitoring for certain industrial processes.
Regulatory frameworks also often include provisions for environmental impact assessments, which are required before the construction or significant modification of industrial facilities. These assessments help identify potential environmental risks associated with glacial acetic acid emissions and guide the implementation of appropriate mitigation measures.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, regulatory frameworks are becoming increasingly stringent. Many jurisdictions are moving towards more comprehensive monitoring requirements, including real-time emission tracking and public reporting of emission data. This trend is likely to continue, placing greater pressure on glacial acetic acid producers to invest in advanced monitoring technologies and emission control systems.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating industrial emissions, including those from glacial acetic acid production. The Clean Air Act (CAA) serves as the primary federal law governing air emissions from stationary and mobile sources. Under the CAA, the EPA has established National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP), which include specific regulations for acetic acid manufacturing facilities.
The European Union has implemented the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) to control emissions from various industrial activities. This directive sets out the main principles for permitting and controlling industrial installations, including those producing glacial acetic acid. The IED requires the use of Best Available Techniques (BAT) to prevent or minimize emissions and their impact on the environment.
In China, the Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE) oversees industrial emissions regulations. The Law on the Prevention and Control of Atmospheric Pollution provides the legal framework for managing air pollutants, including those from acetic acid production. The MEE has also issued specific emission standards for the chemical industry, which apply to glacial acetic acid manufacturers.
Many countries have implemented their own national regulations and standards for industrial emissions. These often include permitting systems, emission limits, monitoring requirements, and reporting obligations. For instance, Japan's Air Pollution Control Act sets emission standards for various pollutants and requires continuous monitoring for certain industrial processes.
Regulatory frameworks also often include provisions for environmental impact assessments, which are required before the construction or significant modification of industrial facilities. These assessments help identify potential environmental risks associated with glacial acetic acid emissions and guide the implementation of appropriate mitigation measures.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, regulatory frameworks are becoming increasingly stringent. Many jurisdictions are moving towards more comprehensive monitoring requirements, including real-time emission tracking and public reporting of emission data. This trend is likely to continue, placing greater pressure on glacial acetic acid producers to invest in advanced monitoring technologies and emission control systems.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of glacial acetic acid emissions is a critical component in understanding the potential consequences of these emissions on ecosystems and human health. Glacial acetic acid, a concentrated form of acetic acid, can have significant effects on the environment when released into the atmosphere or water bodies.
In aquatic ecosystems, the introduction of glacial acetic acid can lead to a rapid decrease in pH levels, causing acidification of water bodies. This acidification can have detrimental effects on aquatic flora and fauna, disrupting the delicate balance of ecosystems. Fish populations may experience reduced reproductive success, while sensitive aquatic plants and microorganisms may struggle to survive in the altered chemical environment.
Terrestrial ecosystems are also at risk from glacial acetic acid emissions. When these emissions settle on soil or vegetation, they can cause localized acidification, potentially altering soil chemistry and affecting plant growth. This can lead to changes in vegetation composition and, consequently, impact the wildlife that depends on these habitats.
Air quality is another significant concern associated with glacial acetic acid emissions. The release of acetic acid vapors can contribute to the formation of photochemical smog and increase the concentration of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the atmosphere. These changes in air composition may lead to respiratory issues in both humans and animals, particularly in areas with high emission concentrations.
The potential for long-term environmental damage must be carefully evaluated. Chronic exposure to low levels of glacial acetic acid emissions may result in cumulative effects on ecosystems, potentially leading to gradual changes in biodiversity and ecosystem functions. This highlights the importance of continuous monitoring and assessment of emission levels and their impacts over extended periods.
Human health considerations are paramount in the environmental impact assessment. Exposure to glacial acetic acid vapors can cause irritation to the eyes, nose, and throat, and in high concentrations, may lead to more severe respiratory issues. Long-term exposure may potentially contribute to the development of chronic health conditions, emphasizing the need for stringent emission controls and worker safety protocols in industrial settings.
The assessment must also consider the potential for accidental releases or spills of glacial acetic acid. Such incidents could have immediate and severe impacts on local environments, requiring rapid response and remediation efforts. Developing comprehensive emergency response plans and implementing robust containment measures are essential components of responsible environmental management.
In aquatic ecosystems, the introduction of glacial acetic acid can lead to a rapid decrease in pH levels, causing acidification of water bodies. This acidification can have detrimental effects on aquatic flora and fauna, disrupting the delicate balance of ecosystems. Fish populations may experience reduced reproductive success, while sensitive aquatic plants and microorganisms may struggle to survive in the altered chemical environment.
Terrestrial ecosystems are also at risk from glacial acetic acid emissions. When these emissions settle on soil or vegetation, they can cause localized acidification, potentially altering soil chemistry and affecting plant growth. This can lead to changes in vegetation composition and, consequently, impact the wildlife that depends on these habitats.
Air quality is another significant concern associated with glacial acetic acid emissions. The release of acetic acid vapors can contribute to the formation of photochemical smog and increase the concentration of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the atmosphere. These changes in air composition may lead to respiratory issues in both humans and animals, particularly in areas with high emission concentrations.
The potential for long-term environmental damage must be carefully evaluated. Chronic exposure to low levels of glacial acetic acid emissions may result in cumulative effects on ecosystems, potentially leading to gradual changes in biodiversity and ecosystem functions. This highlights the importance of continuous monitoring and assessment of emission levels and their impacts over extended periods.
Human health considerations are paramount in the environmental impact assessment. Exposure to glacial acetic acid vapors can cause irritation to the eyes, nose, and throat, and in high concentrations, may lead to more severe respiratory issues. Long-term exposure may potentially contribute to the development of chronic health conditions, emphasizing the need for stringent emission controls and worker safety protocols in industrial settings.
The assessment must also consider the potential for accidental releases or spills of glacial acetic acid. Such incidents could have immediate and severe impacts on local environments, requiring rapid response and remediation efforts. Developing comprehensive emergency response plans and implementing robust containment measures are essential components of responsible environmental management.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!