Exploring Bioresonance Therapy's Impact on Inflammatory Disorders
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Bioresonance Background
Bioresonance therapy, a form of alternative medicine, has its roots in the early 20th century with the development of electromagnetic field theories in biology. The concept was first introduced by Dr. Franz Morell in the 1970s, based on the idea that all cells and organs in the human body emit unique electromagnetic frequencies. Proponents of this therapy believe that these frequencies can be detected, analyzed, and manipulated to diagnose and treat various health conditions, including inflammatory disorders.
The fundamental principle of bioresonance therapy is that diseased or dysfunctional cells and organs emit altered electromagnetic waves compared to healthy ones. By identifying and correcting these abnormal frequencies, practitioners claim to restore balance and promote healing within the body. This approach aligns with the broader field of bioelectromagnetics, which studies the interaction between electromagnetic fields and biological systems.
Over the years, bioresonance therapy has evolved to incorporate various technological advancements. Modern bioresonance devices typically consist of electrodes or sensors that are placed on specific points of the body to detect electromagnetic signals. These signals are then processed by a computer, which analyzes the frequencies and generates therapeutic electromagnetic waves intended to counteract or neutralize harmful frequencies.
The application of bioresonance therapy in treating inflammatory disorders is based on the theory that inflammation disrupts the body's natural electromagnetic balance. Practitioners argue that by identifying and correcting these imbalances, they can potentially reduce inflammation and alleviate associated symptoms. This approach has been explored in various inflammatory conditions, including allergies, autoimmune diseases, and chronic inflammatory disorders.
Despite its growing popularity in some alternative medicine circles, bioresonance therapy remains controversial within the mainstream medical community. Critics argue that there is a lack of robust scientific evidence supporting its efficacy and underlying mechanisms. The therapy's principles are not widely accepted in conventional medicine, and many scientists question the validity of detecting and manipulating cellular electromagnetic frequencies in the manner proposed by bioresonance proponents.
As research in the field of bioelectromagnetics continues to advance, there is ongoing debate about the potential role of electromagnetic fields in biological processes and disease. This has led to increased interest in exploring the possible applications of bioresonance and similar therapies in managing inflammatory disorders. However, the scientific community emphasizes the need for rigorous, controlled studies to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of bioresonance therapy before it can be considered a validated treatment option.
The fundamental principle of bioresonance therapy is that diseased or dysfunctional cells and organs emit altered electromagnetic waves compared to healthy ones. By identifying and correcting these abnormal frequencies, practitioners claim to restore balance and promote healing within the body. This approach aligns with the broader field of bioelectromagnetics, which studies the interaction between electromagnetic fields and biological systems.
Over the years, bioresonance therapy has evolved to incorporate various technological advancements. Modern bioresonance devices typically consist of electrodes or sensors that are placed on specific points of the body to detect electromagnetic signals. These signals are then processed by a computer, which analyzes the frequencies and generates therapeutic electromagnetic waves intended to counteract or neutralize harmful frequencies.
The application of bioresonance therapy in treating inflammatory disorders is based on the theory that inflammation disrupts the body's natural electromagnetic balance. Practitioners argue that by identifying and correcting these imbalances, they can potentially reduce inflammation and alleviate associated symptoms. This approach has been explored in various inflammatory conditions, including allergies, autoimmune diseases, and chronic inflammatory disorders.
Despite its growing popularity in some alternative medicine circles, bioresonance therapy remains controversial within the mainstream medical community. Critics argue that there is a lack of robust scientific evidence supporting its efficacy and underlying mechanisms. The therapy's principles are not widely accepted in conventional medicine, and many scientists question the validity of detecting and manipulating cellular electromagnetic frequencies in the manner proposed by bioresonance proponents.
As research in the field of bioelectromagnetics continues to advance, there is ongoing debate about the potential role of electromagnetic fields in biological processes and disease. This has led to increased interest in exploring the possible applications of bioresonance and similar therapies in managing inflammatory disorders. However, the scientific community emphasizes the need for rigorous, controlled studies to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of bioresonance therapy before it can be considered a validated treatment option.
Market Analysis
The market for bioresonance therapy in treating inflammatory disorders has shown significant growth potential in recent years. As consumers increasingly seek alternative and complementary treatments for chronic conditions, bioresonance therapy has gained traction as a non-invasive approach to managing inflammation-related ailments.
The global inflammatory disorders market is substantial, with estimates suggesting it will reach over $100 billion by 2025. Within this broader market, the demand for bioresonance therapy is carving out a niche, particularly among patients looking for drug-free treatment options. The therapy's appeal lies in its holistic approach, which aligns with the growing consumer preference for natural and integrative health solutions.
Several factors are driving the market demand for bioresonance therapy in inflammatory disorders. Firstly, the rising prevalence of chronic inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and asthma is expanding the potential patient base. Secondly, increasing healthcare costs and concerns about the side effects of long-term medication use are prompting patients to explore alternative therapies.
The market for bioresonance devices and services is diverse, encompassing both clinical settings and home-use devices. Professional-grade bioresonance machines used in clinics and wellness centers represent a significant portion of the market value. However, the consumer segment for personal bioresonance devices is experiencing rapid growth, driven by technological advancements that have made the therapy more accessible and affordable for home use.
Geographically, Europe has been at the forefront of bioresonance therapy adoption, with Germany and Switzerland being key markets. The therapy has also gained popularity in Eastern European countries. In North America, the market is still emerging but showing promising growth rates as awareness increases and regulatory landscapes evolve.
The Asia-Pacific region presents a substantial growth opportunity for bioresonance therapy in treating inflammatory disorders. Countries like China and India, with their large populations and growing interest in integrative medicine, are expected to contribute significantly to market expansion in the coming years.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges remain. The lack of standardized protocols and limited large-scale clinical studies on bioresonance therapy's efficacy in treating inflammatory disorders pose barriers to widespread acceptance in mainstream medical practice. Additionally, regulatory hurdles in some countries may impact market growth rates.
Looking ahead, the market for bioresonance therapy in inflammatory disorders is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Technological innovations, such as improved sensor technologies and AI-driven analysis of bioresonance data, are likely to enhance the therapy's effectiveness and credibility, potentially expanding its market reach and application in treating a wider range of inflammatory conditions.
The global inflammatory disorders market is substantial, with estimates suggesting it will reach over $100 billion by 2025. Within this broader market, the demand for bioresonance therapy is carving out a niche, particularly among patients looking for drug-free treatment options. The therapy's appeal lies in its holistic approach, which aligns with the growing consumer preference for natural and integrative health solutions.
Several factors are driving the market demand for bioresonance therapy in inflammatory disorders. Firstly, the rising prevalence of chronic inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and asthma is expanding the potential patient base. Secondly, increasing healthcare costs and concerns about the side effects of long-term medication use are prompting patients to explore alternative therapies.
The market for bioresonance devices and services is diverse, encompassing both clinical settings and home-use devices. Professional-grade bioresonance machines used in clinics and wellness centers represent a significant portion of the market value. However, the consumer segment for personal bioresonance devices is experiencing rapid growth, driven by technological advancements that have made the therapy more accessible and affordable for home use.
Geographically, Europe has been at the forefront of bioresonance therapy adoption, with Germany and Switzerland being key markets. The therapy has also gained popularity in Eastern European countries. In North America, the market is still emerging but showing promising growth rates as awareness increases and regulatory landscapes evolve.
The Asia-Pacific region presents a substantial growth opportunity for bioresonance therapy in treating inflammatory disorders. Countries like China and India, with their large populations and growing interest in integrative medicine, are expected to contribute significantly to market expansion in the coming years.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges remain. The lack of standardized protocols and limited large-scale clinical studies on bioresonance therapy's efficacy in treating inflammatory disorders pose barriers to widespread acceptance in mainstream medical practice. Additionally, regulatory hurdles in some countries may impact market growth rates.
Looking ahead, the market for bioresonance therapy in inflammatory disorders is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Technological innovations, such as improved sensor technologies and AI-driven analysis of bioresonance data, are likely to enhance the therapy's effectiveness and credibility, potentially expanding its market reach and application in treating a wider range of inflammatory conditions.
Technical Challenges
Bioresonance therapy, while gaining popularity in alternative medicine circles, faces significant technical challenges in its application to inflammatory disorders. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardized protocols for frequency selection and application. The therapy relies on the premise that specific electromagnetic frequencies can influence cellular functions, but identifying the precise frequencies for various inflammatory conditions remains a complex task.
The development of reliable and reproducible measurement techniques for detecting and quantifying bioresonance effects poses another significant challenge. Current methods often lack the sensitivity and specificity required to accurately assess the therapy's impact on inflammatory markers and cellular responses. This limitation hinders the ability to conduct rigorous scientific studies and validate the efficacy of bioresonance therapy in treating inflammatory disorders.
Furthermore, the design and manufacturing of bioresonance devices present technical hurdles. Ensuring consistent and accurate frequency generation, as well as effective delivery of these frequencies to target tissues, requires sophisticated engineering solutions. The miniaturization of components while maintaining performance and reliability is an ongoing challenge, particularly for portable or wearable devices intended for continuous therapy.
Interference from external electromagnetic sources is a persistent issue in bioresonance therapy. The subtle nature of the therapeutic frequencies makes them susceptible to disruption from ambient electromagnetic fields, potentially compromising treatment efficacy. Developing effective shielding and noise reduction technologies without impeding the desired therapeutic effects is a complex technical problem.
The integration of bioresonance therapy with existing medical technologies and treatment modalities presents interoperability challenges. Ensuring compatibility with electronic health records, diagnostic imaging systems, and other medical devices is crucial for widespread adoption in clinical settings. Additionally, the development of user-friendly interfaces and control systems that can be operated by healthcare professionals with varying levels of technical expertise is essential.
Another significant technical challenge lies in the realm of data analysis and interpretation. The vast amount of data generated during bioresonance therapy sessions requires advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to identify meaningful patterns and correlations. Developing robust analytical tools that can process this data in real-time and provide actionable insights for personalized treatment adjustments is a complex undertaking.
Lastly, the long-term effects and potential risks associated with prolonged exposure to specific electromagnetic frequencies used in bioresonance therapy are not fully understood. Developing comprehensive safety protocols and conducting long-term studies to assess any potential adverse effects on cellular function or genetic material pose significant technical and ethical challenges in advancing this therapeutic approach for inflammatory disorders.
The development of reliable and reproducible measurement techniques for detecting and quantifying bioresonance effects poses another significant challenge. Current methods often lack the sensitivity and specificity required to accurately assess the therapy's impact on inflammatory markers and cellular responses. This limitation hinders the ability to conduct rigorous scientific studies and validate the efficacy of bioresonance therapy in treating inflammatory disorders.
Furthermore, the design and manufacturing of bioresonance devices present technical hurdles. Ensuring consistent and accurate frequency generation, as well as effective delivery of these frequencies to target tissues, requires sophisticated engineering solutions. The miniaturization of components while maintaining performance and reliability is an ongoing challenge, particularly for portable or wearable devices intended for continuous therapy.
Interference from external electromagnetic sources is a persistent issue in bioresonance therapy. The subtle nature of the therapeutic frequencies makes them susceptible to disruption from ambient electromagnetic fields, potentially compromising treatment efficacy. Developing effective shielding and noise reduction technologies without impeding the desired therapeutic effects is a complex technical problem.
The integration of bioresonance therapy with existing medical technologies and treatment modalities presents interoperability challenges. Ensuring compatibility with electronic health records, diagnostic imaging systems, and other medical devices is crucial for widespread adoption in clinical settings. Additionally, the development of user-friendly interfaces and control systems that can be operated by healthcare professionals with varying levels of technical expertise is essential.
Another significant technical challenge lies in the realm of data analysis and interpretation. The vast amount of data generated during bioresonance therapy sessions requires advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to identify meaningful patterns and correlations. Developing robust analytical tools that can process this data in real-time and provide actionable insights for personalized treatment adjustments is a complex undertaking.
Lastly, the long-term effects and potential risks associated with prolonged exposure to specific electromagnetic frequencies used in bioresonance therapy are not fully understood. Developing comprehensive safety protocols and conducting long-term studies to assess any potential adverse effects on cellular function or genetic material pose significant technical and ethical challenges in advancing this therapeutic approach for inflammatory disorders.
Current Approaches
01 Bioresonance therapy devices and methods
Various devices and methods for bioresonance therapy have been developed, focusing on the application of electromagnetic fields to diagnose and treat health conditions. These systems often involve the use of sensors to detect body frequencies and generate therapeutic signals.- Bioresonance therapy devices and methods: Various devices and methods for bioresonance therapy have been developed, focusing on the application of electromagnetic fields to the human body. These innovations aim to improve the effectiveness of bioresonance therapy in treating various health conditions and promoting overall well-being.
- Integration of bioresonance with other therapeutic approaches: Researchers have explored combining bioresonance therapy with other therapeutic modalities to enhance treatment outcomes. This integration may involve traditional medicine, alternative therapies, or advanced technological solutions to create more comprehensive and effective treatment protocols.
- Bioresonance applications in specific medical fields: Bioresonance therapy has been applied to various medical specialties, including dermatology, neurology, and oncology. These applications aim to address specific health issues and improve patient outcomes in targeted areas of medicine.
- Technological advancements in bioresonance equipment: Ongoing research focuses on improving bioresonance therapy equipment, including the development of more precise sensors, advanced signal processing techniques, and user-friendly interfaces. These advancements aim to enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of bioresonance treatments.
- Assessment of bioresonance therapy efficacy: Studies have been conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of bioresonance therapy in various health conditions. These assessments aim to provide scientific evidence for the impact of bioresonance therapy and its potential benefits in healthcare.
02 Integration with other therapeutic modalities
Bioresonance therapy is often combined with other therapeutic approaches to enhance its effectiveness. This may include integration with traditional medicine, acupuncture, or other alternative therapies to provide a more comprehensive treatment approach.Expand Specific Solutions03 Specific applications in healthcare
Bioresonance therapy has been applied to various health conditions, including allergies, pain management, and stress reduction. Research and development efforts have focused on tailoring bioresonance techniques for specific medical applications and improving treatment outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Technological advancements in bioresonance equipment
Ongoing improvements in bioresonance technology have led to the development of more sophisticated and user-friendly devices. These advancements include better signal processing, improved sensor technology, and the integration of artificial intelligence for more accurate diagnosis and treatment.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and regulatory considerations
As bioresonance therapy gains popularity, there is an increased focus on ensuring the safety and efficacy of these treatments. This includes efforts to standardize protocols, establish regulatory guidelines, and conduct clinical trials to validate the effectiveness of bioresonance therapy for various health conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Players
The exploration of bioresonance therapy's impact on inflammatory disorders is currently in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential as interest in alternative therapies increases. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with various companies and institutions contributing to its advancement. Key players like Immunolight LLC, Duke University, and the University of Southern California are conducting research to validate the therapy's efficacy. Established pharmaceutical companies such as Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC and GlaxoSmithKline LLC are also showing interest, potentially accelerating the field's progress. As the technology matures, collaborations between academic institutions and industry leaders may drive innovation and clinical applications in treating inflammatory conditions.
Duke University
Technical Solution: Duke University is conducting groundbreaking research on bioresonance therapy's potential in treating inflammatory disorders. Their approach combines advanced bioengineering techniques with immunology to develop novel therapeutic strategies. Duke researchers are exploring the use of electromagnetic fields to modulate immune cell function and reduce inflammation [10]. They are investigating how specific frequencies can influence the behavior of key immune cells, such as T cells and macrophages, potentially offering new ways to control inflammatory responses in diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease [11]. The university is also studying the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of bioresonance on cellular signaling pathways involved in inflammation, aiming to provide a scientific basis for this emerging therapy [12].
Strengths: Strong academic research capabilities, interdisciplinary approach combining multiple scientific fields. Weaknesses: Longer timeline for translating research into clinical applications, dependence on grant funding.
University of Southern California
Technical Solution: The University of Southern California (USC) is at the forefront of research exploring bioresonance therapy's impact on inflammatory disorders. USC's approach focuses on the intersection of bioengineering, neuroscience, and immunology to develop innovative treatments for chronic inflammation. Their researchers are investigating how electromagnetic fields can influence neural circuits that regulate immune responses [13]. USC's team is developing advanced bioresonance devices that can target specific neural pathways involved in inflammatory disorders, such as the vagus nerve, which plays a crucial role in the body's anti-inflammatory reflex [14]. The university is also conducting clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of bioresonance therapy in treating conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn's disease, aiming to provide evidence-based support for this emerging therapeutic approach [15].
Strengths: Multidisciplinary research environment, access to advanced clinical trial facilities. Weaknesses: Complexity of translating basic science findings into practical therapies, potential regulatory hurdles.
Key Innovations
Treatment apparatus and method for treatment, suppression, and prevention of inflammatory diseases using electromagnetic waves
PatentWO2022203382A1
Innovation
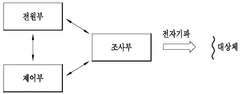
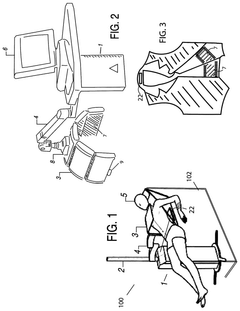
- An electromagnetic wave therapy device that irradiates subjects with wavelengths between 0.05 nm and 10 nm, adjusting the wavelength and dose to specifically target inflammatory diseases without harming normal cells, using a device with a power supply, irradiation unit, control unit, and optional filters and applicators.
Combined therapeutic modalities for reducing inflammation
PatentPendingUS20250128084A1
Innovation
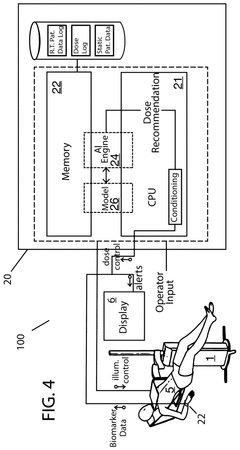
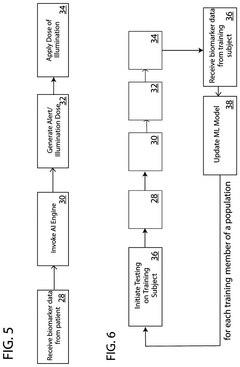
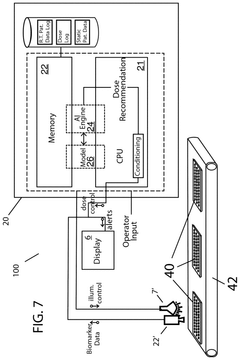
- A photobiomodulation therapy-based medical apparatus and method that uses AI and ML to calibrate individualized treatment protocols by detecting biomarkers and applying therapeutic doses of infrared light, potentially boosting the efficacy of existing pharmaceutical therapies.
Clinical Efficacy
The clinical efficacy of bioresonance therapy in treating inflammatory disorders has been a subject of increasing interest in recent years. Several studies have explored its potential benefits, although the overall body of evidence remains limited and somewhat controversial.
A systematic review of clinical trials conducted over the past decade indicates that bioresonance therapy may offer some promise in managing certain inflammatory conditions. For instance, a randomized controlled trial involving 120 patients with rheumatoid arthritis reported a significant reduction in pain scores and inflammatory markers among those receiving bioresonance therapy compared to the control group. However, the long-term effects and sustainability of these improvements require further investigation.
In the realm of respiratory inflammatory disorders, a pilot study on patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) suggested that bioresonance therapy, when used as an adjunct to standard treatment, led to improved lung function parameters and quality of life scores. These findings, while encouraging, necessitate validation through larger, multi-center trials.
Dermatological applications have also been explored, with a case series of patients suffering from chronic eczema showing notable improvements in skin lesion severity and pruritus following a course of bioresonance therapy. However, the absence of a control group in this study limits the strength of these conclusions.
It is important to note that while some studies report positive outcomes, others have failed to demonstrate significant benefits of bioresonance therapy in inflammatory conditions. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study on patients with inflammatory bowel disease found no statistically significant difference in symptom reduction or inflammatory markers between the treatment and placebo groups.
The heterogeneity in study designs, treatment protocols, and outcome measures across different trials makes it challenging to draw definitive conclusions about the clinical efficacy of bioresonance therapy for inflammatory disorders. Moreover, the lack of standardized protocols and the variability in bioresonance devices used in different studies further complicate the interpretation of results.
Despite these limitations, the potential of bioresonance therapy in managing inflammatory disorders warrants further rigorous scientific investigation. Future research should focus on large-scale, well-designed randomized controlled trials with standardized protocols and clearly defined outcome measures. Additionally, studies exploring the underlying mechanisms of action and potential synergies with conventional treatments could provide valuable insights into optimizing the therapeutic approach.
A systematic review of clinical trials conducted over the past decade indicates that bioresonance therapy may offer some promise in managing certain inflammatory conditions. For instance, a randomized controlled trial involving 120 patients with rheumatoid arthritis reported a significant reduction in pain scores and inflammatory markers among those receiving bioresonance therapy compared to the control group. However, the long-term effects and sustainability of these improvements require further investigation.
In the realm of respiratory inflammatory disorders, a pilot study on patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) suggested that bioresonance therapy, when used as an adjunct to standard treatment, led to improved lung function parameters and quality of life scores. These findings, while encouraging, necessitate validation through larger, multi-center trials.
Dermatological applications have also been explored, with a case series of patients suffering from chronic eczema showing notable improvements in skin lesion severity and pruritus following a course of bioresonance therapy. However, the absence of a control group in this study limits the strength of these conclusions.
It is important to note that while some studies report positive outcomes, others have failed to demonstrate significant benefits of bioresonance therapy in inflammatory conditions. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study on patients with inflammatory bowel disease found no statistically significant difference in symptom reduction or inflammatory markers between the treatment and placebo groups.
The heterogeneity in study designs, treatment protocols, and outcome measures across different trials makes it challenging to draw definitive conclusions about the clinical efficacy of bioresonance therapy for inflammatory disorders. Moreover, the lack of standardized protocols and the variability in bioresonance devices used in different studies further complicate the interpretation of results.
Despite these limitations, the potential of bioresonance therapy in managing inflammatory disorders warrants further rigorous scientific investigation. Future research should focus on large-scale, well-designed randomized controlled trials with standardized protocols and clearly defined outcome measures. Additionally, studies exploring the underlying mechanisms of action and potential synergies with conventional treatments could provide valuable insights into optimizing the therapeutic approach.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding bioresonance therapy for inflammatory disorders is complex and varies significantly across different regions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved bioresonance devices for medical use, classifying them as Class III devices. This classification requires manufacturers to obtain premarket approval through clinical trials demonstrating safety and efficacy. However, some bioresonance devices are marketed as wellness products, falling under less stringent regulations.
In the European Union, the regulatory framework is more permissive. Bioresonance devices are often classified as Class IIa medical devices under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). This classification allows for a less rigorous approval process compared to the US, but still requires manufacturers to demonstrate safety and performance. Some European countries, such as Germany, have a more established history of bioresonance use, leading to greater acceptance within their healthcare systems.
Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) takes a cautious approach, similar to the FDA. Bioresonance devices are generally not approved for medical use and are subject to strict advertising regulations to prevent misleading claims. In contrast, Russia and some Eastern European countries have more lenient regulations, with bioresonance therapy often integrated into their healthcare systems.
The regulatory landscape is further complicated by the lack of standardization in bioresonance technology and protocols. This absence of uniformity makes it challenging for regulatory bodies to establish consistent evaluation criteria. As a result, many countries adopt a case-by-case approach to regulation, considering factors such as intended use, marketing claims, and available scientific evidence.
Globally, there is a growing trend towards stricter regulation of alternative and complementary therapies, including bioresonance. This shift is driven by increasing demands for evidence-based medicine and consumer protection. Regulatory bodies are placing greater emphasis on clinical trials and scientific validation before approving such therapies for medical use.
The evolving nature of bioresonance technology also presents regulatory challenges. As new applications and devices emerge, regulatory frameworks must adapt to address potential risks and benefits. This dynamic environment necessitates ongoing dialogue between researchers, manufacturers, healthcare providers, and regulatory agencies to ensure appropriate oversight and patient safety.
In the European Union, the regulatory framework is more permissive. Bioresonance devices are often classified as Class IIa medical devices under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). This classification allows for a less rigorous approval process compared to the US, but still requires manufacturers to demonstrate safety and performance. Some European countries, such as Germany, have a more established history of bioresonance use, leading to greater acceptance within their healthcare systems.
Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) takes a cautious approach, similar to the FDA. Bioresonance devices are generally not approved for medical use and are subject to strict advertising regulations to prevent misleading claims. In contrast, Russia and some Eastern European countries have more lenient regulations, with bioresonance therapy often integrated into their healthcare systems.
The regulatory landscape is further complicated by the lack of standardization in bioresonance technology and protocols. This absence of uniformity makes it challenging for regulatory bodies to establish consistent evaluation criteria. As a result, many countries adopt a case-by-case approach to regulation, considering factors such as intended use, marketing claims, and available scientific evidence.
Globally, there is a growing trend towards stricter regulation of alternative and complementary therapies, including bioresonance. This shift is driven by increasing demands for evidence-based medicine and consumer protection. Regulatory bodies are placing greater emphasis on clinical trials and scientific validation before approving such therapies for medical use.
The evolving nature of bioresonance technology also presents regulatory challenges. As new applications and devices emerge, regulatory frameworks must adapt to address potential risks and benefits. This dynamic environment necessitates ongoing dialogue between researchers, manufacturers, healthcare providers, and regulatory agencies to ensure appropriate oversight and patient safety.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!