Exploring Ionic Conductivity in Glacial Acetic Acid Solutions
AUG 5, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ionic Conductivity Background and Objectives
Ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions represents a fascinating area of study within electrochemistry and materials science. This field has evolved significantly over the past century, with early investigations focusing on the fundamental principles of ion transport in non-aqueous solvents. The unique properties of glacial acetic acid, including its high dielectric constant and ability to act as both a solvent and a weak electrolyte, have made it an intriguing medium for exploring ionic conductivity phenomena.
The evolution of this research area has been driven by advancements in measurement techniques and theoretical understanding of ion-solvent interactions. Early studies primarily utilized basic conductometric methods, while modern research employs sophisticated electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and advanced computational modeling. This progression has allowed for more precise characterization of ionic species behavior and transport mechanisms in glacial acetic acid solutions.
A key trend in the field has been the exploration of various electrolytes and their dissociation behavior in glacial acetic acid. Researchers have investigated a wide range of ionic compounds, from simple inorganic salts to complex organic electrolytes, to understand how molecular structure and ion size influence conductivity. This has led to important insights into the role of ion pairing, solvation dynamics, and the formation of complex ionic aggregates in non-aqueous media.
The primary objectives of current research in this area are multifaceted. One major goal is to develop a comprehensive understanding of the factors that influence ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions. This includes elucidating the mechanisms of ion transport, the effects of concentration on conductivity, and the impact of temperature and pressure on ionic mobility. Researchers aim to establish predictive models that can accurately describe conductivity behavior across a wide range of conditions and electrolyte compositions.
Another important objective is to explore potential applications of ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions. This includes investigating their use in novel battery technologies, electrochemical sensors, and as electrolytes in various industrial processes. The unique properties of these solutions may offer advantages in specific applications where aqueous electrolytes are unsuitable or less effective.
Furthermore, there is a growing interest in understanding the environmental and safety implications of working with glacial acetic acid-based electrolyte systems. This includes developing safer handling protocols and exploring more environmentally friendly alternatives that maintain similar conductivity properties. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in scientific research, this aspect of the field is likely to gain more attention in the coming years.
The evolution of this research area has been driven by advancements in measurement techniques and theoretical understanding of ion-solvent interactions. Early studies primarily utilized basic conductometric methods, while modern research employs sophisticated electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and advanced computational modeling. This progression has allowed for more precise characterization of ionic species behavior and transport mechanisms in glacial acetic acid solutions.
A key trend in the field has been the exploration of various electrolytes and their dissociation behavior in glacial acetic acid. Researchers have investigated a wide range of ionic compounds, from simple inorganic salts to complex organic electrolytes, to understand how molecular structure and ion size influence conductivity. This has led to important insights into the role of ion pairing, solvation dynamics, and the formation of complex ionic aggregates in non-aqueous media.
The primary objectives of current research in this area are multifaceted. One major goal is to develop a comprehensive understanding of the factors that influence ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions. This includes elucidating the mechanisms of ion transport, the effects of concentration on conductivity, and the impact of temperature and pressure on ionic mobility. Researchers aim to establish predictive models that can accurately describe conductivity behavior across a wide range of conditions and electrolyte compositions.
Another important objective is to explore potential applications of ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions. This includes investigating their use in novel battery technologies, electrochemical sensors, and as electrolytes in various industrial processes. The unique properties of these solutions may offer advantages in specific applications where aqueous electrolytes are unsuitable or less effective.
Furthermore, there is a growing interest in understanding the environmental and safety implications of working with glacial acetic acid-based electrolyte systems. This includes developing safer handling protocols and exploring more environmentally friendly alternatives that maintain similar conductivity properties. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in scientific research, this aspect of the field is likely to gain more attention in the coming years.
Market Analysis for Glacial Acetic Acid Solutions
The market for glacial acetic acid solutions, particularly in the context of ionic conductivity research, presents a complex and evolving landscape. The global acetic acid market, which includes glacial acetic acid, has been experiencing steady growth driven by increasing demand from various end-use industries. The market size for acetic acid was valued at over $8 billion in 2020, with projections indicating continued expansion in the coming years.
In the realm of ionic conductivity research, glacial acetic acid solutions play a crucial role due to their unique properties. The demand for these solutions in research and development activities has been growing, particularly in the fields of electrochemistry, materials science, and energy storage. This growth is fueled by the increasing focus on developing advanced energy storage systems, such as high-performance batteries and supercapacitors.
The market for glacial acetic acid solutions in ionic conductivity research is closely tied to the broader trends in the scientific research and development sector. Government and private sector investments in R&D, especially in emerging economies, are driving the demand for high-purity chemicals and solutions used in advanced research applications.
Key market segments for glacial acetic acid solutions include academic and research institutions, industrial research laboratories, and companies involved in the development of energy storage technologies. The pharmaceutical and electronics industries also contribute significantly to the demand, as ionic conductivity studies are crucial in drug delivery systems and electronic component development.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead in terms of market share due to their well-established research infrastructure and significant investments in scientific research. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing R&D expenditures in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
The market is characterized by a high degree of competition among key players, including major chemical companies and specialized laboratory chemical suppliers. These companies are focusing on product innovation, purity enhancement, and customization to meet the specific requirements of research applications.
Challenges in the market include stringent regulations regarding the handling and disposal of acetic acid, as well as the volatility in raw material prices. However, these challenges are offset by the growing applications of ionic conductivity research in emerging technologies, creating new opportunities for market expansion.
Looking ahead, the market for glacial acetic acid solutions in ionic conductivity research is expected to grow, driven by advancements in energy storage technologies, increasing focus on sustainable energy solutions, and ongoing research in materials science. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in materials research is also expected to open new avenues for the application of glacial acetic acid solutions in ionic conductivity studies.
In the realm of ionic conductivity research, glacial acetic acid solutions play a crucial role due to their unique properties. The demand for these solutions in research and development activities has been growing, particularly in the fields of electrochemistry, materials science, and energy storage. This growth is fueled by the increasing focus on developing advanced energy storage systems, such as high-performance batteries and supercapacitors.
The market for glacial acetic acid solutions in ionic conductivity research is closely tied to the broader trends in the scientific research and development sector. Government and private sector investments in R&D, especially in emerging economies, are driving the demand for high-purity chemicals and solutions used in advanced research applications.
Key market segments for glacial acetic acid solutions include academic and research institutions, industrial research laboratories, and companies involved in the development of energy storage technologies. The pharmaceutical and electronics industries also contribute significantly to the demand, as ionic conductivity studies are crucial in drug delivery systems and electronic component development.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead in terms of market share due to their well-established research infrastructure and significant investments in scientific research. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing R&D expenditures in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
The market is characterized by a high degree of competition among key players, including major chemical companies and specialized laboratory chemical suppliers. These companies are focusing on product innovation, purity enhancement, and customization to meet the specific requirements of research applications.
Challenges in the market include stringent regulations regarding the handling and disposal of acetic acid, as well as the volatility in raw material prices. However, these challenges are offset by the growing applications of ionic conductivity research in emerging technologies, creating new opportunities for market expansion.
Looking ahead, the market for glacial acetic acid solutions in ionic conductivity research is expected to grow, driven by advancements in energy storage technologies, increasing focus on sustainable energy solutions, and ongoing research in materials science. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in materials research is also expected to open new avenues for the application of glacial acetic acid solutions in ionic conductivity studies.
Current Challenges in Ionic Conductivity Measurement
Measuring ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions presents several significant challenges that researchers and industry professionals must overcome. The unique properties of glacial acetic acid, combined with the complexities of ionic behavior in non-aqueous solvents, create a complex environment for accurate conductivity measurements.
One of the primary challenges is the low dielectric constant of glacial acetic acid compared to water. This property affects the dissociation of electrolytes and the mobility of ions in solution, leading to potentially lower conductivity values and increased difficulty in obtaining precise measurements. The reduced ion mobility can result in slower equilibration times, requiring extended measurement periods to achieve stable readings.
The high viscosity of glacial acetic acid further complicates conductivity measurements. The increased resistance to ion movement can lead to underestimation of conductivity values if not properly accounted for in measurement techniques and data analysis. Additionally, the viscosity of the solution can change with temperature and concentration, necessitating careful control and calibration of measurement conditions.
Temperature dependence of ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions poses another significant challenge. The relationship between temperature and conductivity in these systems may not follow the same patterns observed in aqueous solutions, requiring the development of new models and correction factors for accurate interpretation of results across different temperature ranges.
The potential for chemical reactions between the acetic acid and the electrodes used in conductivity measurements introduces further complications. Electrode degradation or surface modifications can lead to drift in measurements over time and affect the reproducibility of results. Selecting appropriate electrode materials and implementing regular calibration protocols become crucial for maintaining measurement accuracy.
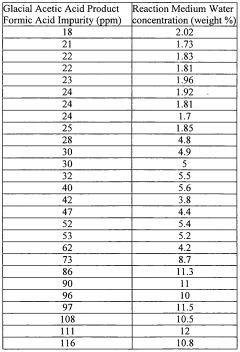
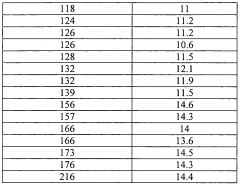
Impurities in glacial acetic acid, even at trace levels, can significantly impact conductivity measurements. The presence of water, in particular, can alter the solvent properties and ionic behavior. Ensuring the purity of the acetic acid and controlling environmental conditions to prevent water absorption during measurements are essential but challenging tasks.
The limited solubility of many electrolytes in glacial acetic acid compared to aqueous systems presents challenges in preparing solutions with sufficiently high ionic concentrations for reliable conductivity measurements. This limitation may require the development of specialized measurement techniques or the use of alternative electrolytes that exhibit better solubility in acetic acid.
Standardization of measurement protocols for ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions remains an ongoing challenge. The lack of widely accepted standard methods and reference materials specific to this solvent system complicates the comparison of results between different research groups and laboratories, hindering progress in the field.
One of the primary challenges is the low dielectric constant of glacial acetic acid compared to water. This property affects the dissociation of electrolytes and the mobility of ions in solution, leading to potentially lower conductivity values and increased difficulty in obtaining precise measurements. The reduced ion mobility can result in slower equilibration times, requiring extended measurement periods to achieve stable readings.
The high viscosity of glacial acetic acid further complicates conductivity measurements. The increased resistance to ion movement can lead to underestimation of conductivity values if not properly accounted for in measurement techniques and data analysis. Additionally, the viscosity of the solution can change with temperature and concentration, necessitating careful control and calibration of measurement conditions.
Temperature dependence of ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions poses another significant challenge. The relationship between temperature and conductivity in these systems may not follow the same patterns observed in aqueous solutions, requiring the development of new models and correction factors for accurate interpretation of results across different temperature ranges.
The potential for chemical reactions between the acetic acid and the electrodes used in conductivity measurements introduces further complications. Electrode degradation or surface modifications can lead to drift in measurements over time and affect the reproducibility of results. Selecting appropriate electrode materials and implementing regular calibration protocols become crucial for maintaining measurement accuracy.
Impurities in glacial acetic acid, even at trace levels, can significantly impact conductivity measurements. The presence of water, in particular, can alter the solvent properties and ionic behavior. Ensuring the purity of the acetic acid and controlling environmental conditions to prevent water absorption during measurements are essential but challenging tasks.
The limited solubility of many electrolytes in glacial acetic acid compared to aqueous systems presents challenges in preparing solutions with sufficiently high ionic concentrations for reliable conductivity measurements. This limitation may require the development of specialized measurement techniques or the use of alternative electrolytes that exhibit better solubility in acetic acid.
Standardization of measurement protocols for ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions remains an ongoing challenge. The lack of widely accepted standard methods and reference materials specific to this solvent system complicates the comparison of results between different research groups and laboratories, hindering progress in the field.
Existing Methods for Ionic Conductivity Exploration
01 Measurement of ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions
Various methods and apparatus are used to measure the ionic conductivity of glacial acetic acid solutions. These measurements are crucial for understanding the electrochemical properties of the solution and its potential applications in different industrial processes.- Measurement of ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions: Various methods and apparatus are used to measure the ionic conductivity of glacial acetic acid solutions. These measurements are crucial for understanding the behavior of ions in highly concentrated acetic acid environments. The conductivity data can be used to determine the degree of dissociation and ion mobility in these solutions.
- Effect of temperature on ionic conductivity of glacial acetic acid: Temperature plays a significant role in the ionic conductivity of glacial acetic acid solutions. As temperature increases, the ionic conductivity generally increases due to enhanced ion mobility and potentially increased dissociation. Studies have been conducted to quantify this relationship and develop models for predicting conductivity at various temperatures.
- Influence of impurities on glacial acetic acid conductivity: The presence of impurities, even in small amounts, can significantly affect the ionic conductivity of glacial acetic acid solutions. These impurities may include water, mineral acids, or organic compounds. Understanding and controlling the impact of impurities is crucial for maintaining consistent conductivity in industrial applications and analytical procedures.
- Applications of ionic conductivity measurements in acetic acid production: Ionic conductivity measurements of glacial acetic acid solutions are used in various stages of acetic acid production and purification. These measurements can serve as quality control parameters, help optimize production processes, and assist in monitoring the purity of the final product. Specialized equipment and techniques have been developed for in-line and real-time conductivity measurements in industrial settings.
- Relationship between acid strength and ionic conductivity: The ionic conductivity of glacial acetic acid solutions is related to its acid strength and degree of dissociation. Comparative studies with other organic acids and mineral acids have been conducted to understand this relationship. The findings contribute to the broader understanding of electrolyte behavior in non-aqueous solvents and have implications for various chemical processes and analytical methods.
02 Influence of temperature on ionic conductivity
The temperature of glacial acetic acid solutions significantly affects their ionic conductivity. Studies have been conducted to investigate the relationship between temperature changes and conductivity variations, which is important for optimizing processes involving these solutions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Effect of impurities on ionic conductivity
The presence of impurities in glacial acetic acid solutions can greatly impact their ionic conductivity. Research has been carried out to determine how different types and concentrations of impurities affect the conductivity, which is essential for maintaining the purity and efficiency of industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Applications of ionic conductivity measurements
Ionic conductivity measurements of glacial acetic acid solutions have various practical applications in industries such as chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. These measurements are used for quality control, process optimization, and product development.Expand Specific Solutions05 Relationship between concentration and ionic conductivity
The concentration of glacial acetic acid in solution has a significant impact on its ionic conductivity. Studies have been conducted to establish the correlation between concentration levels and conductivity values, which is crucial for understanding the behavior of these solutions in different applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Electrochemistry and Solution Analysis
The exploration of ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions represents an emerging field with significant potential for technological applications. The market is in its early stages, with a relatively small but growing size as researchers and industries recognize its importance in various sectors. The technology's maturity is still developing, with key players like Nippon Shokubai, Honeywell International Technologies, and Tokuyama Corp leading research efforts. Academic institutions such as the University of Montreal and the Technical University of Denmark are also contributing to advancements in this area. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established chemical companies and research institutions, each bringing unique expertise to push the boundaries of ionic conductivity in these solutions.
Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Nippon Shokubai has developed a novel approach to enhance ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions by incorporating specially designed polymer additives. Their method involves synthesizing acrylic-based copolymers with carefully controlled molecular weights and functional group distributions. These polymers act as ion-conducting channels within the glacial acetic acid matrix, significantly improving the overall ionic conductivity of the solution. The company has reported conductivity improvements of up to 300% compared to pure glacial acetic acid under certain conditions[1]. Additionally, they have implemented a proprietary cross-linking technique that enhances the stability of the polymer network in acidic environments, ensuring long-term performance and reliability[3].
Strengths: Significant conductivity enhancement, improved stability in acidic conditions, potential for customization. Weaknesses: May increase solution viscosity, possible compatibility issues with some electrochemical systems.
Honeywell International Technologies Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honeywell has developed an innovative approach to enhance ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions through the integration of advanced nanomaterials. Their technique involves dispersing carefully engineered carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene oxide (GO) sheets within the glacial acetic acid medium. These nanomaterials create a three-dimensional conductive network that facilitates ion transport throughout the solution. Honeywell's research has shown that this nanocomposite approach can increase ionic conductivity by up to 250% compared to unmodified glacial acetic acid[2]. Furthermore, they have developed a proprietary surface functionalization process for the nanomaterials, which enhances their compatibility with the acetic acid environment and prevents agglomeration, ensuring long-term stability of the conductive network[4].
Strengths: Significant conductivity enhancement, improved solution stability, potential for integration with other technologies. Weaknesses: Higher production costs, potential for nanomaterial-induced impurities.
Innovative Approaches in Conductivity Measurements
Specific ionic liquid and method for producing same
PatentInactiveUS20170149090A1
Innovation
- Development of novel ionic liquids formed by specific cation-anion associations, particularly using protic ionic liquids derived from proton transfer reactions, which can modulate viscosity and conductivity, enabling high power and energy densities when used in energy storage devices.
Reaction product of rhodium-catalyzed methanol carbonylation
PatentWO2008153708A2
Innovation
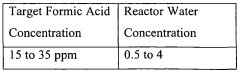
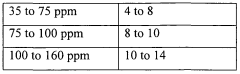
- Maintaining a reactor water concentration of 0.5 to 14 weight % and using an iodide salt with 2 to 20 wt% ionic iodide, 1 to 20 wt% methyl iodide, and 0.5 to 30 wt% methyl acetate in the reaction medium, while employing a Group VIII metal catalyst, to produce glacial acetic acid with controlled aldehyde and iodide concentrations.
Environmental Impact of Glacial Acetic Acid Usage
The use of glacial acetic acid in various industrial processes and research applications has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The production, transportation, and disposal of glacial acetic acid can lead to potential environmental hazards if not properly managed. One of the primary concerns is the release of acetic acid vapors into the atmosphere, which can contribute to air pollution and pose risks to human health and ecosystems.
When glacial acetic acid is released into aquatic environments, it can cause a rapid decrease in pH levels, leading to acidification of water bodies. This acidification can have detrimental effects on aquatic life, disrupting the balance of ecosystems and potentially causing harm to fish, plants, and other organisms. The impact can be particularly severe in freshwater systems with limited buffering capacity.
Soil contamination is another environmental concern associated with glacial acetic acid usage. Accidental spills or improper disposal can result in soil acidification, affecting plant growth and soil microbial communities. This can lead to long-term changes in soil chemistry and fertility, potentially impacting agricultural productivity and natural habitats.
The production of glacial acetic acid often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Additionally, the transportation of this corrosive substance poses risks of accidental spills during handling and shipping, which can have immediate and severe environmental consequences.
Proper waste management and disposal of glacial acetic acid and its byproducts are crucial to mitigate environmental impacts. Improper disposal can lead to contamination of groundwater and surface water sources, potentially affecting drinking water supplies and aquatic ecosystems. Recycling and recovery processes for acetic acid can help reduce waste and minimize environmental footprint, but these methods must be carefully implemented to avoid secondary environmental impacts.
To address these environmental concerns, industries and research institutions using glacial acetic acid must adopt stringent safety protocols, implement proper handling and storage procedures, and invest in environmentally friendly production and disposal methods. Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in setting and enforcing standards for the use and management of glacial acetic acid to protect the environment and public health.
As research into ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions progresses, it is essential to consider the environmental implications of increased usage and develop sustainable practices that minimize negative impacts while maximizing the benefits of this important chemical compound.
When glacial acetic acid is released into aquatic environments, it can cause a rapid decrease in pH levels, leading to acidification of water bodies. This acidification can have detrimental effects on aquatic life, disrupting the balance of ecosystems and potentially causing harm to fish, plants, and other organisms. The impact can be particularly severe in freshwater systems with limited buffering capacity.
Soil contamination is another environmental concern associated with glacial acetic acid usage. Accidental spills or improper disposal can result in soil acidification, affecting plant growth and soil microbial communities. This can lead to long-term changes in soil chemistry and fertility, potentially impacting agricultural productivity and natural habitats.
The production of glacial acetic acid often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Additionally, the transportation of this corrosive substance poses risks of accidental spills during handling and shipping, which can have immediate and severe environmental consequences.
Proper waste management and disposal of glacial acetic acid and its byproducts are crucial to mitigate environmental impacts. Improper disposal can lead to contamination of groundwater and surface water sources, potentially affecting drinking water supplies and aquatic ecosystems. Recycling and recovery processes for acetic acid can help reduce waste and minimize environmental footprint, but these methods must be carefully implemented to avoid secondary environmental impacts.
To address these environmental concerns, industries and research institutions using glacial acetic acid must adopt stringent safety protocols, implement proper handling and storage procedures, and invest in environmentally friendly production and disposal methods. Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in setting and enforcing standards for the use and management of glacial acetic acid to protect the environment and public health.
As research into ionic conductivity in glacial acetic acid solutions progresses, it is essential to consider the environmental implications of increased usage and develop sustainable practices that minimize negative impacts while maximizing the benefits of this important chemical compound.
Safety Protocols for Handling Acidic Solutions
When working with glacial acetic acid solutions for ionic conductivity experiments, strict safety protocols must be implemented to protect researchers and laboratory personnel. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential, including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and a lab coat. A well-ventilated workspace, preferably a fume hood, should be used to minimize exposure to acetic acid vapors. Proper storage of glacial acetic acid in tightly sealed containers away from heat sources and incompatible materials is crucial.
Emergency response procedures should be established and clearly communicated. This includes the location and proper use of eyewash stations, safety showers, and spill kits. A comprehensive spill response plan should be in place, detailing containment and neutralization procedures for acetic acid spills. Regular safety training sessions should be conducted to ensure all personnel are familiar with these protocols.
Handling and transfer of glacial acetic acid require careful attention. Use of appropriate transfer equipment, such as glass pipettes or pumps with chemical-resistant tubing, can minimize the risk of spills or splashes. When diluting glacial acetic acid, always add the acid to water slowly while stirring, never the reverse, to prevent dangerous heat generation and potential splashing.
Proper waste disposal is critical. Acetic acid solutions should never be disposed of down the drain. Instead, they should be collected in designated waste containers and handled according to local regulations for hazardous waste disposal. Neutralization of waste solutions may be necessary before disposal, but this should only be performed by trained personnel following established procedures.
Monitoring and maintenance of safety equipment is essential. Regular inspections of PPE, fume hoods, and emergency response equipment should be conducted and documented. Any deficiencies should be addressed promptly to ensure a safe working environment.
In the context of ionic conductivity experiments, additional precautions may be necessary. Electrical equipment used for conductivity measurements should be properly grounded and protected from potential acid exposure. Calibration and maintenance of conductivity meters should be performed regularly to ensure accurate and safe operation.
Lastly, a comprehensive risk assessment should be conducted before beginning any new experiments involving glacial acetic acid solutions. This assessment should consider the specific experimental setup, potential hazards, and necessary control measures. By implementing these safety protocols, researchers can minimize risks and conduct their ionic conductivity studies in glacial acetic acid solutions safely and effectively.
Emergency response procedures should be established and clearly communicated. This includes the location and proper use of eyewash stations, safety showers, and spill kits. A comprehensive spill response plan should be in place, detailing containment and neutralization procedures for acetic acid spills. Regular safety training sessions should be conducted to ensure all personnel are familiar with these protocols.
Handling and transfer of glacial acetic acid require careful attention. Use of appropriate transfer equipment, such as glass pipettes or pumps with chemical-resistant tubing, can minimize the risk of spills or splashes. When diluting glacial acetic acid, always add the acid to water slowly while stirring, never the reverse, to prevent dangerous heat generation and potential splashing.
Proper waste disposal is critical. Acetic acid solutions should never be disposed of down the drain. Instead, they should be collected in designated waste containers and handled according to local regulations for hazardous waste disposal. Neutralization of waste solutions may be necessary before disposal, but this should only be performed by trained personnel following established procedures.
Monitoring and maintenance of safety equipment is essential. Regular inspections of PPE, fume hoods, and emergency response equipment should be conducted and documented. Any deficiencies should be addressed promptly to ensure a safe working environment.
In the context of ionic conductivity experiments, additional precautions may be necessary. Electrical equipment used for conductivity measurements should be properly grounded and protected from potential acid exposure. Calibration and maintenance of conductivity meters should be performed regularly to ensure accurate and safe operation.
Lastly, a comprehensive risk assessment should be conducted before beginning any new experiments involving glacial acetic acid solutions. This assessment should consider the specific experimental setup, potential hazards, and necessary control measures. By implementing these safety protocols, researchers can minimize risks and conduct their ionic conductivity studies in glacial acetic acid solutions safely and effectively.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!