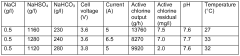
Exploring Sodium Bisulfate's Effectiveness in Pools
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Bisulfate in Pools: Background and Objectives
Sodium bisulfate, a chemical compound with the formula NaHSO4, has been utilized in pool maintenance for decades. This versatile substance plays a crucial role in maintaining water quality and ensuring a safe swimming environment. The evolution of pool chemistry has seen sodium bisulfate emerge as a preferred choice for pH adjustment due to its effectiveness and relative safety compared to other acidic compounds.
The primary objective of exploring sodium bisulfate's effectiveness in pools is to optimize water chemistry management and enhance overall pool maintenance practices. By understanding the compound's properties and applications, pool owners and operators can make informed decisions about its use, potentially improving water quality, reducing maintenance costs, and extending the lifespan of pool equipment.
Historically, pool maintenance relied on a variety of chemicals, including hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid, for pH control. However, these substances posed significant handling risks and could potentially damage pool surfaces. The introduction of sodium bisulfate as a safer alternative marked a significant milestone in pool chemistry. Its granular form and lower corrosivity made it more user-friendly while still effectively lowering pool water pH.
The technical evolution of sodium bisulfate in pool applications has focused on improving its dissolution rate, storage stability, and ease of application. Manufacturers have developed various formulations, including fast-dissolving granules and pre-measured packets, to enhance user convenience and ensure accurate dosing. These advancements have contributed to the widespread adoption of sodium bisulfate in both residential and commercial pool settings.
Current research and development efforts in this field aim to further optimize the use of sodium bisulfate in pools. Areas of focus include developing more environmentally friendly production methods, improving the compound's stability in varying water conditions, and exploring potential synergies with other pool chemicals to enhance overall water treatment efficacy.
As the pool industry continues to evolve, driven by factors such as increased environmental awareness and the demand for more efficient maintenance solutions, the role of sodium bisulfate is likely to expand. Future objectives may include developing smart dosing systems that automatically adjust pH levels using sodium bisulfate, integrating its use with IoT-enabled pool monitoring devices, and exploring novel formulations that combine pH adjustment with other water treatment functions.
The primary objective of exploring sodium bisulfate's effectiveness in pools is to optimize water chemistry management and enhance overall pool maintenance practices. By understanding the compound's properties and applications, pool owners and operators can make informed decisions about its use, potentially improving water quality, reducing maintenance costs, and extending the lifespan of pool equipment.
Historically, pool maintenance relied on a variety of chemicals, including hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid, for pH control. However, these substances posed significant handling risks and could potentially damage pool surfaces. The introduction of sodium bisulfate as a safer alternative marked a significant milestone in pool chemistry. Its granular form and lower corrosivity made it more user-friendly while still effectively lowering pool water pH.
The technical evolution of sodium bisulfate in pool applications has focused on improving its dissolution rate, storage stability, and ease of application. Manufacturers have developed various formulations, including fast-dissolving granules and pre-measured packets, to enhance user convenience and ensure accurate dosing. These advancements have contributed to the widespread adoption of sodium bisulfate in both residential and commercial pool settings.
Current research and development efforts in this field aim to further optimize the use of sodium bisulfate in pools. Areas of focus include developing more environmentally friendly production methods, improving the compound's stability in varying water conditions, and exploring potential synergies with other pool chemicals to enhance overall water treatment efficacy.
As the pool industry continues to evolve, driven by factors such as increased environmental awareness and the demand for more efficient maintenance solutions, the role of sodium bisulfate is likely to expand. Future objectives may include developing smart dosing systems that automatically adjust pH levels using sodium bisulfate, integrating its use with IoT-enabled pool monitoring devices, and exploring novel formulations that combine pH adjustment with other water treatment functions.
Market Analysis for Pool Chemical Solutions
The pool chemical solutions market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing number of residential and commercial swimming pools worldwide. This market segment encompasses a wide range of products, including sanitizers, pH adjusters, algaecides, and specialty chemicals. Among these, sodium bisulfate has emerged as a key player in pH adjustment and water treatment.
The global pool chemical market was valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.3 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 5.8%. This growth is attributed to factors such as rising disposable incomes, growing awareness of pool hygiene, and the expansion of the hospitality industry. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific.
Sodium bisulfate, also known as dry acid or pH decreaser, has gained popularity due to its effectiveness in lowering pool water pH and its safer handling compared to traditional liquid acids. The demand for sodium bisulfate in pool applications is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% from 2021 to 2026, outpacing the overall pool chemical market growth.
The market for sodium bisulfate in pool applications is characterized by a mix of large multinational chemical companies and specialized pool chemical manufacturers. Key players include Chemtrade Logistics, Olin Corporation, Southern Ionics, and Thatcher Group. These companies are investing in research and development to improve product formulations and expand their product lines to meet evolving customer needs.
Consumer trends indicate a growing preference for easy-to-use, multifunctional pool chemicals that simplify pool maintenance. This has led to the development of combination products that include sodium bisulfate along with other active ingredients. Additionally, there is an increasing demand for eco-friendly and low-impact pool chemicals, presenting opportunities for innovation in sodium bisulfate formulations and packaging.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the pool chemical solutions market. While commercial pool closures initially led to a decrease in demand, the surge in residential pool installations and increased focus on home maintenance have offset these losses. The pandemic has also accelerated the adoption of online sales channels for pool chemicals, with many consumers preferring contactless purchasing options.
Looking ahead, the market for sodium bisulfate and other pool chemical solutions is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as urbanization, increasing health consciousness, and the growing popularity of private pools in emerging markets will drive demand. However, manufacturers will need to address challenges such as regulatory pressures, raw material price fluctuations, and the need for sustainable packaging solutions to maintain their competitive edge in this evolving market landscape.
The global pool chemical market was valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.3 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 5.8%. This growth is attributed to factors such as rising disposable incomes, growing awareness of pool hygiene, and the expansion of the hospitality industry. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific.
Sodium bisulfate, also known as dry acid or pH decreaser, has gained popularity due to its effectiveness in lowering pool water pH and its safer handling compared to traditional liquid acids. The demand for sodium bisulfate in pool applications is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% from 2021 to 2026, outpacing the overall pool chemical market growth.
The market for sodium bisulfate in pool applications is characterized by a mix of large multinational chemical companies and specialized pool chemical manufacturers. Key players include Chemtrade Logistics, Olin Corporation, Southern Ionics, and Thatcher Group. These companies are investing in research and development to improve product formulations and expand their product lines to meet evolving customer needs.
Consumer trends indicate a growing preference for easy-to-use, multifunctional pool chemicals that simplify pool maintenance. This has led to the development of combination products that include sodium bisulfate along with other active ingredients. Additionally, there is an increasing demand for eco-friendly and low-impact pool chemicals, presenting opportunities for innovation in sodium bisulfate formulations and packaging.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the pool chemical solutions market. While commercial pool closures initially led to a decrease in demand, the surge in residential pool installations and increased focus on home maintenance have offset these losses. The pandemic has also accelerated the adoption of online sales channels for pool chemicals, with many consumers preferring contactless purchasing options.
Looking ahead, the market for sodium bisulfate and other pool chemical solutions is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as urbanization, increasing health consciousness, and the growing popularity of private pools in emerging markets will drive demand. However, manufacturers will need to address challenges such as regulatory pressures, raw material price fluctuations, and the need for sustainable packaging solutions to maintain their competitive edge in this evolving market landscape.
Current Challenges in Pool Water Treatment
Pool water treatment faces several significant challenges in maintaining water quality, safety, and user comfort. One of the primary issues is the constant struggle to maintain proper pH levels. Fluctuations in pH can lead to various problems, including eye and skin irritation, reduced effectiveness of disinfectants, and damage to pool equipment.
Chlorine management presents another major challenge. While chlorine is essential for disinfection, maintaining the right balance is crucial. Insufficient chlorine levels can lead to bacterial growth, while excessive levels can cause health issues and equipment damage. Additionally, the formation of chloramines, which result from chlorine combining with organic compounds, can create unpleasant odors and eye irritation.
Algae control remains a persistent challenge in pool maintenance. Algae growth can occur rapidly under favorable conditions, leading to slippery surfaces, cloudy water, and increased demand for chemicals. Preventing and treating algae outbreaks requires vigilant monitoring and timely intervention.
Water hardness and mineral content pose additional complications. High calcium hardness can lead to scale formation on pool surfaces and equipment, while low hardness can cause corrosion. Balancing these factors is essential for both pool longevity and water quality.
The presence of organic contaminants, such as body oils, sunscreen, and leaves, introduces another layer of complexity to pool water treatment. These substances can react with chlorine, reducing its effectiveness and potentially forming harmful byproducts.
Cyanuric acid (CYA) management is becoming an increasingly important aspect of pool maintenance. While CYA helps protect chlorine from UV degradation, excessive levels can reduce chlorine's effectiveness, leading to a condition known as "chlorine lock."
Water circulation and filtration efficiency also present ongoing challenges. Inadequate circulation can lead to dead spots where contaminants accumulate, while inefficient filtration can fail to remove fine particles and pathogens effectively.
Lastly, the environmental impact of pool chemicals and water usage is a growing concern. Balancing the need for effective water treatment with environmental responsibility requires careful consideration of chemical choices and water conservation strategies.
In light of these challenges, the exploration of sodium bisulfate's effectiveness in pools offers potential solutions, particularly in pH management and as an alternative to traditional chlorine-based treatments. Its ability to lower pH without introducing additional chlorine could address several of the issues mentioned, making it a promising area for further research and application in pool water treatment.
Chlorine management presents another major challenge. While chlorine is essential for disinfection, maintaining the right balance is crucial. Insufficient chlorine levels can lead to bacterial growth, while excessive levels can cause health issues and equipment damage. Additionally, the formation of chloramines, which result from chlorine combining with organic compounds, can create unpleasant odors and eye irritation.
Algae control remains a persistent challenge in pool maintenance. Algae growth can occur rapidly under favorable conditions, leading to slippery surfaces, cloudy water, and increased demand for chemicals. Preventing and treating algae outbreaks requires vigilant monitoring and timely intervention.
Water hardness and mineral content pose additional complications. High calcium hardness can lead to scale formation on pool surfaces and equipment, while low hardness can cause corrosion. Balancing these factors is essential for both pool longevity and water quality.
The presence of organic contaminants, such as body oils, sunscreen, and leaves, introduces another layer of complexity to pool water treatment. These substances can react with chlorine, reducing its effectiveness and potentially forming harmful byproducts.
Cyanuric acid (CYA) management is becoming an increasingly important aspect of pool maintenance. While CYA helps protect chlorine from UV degradation, excessive levels can reduce chlorine's effectiveness, leading to a condition known as "chlorine lock."
Water circulation and filtration efficiency also present ongoing challenges. Inadequate circulation can lead to dead spots where contaminants accumulate, while inefficient filtration can fail to remove fine particles and pathogens effectively.
Lastly, the environmental impact of pool chemicals and water usage is a growing concern. Balancing the need for effective water treatment with environmental responsibility requires careful consideration of chemical choices and water conservation strategies.
In light of these challenges, the exploration of sodium bisulfate's effectiveness in pools offers potential solutions, particularly in pH management and as an alternative to traditional chlorine-based treatments. Its ability to lower pH without introducing additional chlorine could address several of the issues mentioned, making it a promising area for further research and application in pool water treatment.
Existing Sodium Bisulfate Applications in Pools
01 Antimicrobial effectiveness
Sodium bisulfate demonstrates significant antimicrobial properties, making it effective in various applications such as food preservation, water treatment, and disinfection. Its ability to lower pH and create an acidic environment inhibits the growth of harmful microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses.- Antimicrobial effectiveness: Sodium bisulfate demonstrates significant antimicrobial properties, making it effective in various applications such as food preservation, water treatment, and disinfection. Its ability to lower pH and create an acidic environment inhibits the growth of harmful microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
- pH adjustment and acidification: Sodium bisulfate is widely used as an effective pH adjuster and acidifying agent in various industries. It can rapidly lower the pH of solutions, making it useful in water treatment, cleaning products, and industrial processes where precise pH control is crucial.
- Cleaning and descaling applications: The effectiveness of sodium bisulfate in cleaning and descaling applications is notable. It is used in formulations for removing mineral deposits, limescale, and rust from various surfaces and equipment. Its acidic nature helps dissolve and remove stubborn stains and buildup.
- Water treatment and purification: Sodium bisulfate is effective in water treatment processes, including the removal of chlorine, adjustment of alkalinity, and control of algae growth in swimming pools and industrial water systems. It helps maintain water quality and balance in various aquatic environments.
- Industrial and agricultural applications: The effectiveness of sodium bisulfate extends to various industrial and agricultural applications. It is used in metal processing, textile manufacturing, and as a soil amendment in agriculture. Its versatility and ability to modify pH make it valuable in diverse sectors.
02 pH adjustment and acidification
Sodium bisulfate is widely used as an effective pH adjuster and acidifying agent in various industries. It can rapidly lower the pH of solutions, making it useful in water treatment, cleaning products, and industrial processes where precise pH control is crucial.Expand Specific Solutions03 Cleaning and descaling applications
The effectiveness of sodium bisulfate in cleaning and descaling applications is notable. It is used in formulations for removing mineral deposits, limescale, and rust from various surfaces and equipment. Its acidic nature helps dissolve and remove stubborn buildup without causing damage to many materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Water treatment and purification
Sodium bisulfate is effective in water treatment and purification processes. It is used to adjust pH levels in swimming pools, spas, and industrial water systems. Additionally, it aids in the removal of chloramines and other contaminants, improving water quality and safety.Expand Specific Solutions05 Agricultural and horticultural applications
In agriculture and horticulture, sodium bisulfate demonstrates effectiveness in soil pH adjustment, nutrient availability enhancement, and plant disease control. It can be used to acidify alkaline soils, improve nutrient uptake by plants, and create unfavorable conditions for certain plant pathogens.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Pool Chemical Industry
The exploration of sodium bisulfate's effectiveness in pools is currently in a developing stage, with the market showing potential for growth. The global pool chemicals market, which includes sodium bisulfate, is expected to expand due to increasing pool installations and growing awareness of water hygiene. While the technology is relatively mature, there's ongoing research to optimize its application. Key players like Crystal Lagoons Technologies, Inc. and Waterco Ltd. are at the forefront, developing innovative solutions for pool water treatment. Companies such as Innovative Water Care LLC and Arch Chemicals, Inc. are also contributing to advancements in this field, focusing on improving the efficacy and safety of pool chemicals including sodium bisulfate.
Crystal Lagoons Technologies, Inc.
Technical Solution: Crystal Lagoons has pioneered a unique approach to sodium bisulfate usage in their large-scale artificial lagoons. Their patented technology involves a pulsed-oxidation system that works in conjunction with sodium bisulfate to maintain water quality in massive bodies of water[11]. The company has developed a proprietary algorithm that calculates optimal sodium bisulfate dosage based on factors such as water volume, environmental conditions, and user activity. Crystal Lagoons' system also incorporates ultrasonic sensors to detect algae growth, triggering targeted sodium bisulfate applications to prevent bloom formation[13]. Additionally, they have implemented a circulation strategy that ensures even distribution of sodium bisulfate throughout their lagoons, maintaining consistent pH levels across vast water surfaces.
Strengths: Effective for very large water bodies, integrated approach to water quality management, and environmentally friendly. Weaknesses: Specialized technology may not be directly applicable to standard pool sizes, and high implementation costs for smaller facilities.
Innovative Water Care LLC
Technical Solution: Innovative Water Care LLC has developed a comprehensive approach to sodium bisulfate usage in pools. Their technology involves a controlled-release system that gradually introduces sodium bisulfate into pool water, maintaining optimal pH levels over extended periods[1]. This system utilizes specially designed dispensers that can be adjusted based on pool size and usage patterns. The company has also formulated a proprietary blend of sodium bisulfate with other pH-balancing agents, enhancing its effectiveness and reducing the frequency of application[3]. Additionally, they have implemented a smart monitoring system that continuously measures water chemistry and automatically adjusts sodium bisulfate dosage, ensuring consistent water quality[5].
Strengths: Automated pH control, reduced manual intervention, and consistent water quality. Weaknesses: Higher initial setup costs and potential over-reliance on technology for pool maintenance.
Core Innovations in Sodium Bisulfate Technology
Purification of water
PatentInactiveUS5700377A
Innovation
- A chemical composition comprising alkaline persulphate, sodium bisulphate, ammonium chloride, sodium bicarbonate, calcium chloride, and EDTA, which maintains pH balance between 7.2 and 7.6, effectively disinfects, and complexes heavy metals, preventing pool lining damage.
Electrochlorination method for above-ground swimming pools
PatentWO2011107561A1
Innovation
- Adding a mixture of non-halide salts like sodium bisulphate, sodium bicarbonate, or sodium carbonate to the pool water to enhance electrical conductivity and maintain a pH range of 7.0 to 8.0, allowing for the safe use of bipolar-type electrolysers and reducing corrosion risks.
Environmental Impact of Pool Chemicals
The use of sodium bisulfate and other pool chemicals has significant environmental implications that extend beyond the confines of swimming pools. These chemicals, while essential for maintaining water quality and swimmer safety, can have far-reaching effects on ecosystems when released into the environment.
Sodium bisulfate, commonly used to lower pH levels in pools, can contribute to soil and water acidification if not properly managed. When pool water containing this chemical is discharged or leaks into surrounding soil or water bodies, it can alter the pH balance of these environments. This acidification can negatively impact plant growth, disrupt aquatic ecosystems, and potentially harm wildlife.
Furthermore, the production and transportation of pool chemicals, including sodium bisulfate, contribute to carbon emissions and energy consumption. The manufacturing process of these chemicals often involves energy-intensive procedures and the use of non-renewable resources, adding to the overall environmental footprint of pool maintenance.
Chlorine-based disinfectants, another common pool chemical, pose additional environmental concerns. When chlorinated pool water enters natural water systems, it can form harmful byproducts such as trihalomethanes (THMs) and haloacetic acids (HAAs). These compounds are known to be toxic to aquatic life and can persist in the environment for extended periods.
The impact of pool chemicals on air quality is another consideration. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released from pool chemicals can contribute to smog formation and indoor air pollution. This is particularly relevant in indoor pool settings where proper ventilation is crucial to mitigate these effects.
Algaecides and other specialty pool chemicals can also have detrimental effects on non-target organisms when released into the environment. These substances may harm beneficial algae and microorganisms that play crucial roles in aquatic ecosystems, potentially disrupting food chains and biodiversity.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, there is a growing trend towards more sustainable pool maintenance practices. This includes the use of alternative sanitization methods such as saltwater systems, UV treatment, and ozonation, which can reduce the reliance on traditional chemical treatments. Additionally, proper chemical management, including precise dosing and responsible disposal of pool water, can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of pool maintenance.
Research into eco-friendly pool chemicals and treatment methods continues to evolve, with a focus on developing products that are effective in pool sanitation while minimizing environmental harm. This includes exploring biodegradable alternatives and chemicals that break down more readily in the environment.
Sodium bisulfate, commonly used to lower pH levels in pools, can contribute to soil and water acidification if not properly managed. When pool water containing this chemical is discharged or leaks into surrounding soil or water bodies, it can alter the pH balance of these environments. This acidification can negatively impact plant growth, disrupt aquatic ecosystems, and potentially harm wildlife.
Furthermore, the production and transportation of pool chemicals, including sodium bisulfate, contribute to carbon emissions and energy consumption. The manufacturing process of these chemicals often involves energy-intensive procedures and the use of non-renewable resources, adding to the overall environmental footprint of pool maintenance.
Chlorine-based disinfectants, another common pool chemical, pose additional environmental concerns. When chlorinated pool water enters natural water systems, it can form harmful byproducts such as trihalomethanes (THMs) and haloacetic acids (HAAs). These compounds are known to be toxic to aquatic life and can persist in the environment for extended periods.
The impact of pool chemicals on air quality is another consideration. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released from pool chemicals can contribute to smog formation and indoor air pollution. This is particularly relevant in indoor pool settings where proper ventilation is crucial to mitigate these effects.
Algaecides and other specialty pool chemicals can also have detrimental effects on non-target organisms when released into the environment. These substances may harm beneficial algae and microorganisms that play crucial roles in aquatic ecosystems, potentially disrupting food chains and biodiversity.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, there is a growing trend towards more sustainable pool maintenance practices. This includes the use of alternative sanitization methods such as saltwater systems, UV treatment, and ozonation, which can reduce the reliance on traditional chemical treatments. Additionally, proper chemical management, including precise dosing and responsible disposal of pool water, can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of pool maintenance.
Research into eco-friendly pool chemicals and treatment methods continues to evolve, with a focus on developing products that are effective in pool sanitation while minimizing environmental harm. This includes exploring biodegradable alternatives and chemicals that break down more readily in the environment.
Safety Regulations for Pool Chemical Usage
The use of sodium bisulfate in swimming pools is subject to strict safety regulations to ensure the health and well-being of pool users and operators. These regulations are typically established by national and local health authorities, as well as industry organizations. In the United States, the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) play crucial roles in setting and enforcing safety standards for pool chemicals.
One of the primary safety regulations concerns the proper storage of sodium bisulfate. The chemical must be kept in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. It should be stored in its original, tightly sealed container to prevent moisture absorption and potential chemical reactions. Storage areas must be well-ventilated and separate from other incompatible chemicals, such as chlorine-based products, to avoid hazardous interactions.
Handling and application of sodium bisulfate are also strictly regulated. Pool operators are required to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing. The chemical should never be mixed with other pool chemicals, especially chlorine-based products, as this can result in the release of toxic gases.
Dosage regulations are another critical aspect of sodium bisulfate usage in pools. Manufacturers are required to provide clear instructions on proper dosing, and pool operators must adhere to these guidelines. Overdosing can lead to excessively low pH levels, potentially causing skin and eye irritation for swimmers, as well as damage to pool equipment and surfaces.
Water quality testing is an essential component of safety regulations. Pool operators are required to regularly test and monitor pH levels, typically multiple times per day, to ensure they remain within the recommended range of 7.2 to 7.8. Many jurisdictions mandate the keeping of detailed logs of chemical additions and water quality parameters.
Emergency response procedures are also regulated. Pool facilities must have clearly visible safety data sheets (SDS) for all chemicals used, including sodium bisulfate. These sheets provide crucial information on handling, storage, and emergency measures. Additionally, facilities are required to have emergency eyewash stations and safety showers readily accessible in chemical storage and handling areas.
Training and certification requirements for pool operators form another important aspect of safety regulations. Many jurisdictions require pool operators to undergo specific training on chemical handling and pool maintenance, including the safe use of sodium bisulfate and other pH-lowering agents.
Lastly, regulations often address the disposal of sodium bisulfate and its containers. The chemical and its packaging must be disposed of in accordance with local, state, and federal regulations to prevent environmental contamination and ensure public safety.
One of the primary safety regulations concerns the proper storage of sodium bisulfate. The chemical must be kept in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. It should be stored in its original, tightly sealed container to prevent moisture absorption and potential chemical reactions. Storage areas must be well-ventilated and separate from other incompatible chemicals, such as chlorine-based products, to avoid hazardous interactions.
Handling and application of sodium bisulfate are also strictly regulated. Pool operators are required to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing. The chemical should never be mixed with other pool chemicals, especially chlorine-based products, as this can result in the release of toxic gases.
Dosage regulations are another critical aspect of sodium bisulfate usage in pools. Manufacturers are required to provide clear instructions on proper dosing, and pool operators must adhere to these guidelines. Overdosing can lead to excessively low pH levels, potentially causing skin and eye irritation for swimmers, as well as damage to pool equipment and surfaces.
Water quality testing is an essential component of safety regulations. Pool operators are required to regularly test and monitor pH levels, typically multiple times per day, to ensure they remain within the recommended range of 7.2 to 7.8. Many jurisdictions mandate the keeping of detailed logs of chemical additions and water quality parameters.
Emergency response procedures are also regulated. Pool facilities must have clearly visible safety data sheets (SDS) for all chemicals used, including sodium bisulfate. These sheets provide crucial information on handling, storage, and emergency measures. Additionally, facilities are required to have emergency eyewash stations and safety showers readily accessible in chemical storage and handling areas.
Training and certification requirements for pool operators form another important aspect of safety regulations. Many jurisdictions require pool operators to undergo specific training on chemical handling and pool maintenance, including the safe use of sodium bisulfate and other pH-lowering agents.
Lastly, regulations often address the disposal of sodium bisulfate and its containers. The chemical and its packaging must be disposed of in accordance with local, state, and federal regulations to prevent environmental contamination and ensure public safety.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!