How to Apply Sodium Bisulfate in Hydroponic Systems?
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Bisulfate in Hydroponics: Background and Objectives
Sodium bisulfate has emerged as a promising compound in hydroponic systems, offering potential benefits for pH control and nutrient management. The application of this chemical in soilless cultivation techniques represents a convergence of agricultural innovation and chemical engineering. As hydroponic farming continues to gain traction in both commercial and residential settings, understanding the role of sodium bisulfate becomes increasingly crucial for optimizing plant growth and system efficiency.
The historical context of sodium bisulfate in agriculture dates back to its use as a soil amendment and water treatment agent. However, its specific application in hydroponics is a more recent development, driven by the need for precise control over nutrient solutions. The evolution of hydroponic technologies has created a demand for versatile compounds that can address multiple aspects of plant nutrition and system maintenance simultaneously.
The primary objective of incorporating sodium bisulfate into hydroponic systems is to achieve and maintain optimal pH levels in nutrient solutions. Plants grown hydroponically require a specific pH range, typically between 5.5 and 6.5, to ensure maximum nutrient uptake. Sodium bisulfate's ability to lower pH effectively makes it an attractive option for growers seeking to fine-tune their nutrient management strategies.
Beyond pH adjustment, sodium bisulfate serves several secondary objectives in hydroponic cultivation. These include enhancing nutrient availability, particularly for micronutrients that become more soluble at lower pH levels, and potentially mitigating certain pathogens that thrive in alkaline environments. Additionally, the compound's role in water treatment can contribute to overall system hygiene, potentially reducing the risk of algae growth and bacterial contamination.
The technical goals associated with sodium bisulfate application in hydroponics encompass developing precise dosing protocols, understanding its interactions with various nutrient formulations, and assessing its long-term effects on plant health and yield. Researchers and practitioners aim to establish best practices for integrating sodium bisulfate into existing hydroponic setups, considering factors such as plant species, growth stage, and environmental conditions.
As the hydroponic industry continues to expand, the exploration of sodium bisulfate's potential extends beyond traditional crop production. There is growing interest in its application in vertical farming systems, aquaponics, and even in extraterrestrial agriculture projects. These emerging fields present new challenges and opportunities for sodium bisulfate utilization, driving further research and innovation in hydroponic technologies.
The trajectory of sodium bisulfate in hydroponics aligns with broader trends in sustainable agriculture and resource-efficient food production. As global concerns about water scarcity and land use intensify, hydroponic systems offer promising solutions. The role of compounds like sodium bisulfate in enhancing the efficiency and reliability of these systems positions them as key components in the future of agriculture.
The historical context of sodium bisulfate in agriculture dates back to its use as a soil amendment and water treatment agent. However, its specific application in hydroponics is a more recent development, driven by the need for precise control over nutrient solutions. The evolution of hydroponic technologies has created a demand for versatile compounds that can address multiple aspects of plant nutrition and system maintenance simultaneously.
The primary objective of incorporating sodium bisulfate into hydroponic systems is to achieve and maintain optimal pH levels in nutrient solutions. Plants grown hydroponically require a specific pH range, typically between 5.5 and 6.5, to ensure maximum nutrient uptake. Sodium bisulfate's ability to lower pH effectively makes it an attractive option for growers seeking to fine-tune their nutrient management strategies.
Beyond pH adjustment, sodium bisulfate serves several secondary objectives in hydroponic cultivation. These include enhancing nutrient availability, particularly for micronutrients that become more soluble at lower pH levels, and potentially mitigating certain pathogens that thrive in alkaline environments. Additionally, the compound's role in water treatment can contribute to overall system hygiene, potentially reducing the risk of algae growth and bacterial contamination.
The technical goals associated with sodium bisulfate application in hydroponics encompass developing precise dosing protocols, understanding its interactions with various nutrient formulations, and assessing its long-term effects on plant health and yield. Researchers and practitioners aim to establish best practices for integrating sodium bisulfate into existing hydroponic setups, considering factors such as plant species, growth stage, and environmental conditions.
As the hydroponic industry continues to expand, the exploration of sodium bisulfate's potential extends beyond traditional crop production. There is growing interest in its application in vertical farming systems, aquaponics, and even in extraterrestrial agriculture projects. These emerging fields present new challenges and opportunities for sodium bisulfate utilization, driving further research and innovation in hydroponic technologies.
The trajectory of sodium bisulfate in hydroponics aligns with broader trends in sustainable agriculture and resource-efficient food production. As global concerns about water scarcity and land use intensify, hydroponic systems offer promising solutions. The role of compounds like sodium bisulfate in enhancing the efficiency and reliability of these systems positions them as key components in the future of agriculture.
Market Analysis for Hydroponic pH Regulators
The hydroponic pH regulator market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing adoption of hydroponic farming techniques and the growing demand for precision agriculture. As hydroponic systems require careful control of nutrient solutions, pH regulators play a crucial role in maintaining optimal growing conditions for plants.
The global market for hydroponic pH regulators is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to be in the high single digits over the next five years. This growth is primarily attributed to the expansion of commercial hydroponic operations, particularly in regions facing land scarcity and water conservation challenges.
North America and Europe currently dominate the market, accounting for a substantial share of the global hydroponic pH regulator consumption. However, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing investments in hydroponic farming in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
The market is segmented based on product type, with liquid pH regulators holding the largest market share due to their ease of use and precise application. Powder and granular forms are also gaining traction, especially in smaller-scale operations and hobbyist markets.
Key market drivers include the rising demand for year-round crop production, increasing focus on sustainable agriculture practices, and the need for higher crop yields to meet growing food demands. Additionally, the trend towards urban farming and vertical agriculture is creating new opportunities for pH regulator manufacturers.
However, the market faces challenges such as the high initial investment required for hydroponic systems and the lack of awareness among traditional farmers about hydroponic techniques. These factors may hinder market growth in some regions, particularly in developing countries.
The competitive landscape of the hydroponic pH regulator market is characterized by the presence of both established players and new entrants. Major companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their market position. There is a growing emphasis on developing eco-friendly and organic pH regulators to cater to the increasing demand for organic hydroponic produce.
In terms of distribution channels, online retail platforms are gaining prominence, especially among small-scale growers and hobbyists. However, direct sales to large commercial hydroponic operations remain a significant revenue stream for manufacturers.
Looking ahead, the market is expected to witness further innovations in pH regulation technologies, including the development of smart pH monitoring and adjustment systems integrated with IoT and AI capabilities. This trend aligns with the broader movement towards precision agriculture and data-driven farming practices.
The global market for hydroponic pH regulators is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to be in the high single digits over the next five years. This growth is primarily attributed to the expansion of commercial hydroponic operations, particularly in regions facing land scarcity and water conservation challenges.
North America and Europe currently dominate the market, accounting for a substantial share of the global hydroponic pH regulator consumption. However, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing investments in hydroponic farming in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
The market is segmented based on product type, with liquid pH regulators holding the largest market share due to their ease of use and precise application. Powder and granular forms are also gaining traction, especially in smaller-scale operations and hobbyist markets.
Key market drivers include the rising demand for year-round crop production, increasing focus on sustainable agriculture practices, and the need for higher crop yields to meet growing food demands. Additionally, the trend towards urban farming and vertical agriculture is creating new opportunities for pH regulator manufacturers.
However, the market faces challenges such as the high initial investment required for hydroponic systems and the lack of awareness among traditional farmers about hydroponic techniques. These factors may hinder market growth in some regions, particularly in developing countries.
The competitive landscape of the hydroponic pH regulator market is characterized by the presence of both established players and new entrants. Major companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their market position. There is a growing emphasis on developing eco-friendly and organic pH regulators to cater to the increasing demand for organic hydroponic produce.
In terms of distribution channels, online retail platforms are gaining prominence, especially among small-scale growers and hobbyists. However, direct sales to large commercial hydroponic operations remain a significant revenue stream for manufacturers.
Looking ahead, the market is expected to witness further innovations in pH regulation technologies, including the development of smart pH monitoring and adjustment systems integrated with IoT and AI capabilities. This trend aligns with the broader movement towards precision agriculture and data-driven farming practices.
Current Challenges in Hydroponic pH Management
Hydroponic systems face several challenges in maintaining optimal pH levels, which are crucial for plant growth and nutrient absorption. One of the primary issues is the tendency for pH to drift upwards over time. This occurs due to the uptake of nutrients by plants, which can lead to an accumulation of hydroxide ions in the nutrient solution. As a result, growers must constantly monitor and adjust pH levels to ensure they remain within the ideal range of 5.5 to 6.5 for most crops.
Another significant challenge is the variability of water sources used in hydroponic systems. Different water sources can have vastly different mineral content and initial pH levels, making it difficult to standardize pH management practices across different locations or even within the same facility using multiple water sources. This variability necessitates frequent testing and customized adjustment strategies for each system.
The use of chemical pH adjusters, while effective, presents its own set of challenges. Many traditional pH down products contain strong acids that can cause rapid pH fluctuations if not applied carefully. These sudden changes can stress plants and lead to nutrient lockout, where certain nutrients become unavailable for uptake due to chemical reactions at extreme pH levels. Additionally, the repeated use of strong acids can degrade the overall buffering capacity of the nutrient solution, making it more susceptible to future pH swings.
Organic hydroponic systems face unique pH management difficulties. Organic nutrients often have a higher pH and can be less stable than their synthetic counterparts. This instability can lead to more frequent pH fluctuations and require more diligent monitoring and adjustment. Furthermore, many organic growers prefer to avoid synthetic pH adjusters, limiting their options for pH control.
The interaction between pH and nutrient availability adds another layer of complexity to hydroponic pH management. Different nutrients have optimal absorption ranges, and as pH levels shift, certain nutrients may become less available to plants. This dynamic relationship means that pH management is not just about maintaining a specific number, but about optimizing the overall nutrient profile available to plants.
Automation and technology integration in pH management, while beneficial, also present challenges. Calibration and maintenance of pH sensors and automated dosing systems require technical expertise and regular attention. Malfunctions in these systems can lead to severe pH imbalances if not detected and addressed promptly.
Lastly, the environmental impact of pH management practices is an emerging concern. The disposal of nutrient solutions and pH adjusters can have ecological consequences, particularly in large-scale hydroponic operations. Developing sustainable pH management strategies that minimize waste and environmental impact while maintaining optimal growing conditions remains an ongoing challenge for the hydroponic industry.
Another significant challenge is the variability of water sources used in hydroponic systems. Different water sources can have vastly different mineral content and initial pH levels, making it difficult to standardize pH management practices across different locations or even within the same facility using multiple water sources. This variability necessitates frequent testing and customized adjustment strategies for each system.
The use of chemical pH adjusters, while effective, presents its own set of challenges. Many traditional pH down products contain strong acids that can cause rapid pH fluctuations if not applied carefully. These sudden changes can stress plants and lead to nutrient lockout, where certain nutrients become unavailable for uptake due to chemical reactions at extreme pH levels. Additionally, the repeated use of strong acids can degrade the overall buffering capacity of the nutrient solution, making it more susceptible to future pH swings.
Organic hydroponic systems face unique pH management difficulties. Organic nutrients often have a higher pH and can be less stable than their synthetic counterparts. This instability can lead to more frequent pH fluctuations and require more diligent monitoring and adjustment. Furthermore, many organic growers prefer to avoid synthetic pH adjusters, limiting their options for pH control.
The interaction between pH and nutrient availability adds another layer of complexity to hydroponic pH management. Different nutrients have optimal absorption ranges, and as pH levels shift, certain nutrients may become less available to plants. This dynamic relationship means that pH management is not just about maintaining a specific number, but about optimizing the overall nutrient profile available to plants.
Automation and technology integration in pH management, while beneficial, also present challenges. Calibration and maintenance of pH sensors and automated dosing systems require technical expertise and regular attention. Malfunctions in these systems can lead to severe pH imbalances if not detected and addressed promptly.
Lastly, the environmental impact of pH management practices is an emerging concern. The disposal of nutrient solutions and pH adjusters can have ecological consequences, particularly in large-scale hydroponic operations. Developing sustainable pH management strategies that minimize waste and environmental impact while maintaining optimal growing conditions remains an ongoing challenge for the hydroponic industry.
Existing Sodium Bisulfate Application Techniques
01 Use of sodium bisulfate in oral care products
Sodium bisulfate is utilized in oral care formulations such as toothpaste, mouthwash, and dental rinses. It acts as a pH adjuster and can help in reducing bacterial growth in the oral cavity. The compound's acidic nature contributes to its effectiveness in maintaining oral hygiene and freshness.- Use of sodium bisulfate in oral care products: Sodium bisulfate is utilized in oral care formulations such as toothpaste, mouthwash, and dental rinses. It acts as a pH adjuster and can help in reducing bacterial growth in the oral cavity. The compound may also contribute to the overall cleaning and freshening effects of these products.
- Application in water treatment and purification: Sodium bisulfate is employed in water treatment processes for pH adjustment and as a disinfectant. It can help in removing chlorine from water, making it useful in swimming pool maintenance and industrial water treatment applications. The compound's ability to lower pH makes it effective in controlling algae growth and improving water clarity.
- Use as a cleaning and descaling agent: Sodium bisulfate is incorporated into cleaning formulations for its ability to remove mineral deposits and scale. It is particularly effective in bathroom and kitchen cleaners, as well as in industrial descaling applications. The compound's acidic nature helps in dissolving calcium and lime deposits, making it useful in maintaining various household and industrial equipment.
- Application in food processing and preservation: Sodium bisulfate finds use in the food industry as a preservative and pH regulator. It can help extend the shelf life of certain food products by inhibiting microbial growth. The compound is also used in meat processing to control pathogens and improve food safety. Its acidic properties make it suitable for various food applications where pH control is crucial.
- Use in agricultural and horticultural applications: Sodium bisulfate is utilized in agriculture and horticulture for soil pH adjustment and as a fertilizer component. It can help in reducing soil alkalinity and improving nutrient availability for plants. The compound may also be used in animal feed additives to enhance digestibility and promote animal health. Its acidic nature makes it effective in controlling certain plant diseases and pests.
02 Application in water treatment and purification
Sodium bisulfate finds extensive use in water treatment processes. It is employed as a pH reducer in swimming pools, spas, and industrial water systems. The compound helps in maintaining proper water chemistry, preventing scale formation, and controlling algae growth. It is also used in the treatment of wastewater and in the purification of drinking water.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use as a cleaning and descaling agent
Sodium bisulfate is utilized in various cleaning and descaling applications. It is effective in removing mineral deposits, lime scale, and rust from surfaces and equipment. The compound is incorporated into cleaning products for household and industrial use, particularly for bathroom and kitchen cleaning, as well as in descaling solutions for appliances like coffee makers and dishwashers.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application in food processing and preservation
Sodium bisulfate is used in the food industry as a preservative and pH control agent. It helps extend the shelf life of certain food products by inhibiting microbial growth. The compound is also employed in meat processing to control pathogens and improve food safety. Additionally, it finds use in the production of beverages and as a leavening agent in baked goods.Expand Specific Solutions05 Use in agricultural and environmental applications
Sodium bisulfate has various applications in agriculture and environmental management. It is used as a soil amendment to lower soil pH and improve nutrient availability for certain crops. The compound is also employed in animal feed additives to enhance digestibility and reduce ammonia emissions in livestock facilities. Furthermore, it is utilized in the treatment of animal waste and in composting processes to control odors and pH levels.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Hydroponic Nutrient Solutions
The application of sodium bisulfate in hydroponic systems represents an emerging niche within the broader hydroponics market, which is currently in a growth phase. The global hydroponics market is expanding rapidly, with projections estimating it to reach $16 billion by 2025. While the technology for using sodium bisulfate in hydroponics is still developing, several key players are advancing its application. Companies like Revol Greens and Growee Technologies are exploring innovative hydroponic solutions, while established firms such as Toray Industries and Sumitomo Chemical are leveraging their expertise in chemical manufacturing to develop specialized products for this sector. Research institutions like Huazhong Agricultural University and Nanjing Agricultural University are also contributing to the advancement of hydroponic technologies, including the use of sodium bisulfate.
Earth Renaissance Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Earth Renaissance Technologies LLC has developed a novel approach to sodium bisulfate application in hydroponic systems, focusing on sustainability and organic compatibility. Their method utilizes a bio-based carrier for sodium bisulfate, derived from agricultural waste products. This carrier not only helps in the controlled release of sodium bisulfate but also contributes beneficial organic compounds to the hydroponic solution. The company's system includes a patented biofiltration unit that works in tandem with the sodium bisulfate application, helping to maintain optimal microbial balance in the nutrient solution. This integrated approach has shown to reduce the overall sodium load in hydroponic systems by up to 25%, while maintaining effective pH control. Additionally, their method has been certified for use in organic hydroponic production, opening new markets for hydroponic growers[8][10].
Strengths: Eco-friendly approach, organic certification compatibility, and reduced sodium accumulation. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost due to specialized formulation and limited long-term data on effectiveness across diverse crop types.
Revol Greens, GBC
Technical Solution: Revol Greens, GBC has implemented an advanced sodium bisulfate application system in their large-scale hydroponic facilities. Their approach combines precision fertigation with a proprietary sodium bisulfate blend optimized for leafy greens. The system uses AI-driven predictive modeling to anticipate pH changes based on crop growth stages, water quality, and environmental factors. Sodium bisulfate is then applied through a mist-based delivery system, ensuring even distribution throughout the growing area. This method has reportedly reduced water usage by 20% and improved crop yields by 8-12% compared to traditional hydroponic systems. Revol Greens also incorporates a recirculation and filtration system that removes excess sodium, mitigating potential salt buildup issues associated with sodium bisulfate use[7][9].
Strengths: Highly efficient water and resource use, improved crop yields, and scalability for large operations. Weaknesses: High initial investment and potential over-reliance on proprietary technology.
Innovations in Sodium Bisulfate Formulations
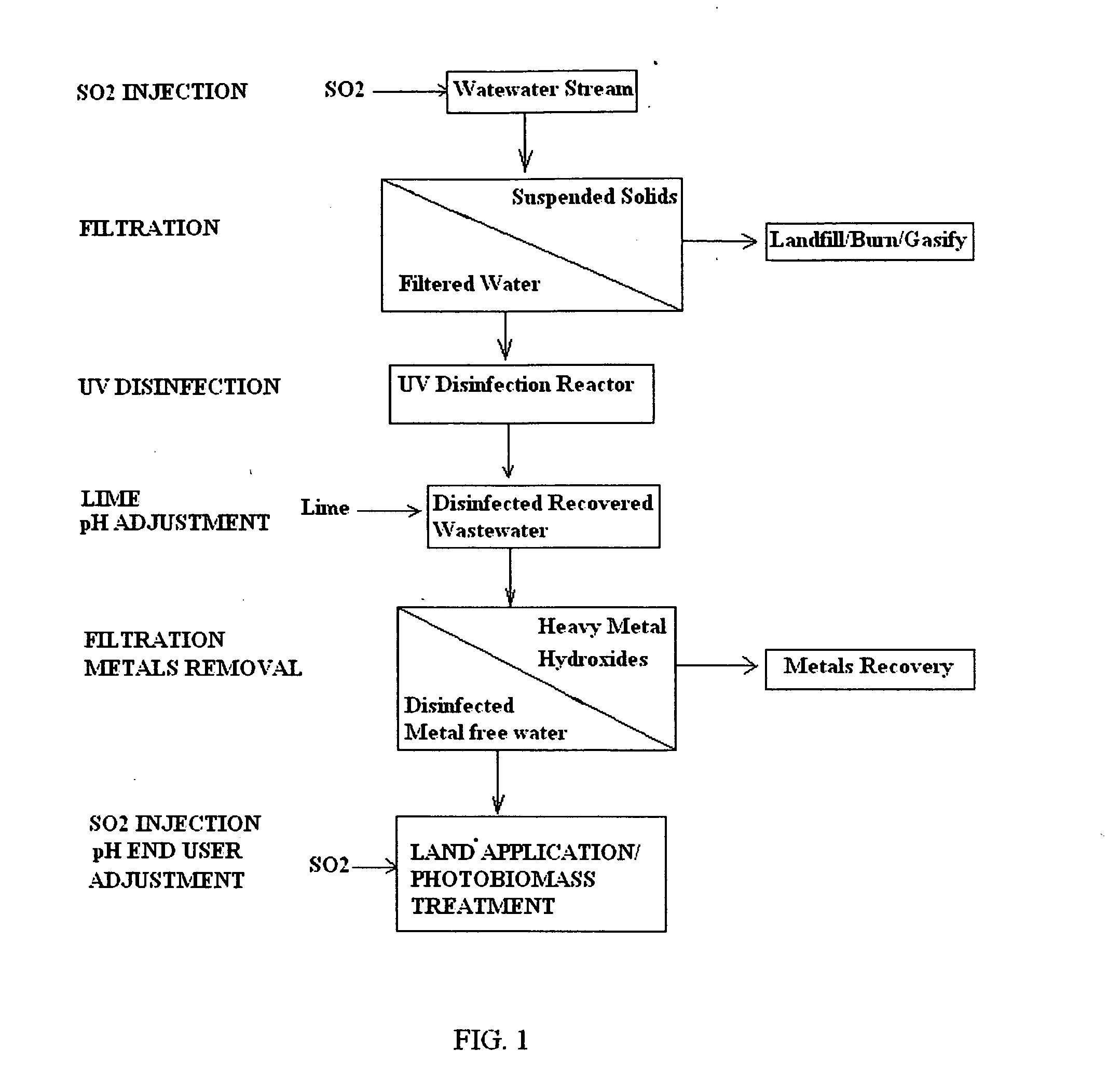
Acidification pre-treatment for UV water disinfection
PatentInactiveUS20110243665A1
Innovation
- A pre-treatment method using sulfurous acid to self-agglomerate suspended solids for easier filtration and reduce mineral scaling and microbial buildup on UV light tubes, achieved by injecting sulfur dioxide to generate sulfurous acid, which acts as a surfactant and biocide, preventing film formation and extending the time between cleanings.
Method of fertilization and/or irrigation using potassium bisulfate
PatentActiveUS20240092704A1
Innovation
- The method involves adding potassium bisulfate to irrigation water, either by mixing sulfuric acid and potassium sulfate or using an aqueous solution of potassium bisulfate, to provide a safer and more soluble source of potassium, allowing for controlled delivery and increased solubility, thereby reducing heat release and improving mineral availability to crops.
Environmental Impact of Sodium Bisulfate Use
The use of sodium bisulfate in hydroponic systems has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. As an acidifying agent, sodium bisulfate can alter the pH levels of water and soil, potentially affecting local ecosystems if not properly managed. When applied in hydroponic systems, excess sodium bisulfate may be discharged into the environment through wastewater, leading to potential impacts on aquatic life and water quality.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential for soil acidification. If sodium bisulfate-rich water from hydroponic systems is released onto land, it can lower the pH of the soil, affecting plant growth and microbial activity. This acidification process can also lead to the mobilization of heavy metals in the soil, making them more bioavailable and potentially toxic to plants and soil organisms.
In aquatic environments, the discharge of sodium bisulfate can have detrimental effects on fish and other aquatic organisms. Sudden changes in pH levels can stress or even kill sensitive species, disrupting the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems. Furthermore, the increased acidity can lead to the dissolution of carbonates, affecting organisms with calcium carbonate shells or skeletons.
However, when used responsibly and in controlled amounts, the environmental impact of sodium bisulfate in hydroponic systems can be minimized. Proper dosing and monitoring of pH levels can prevent excessive use and reduce the risk of environmental contamination. Additionally, implementing closed-loop systems and water recycling techniques can significantly reduce the amount of sodium bisulfate-containing wastewater released into the environment.
It is also important to consider the broader environmental implications of hydroponic systems using sodium bisulfate. These systems often have a smaller land footprint compared to traditional agriculture and can reduce water consumption and pesticide use. This can lead to overall positive environmental outcomes, provided that the use of chemicals like sodium bisulfate is carefully managed.
To mitigate potential environmental risks, it is crucial to implement best practices in the use of sodium bisulfate in hydroponic systems. This includes regular monitoring of pH levels, proper disposal of wastewater, and the use of buffer solutions to stabilize pH fluctuations. Additionally, exploring alternative pH control methods or organic acids may provide more environmentally friendly options for hydroponic cultivation.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential for soil acidification. If sodium bisulfate-rich water from hydroponic systems is released onto land, it can lower the pH of the soil, affecting plant growth and microbial activity. This acidification process can also lead to the mobilization of heavy metals in the soil, making them more bioavailable and potentially toxic to plants and soil organisms.
In aquatic environments, the discharge of sodium bisulfate can have detrimental effects on fish and other aquatic organisms. Sudden changes in pH levels can stress or even kill sensitive species, disrupting the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems. Furthermore, the increased acidity can lead to the dissolution of carbonates, affecting organisms with calcium carbonate shells or skeletons.
However, when used responsibly and in controlled amounts, the environmental impact of sodium bisulfate in hydroponic systems can be minimized. Proper dosing and monitoring of pH levels can prevent excessive use and reduce the risk of environmental contamination. Additionally, implementing closed-loop systems and water recycling techniques can significantly reduce the amount of sodium bisulfate-containing wastewater released into the environment.
It is also important to consider the broader environmental implications of hydroponic systems using sodium bisulfate. These systems often have a smaller land footprint compared to traditional agriculture and can reduce water consumption and pesticide use. This can lead to overall positive environmental outcomes, provided that the use of chemicals like sodium bisulfate is carefully managed.
To mitigate potential environmental risks, it is crucial to implement best practices in the use of sodium bisulfate in hydroponic systems. This includes regular monitoring of pH levels, proper disposal of wastewater, and the use of buffer solutions to stabilize pH fluctuations. Additionally, exploring alternative pH control methods or organic acids may provide more environmentally friendly options for hydroponic cultivation.
Safety Protocols for Chemical Handling in Hydroponics
Safety protocols for chemical handling in hydroponics are crucial to ensure the well-being of workers and the integrity of the hydroponic system. When dealing with sodium bisulfate, a strong acid salt commonly used in pH adjustment, proper precautions must be taken. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential and should include chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and appropriate clothing to prevent skin contact. A well-ventilated area or the use of respiratory protection may be necessary when handling large quantities or in enclosed spaces.
Storage of sodium bisulfate requires careful consideration. The chemical should be kept in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Containers must be properly labeled and sealed to prevent contamination and accidental exposure. It is important to store sodium bisulfate separately from incompatible materials, such as strong bases or oxidizing agents, to avoid potentially dangerous reactions.
Proper handling procedures are vital to minimize risks. When measuring and applying sodium bisulfate, use clean, dry utensils and containers specifically designated for this purpose. Avoid generating dust, as inhalation can cause respiratory irritation. If the chemical needs to be dissolved, add it slowly to water, never the reverse, to prevent splashing and excessive heat generation.
Emergency protocols should be established and clearly communicated to all personnel working with hydroponic chemicals. This includes the location and proper use of eyewash stations and safety showers. A spill response plan should be in place, detailing the steps to contain and clean up any accidental releases. Neutralizing agents, such as sodium bicarbonate, should be readily available to treat spills before disposal.
Training is a critical component of safety protocols. All staff members involved in handling sodium bisulfate or other chemicals should receive comprehensive instruction on proper use, potential hazards, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher courses and safety drills can help maintain awareness and preparedness.
Documentation plays a significant role in maintaining safety standards. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for sodium bisulfate and all other chemicals used in the hydroponic system must be easily accessible. A chemical inventory system should be implemented to track usage, storage levels, and expiration dates, ensuring that outdated or degraded chemicals are properly disposed of and replaced.
Monitoring and maintenance of the hydroponic system are essential to prevent chemical-related incidents. Regular checks of pH levels, nutrient concentrations, and equipment integrity can help identify potential issues before they become hazardous. Automated dosing systems, if used, should be regularly calibrated and maintained to prevent over-application of sodium bisulfate or other chemicals.
By implementing and adhering to these comprehensive safety protocols, hydroponic operators can significantly reduce the risks associated with chemical handling, creating a safer working environment and ensuring the quality and safety of their produce.
Storage of sodium bisulfate requires careful consideration. The chemical should be kept in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Containers must be properly labeled and sealed to prevent contamination and accidental exposure. It is important to store sodium bisulfate separately from incompatible materials, such as strong bases or oxidizing agents, to avoid potentially dangerous reactions.
Proper handling procedures are vital to minimize risks. When measuring and applying sodium bisulfate, use clean, dry utensils and containers specifically designated for this purpose. Avoid generating dust, as inhalation can cause respiratory irritation. If the chemical needs to be dissolved, add it slowly to water, never the reverse, to prevent splashing and excessive heat generation.
Emergency protocols should be established and clearly communicated to all personnel working with hydroponic chemicals. This includes the location and proper use of eyewash stations and safety showers. A spill response plan should be in place, detailing the steps to contain and clean up any accidental releases. Neutralizing agents, such as sodium bicarbonate, should be readily available to treat spills before disposal.
Training is a critical component of safety protocols. All staff members involved in handling sodium bisulfate or other chemicals should receive comprehensive instruction on proper use, potential hazards, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher courses and safety drills can help maintain awareness and preparedness.
Documentation plays a significant role in maintaining safety standards. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for sodium bisulfate and all other chemicals used in the hydroponic system must be easily accessible. A chemical inventory system should be implemented to track usage, storage levels, and expiration dates, ensuring that outdated or degraded chemicals are properly disposed of and replaced.
Monitoring and maintenance of the hydroponic system are essential to prevent chemical-related incidents. Regular checks of pH levels, nutrient concentrations, and equipment integrity can help identify potential issues before they become hazardous. Automated dosing systems, if used, should be regularly calibrated and maintained to prevent over-application of sodium bisulfate or other chemicals.
By implementing and adhering to these comprehensive safety protocols, hydroponic operators can significantly reduce the risks associated with chemical handling, creating a safer working environment and ensuring the quality and safety of their produce.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!