How to Enhance Hypochlorous Acid's Antiseptic Properties?
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCl Enhancement Goals
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has long been recognized for its potent antimicrobial properties, making it a valuable tool in various disinfection and sanitization applications. The primary goal in enhancing HOCl's antiseptic properties is to improve its efficacy, stability, and versatility across a wider range of environmental conditions and target pathogens.
One key objective is to increase HOCl's stability and shelf life. Currently, HOCl solutions tend to degrade relatively quickly, limiting their practical use in many settings. By developing formulations or storage methods that preserve HOCl's active form for extended periods, we can significantly expand its utility in both medical and industrial applications.
Another critical aim is to enhance HOCl's effectiveness against a broader spectrum of microorganisms, including antibiotic-resistant bacteria, viruses, and fungi. This involves optimizing the concentration and pH of HOCl solutions to maximize their antimicrobial activity while minimizing potential side effects or environmental impact.
Improving HOCl's penetration capabilities is also a crucial goal. By enhancing its ability to penetrate biofilms and reach microorganisms in complex environments, we can increase its effectiveness in challenging applications such as wound care, dental hygiene, and industrial cleaning processes.
Furthermore, there is a strong focus on developing HOCl-based products with improved user-friendliness and application methods. This includes creating stable, ready-to-use formulations that do not require on-site generation, as well as exploring novel delivery systems such as foams, gels, or impregnated materials that can extend contact time and improve overall efficacy.
Researchers are also aiming to enhance HOCl's compatibility with other materials and chemicals. This would allow for its integration into a wider range of products and applications, from medical devices to consumer goods, without compromising its antiseptic properties or the integrity of the materials it comes into contact with.
Lastly, there is a growing emphasis on developing eco-friendly and sustainable HOCl production methods. This includes exploring renewable energy sources for electrolysis processes and optimizing production efficiency to reduce resource consumption and environmental impact.
By achieving these enhancement goals, HOCl can become an even more powerful and versatile tool in the fight against pathogens, offering improved safety, efficacy, and sustainability across various sectors, from healthcare and food safety to water treatment and beyond.
One key objective is to increase HOCl's stability and shelf life. Currently, HOCl solutions tend to degrade relatively quickly, limiting their practical use in many settings. By developing formulations or storage methods that preserve HOCl's active form for extended periods, we can significantly expand its utility in both medical and industrial applications.
Another critical aim is to enhance HOCl's effectiveness against a broader spectrum of microorganisms, including antibiotic-resistant bacteria, viruses, and fungi. This involves optimizing the concentration and pH of HOCl solutions to maximize their antimicrobial activity while minimizing potential side effects or environmental impact.
Improving HOCl's penetration capabilities is also a crucial goal. By enhancing its ability to penetrate biofilms and reach microorganisms in complex environments, we can increase its effectiveness in challenging applications such as wound care, dental hygiene, and industrial cleaning processes.
Furthermore, there is a strong focus on developing HOCl-based products with improved user-friendliness and application methods. This includes creating stable, ready-to-use formulations that do not require on-site generation, as well as exploring novel delivery systems such as foams, gels, or impregnated materials that can extend contact time and improve overall efficacy.
Researchers are also aiming to enhance HOCl's compatibility with other materials and chemicals. This would allow for its integration into a wider range of products and applications, from medical devices to consumer goods, without compromising its antiseptic properties or the integrity of the materials it comes into contact with.
Lastly, there is a growing emphasis on developing eco-friendly and sustainable HOCl production methods. This includes exploring renewable energy sources for electrolysis processes and optimizing production efficiency to reduce resource consumption and environmental impact.
By achieving these enhancement goals, HOCl can become an even more powerful and versatile tool in the fight against pathogens, offering improved safety, efficacy, and sustainability across various sectors, from healthcare and food safety to water treatment and beyond.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for enhanced hypochlorous acid (HOCl) antiseptic properties has been steadily growing, driven by increasing awareness of its effectiveness and safety profile across various sectors. Healthcare institutions, including hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities, represent a significant portion of this demand. These establishments are constantly seeking more potent yet safe disinfectants to combat healthcare-associated infections and antibiotic-resistant pathogens.
The food and beverage industry also contributes substantially to the market demand for improved HOCl solutions. With stringent food safety regulations and consumer expectations for hygienic food processing environments, there is a growing need for effective, non-toxic sanitizers. Enhanced HOCl formulations could provide a competitive edge in this sector, offering superior pathogen control without leaving harmful residues.
Water treatment facilities have shown increasing interest in advanced HOCl technologies. As concerns over waterborne diseases and emerging contaminants rise, the demand for more efficient water disinfection methods grows. Enhanced HOCl solutions could potentially offer a more effective and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional chlorine-based treatments.
The personal care and cosmetics industry presents another significant market opportunity. Consumers are increasingly seeking natural, gentle, yet effective antimicrobial products for personal hygiene. Improved HOCl formulations could meet this demand, offering powerful antiseptic properties without the harshness associated with some conventional products.
Agriculture and horticulture sectors are exploring HOCl applications for crop protection and post-harvest treatments. The demand for alternatives to chemical pesticides and fungicides is driving interest in enhanced HOCl solutions that can effectively control plant pathogens while being safe for crops and the environment.
The ongoing global health crises have further amplified the demand for powerful yet safe disinfectants. This has led to increased interest in HOCl across various industries, from public transportation to hospitality, seeking effective solutions for surface and air disinfection.
Market analysis indicates a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the HOCl market, with particular emphasis on enhanced formulations. This growth is expected to continue as research advances and new applications emerge. The potential for HOCl to replace less environmentally friendly or more toxic alternatives in various industries suggests a substantial untapped market.
As environmental regulations become more stringent and public health concerns remain at the forefront, the demand for enhanced HOCl antiseptic properties is likely to expand further. This presents significant opportunities for innovation and market growth in the coming years, particularly for formulations that can demonstrate superior efficacy, stability, and versatility across multiple applications.
The food and beverage industry also contributes substantially to the market demand for improved HOCl solutions. With stringent food safety regulations and consumer expectations for hygienic food processing environments, there is a growing need for effective, non-toxic sanitizers. Enhanced HOCl formulations could provide a competitive edge in this sector, offering superior pathogen control without leaving harmful residues.
Water treatment facilities have shown increasing interest in advanced HOCl technologies. As concerns over waterborne diseases and emerging contaminants rise, the demand for more efficient water disinfection methods grows. Enhanced HOCl solutions could potentially offer a more effective and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional chlorine-based treatments.
The personal care and cosmetics industry presents another significant market opportunity. Consumers are increasingly seeking natural, gentle, yet effective antimicrobial products for personal hygiene. Improved HOCl formulations could meet this demand, offering powerful antiseptic properties without the harshness associated with some conventional products.
Agriculture and horticulture sectors are exploring HOCl applications for crop protection and post-harvest treatments. The demand for alternatives to chemical pesticides and fungicides is driving interest in enhanced HOCl solutions that can effectively control plant pathogens while being safe for crops and the environment.
The ongoing global health crises have further amplified the demand for powerful yet safe disinfectants. This has led to increased interest in HOCl across various industries, from public transportation to hospitality, seeking effective solutions for surface and air disinfection.
Market analysis indicates a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the HOCl market, with particular emphasis on enhanced formulations. This growth is expected to continue as research advances and new applications emerge. The potential for HOCl to replace less environmentally friendly or more toxic alternatives in various industries suggests a substantial untapped market.
As environmental regulations become more stringent and public health concerns remain at the forefront, the demand for enhanced HOCl antiseptic properties is likely to expand further. This presents significant opportunities for innovation and market growth in the coming years, particularly for formulations that can demonstrate superior efficacy, stability, and versatility across multiple applications.
HOCl Challenges
Despite the proven efficacy of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) as a potent antiseptic, several challenges hinder its widespread adoption and optimal utilization in various applications. One of the primary obstacles is the stability of HOCl solutions. The compound is inherently unstable and tends to degrade rapidly, especially when exposed to light, heat, or organic matter. This instability significantly limits its shelf life and effectiveness over time, posing difficulties in storage, transportation, and long-term use.
Another critical challenge is the pH-dependent nature of HOCl's antimicrobial activity. The acid exhibits maximum efficacy within a narrow pH range, typically between 3.5 and 6.5. Maintaining this optimal pH in diverse environments and applications can be problematic, as slight variations can dramatically reduce its antiseptic properties. This sensitivity to pH fluctuations complicates its use in complex biological systems or industrial settings where pH control may be challenging.
The concentration of HOCl also presents a significant hurdle. While higher concentrations generally yield stronger antimicrobial effects, they can also increase the potential for irritation and toxicity, particularly in sensitive tissues. Conversely, lower concentrations may not provide sufficient antimicrobial activity. Striking the right balance between efficacy and safety across various applications remains a persistent challenge.
Furthermore, the interaction of HOCl with organic matter poses another obstacle. In the presence of high organic loads, such as in wound environments or contaminated surfaces, HOCl can be rapidly neutralized, diminishing its antiseptic properties. This necessitates either higher initial concentrations or more frequent applications, both of which have practical and economic implications.
The production and standardization of HOCl solutions also present challenges. Current methods of generating HOCl, such as electrolysis of saline solutions, can result in variations in concentration and purity. Ensuring consistent quality and potency across different batches and production methods is crucial for reliable antimicrobial performance but remains a significant technical hurdle.
Lastly, regulatory and perception issues compound these technical challenges. The classification and approval of HOCl products vary across different regions and applications, creating a complex regulatory landscape. Additionally, public and professional perceptions of chlorine-based products can sometimes be negative, necessitating education and awareness efforts to promote the unique benefits and safety profile of HOCl compared to other chlorine-based disinfectants.
Another critical challenge is the pH-dependent nature of HOCl's antimicrobial activity. The acid exhibits maximum efficacy within a narrow pH range, typically between 3.5 and 6.5. Maintaining this optimal pH in diverse environments and applications can be problematic, as slight variations can dramatically reduce its antiseptic properties. This sensitivity to pH fluctuations complicates its use in complex biological systems or industrial settings where pH control may be challenging.
The concentration of HOCl also presents a significant hurdle. While higher concentrations generally yield stronger antimicrobial effects, they can also increase the potential for irritation and toxicity, particularly in sensitive tissues. Conversely, lower concentrations may not provide sufficient antimicrobial activity. Striking the right balance between efficacy and safety across various applications remains a persistent challenge.
Furthermore, the interaction of HOCl with organic matter poses another obstacle. In the presence of high organic loads, such as in wound environments or contaminated surfaces, HOCl can be rapidly neutralized, diminishing its antiseptic properties. This necessitates either higher initial concentrations or more frequent applications, both of which have practical and economic implications.
The production and standardization of HOCl solutions also present challenges. Current methods of generating HOCl, such as electrolysis of saline solutions, can result in variations in concentration and purity. Ensuring consistent quality and potency across different batches and production methods is crucial for reliable antimicrobial performance but remains a significant technical hurdle.
Lastly, regulatory and perception issues compound these technical challenges. The classification and approval of HOCl products vary across different regions and applications, creating a complex regulatory landscape. Additionally, public and professional perceptions of chlorine-based products can sometimes be negative, necessitating education and awareness efforts to promote the unique benefits and safety profile of HOCl compared to other chlorine-based disinfectants.
Current HOCl Solutions
01 Antimicrobial properties of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid exhibits strong antimicrobial properties, making it effective against a wide range of pathogens including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Its mechanism of action involves oxidative damage to cellular components, disrupting microbial cell walls and membranes. This broad-spectrum activity makes it a valuable antiseptic agent for various applications in healthcare and sanitation.- Antimicrobial properties of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid exhibits strong antimicrobial properties, making it effective against a wide range of pathogens including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Its ability to rapidly kill microorganisms makes it a valuable antiseptic agent for various applications in healthcare and sanitation.
- Hypochlorous acid in wound care and disinfection: Hypochlorous acid is utilized in wound care products and disinfectants due to its potent antimicrobial activity and low toxicity to human cells. It can effectively clean and disinfect wounds, promoting healing while reducing the risk of infection.
- Stabilization and formulation of hypochlorous acid solutions: Various methods and compositions are developed to stabilize hypochlorous acid solutions, maintaining their efficacy over time. These formulations may include specific pH ranges, additives, or packaging technologies to preserve the antiseptic properties of hypochlorous acid.
- Hypochlorous acid in medical device sterilization: Hypochlorous acid is employed in the sterilization of medical devices and equipment due to its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. It provides an effective and safe alternative to traditional sterilization methods, particularly for heat-sensitive materials.
- Generation and application methods of hypochlorous acid: Various techniques and devices are developed for the generation and application of hypochlorous acid. These may include electrolytic systems, spray devices, or other specialized equipment designed to produce and deliver hypochlorous acid for antiseptic purposes in different settings.
02 Hypochlorous acid in wound care and disinfection
Hypochlorous acid is utilized in wound care products and disinfectants due to its potent antimicrobial activity and low toxicity to human cells. It can effectively clean and disinfect wounds, promoting healing while reducing the risk of infection. Additionally, it is used in surface disinfection in healthcare settings and public spaces to maintain hygiene and prevent the spread of pathogens.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stabilization and formulation of hypochlorous acid solutions
Developing stable formulations of hypochlorous acid is crucial for maintaining its antiseptic properties over time. Various techniques and additives are employed to stabilize hypochlorous acid solutions, preventing degradation and ensuring consistent efficacy. These formulations may include pH adjusters, buffers, and other components to enhance stability and shelf life.Expand Specific Solutions04 Hypochlorous acid generation and delivery systems
Innovative systems for generating and delivering hypochlorous acid have been developed to ensure its effectiveness as an antiseptic. These may include on-site generation devices, specialized packaging, or application methods that maintain the acid's potency until use. Such systems aim to overcome challenges related to the stability and storage of hypochlorous acid solutions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications in personal care and hygiene products
Hypochlorous acid is incorporated into various personal care and hygiene products due to its antiseptic properties. These may include hand sanitizers, mouthwashes, and skincare products. The acid's ability to effectively eliminate pathogens while being gentle on human tissue makes it suitable for regular use in maintaining personal hygiene and preventing infections.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for enhancing hypochlorous acid's antiseptic properties is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for effective disinfectants. The global market size for hypochlorous acid-based products is expanding, with applications in healthcare, water treatment, and consumer goods. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Annihilare Medical Systems, Industrie De Nora, and Bactiguard AB leading innovation. These firms are developing novel formulations and delivery systems to improve stability and efficacy. Emerging players such as Aquaox and SANIGEN are also contributing to technological advancements, focusing on on-site generation and specialized applications. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established chemical companies and innovative startups vying for market share in this promising sector.
ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS, INC.
Technical Solution: ANNIHILARE has developed a proprietary electrolysis process to produce highly stable and effective hypochlorous acid (HOCl) solutions. Their technology focuses on maintaining the optimal pH range of 5.5-6.5, which enhances the stability and efficacy of HOCl[1]. The company utilizes a unique membrane cell electrolysis system that allows for precise control of chlorine species generation, resulting in a consistent and pure HOCl product[2]. Additionally, ANNIHILARE has implemented a patented packaging system that preserves the potency of their HOCl solutions for extended periods, addressing one of the key challenges in HOCl stability[3].
Strengths: Highly stable HOCl formulation, precise control over production process, extended shelf life. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs due to specialized equipment, limited scalability for mass production.
Industrie De Nora SpA
Technical Solution: De Nora has developed advanced electrochemical cell technology for on-site generation of hypochlorous acid. Their system employs specialized electrode materials and coatings that enhance the efficiency of HOCl production[4]. The company's approach focuses on maximizing the conversion of chloride ions to HOCl while minimizing the formation of unwanted byproducts. De Nora's technology also incorporates real-time monitoring and adjustment of electrolysis parameters to maintain optimal HOCl concentration and pH levels[5]. Furthermore, they have implemented a novel post-production treatment process that removes trace impurities, resulting in a highly pure and more effective HOCl solution[6].
Strengths: High-efficiency HOCl production, real-time process optimization, superior product purity. Weaknesses: High initial investment for equipment, complexity of operation requiring specialized training.
HOCl Innovations
Compositions of hypochlorous acid and methods of manufacture thereof
PatentActiveUS12115185B2
Innovation
- An air-free mixing method producing stable HOCl by combining a compound that generates protons (H+) with one that generates hypochlorite anions (OCl-) in water, without using chlorine gas or electrolysis, maintaining a controlled pH and using buffering agents to stabilize the product.
Semi-fluidic composition for lubricating, moisture retaining, disinfecting, sterilizing and method using the same
PatentInactiveEP2937101A1
Innovation
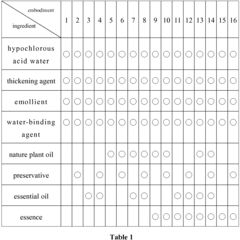
- A semi-fluid composition combining hypochlorous acid with a thickening agent, emollient, and water-binding agent to create a stable, slow-release hydrogel or viscous substance that adheres well to surfaces and provides extended-spectrum disinfection and sterilization, while also lubricating and retaining moisture, using ingredients like agar powder, glyceryl caprylate, and glycerin.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of enhancing hypochlorous acid's antiseptic properties, as it ensures the safety and efficacy of the product for public use. The regulatory landscape for hypochlorous acid varies across different regions and applications, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of the relevant guidelines and standards.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates hypochlorous acid as an over-the-counter (OTC) antiseptic when used for wound care or skin disinfection. Manufacturers must adhere to the FDA's Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and provide substantial evidence of safety and effectiveness through clinical trials. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also plays a role in regulating hypochlorous acid when used as a surface disinfectant, requiring registration and adherence to specific labeling requirements.
The European Union (EU) has its own set of regulations governing the use of hypochlorous acid in antiseptic products. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees the approval process for medicinal products containing hypochlorous acid, while the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) regulates its use in biocidal products under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR).
To enhance hypochlorous acid's antiseptic properties while maintaining regulatory compliance, manufacturers must focus on several key areas. Firstly, ensuring consistent product quality and stability is crucial. This involves developing robust manufacturing processes that produce hypochlorous acid solutions with precise concentrations and pH levels, as these factors significantly impact its efficacy and safety profile.
Secondly, comprehensive toxicology studies are essential to demonstrate the safety of enhanced hypochlorous acid formulations. These studies should address potential skin irritation, sensitization, and systemic toxicity concerns. Long-term stability testing is also necessary to determine the product's shelf life and storage requirements, which are critical factors in regulatory approval.
Thirdly, efficacy testing against a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, is required to support claims of enhanced antiseptic properties. These tests should follow standardized protocols recognized by regulatory bodies, such as those outlined by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) or the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST).
Lastly, manufacturers must carefully consider the environmental impact of their enhanced hypochlorous acid products. Many regulatory agencies now require environmental risk assessments, particularly for products that may be released into water systems. Demonstrating biodegradability and minimal ecotoxicity can be crucial for obtaining regulatory approval and meeting sustainability standards.
By addressing these regulatory compliance aspects, manufacturers can develop enhanced hypochlorous acid antiseptic products that not only meet regulatory requirements but also provide improved efficacy and safety for consumers. This approach ensures that innovations in hypochlorous acid technology can be successfully brought to market while maintaining the highest standards of public health protection.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates hypochlorous acid as an over-the-counter (OTC) antiseptic when used for wound care or skin disinfection. Manufacturers must adhere to the FDA's Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and provide substantial evidence of safety and effectiveness through clinical trials. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also plays a role in regulating hypochlorous acid when used as a surface disinfectant, requiring registration and adherence to specific labeling requirements.
The European Union (EU) has its own set of regulations governing the use of hypochlorous acid in antiseptic products. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees the approval process for medicinal products containing hypochlorous acid, while the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) regulates its use in biocidal products under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR).
To enhance hypochlorous acid's antiseptic properties while maintaining regulatory compliance, manufacturers must focus on several key areas. Firstly, ensuring consistent product quality and stability is crucial. This involves developing robust manufacturing processes that produce hypochlorous acid solutions with precise concentrations and pH levels, as these factors significantly impact its efficacy and safety profile.
Secondly, comprehensive toxicology studies are essential to demonstrate the safety of enhanced hypochlorous acid formulations. These studies should address potential skin irritation, sensitization, and systemic toxicity concerns. Long-term stability testing is also necessary to determine the product's shelf life and storage requirements, which are critical factors in regulatory approval.
Thirdly, efficacy testing against a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, is required to support claims of enhanced antiseptic properties. These tests should follow standardized protocols recognized by regulatory bodies, such as those outlined by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) or the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST).
Lastly, manufacturers must carefully consider the environmental impact of their enhanced hypochlorous acid products. Many regulatory agencies now require environmental risk assessments, particularly for products that may be released into water systems. Demonstrating biodegradability and minimal ecotoxicity can be crucial for obtaining regulatory approval and meeting sustainability standards.
By addressing these regulatory compliance aspects, manufacturers can develop enhanced hypochlorous acid antiseptic products that not only meet regulatory requirements but also provide improved efficacy and safety for consumers. This approach ensures that innovations in hypochlorous acid technology can be successfully brought to market while maintaining the highest standards of public health protection.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of enhancing hypochlorous acid's antiseptic properties is a crucial consideration in the development and application of this technology. Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) is known for its potent antimicrobial properties and is widely used in various industries, including healthcare, water treatment, and food processing. As efforts to enhance its antiseptic properties continue, it is essential to evaluate the potential environmental consequences.
One of the primary environmental advantages of hypochlorous acid is its eco-friendly nature. HOCl naturally breaks down into salt and water, leaving no harmful residues or by-products. This characteristic makes it an attractive alternative to traditional chemical disinfectants, which often have more significant environmental footprints. Enhanced HOCl formulations could potentially reduce the overall use of more environmentally harmful disinfectants, leading to a positive impact on ecosystems and water quality.
However, the production process of hypochlorous acid and its enhanced formulations may have environmental implications. The energy consumption and resource utilization associated with manufacturing HOCl solutions should be carefully assessed. Efforts to enhance its antiseptic properties may involve additional chemical processes or ingredients, which could potentially increase the environmental burden of production.
Water usage is another critical factor to consider. While HOCl is often used in water treatment applications, the production of enhanced formulations may require significant water resources. Sustainable water management practices should be implemented to minimize the environmental impact of increased HOCl production and use.
The disposal of HOCl solutions, even in their enhanced forms, generally poses minimal environmental risks due to their rapid decomposition. However, the increased efficacy of enhanced formulations may lead to more widespread use, potentially resulting in larger volumes being released into the environment. Although HOCl breaks down quickly, the cumulative effect of increased discharge should be monitored to ensure no unforeseen ecological consequences arise.
Biodiversity impact is another aspect that requires attention. While HOCl is generally considered safe for most organisms when used as directed, enhanced formulations may have different effects on aquatic life and microorganisms. Comprehensive ecological studies should be conducted to assess any potential impacts on sensitive ecosystems, particularly in aquatic environments where HOCl may be used for water treatment or discharged as waste.
In conclusion, while enhancing hypochlorous acid's antiseptic properties offers promising benefits, a thorough evaluation of its environmental impact is essential. Balancing the improved efficacy with sustainable production methods, responsible use, and proper disposal practices will be crucial in maximizing the benefits of enhanced HOCl formulations while minimizing potential environmental risks.
One of the primary environmental advantages of hypochlorous acid is its eco-friendly nature. HOCl naturally breaks down into salt and water, leaving no harmful residues or by-products. This characteristic makes it an attractive alternative to traditional chemical disinfectants, which often have more significant environmental footprints. Enhanced HOCl formulations could potentially reduce the overall use of more environmentally harmful disinfectants, leading to a positive impact on ecosystems and water quality.
However, the production process of hypochlorous acid and its enhanced formulations may have environmental implications. The energy consumption and resource utilization associated with manufacturing HOCl solutions should be carefully assessed. Efforts to enhance its antiseptic properties may involve additional chemical processes or ingredients, which could potentially increase the environmental burden of production.
Water usage is another critical factor to consider. While HOCl is often used in water treatment applications, the production of enhanced formulations may require significant water resources. Sustainable water management practices should be implemented to minimize the environmental impact of increased HOCl production and use.
The disposal of HOCl solutions, even in their enhanced forms, generally poses minimal environmental risks due to their rapid decomposition. However, the increased efficacy of enhanced formulations may lead to more widespread use, potentially resulting in larger volumes being released into the environment. Although HOCl breaks down quickly, the cumulative effect of increased discharge should be monitored to ensure no unforeseen ecological consequences arise.
Biodiversity impact is another aspect that requires attention. While HOCl is generally considered safe for most organisms when used as directed, enhanced formulations may have different effects on aquatic life and microorganisms. Comprehensive ecological studies should be conducted to assess any potential impacts on sensitive ecosystems, particularly in aquatic environments where HOCl may be used for water treatment or discharged as waste.
In conclusion, while enhancing hypochlorous acid's antiseptic properties offers promising benefits, a thorough evaluation of its environmental impact is essential. Balancing the improved efficacy with sustainable production methods, responsible use, and proper disposal practices will be crucial in maximizing the benefits of enhanced HOCl formulations while minimizing potential environmental risks.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!