How to Enhance the Compatibility of Hypochlorous Acid with Surfactants?
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCl-Surfactant Compatibility Background
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potent antimicrobial properties and eco-friendly nature. As a weak acid produced naturally by the human immune system, HOCl has found applications in various industries, including healthcare, food processing, and water treatment. However, its widespread adoption has been hindered by compatibility issues with surfactants, which are essential components in many cleaning and disinfection formulations.
The challenge of enhancing HOCl-surfactant compatibility stems from the inherent chemical properties of both substances. HOCl is a highly reactive oxidizing agent, while surfactants are complex molecules designed to reduce surface tension and facilitate cleaning. When combined, these components often interact in ways that can compromise the stability and efficacy of the overall solution.
Historically, the use of HOCl has been limited by its instability and short shelf life. Early attempts to stabilize HOCl solutions focused on pH control and the addition of various buffers. However, these methods often resulted in reduced antimicrobial efficacy or introduced unwanted chemical residues. The introduction of surfactants to HOCl formulations presented an additional layer of complexity, as many common surfactants were found to rapidly degrade in the presence of HOCl.
The evolution of HOCl technology has seen several key developments aimed at addressing these compatibility issues. Researchers have explored novel surfactant chemistries specifically designed to withstand oxidative stress. Concurrently, efforts have been made to develop HOCl generation and stabilization techniques that minimize unwanted reactions with surfactants.
Understanding the molecular interactions between HOCl and surfactants has become a critical area of study. Factors such as pH, temperature, and concentration play crucial roles in determining the stability and effectiveness of HOCl-surfactant combinations. The development of advanced analytical techniques has enabled researchers to better characterize these interactions and design more compatible formulations.
The quest for enhanced HOCl-surfactant compatibility is driven by the growing demand for effective, safe, and environmentally friendly cleaning and disinfection solutions. As concerns over traditional chemical disinfectants continue to rise, the potential for HOCl-based products to fill this gap has become increasingly apparent. However, realizing this potential requires overcoming the technical challenges associated with formulating stable and effective HOCl-surfactant combinations.
The challenge of enhancing HOCl-surfactant compatibility stems from the inherent chemical properties of both substances. HOCl is a highly reactive oxidizing agent, while surfactants are complex molecules designed to reduce surface tension and facilitate cleaning. When combined, these components often interact in ways that can compromise the stability and efficacy of the overall solution.
Historically, the use of HOCl has been limited by its instability and short shelf life. Early attempts to stabilize HOCl solutions focused on pH control and the addition of various buffers. However, these methods often resulted in reduced antimicrobial efficacy or introduced unwanted chemical residues. The introduction of surfactants to HOCl formulations presented an additional layer of complexity, as many common surfactants were found to rapidly degrade in the presence of HOCl.
The evolution of HOCl technology has seen several key developments aimed at addressing these compatibility issues. Researchers have explored novel surfactant chemistries specifically designed to withstand oxidative stress. Concurrently, efforts have been made to develop HOCl generation and stabilization techniques that minimize unwanted reactions with surfactants.
Understanding the molecular interactions between HOCl and surfactants has become a critical area of study. Factors such as pH, temperature, and concentration play crucial roles in determining the stability and effectiveness of HOCl-surfactant combinations. The development of advanced analytical techniques has enabled researchers to better characterize these interactions and design more compatible formulations.
The quest for enhanced HOCl-surfactant compatibility is driven by the growing demand for effective, safe, and environmentally friendly cleaning and disinfection solutions. As concerns over traditional chemical disinfectants continue to rise, the potential for HOCl-based products to fill this gap has become increasingly apparent. However, realizing this potential requires overcoming the technical challenges associated with formulating stable and effective HOCl-surfactant combinations.
Market Analysis for HOCl-Surfactant Products
The market for HOCl-surfactant products is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for effective and environmentally friendly cleaning and disinfection solutions. The global market size for these products is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding industry averages. This growth is primarily fueled by the rising awareness of hygiene and sanitation, particularly in healthcare, food processing, and household sectors.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards safer, non-toxic cleaning products, creating a favorable environment for HOCl-surfactant combinations. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, with heightened focus on disinfection in both commercial and residential settings. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly investing in research and development to improve the compatibility and efficacy of HOCl-surfactant formulations.
The healthcare sector represents a significant market segment for HOCl-surfactant products, with hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities seeking powerful yet safe disinfection solutions. The food and beverage industry is another key market, where these products are used for sanitizing food contact surfaces and equipment. Additionally, the household cleaning market shows promising growth potential as consumers become more health-conscious and environmentally aware.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for HOCl-surfactant products, owing to stringent regulations on chemical safety and environmental protection. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing disposable incomes in countries like China and India.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the need for continuous innovation to improve product stability and shelf life. Manufacturers must also address concerns about the potential environmental impact of surfactants and educate consumers about the benefits of HOCl-based products compared to traditional chemical disinfectants.
In conclusion, the market for HOCl-surfactant products shows strong growth potential, driven by increasing demand for safe and effective cleaning solutions across various industries. To capitalize on this opportunity, companies must focus on enhancing product compatibility, improving stability, and educating consumers about the benefits of these innovative cleaning and disinfection solutions.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards safer, non-toxic cleaning products, creating a favorable environment for HOCl-surfactant combinations. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, with heightened focus on disinfection in both commercial and residential settings. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly investing in research and development to improve the compatibility and efficacy of HOCl-surfactant formulations.
The healthcare sector represents a significant market segment for HOCl-surfactant products, with hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities seeking powerful yet safe disinfection solutions. The food and beverage industry is another key market, where these products are used for sanitizing food contact surfaces and equipment. Additionally, the household cleaning market shows promising growth potential as consumers become more health-conscious and environmentally aware.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for HOCl-surfactant products, owing to stringent regulations on chemical safety and environmental protection. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing disposable incomes in countries like China and India.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the need for continuous innovation to improve product stability and shelf life. Manufacturers must also address concerns about the potential environmental impact of surfactants and educate consumers about the benefits of HOCl-based products compared to traditional chemical disinfectants.
In conclusion, the market for HOCl-surfactant products shows strong growth potential, driven by increasing demand for safe and effective cleaning solutions across various industries. To capitalize on this opportunity, companies must focus on enhancing product compatibility, improving stability, and educating consumers about the benefits of these innovative cleaning and disinfection solutions.
Current Challenges in HOCl-Surfactant Formulations
The formulation of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) with surfactants presents several significant challenges that hinder the development of stable and effective products. One of the primary issues is the inherent instability of HOCl in the presence of organic compounds, including many surfactants. HOCl tends to react with these organic molecules, leading to rapid degradation and loss of antimicrobial efficacy.
The pH sensitivity of HOCl further complicates its compatibility with surfactants. HOCl is most stable and effective at a slightly acidic pH range of 4-6. However, many surfactants perform optimally at different pH levels, creating a conflict in formulation requirements. Balancing the pH to maintain HOCl stability while ensuring surfactant functionality remains a significant challenge.
Another critical issue is the potential for oxidation reactions between HOCl and certain surfactants. HOCl's strong oxidizing properties can lead to the breakdown of surfactant molecules, particularly those with unsaturated bonds or reactive functional groups. This not only reduces the effectiveness of the surfactant but can also result in the formation of undesirable by-products.
The ionic nature of many surfactants poses additional compatibility challenges. Cationic surfactants, for instance, can interact with the negatively charged hypochlorite ion (OCl-) present in HOCl solutions, potentially leading to precipitation or reduced antimicrobial activity. Similarly, anionic surfactants may interfere with the equilibrium between HOCl and OCl-, affecting the overall efficacy of the formulation.
Formulation stability over time is another significant concern. Even when initial compatibility is achieved, long-term storage can lead to gradual degradation of both HOCl and surfactants. This results in reduced shelf life and potential changes in product performance, color, or odor.
The challenge of maintaining HOCl concentration in surfactant-containing formulations is also noteworthy. HOCl is volatile and can be lost through off-gassing, particularly in formulations with increased surface area due to the presence of surfactants. This loss of active ingredient can significantly impact the product's antimicrobial efficacy over time.
Lastly, the potential for synergistic or antagonistic effects between HOCl and surfactants on antimicrobial activity presents both a challenge and an opportunity. While some surfactants may enhance HOCl's penetration into microbial cells, others might form protective barriers that reduce its effectiveness. Understanding and optimizing these interactions is crucial for developing high-performance formulations.
The pH sensitivity of HOCl further complicates its compatibility with surfactants. HOCl is most stable and effective at a slightly acidic pH range of 4-6. However, many surfactants perform optimally at different pH levels, creating a conflict in formulation requirements. Balancing the pH to maintain HOCl stability while ensuring surfactant functionality remains a significant challenge.
Another critical issue is the potential for oxidation reactions between HOCl and certain surfactants. HOCl's strong oxidizing properties can lead to the breakdown of surfactant molecules, particularly those with unsaturated bonds or reactive functional groups. This not only reduces the effectiveness of the surfactant but can also result in the formation of undesirable by-products.
The ionic nature of many surfactants poses additional compatibility challenges. Cationic surfactants, for instance, can interact with the negatively charged hypochlorite ion (OCl-) present in HOCl solutions, potentially leading to precipitation or reduced antimicrobial activity. Similarly, anionic surfactants may interfere with the equilibrium between HOCl and OCl-, affecting the overall efficacy of the formulation.
Formulation stability over time is another significant concern. Even when initial compatibility is achieved, long-term storage can lead to gradual degradation of both HOCl and surfactants. This results in reduced shelf life and potential changes in product performance, color, or odor.
The challenge of maintaining HOCl concentration in surfactant-containing formulations is also noteworthy. HOCl is volatile and can be lost through off-gassing, particularly in formulations with increased surface area due to the presence of surfactants. This loss of active ingredient can significantly impact the product's antimicrobial efficacy over time.
Lastly, the potential for synergistic or antagonistic effects between HOCl and surfactants on antimicrobial activity presents both a challenge and an opportunity. While some surfactants may enhance HOCl's penetration into microbial cells, others might form protective barriers that reduce its effectiveness. Understanding and optimizing these interactions is crucial for developing high-performance formulations.
Existing HOCl-Surfactant Compatibility Solutions
01 Compatibility with materials
Hypochlorous acid's compatibility with various materials is crucial for its application in different industries. Studies have been conducted to determine its interaction with metals, plastics, and other common materials used in manufacturing and storage. The compatibility of hypochlorous acid with different materials affects its storage, transportation, and application methods.- Compatibility with cleaning and disinfecting agents: Hypochlorous acid shows compatibility with various cleaning and disinfecting agents, enhancing its effectiveness in sanitization applications. This compatibility allows for the formulation of multi-functional cleaning products that combine the antimicrobial properties of hypochlorous acid with other cleaning agents.
- Stability in different pH environments: The stability of hypochlorous acid is influenced by pH levels. Research has focused on developing formulations that maintain the acid's stability across a range of pH environments, ensuring its effectiveness in various applications and extending its shelf life.
- Compatibility with packaging materials: Studies have been conducted on the compatibility of hypochlorous acid with different packaging materials to prevent degradation and maintain its efficacy during storage. This research aims to identify suitable materials that do not react with the acid and preserve its properties over time.
- Synergistic effects with other antimicrobial agents: Hypochlorous acid has shown potential for synergistic effects when combined with other antimicrobial agents. This compatibility allows for the development of more potent disinfectant formulations with broader spectrum activity against various pathogens.
- Compatibility in medical and healthcare applications: Research has explored the compatibility of hypochlorous acid in medical and healthcare settings, including its use in wound care, sterilization of medical equipment, and as a general disinfectant. These studies focus on ensuring the acid's safety and efficacy when in contact with human tissues and medical materials.
02 Stability and preservation
The stability of hypochlorous acid solutions is a key factor in their effectiveness and shelf life. Research has focused on developing methods to preserve hypochlorous acid and maintain its potency over time. This includes the use of stabilizers, pH adjustments, and specialized packaging to prevent degradation and ensure long-term efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions03 Formulation with other compounds
Hypochlorous acid can be formulated with other compounds to enhance its properties or create specialized products. Studies have explored its compatibility with various additives, surfactants, and active ingredients. These formulations aim to improve the acid's effectiveness, stability, or application-specific properties while maintaining its core benefits.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application in disinfection and sanitization
Hypochlorous acid's compatibility in disinfection and sanitization applications is a significant area of research. Studies have focused on its effectiveness against various pathogens, its safety for use on different surfaces, and its potential as an alternative to traditional disinfectants. The compatibility of hypochlorous acid with existing cleaning protocols and equipment is also being investigated.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
The environmental impact and safety aspects of hypochlorous acid are important factors in its compatibility for various applications. Research has been conducted on its biodegradability, potential for by-product formation, and effects on aquatic life. Additionally, studies have examined its safety for human exposure and potential irritation or sensitization effects, which are crucial for its use in consumer products and industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HOCl and Surfactant Industries
The compatibility of hypochlorous acid with surfactants is a growing area of interest in the chemical industry, currently in its early development stage. The market size is expanding as more companies recognize the potential applications in disinfection and cleaning products. Technologically, it's still evolving, with varying levels of maturity among key players. Companies like Procter & Gamble, Kao Corp., and Unilever are leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities to advance this technology. Smaller specialized firms such as WIAB WATER INNOVATION AB and Industrie De Nora SpA are also making significant contributions. The Clorox Co. and S.C. Johnson & Son, with their expertise in household cleaning products, are likely to play crucial roles in commercializing these innovations.
Procter & Gamble Deutschland GmbH
Technical Solution: Procter & Gamble has developed a novel approach to enhance the compatibility of hypochlorous acid with surfactants. Their method involves creating a stabilized aqueous composition containing hypochlorous acid and at least one surfactant. The composition is formulated with a specific pH range of 3 to 8.5, which helps maintain the stability of hypochlorous acid while allowing for effective surfactant action[1]. Additionally, they have incorporated buffer systems to control pH fluctuations and added stabilizing agents such as phosphates or carbonates to further improve the compatibility[2]. This innovative formulation allows for the creation of cleaning products that harness both the disinfecting power of hypochlorous acid and the cleaning efficacy of surfactants, without compromising the stability or effectiveness of either component[3].
Strengths: Improved stability and efficacy of hypochlorous acid in surfactant-containing formulations. Broader application range in cleaning and disinfecting products. Weaknesses: May require careful pH control and additional stabilizing agents, potentially increasing production complexity and costs.
Kao Corp.
Technical Solution: Kao Corporation has developed an innovative approach to enhance the compatibility of hypochlorous acid with surfactants. Their method involves the use of specific surfactant blends that are less reactive with hypochlorous acid, such as amine oxide surfactants and betaines[1]. These surfactants are carefully selected for their stability in the presence of oxidizing agents. Additionally, Kao has implemented a unique emulsion system that encapsulates the hypochlorous acid, protecting it from direct contact with the surfactants[2]. This emulsion system utilizes nano-sized droplets to create a barrier between the hypochlorous acid and the surfactants, allowing both components to coexist in the same formulation without significant degradation[3]. The company has also developed a proprietary stabilization technology that involves the addition of specific antioxidants and chelating agents to further enhance the stability of the hypochlorous acid-surfactant system[4].
Strengths: Innovative emulsion system provides excellent stability. Use of specialized surfactants enhances compatibility. Weaknesses: May limit the types of surfactants that can be used, potentially affecting cleaning performance in certain applications.
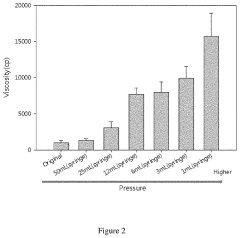
Innovative Approaches to HOCl Stabilization
Hypochlorous acid composition
PatentPendingUS20230329240A1
Innovation
- A hypochlorous acid composition whose viscosity can be dynamically changed by exerting different pressures, transforming from a liquid to a high-viscosity gel upon spraying, allowing for improved adhesion and reduced contamination risks.
Environmental Impact of HOCl-Surfactant Products
The environmental impact of HOCl-surfactant products is a critical consideration in their development and application. These products, which combine hypochlorous acid (HOCl) with surfactants, have gained attention due to their potential for enhanced cleaning and disinfection capabilities. However, their widespread use raises important questions about their effects on ecosystems and human health.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential for these products to contribute to water pollution. When released into aquatic environments, the combination of HOCl and surfactants can have complex interactions with existing ecosystems. Surfactants, known for their ability to reduce surface tension, may affect the natural balance of aquatic organisms by altering the surface properties of water. This can impact the respiratory processes of aquatic life and potentially disrupt food chains.
The decomposition of HOCl in water bodies is another factor to consider. While HOCl itself is generally considered environmentally friendly due to its rapid breakdown into harmless components, its interaction with surfactants may alter this process. The presence of surfactants could potentially slow down the decomposition rate of HOCl, leading to prolonged exposure of aquatic life to chlorine-based compounds.
Soil contamination is another potential environmental impact of HOCl-surfactant products. When these solutions are used in outdoor settings or disposed of improperly, they can seep into the soil. This may affect soil microorganisms, which play crucial roles in nutrient cycling and overall soil health. The alteration of soil microbial communities could have cascading effects on plant growth and ecosystem functioning.
The production and disposal of HOCl-surfactant products also contribute to their environmental footprint. Manufacturing processes may involve energy-intensive steps and the use of various chemicals, potentially leading to greenhouse gas emissions and chemical waste. Proper disposal methods must be developed and implemented to minimize the release of these products into the environment.
On a positive note, the use of HOCl-surfactant products may have some environmental benefits. Their enhanced cleaning and disinfection properties could potentially reduce the need for more harmful chemical alternatives, thereby decreasing the overall environmental impact of cleaning and sanitation practices. Additionally, if these products prove to be more effective at lower concentrations, it could lead to reduced chemical usage and waste generation.
Research into the long-term environmental effects of HOCl-surfactant products is ongoing. As their use becomes more widespread, it is crucial to conduct comprehensive environmental impact assessments. These studies should focus on biodegradability, bioaccumulation potential, and effects on non-target organisms. The development of eco-friendly formulations and sustainable production methods will be key to mitigating potential negative environmental impacts while harnessing the benefits of these innovative cleaning solutions.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential for these products to contribute to water pollution. When released into aquatic environments, the combination of HOCl and surfactants can have complex interactions with existing ecosystems. Surfactants, known for their ability to reduce surface tension, may affect the natural balance of aquatic organisms by altering the surface properties of water. This can impact the respiratory processes of aquatic life and potentially disrupt food chains.
The decomposition of HOCl in water bodies is another factor to consider. While HOCl itself is generally considered environmentally friendly due to its rapid breakdown into harmless components, its interaction with surfactants may alter this process. The presence of surfactants could potentially slow down the decomposition rate of HOCl, leading to prolonged exposure of aquatic life to chlorine-based compounds.
Soil contamination is another potential environmental impact of HOCl-surfactant products. When these solutions are used in outdoor settings or disposed of improperly, they can seep into the soil. This may affect soil microorganisms, which play crucial roles in nutrient cycling and overall soil health. The alteration of soil microbial communities could have cascading effects on plant growth and ecosystem functioning.
The production and disposal of HOCl-surfactant products also contribute to their environmental footprint. Manufacturing processes may involve energy-intensive steps and the use of various chemicals, potentially leading to greenhouse gas emissions and chemical waste. Proper disposal methods must be developed and implemented to minimize the release of these products into the environment.
On a positive note, the use of HOCl-surfactant products may have some environmental benefits. Their enhanced cleaning and disinfection properties could potentially reduce the need for more harmful chemical alternatives, thereby decreasing the overall environmental impact of cleaning and sanitation practices. Additionally, if these products prove to be more effective at lower concentrations, it could lead to reduced chemical usage and waste generation.
Research into the long-term environmental effects of HOCl-surfactant products is ongoing. As their use becomes more widespread, it is crucial to conduct comprehensive environmental impact assessments. These studies should focus on biodegradability, bioaccumulation potential, and effects on non-target organisms. The development of eco-friendly formulations and sustainable production methods will be key to mitigating potential negative environmental impacts while harnessing the benefits of these innovative cleaning solutions.
Regulatory Framework for HOCl-Based Formulations
The regulatory framework for hypochlorous acid (HOCl)-based formulations is a critical aspect of product development and commercialization. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a pivotal role in regulating HOCl as an antimicrobial agent. The EPA has approved HOCl for various applications, including surface disinfection and water treatment, under specific concentration and use guidelines.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also oversees HOCl-based products, particularly those intended for medical or personal care use. The FDA has classified HOCl solutions as generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used as specified, which has facilitated its incorporation into various consumer products.
In the European Union, the regulatory landscape for HOCl is governed by the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR). This regulation ensures that biocidal products, including those containing HOCl, are thoroughly assessed for their efficacy and potential risks before being made available on the market. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) manages the technical and scientific work under the BPR.
When formulating HOCl with surfactants, manufacturers must adhere to specific guidelines to maintain product integrity and safety. The concentration of HOCl in these formulations is typically regulated to ensure effectiveness while minimizing potential adverse effects. Stability testing and shelf-life studies are often required to demonstrate the product's longevity and continued efficacy over time.
Labeling requirements for HOCl-based products vary depending on their intended use and jurisdiction. In general, products must clearly state the active ingredient concentration, intended use, and any necessary precautions or warnings. For products claiming antimicrobial properties, specific efficacy data may be required to support such claims.
The regulatory framework also addresses the environmental impact of HOCl-based formulations. Many regulatory bodies require environmental risk assessments, particularly for products that may enter water systems or have widespread use. The biodegradability and potential ecological effects of both HOCl and the surfactants used in the formulation are considered in these assessments.
As research continues to explore new applications for HOCl-surfactant combinations, regulatory bodies are likely to adapt their frameworks to accommodate these innovations. This may include developing new testing protocols or adjusting existing guidelines to ensure the safety and efficacy of novel formulations. Manufacturers and researchers must stay informed about these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and facilitate the successful development of HOCl-based products.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also oversees HOCl-based products, particularly those intended for medical or personal care use. The FDA has classified HOCl solutions as generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used as specified, which has facilitated its incorporation into various consumer products.
In the European Union, the regulatory landscape for HOCl is governed by the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR). This regulation ensures that biocidal products, including those containing HOCl, are thoroughly assessed for their efficacy and potential risks before being made available on the market. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) manages the technical and scientific work under the BPR.
When formulating HOCl with surfactants, manufacturers must adhere to specific guidelines to maintain product integrity and safety. The concentration of HOCl in these formulations is typically regulated to ensure effectiveness while minimizing potential adverse effects. Stability testing and shelf-life studies are often required to demonstrate the product's longevity and continued efficacy over time.
Labeling requirements for HOCl-based products vary depending on their intended use and jurisdiction. In general, products must clearly state the active ingredient concentration, intended use, and any necessary precautions or warnings. For products claiming antimicrobial properties, specific efficacy data may be required to support such claims.
The regulatory framework also addresses the environmental impact of HOCl-based formulations. Many regulatory bodies require environmental risk assessments, particularly for products that may enter water systems or have widespread use. The biodegradability and potential ecological effects of both HOCl and the surfactants used in the formulation are considered in these assessments.
As research continues to explore new applications for HOCl-surfactant combinations, regulatory bodies are likely to adapt their frameworks to accommodate these innovations. This may include developing new testing protocols or adjusting existing guidelines to ensure the safety and efficacy of novel formulations. Manufacturers and researchers must stay informed about these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and facilitate the successful development of HOCl-based products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!