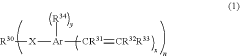How to Extend Acrylic Resin Shelf Life in Storage
OCT 11, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Acrylic Resin Shelf Life Background and Objectives
Acrylic resins have become indispensable materials in various industries including coatings, adhesives, dental applications, and construction due to their exceptional properties such as transparency, weather resistance, and versatility. The evolution of these polymers began in the 1930s with the development of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as Plexiglas or Lucite, and has since expanded to include numerous formulations tailored for specific applications.
The shelf life of acrylic resins represents a critical factor affecting both manufacturers and end-users, with significant economic and performance implications. Typically, these resins have a shelf life ranging from 6 months to 2 years depending on formulation and storage conditions. However, premature degradation remains a persistent challenge, resulting in substantial material waste, increased production costs, and compromised product quality.
Recent market analyses indicate that the global acrylic resin market is projected to reach $21.9 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.2%. This growth trajectory underscores the importance of addressing shelf life limitations as a means to reduce waste and enhance sustainability across the supply chain. Furthermore, regulatory pressures regarding volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and environmental impact have accelerated the need for stable, long-lasting formulations.
The technical evolution of acrylic resins has seen significant advancements in polymerization techniques, from conventional free radical polymerization to controlled radical polymerization methods such as ATRP (Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization) and RAFT (Reversible Addition-Fragmentation chain Transfer). These developments have improved molecular weight distribution control but have not fully addressed stability challenges during storage.
Primary degradation mechanisms affecting acrylic resin shelf life include thermal degradation, photo-oxidation, hydrolysis, and residual monomer reactions. Temperature fluctuations, exposure to UV radiation, moisture ingress, and oxygen exposure accelerate these processes, leading to viscosity changes, yellowing, reduced reactivity, and ultimately, product failure.
The objective of this technical research is to comprehensively investigate and develop innovative strategies to extend the shelf life of acrylic resins under various storage conditions. Specifically, we aim to identify optimal stabilization systems, explore novel packaging solutions, evaluate the effectiveness of various inhibitors and antioxidants, and establish precise storage protocols that can reliably extend shelf life by at least 50% beyond current industry standards.
Additionally, this research seeks to develop predictive models for acrylic resin degradation based on accelerated aging studies, enabling more accurate shelf life predictions and quality control measures. The ultimate goal is to establish a holistic approach to acrylic resin preservation that addresses both formulation and storage aspects, providing sustainable solutions for manufacturers and end-users throughout the supply chain.
The shelf life of acrylic resins represents a critical factor affecting both manufacturers and end-users, with significant economic and performance implications. Typically, these resins have a shelf life ranging from 6 months to 2 years depending on formulation and storage conditions. However, premature degradation remains a persistent challenge, resulting in substantial material waste, increased production costs, and compromised product quality.
Recent market analyses indicate that the global acrylic resin market is projected to reach $21.9 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.2%. This growth trajectory underscores the importance of addressing shelf life limitations as a means to reduce waste and enhance sustainability across the supply chain. Furthermore, regulatory pressures regarding volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and environmental impact have accelerated the need for stable, long-lasting formulations.
The technical evolution of acrylic resins has seen significant advancements in polymerization techniques, from conventional free radical polymerization to controlled radical polymerization methods such as ATRP (Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization) and RAFT (Reversible Addition-Fragmentation chain Transfer). These developments have improved molecular weight distribution control but have not fully addressed stability challenges during storage.
Primary degradation mechanisms affecting acrylic resin shelf life include thermal degradation, photo-oxidation, hydrolysis, and residual monomer reactions. Temperature fluctuations, exposure to UV radiation, moisture ingress, and oxygen exposure accelerate these processes, leading to viscosity changes, yellowing, reduced reactivity, and ultimately, product failure.
The objective of this technical research is to comprehensively investigate and develop innovative strategies to extend the shelf life of acrylic resins under various storage conditions. Specifically, we aim to identify optimal stabilization systems, explore novel packaging solutions, evaluate the effectiveness of various inhibitors and antioxidants, and establish precise storage protocols that can reliably extend shelf life by at least 50% beyond current industry standards.
Additionally, this research seeks to develop predictive models for acrylic resin degradation based on accelerated aging studies, enabling more accurate shelf life predictions and quality control measures. The ultimate goal is to establish a holistic approach to acrylic resin preservation that addresses both formulation and storage aspects, providing sustainable solutions for manufacturers and end-users throughout the supply chain.
Market Demand Analysis for Extended-Life Acrylic Resins
The global market for acrylic resins has been experiencing steady growth, with increasing demand across various industries including paints and coatings, adhesives, construction, automotive, and electronics. The market value for acrylic resins reached approximately $18.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% through 2030, potentially reaching $28.7 billion by the end of the forecast period.
A significant emerging segment within this market is specifically for extended-life acrylic resins, driven by manufacturers' and end-users' needs to reduce waste, lower operational costs, and improve supply chain efficiency. Industry surveys indicate that approximately 12-15% of acrylic resins are discarded due to shelf-life expiration before use, representing substantial financial losses estimated at $2.2 billion annually across the global supply chain.
The construction sector remains the largest consumer of acrylic resins, accounting for 38% of total consumption, followed by the automotive industry at 22% and consumer goods at 17%. These industries have expressed particular interest in extended shelf-life formulations due to their project-based consumption patterns and seasonal demand fluctuations, which often result in inventory management challenges.
Regional analysis shows that Asia-Pacific dominates the market with 42% share, followed by North America (27%) and Europe (21%). Notably, emerging economies in Southeast Asia and Latin America are showing accelerated demand growth rates of 7.3% and 6.8% respectively, significantly above the global average.
Environmental regulations are also driving market demand for extended-life formulations. The European Union's waste reduction directives and similar regulations in North America have established targets to reduce chemical waste by 30% by 2030, creating regulatory pressure for longer-lasting materials. Additionally, sustainability initiatives from major corporations have established goals to reduce material waste by 25-40% within their supply chains by 2025.
Consumer behavior analysis reveals a willingness to pay a premium of 15-20% for acrylic resin products with double the standard shelf life. This price elasticity is particularly evident in high-value applications such as specialty coatings and medical-grade adhesives, where the cost of material failure or replacement far exceeds the premium paid for extended stability.
Market research indicates that the demand-supply gap for extended-life acrylic resins currently stands at approximately 1.2 million tons annually, representing a significant opportunity for innovation and market entry. This gap is expected to widen as industries increasingly prioritize inventory optimization and waste reduction in their operational strategies.
A significant emerging segment within this market is specifically for extended-life acrylic resins, driven by manufacturers' and end-users' needs to reduce waste, lower operational costs, and improve supply chain efficiency. Industry surveys indicate that approximately 12-15% of acrylic resins are discarded due to shelf-life expiration before use, representing substantial financial losses estimated at $2.2 billion annually across the global supply chain.
The construction sector remains the largest consumer of acrylic resins, accounting for 38% of total consumption, followed by the automotive industry at 22% and consumer goods at 17%. These industries have expressed particular interest in extended shelf-life formulations due to their project-based consumption patterns and seasonal demand fluctuations, which often result in inventory management challenges.
Regional analysis shows that Asia-Pacific dominates the market with 42% share, followed by North America (27%) and Europe (21%). Notably, emerging economies in Southeast Asia and Latin America are showing accelerated demand growth rates of 7.3% and 6.8% respectively, significantly above the global average.
Environmental regulations are also driving market demand for extended-life formulations. The European Union's waste reduction directives and similar regulations in North America have established targets to reduce chemical waste by 30% by 2030, creating regulatory pressure for longer-lasting materials. Additionally, sustainability initiatives from major corporations have established goals to reduce material waste by 25-40% within their supply chains by 2025.
Consumer behavior analysis reveals a willingness to pay a premium of 15-20% for acrylic resin products with double the standard shelf life. This price elasticity is particularly evident in high-value applications such as specialty coatings and medical-grade adhesives, where the cost of material failure or replacement far exceeds the premium paid for extended stability.
Market research indicates that the demand-supply gap for extended-life acrylic resins currently stands at approximately 1.2 million tons annually, representing a significant opportunity for innovation and market entry. This gap is expected to widen as industries increasingly prioritize inventory optimization and waste reduction in their operational strategies.
Current Preservation Challenges and Limitations
Acrylic resins face significant preservation challenges during storage that directly impact their shelf life and ultimate performance in applications. The primary degradation mechanism involves premature polymerization, which occurs when free radicals form within the resin due to exposure to heat, light, oxygen, or contaminants. This unintended polymerization process transforms the liquid resin into a semi-solid or solid state before its intended use, rendering it unusable for manufacturing processes.
Temperature fluctuations represent a critical limitation in current preservation methods. Most acrylic resins require storage between 15-25°C, with even brief exposures to temperatures exceeding 30°C potentially triggering accelerated degradation. Many storage facilities lack precise temperature control systems capable of maintaining these narrow parameters, especially during transportation phases where temperature monitoring becomes particularly challenging.
Light exposure, particularly UV radiation, presents another significant preservation hurdle. Current packaging solutions often provide insufficient protection against light penetration, with standard containers allowing wavelengths that catalyze polymerization reactions to reach the resin. This limitation becomes especially problematic during extended storage periods or when containers are stored in areas with significant natural or artificial light exposure.
Oxygen contamination remains one of the most persistent challenges in acrylic resin preservation. Despite advances in container technology, oxygen permeation through packaging materials continues to occur over time. The industry currently lacks cost-effective, scalable solutions for creating truly oxygen-impermeable storage environments without significantly increasing packaging costs or complicating the handling process.
Inhibitor depletion represents a fundamental limitation of current preservation approaches. Most commercial acrylic resins contain polymerization inhibitors like hydroquinone or methyl ether hydroquinone (MEHQ), but these compounds gradually deplete during storage. Current technologies cannot effectively monitor inhibitor levels non-invasively, making it difficult to determine when resins approach critical stability thresholds without potentially compromising the product through sampling.
Microbial contamination has emerged as an increasingly recognized preservation challenge. While acrylic resins are not ideal growth media for microorganisms, certain bacterial and fungal species can metabolize components within the formulation, altering pH levels and potentially accelerating degradation processes. Current antimicrobial additives often have limited effectiveness over extended storage periods or may themselves impact resin performance characteristics.
The industry also faces significant challenges with batch-to-batch consistency in preservation effectiveness. Manufacturing variations in inhibitor concentrations, trace contaminants, and initial free radical content can dramatically affect storage stability, making standardized shelf-life predictions unreliable across production runs. This inconsistency complicates inventory management and increases waste from expired materials.
Temperature fluctuations represent a critical limitation in current preservation methods. Most acrylic resins require storage between 15-25°C, with even brief exposures to temperatures exceeding 30°C potentially triggering accelerated degradation. Many storage facilities lack precise temperature control systems capable of maintaining these narrow parameters, especially during transportation phases where temperature monitoring becomes particularly challenging.
Light exposure, particularly UV radiation, presents another significant preservation hurdle. Current packaging solutions often provide insufficient protection against light penetration, with standard containers allowing wavelengths that catalyze polymerization reactions to reach the resin. This limitation becomes especially problematic during extended storage periods or when containers are stored in areas with significant natural or artificial light exposure.
Oxygen contamination remains one of the most persistent challenges in acrylic resin preservation. Despite advances in container technology, oxygen permeation through packaging materials continues to occur over time. The industry currently lacks cost-effective, scalable solutions for creating truly oxygen-impermeable storage environments without significantly increasing packaging costs or complicating the handling process.
Inhibitor depletion represents a fundamental limitation of current preservation approaches. Most commercial acrylic resins contain polymerization inhibitors like hydroquinone or methyl ether hydroquinone (MEHQ), but these compounds gradually deplete during storage. Current technologies cannot effectively monitor inhibitor levels non-invasively, making it difficult to determine when resins approach critical stability thresholds without potentially compromising the product through sampling.
Microbial contamination has emerged as an increasingly recognized preservation challenge. While acrylic resins are not ideal growth media for microorganisms, certain bacterial and fungal species can metabolize components within the formulation, altering pH levels and potentially accelerating degradation processes. Current antimicrobial additives often have limited effectiveness over extended storage periods or may themselves impact resin performance characteristics.
The industry also faces significant challenges with batch-to-batch consistency in preservation effectiveness. Manufacturing variations in inhibitor concentrations, trace contaminants, and initial free radical content can dramatically affect storage stability, making standardized shelf-life predictions unreliable across production runs. This inconsistency complicates inventory management and increases waste from expired materials.
Current Preservation Methods and Solutions
01 Stabilizers and inhibitors for extending shelf life
Various stabilizers and inhibitors can be added to acrylic resin formulations to prevent premature polymerization and extend shelf life. These additives work by scavenging free radicals or inhibiting oxidation processes that lead to degradation. Common stabilizers include phenolic compounds, quinones, and certain metal salts that effectively maintain the resin's properties during storage, ensuring consistent performance when the product is eventually used.- Stabilizers and inhibitors for extending shelf life: Various stabilizers and inhibitors can be added to acrylic resin formulations to extend their shelf life. These additives prevent premature polymerization and degradation during storage. Common stabilizers include phenolic compounds, quinones, and certain metal salts that scavenge free radicals. The incorporation of these stabilizers at optimal concentrations can significantly increase the storage stability of acrylic resins, allowing them to maintain their properties for longer periods under normal storage conditions.
- Storage conditions affecting shelf life: The shelf life of acrylic resins is heavily influenced by storage conditions. Temperature control is critical, with most acrylic resins requiring storage between 5-25°C to maintain stability. Exposure to light, particularly UV radiation, can trigger degradation reactions. Humidity control is also important as moisture can affect certain acrylic formulations. Proper packaging that limits exposure to oxygen and contaminants can significantly extend the usable life of these materials. Manufacturers often specify optimal storage parameters to ensure maximum shelf life.
- Modified acrylic resin compositions with improved stability: Specially modified acrylic resin compositions have been developed with enhanced stability characteristics. These modifications include copolymerization with stabilizing monomers, incorporation of specific functional groups that resist degradation, and structural modifications that reduce susceptibility to hydrolysis or oxidation. Some formulations include core-shell structures or cross-linking agents that improve long-term stability. These modified compositions can maintain their application properties for extended periods, even under challenging storage conditions.
- Packaging systems for preserving acrylic resin quality: Specialized packaging systems have been developed to preserve the quality and extend the shelf life of acrylic resins. These include oxygen barrier containers, light-blocking materials, and multi-layer packaging that prevents contamination and moisture ingress. Some packaging incorporates oxygen scavengers or desiccants to maintain an optimal internal environment. Certain systems use inert gas flushing to displace oxygen before sealing. The design of closures and dispensing mechanisms also plays a crucial role in preventing premature degradation after the package is initially opened.
- Testing and prediction methods for shelf life determination: Various testing and prediction methods have been developed to accurately determine the shelf life of acrylic resins. These include accelerated aging tests under elevated temperatures, humidity cycling, and UV exposure to simulate long-term storage effects in shorter timeframes. Analytical techniques such as viscosity measurements, molecular weight determination, and spectroscopic analysis can track degradation markers. Some approaches use mathematical models to predict shelf life based on initial properties and degradation kinetics. These methods allow manufacturers to establish reliable expiration dates and storage recommendations for different acrylic resin formulations.
02 Storage conditions affecting shelf life
The shelf life of acrylic resins is significantly influenced by storage conditions. Factors such as temperature, light exposure, and humidity play crucial roles in maintaining stability. Storing acrylic resins at lower temperatures (typically below 25°C) in dark, dry environments can substantially extend their usable life. Proper packaging that limits exposure to oxygen and UV radiation further contributes to preserving the resin's chemical properties and performance characteristics over time.Expand Specific Solutions03 Modified acrylic resin compositions with improved stability
Specially modified acrylic resin formulations have been developed to achieve enhanced stability and longer shelf life. These modifications include copolymerization with specific monomers, incorporation of specialized functional groups, or creation of unique molecular architectures. Such structural modifications can reduce the resin's susceptibility to degradation mechanisms like hydrolysis or oxidation, resulting in products that maintain their application properties for extended periods without requiring special storage conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Packaging technologies for preserving acrylic resins
Advanced packaging technologies play a critical role in extending the shelf life of acrylic resins. Barrier packaging materials that prevent oxygen permeation, moisture-resistant containers, and specialized closure systems help maintain the integrity of the resin during storage and transportation. Some packaging solutions incorporate oxygen scavengers or UV blockers directly into the container material, providing additional protection against degradation factors and ensuring the resin remains usable for its intended application throughout its stated shelf life.Expand Specific Solutions05 Testing and prediction methods for shelf life determination
Various analytical techniques and accelerated aging protocols have been developed to accurately predict and test the shelf life of acrylic resins. These methods include thermal analysis, spectroscopic monitoring, viscosity measurements, and accelerated aging under controlled conditions. By subjecting samples to elevated temperatures or other stress factors and monitoring key properties, manufacturers can establish reliable shelf life estimates and develop quality control parameters that ensure product consistency throughout the storage period.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Manufacturers
The acrylic resin shelf life extension market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by industries requiring longer storage stability for these versatile materials. The global market size for specialized acrylic resin preservation technologies is estimated at $3.2 billion, expanding at 5.7% CAGR. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with ongoing innovation. Leading players include RESONAC CORP and Nippon Shokubai, who have developed proprietary stabilizer systems, while Mitsui Chemicals and LG Chem focus on molecular engineering approaches. DIC Corp and Kuraray have introduced advanced packaging solutions, and Jiangsu Sanmu Group specializes in environmentally-friendly preservation methods. Research institutions like Case Western Reserve University collaborate with companies like 3M Innovative Properties to develop next-generation preservation technologies combining chemical stabilization with smart packaging.
RESONAC CORP
Technical Solution: RESONAC (formerly Hitachi Chemical) has developed a comprehensive stabilization system for acrylic resins that combines multiple approaches to extend shelf life. Their technology employs a three-tier protection strategy: (1) Oxygen scavengers that selectively react with dissolved oxygen before it can initiate polymerization; (2) Specialized inhibitor packages containing both primary inhibitors (hydroquinone derivatives) and secondary inhibitors (phenothiazine compounds) that work synergistically to prevent premature polymerization; and (3) UV-blocking additives incorporated into storage containers to prevent photo-initiated polymerization. Their research shows this combined approach can extend shelf life by 40-50% compared to conventional methods while maintaining product performance characteristics. RESONAC has also developed temperature-responsive packaging that changes color when storage conditions exceed recommended temperatures, allowing for visual monitoring of storage conditions.
Strengths: Comprehensive multi-mechanism approach provides redundant protection against different polymerization triggers. The visual temperature indicators offer practical monitoring solution for end-users. Weaknesses: The complex inhibitor system may require additional purification steps before use in certain applications where inhibitor residues could affect final product performance. Higher production costs compared to simpler stabilization methods.
Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Nippon Shokubai has pioneered an innovative approach to acrylic resin preservation through their "Controlled Atmosphere Packaging" (CAP) technology. This system involves replacing the headspace in storage containers with an inert gas mixture (primarily nitrogen with trace amounts of carbon dioxide) that effectively prevents oxidative degradation. Their proprietary process includes a multi-stage purging system that reduces oxygen content to below 0.01%, significantly below the threshold needed to initiate polymerization. Additionally, they've developed specialized metal deactivator additives that chelate with trace metal ions (particularly copper and iron) that could catalyze decomposition reactions. Their research demonstrates that this combination can extend shelf life by up to 24 months when stored at temperatures below 20°C. The company has also formulated a novel "hibernation additive" that temporarily modifies the reactivity of the acrylic functional groups without affecting the final curing properties when activated.
Strengths: Exceptional shelf life extension without compromising the resin's reactivity when needed. The inert atmosphere approach eliminates concerns about inhibitor contamination in sensitive applications. Weaknesses: Requires specialized packaging and handling equipment, increasing costs. The system is more vulnerable to failure if package integrity is compromised, potentially leading to rapid polymerization once exposed to air.
Critical Patents and Research on Stabilization Technologies
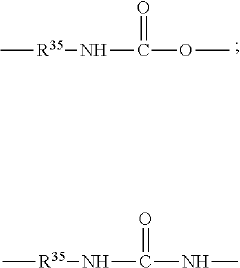
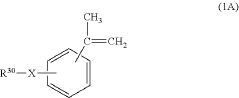
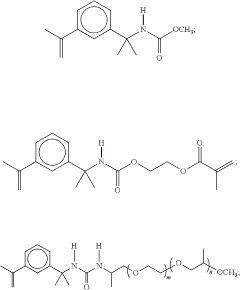
Curable precursor of an adhesive composition
PatentPendingUS20240199783A1
Innovation
- A curable precursor composition is developed with a two-part formulation, where the (meth)acrylate-based component is separated from the initiator and diluted with a vinyl aromatic compound, which acts as a comonomer or crosslinker during polymerization, preventing premature reaction and allowing storage in large containers at room temperature without cooling.
Method for extending shelf life of vinyl ester resin or unsaturated polyester resin
PatentActiveUS8048965B2
Innovation
- Enhancing the oxygen content of the resin by introducing an oxygen-containing gas or using chemical substances to produce oxygen, which reacts with free radicals to slow down or terminate self-polymerization reactions, thereby reducing gelation and extending shelf life.
Environmental Factors Affecting Acrylic Resin Stability
Acrylic resin stability is significantly influenced by various environmental factors that can accelerate degradation processes and reduce shelf life. Temperature fluctuations represent one of the most critical factors affecting stability. When stored at temperatures exceeding 25°C, acrylic resins experience accelerated polymerization reactions, leading to increased viscosity and premature gelation. Conversely, extremely low temperatures can cause phase separation in certain formulations, resulting in irreversible damage to the resin structure.
Humidity levels play an equally important role in determining stability. High relative humidity environments (above 60%) promote hydrolysis reactions within the resin matrix, particularly affecting ester linkages in methacrylate-based formulations. This hydrolytic degradation progressively compromises mechanical properties and reduces the resin's functional lifespan. Studies have demonstrated that maintaining relative humidity below 40% can extend shelf life by up to 30% compared to storage in humid conditions.
Light exposure, particularly UV radiation, triggers photochemical reactions that generate free radicals within the resin. These free radicals initiate undesired polymerization chains and oxidative degradation pathways. Even brief exposure to direct sunlight or fluorescent lighting can significantly reduce shelf stability. Spectroscopic analyses have shown that UV wavelengths between 300-400nm are particularly damaging to common acrylic resin formulations.
Oxygen availability constitutes another critical environmental factor. Atmospheric oxygen readily diffuses into resin containers and reacts with monomers and oligomers, forming peroxides that serve as polymerization initiators. This auto-oxidation process accelerates as temperature increases, creating a compounding effect when multiple adverse environmental conditions exist simultaneously.
Contaminants introduced during handling or from storage containers can also dramatically impact stability. Metal ions, particularly transition metals like iron and copper, catalyze decomposition reactions of peroxides present in the resin, leading to rapid polymerization. Similarly, alkaline contaminants can neutralize stabilizers and inhibitors intentionally added to extend shelf life.
Pressure variations, though less significant than other factors, can affect volatile component retention in certain formulations. Reduced pressure environments may accelerate the evaporation of volatile stabilizers or monomers, altering the resin's composition and reactivity profile over time.
The combined effect of these environmental factors often produces synergistic degradation that exceeds the sum of individual impacts. For instance, the combination of elevated temperature and UV exposure can reduce shelf life by up to 75% compared to optimal storage conditions, highlighting the importance of comprehensive environmental control strategies for maximizing acrylic resin stability during storage.
Humidity levels play an equally important role in determining stability. High relative humidity environments (above 60%) promote hydrolysis reactions within the resin matrix, particularly affecting ester linkages in methacrylate-based formulations. This hydrolytic degradation progressively compromises mechanical properties and reduces the resin's functional lifespan. Studies have demonstrated that maintaining relative humidity below 40% can extend shelf life by up to 30% compared to storage in humid conditions.
Light exposure, particularly UV radiation, triggers photochemical reactions that generate free radicals within the resin. These free radicals initiate undesired polymerization chains and oxidative degradation pathways. Even brief exposure to direct sunlight or fluorescent lighting can significantly reduce shelf stability. Spectroscopic analyses have shown that UV wavelengths between 300-400nm are particularly damaging to common acrylic resin formulations.
Oxygen availability constitutes another critical environmental factor. Atmospheric oxygen readily diffuses into resin containers and reacts with monomers and oligomers, forming peroxides that serve as polymerization initiators. This auto-oxidation process accelerates as temperature increases, creating a compounding effect when multiple adverse environmental conditions exist simultaneously.
Contaminants introduced during handling or from storage containers can also dramatically impact stability. Metal ions, particularly transition metals like iron and copper, catalyze decomposition reactions of peroxides present in the resin, leading to rapid polymerization. Similarly, alkaline contaminants can neutralize stabilizers and inhibitors intentionally added to extend shelf life.
Pressure variations, though less significant than other factors, can affect volatile component retention in certain formulations. Reduced pressure environments may accelerate the evaporation of volatile stabilizers or monomers, altering the resin's composition and reactivity profile over time.
The combined effect of these environmental factors often produces synergistic degradation that exceeds the sum of individual impacts. For instance, the combination of elevated temperature and UV exposure can reduce shelf life by up to 75% compared to optimal storage conditions, highlighting the importance of comprehensive environmental control strategies for maximizing acrylic resin stability during storage.
Quality Control Standards and Testing Protocols
Establishing robust quality control standards and testing protocols is essential for effectively monitoring and maintaining acrylic resin shelf life. Industry standards such as ASTM D1639 for acid value determination and ASTM D1544 for color assessment provide foundational metrics for evaluating resin quality over time. These standardized tests enable manufacturers to establish baseline properties and detect early signs of degradation during storage.
Viscosity measurement represents a critical quality parameter, with variations often indicating polymerization progression or degradation. Regular testing using Brookfield or cone-and-plate viscometers at controlled temperatures (typically 25°C) allows for precise tracking of rheological changes. Acceptable viscosity ranges should be established based on specific application requirements, with deviations beyond ±10% typically warranting further investigation.
Molecular weight distribution analysis via gel permeation chromatography (GPC) provides deeper insights into polymer stability during storage. Increases in polydispersity index (PDI) or shifts in molecular weight distribution curves can signal ongoing polymerization or chain scission processes that may compromise performance. Establishing testing frequencies based on storage conditions—monthly for ambient storage and bi-weekly for higher temperature environments—ensures timely detection of quality deviations.
Functional group analysis through FTIR spectroscopy enables monitoring of chemical changes within the resin. Particular attention should be paid to carbonyl peaks (~1730 cm⁻¹) and hydroxyl regions (~3400-3600 cm⁻¹), as changes in these areas often correlate with oxidation or hydrolysis reactions. Establishing spectral fingerprints for fresh resin provides valuable reference points for comparative analysis during storage.
Performance-based testing protocols that simulate end-use applications provide practical assessments of resin viability. These may include film formation characteristics, adhesion testing (ASTM D3359), hardness measurements (ASTM D2240), and accelerated weathering tests. Such application-specific evaluations often reveal functional deterioration before analytical methods detect significant chemical changes.
Documentation and statistical process control methods are equally important components of quality systems. Implementing control charts with defined action and specification limits enables trend analysis and early intervention. Modern quality management approaches incorporate digital monitoring systems that automatically flag deviations and predict remaining shelf life based on historical degradation patterns and current storage conditions.
Validation of testing methods through round-robin studies and certified reference materials ensures measurement reliability across different operators and instruments. This metrological foundation supports confident decision-making regarding resin usability and storage extension strategies.
Viscosity measurement represents a critical quality parameter, with variations often indicating polymerization progression or degradation. Regular testing using Brookfield or cone-and-plate viscometers at controlled temperatures (typically 25°C) allows for precise tracking of rheological changes. Acceptable viscosity ranges should be established based on specific application requirements, with deviations beyond ±10% typically warranting further investigation.
Molecular weight distribution analysis via gel permeation chromatography (GPC) provides deeper insights into polymer stability during storage. Increases in polydispersity index (PDI) or shifts in molecular weight distribution curves can signal ongoing polymerization or chain scission processes that may compromise performance. Establishing testing frequencies based on storage conditions—monthly for ambient storage and bi-weekly for higher temperature environments—ensures timely detection of quality deviations.
Functional group analysis through FTIR spectroscopy enables monitoring of chemical changes within the resin. Particular attention should be paid to carbonyl peaks (~1730 cm⁻¹) and hydroxyl regions (~3400-3600 cm⁻¹), as changes in these areas often correlate with oxidation or hydrolysis reactions. Establishing spectral fingerprints for fresh resin provides valuable reference points for comparative analysis during storage.
Performance-based testing protocols that simulate end-use applications provide practical assessments of resin viability. These may include film formation characteristics, adhesion testing (ASTM D3359), hardness measurements (ASTM D2240), and accelerated weathering tests. Such application-specific evaluations often reveal functional deterioration before analytical methods detect significant chemical changes.
Documentation and statistical process control methods are equally important components of quality systems. Implementing control charts with defined action and specification limits enables trend analysis and early intervention. Modern quality management approaches incorporate digital monitoring systems that automatically flag deviations and predict remaining shelf life based on historical degradation patterns and current storage conditions.
Validation of testing methods through round-robin studies and certified reference materials ensures measurement reliability across different operators and instruments. This metrological foundation supports confident decision-making regarding resin usability and storage extension strategies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!