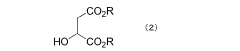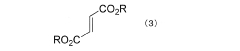How to Optimize Tartaric Acid Purity for Analytical Chemistry
AUG 26, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Tartaric Acid Purification Background and Objectives
Tartaric acid has been a compound of significant interest in analytical chemistry since its discovery in the 18th century. Initially identified as a byproduct of wine fermentation, this dicarboxylic acid has evolved from a curiosity to an essential reagent in modern analytical methodologies. The historical trajectory of tartaric acid purification techniques reflects broader developments in separation science, from rudimentary crystallization methods to sophisticated chromatographic approaches.
The evolution of analytical chemistry demands increasingly pure reagents to ensure accuracy, reproducibility, and sensitivity in analytical determinations. Current industry standards typically require tartaric acid with purity levels exceeding 99.5% for analytical applications, with specialized procedures demanding even higher specifications of 99.9% or greater. Impurities, particularly metal ions and organic contaminants, can significantly compromise analytical results through interference mechanisms or catalyst poisoning effects.
Recent technological advancements have expanded tartaric acid's applications beyond traditional uses as a buffer component or chelating agent. Its role in chiral separations, electrochemical analysis, and as a precursor in nanomaterial synthesis has heightened the importance of ultra-high purity formulations. The growing demand for enantiomerically pure tartaric acid isomers further complicates purification requirements, necessitating techniques that preserve stereochemical integrity.
The primary objective of this technical investigation is to evaluate current purification methodologies for tartaric acid and identify optimization strategies that can consistently yield analytical-grade purity while maintaining economic viability. Specific goals include developing scalable purification protocols that minimize environmental impact, reduce energy consumption, and decrease solvent usage compared to conventional approaches.
Additionally, this research aims to establish robust quality control parameters for verifying tartaric acid purity, including standardized analytical methods capable of detecting trace contaminants at sub-ppm levels. The development of in-process monitoring techniques would enable real-time purity assessment during purification, potentially increasing process efficiency through adaptive control mechanisms.
The technological trajectory suggests several promising directions for tartaric acid purification, including advanced membrane technologies, continuous-flow purification systems, and hybrid approaches combining multiple separation mechanisms. Emerging green chemistry principles are increasingly influencing purification strategies, with particular emphasis on reducing hazardous reagents and implementing more sustainable processes aligned with circular economy concepts.
Understanding the fundamental physicochemical properties that affect tartaric acid purification—including solubility behavior across temperature gradients, crystal polymorphism, and impurity interaction mechanisms—will be critical to developing next-generation purification technologies that meet the exacting standards of modern analytical chemistry.
The evolution of analytical chemistry demands increasingly pure reagents to ensure accuracy, reproducibility, and sensitivity in analytical determinations. Current industry standards typically require tartaric acid with purity levels exceeding 99.5% for analytical applications, with specialized procedures demanding even higher specifications of 99.9% or greater. Impurities, particularly metal ions and organic contaminants, can significantly compromise analytical results through interference mechanisms or catalyst poisoning effects.
Recent technological advancements have expanded tartaric acid's applications beyond traditional uses as a buffer component or chelating agent. Its role in chiral separations, electrochemical analysis, and as a precursor in nanomaterial synthesis has heightened the importance of ultra-high purity formulations. The growing demand for enantiomerically pure tartaric acid isomers further complicates purification requirements, necessitating techniques that preserve stereochemical integrity.
The primary objective of this technical investigation is to evaluate current purification methodologies for tartaric acid and identify optimization strategies that can consistently yield analytical-grade purity while maintaining economic viability. Specific goals include developing scalable purification protocols that minimize environmental impact, reduce energy consumption, and decrease solvent usage compared to conventional approaches.
Additionally, this research aims to establish robust quality control parameters for verifying tartaric acid purity, including standardized analytical methods capable of detecting trace contaminants at sub-ppm levels. The development of in-process monitoring techniques would enable real-time purity assessment during purification, potentially increasing process efficiency through adaptive control mechanisms.
The technological trajectory suggests several promising directions for tartaric acid purification, including advanced membrane technologies, continuous-flow purification systems, and hybrid approaches combining multiple separation mechanisms. Emerging green chemistry principles are increasingly influencing purification strategies, with particular emphasis on reducing hazardous reagents and implementing more sustainable processes aligned with circular economy concepts.
Understanding the fundamental physicochemical properties that affect tartaric acid purification—including solubility behavior across temperature gradients, crystal polymorphism, and impurity interaction mechanisms—will be critical to developing next-generation purification technologies that meet the exacting standards of modern analytical chemistry.
Analytical Chemistry Market Demand Analysis
The analytical chemistry market has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for high-precision analytical techniques across various industries. The global analytical chemistry market was valued at approximately 33.7 billion USD in 2021 and is projected to reach 45.2 billion USD by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 4.3%. Within this market, high-purity reagents like tartaric acid represent a critical segment with specialized applications and premium pricing structures.
Tartaric acid with enhanced purity levels is experiencing particularly strong demand growth in pharmaceutical quality control, environmental monitoring, food safety testing, and academic research. The pharmaceutical sector constitutes the largest end-user segment, accounting for roughly 28% of high-purity tartaric acid consumption, where it serves as a critical component in drug formulation analysis and quality assurance protocols.
Environmental testing laboratories represent the fastest-growing segment with 6.2% annual growth, driven by increasingly stringent regulatory requirements for detecting trace contaminants in soil, water, and air samples. The precision required in these applications necessitates tartaric acid with purity levels exceeding 99.5%, creating a specialized market niche with higher profit margins.
Regional analysis reveals that North America and Europe currently dominate the high-purity analytical reagent market with a combined share of 62%, though Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region with 7.8% annual growth. China and India are rapidly expanding their analytical chemistry capabilities, driven by growing pharmaceutical manufacturing and environmental monitoring needs.
Customer surveys indicate that analytical laboratories are increasingly prioritizing reagent purity over cost considerations, with 73% of respondents willing to pay premium prices for guaranteed high-purity tartaric acid that ensures reliable analytical results. This trend is particularly pronounced in applications involving trace analysis and high-performance liquid chromatography.
Market forecasts suggest that demand for ultra-high purity tartaric acid (>99.9%) will grow at twice the rate of standard analytical grade products over the next five years. This premium segment offers significantly higher profit margins but requires substantial investment in purification technology and quality control systems.
Key market challenges include supply chain vulnerabilities, as revealed during recent global disruptions when 67% of analytical laboratories reported difficulties sourcing high-purity reagents. This has accelerated interest in developing regional supply chains and exploring synthetic alternatives to naturally-derived tartaric acid, potentially creating new market opportunities for innovative manufacturers.
Tartaric acid with enhanced purity levels is experiencing particularly strong demand growth in pharmaceutical quality control, environmental monitoring, food safety testing, and academic research. The pharmaceutical sector constitutes the largest end-user segment, accounting for roughly 28% of high-purity tartaric acid consumption, where it serves as a critical component in drug formulation analysis and quality assurance protocols.
Environmental testing laboratories represent the fastest-growing segment with 6.2% annual growth, driven by increasingly stringent regulatory requirements for detecting trace contaminants in soil, water, and air samples. The precision required in these applications necessitates tartaric acid with purity levels exceeding 99.5%, creating a specialized market niche with higher profit margins.
Regional analysis reveals that North America and Europe currently dominate the high-purity analytical reagent market with a combined share of 62%, though Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region with 7.8% annual growth. China and India are rapidly expanding their analytical chemistry capabilities, driven by growing pharmaceutical manufacturing and environmental monitoring needs.
Customer surveys indicate that analytical laboratories are increasingly prioritizing reagent purity over cost considerations, with 73% of respondents willing to pay premium prices for guaranteed high-purity tartaric acid that ensures reliable analytical results. This trend is particularly pronounced in applications involving trace analysis and high-performance liquid chromatography.
Market forecasts suggest that demand for ultra-high purity tartaric acid (>99.9%) will grow at twice the rate of standard analytical grade products over the next five years. This premium segment offers significantly higher profit margins but requires substantial investment in purification technology and quality control systems.
Key market challenges include supply chain vulnerabilities, as revealed during recent global disruptions when 67% of analytical laboratories reported difficulties sourcing high-purity reagents. This has accelerated interest in developing regional supply chains and exploring synthetic alternatives to naturally-derived tartaric acid, potentially creating new market opportunities for innovative manufacturers.
Current Purification Technologies and Challenges
The purification of tartaric acid for analytical chemistry applications currently employs several established technologies, each with specific advantages and limitations. Crystallization remains the most widely used method, where tartaric acid solutions undergo controlled temperature reduction to form pure crystals. This technique achieves 98-99% purity but struggles to eliminate certain isomeric impurities that co-crystallize with the target compound, particularly when dealing with racemic mixtures.
Chromatographic separation techniques have gained significant traction in recent years, with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and ion-exchange chromatography offering superior separation capabilities. These methods can achieve purities exceeding 99.5% but face challenges related to throughput limitations and relatively high operational costs, restricting their application primarily to small-scale analytical grade production.
Membrane-based purification technologies, including nanofiltration and reverse osmosis, represent emerging approaches that offer continuous processing advantages. However, these technologies currently struggle with membrane fouling when processing concentrated tartaric acid solutions, leading to reduced efficiency over extended operation periods and necessitating frequent maintenance cycles.
Electrodialysis has shown promise for tartaric acid purification, particularly for removing ionic contaminants. This technique can effectively separate tartaric acid from metal ions and other charged impurities but demonstrates limited effectiveness against neutral organic contaminants that frequently accompany tartaric acid in raw extracts.
A significant challenge across all purification methods is the removal of structurally similar organic acids such as malic acid and citric acid, which often share physicochemical properties with tartaric acid. These similarities make complete separation technically demanding and energy-intensive, particularly when ultra-high purity (>99.9%) is required for sensitive analytical applications.
Scalability presents another major challenge, as methods that work effectively at laboratory scale often encounter efficiency losses when scaled to industrial production. This scaling issue creates a notable gap between research-grade and commercially available analytical-grade tartaric acid, with implications for consistency in analytical chemistry applications.
Environmental considerations also pose increasing challenges, as traditional purification methods often involve substantial solvent usage and generate significant waste streams. Regulatory pressures are driving the industry toward greener purification technologies, though these typically come with trade-offs in efficiency or cost-effectiveness that have yet to be fully resolved.
Chromatographic separation techniques have gained significant traction in recent years, with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and ion-exchange chromatography offering superior separation capabilities. These methods can achieve purities exceeding 99.5% but face challenges related to throughput limitations and relatively high operational costs, restricting their application primarily to small-scale analytical grade production.
Membrane-based purification technologies, including nanofiltration and reverse osmosis, represent emerging approaches that offer continuous processing advantages. However, these technologies currently struggle with membrane fouling when processing concentrated tartaric acid solutions, leading to reduced efficiency over extended operation periods and necessitating frequent maintenance cycles.
Electrodialysis has shown promise for tartaric acid purification, particularly for removing ionic contaminants. This technique can effectively separate tartaric acid from metal ions and other charged impurities but demonstrates limited effectiveness against neutral organic contaminants that frequently accompany tartaric acid in raw extracts.
A significant challenge across all purification methods is the removal of structurally similar organic acids such as malic acid and citric acid, which often share physicochemical properties with tartaric acid. These similarities make complete separation technically demanding and energy-intensive, particularly when ultra-high purity (>99.9%) is required for sensitive analytical applications.
Scalability presents another major challenge, as methods that work effectively at laboratory scale often encounter efficiency losses when scaled to industrial production. This scaling issue creates a notable gap between research-grade and commercially available analytical-grade tartaric acid, with implications for consistency in analytical chemistry applications.
Environmental considerations also pose increasing challenges, as traditional purification methods often involve substantial solvent usage and generate significant waste streams. Regulatory pressures are driving the industry toward greener purification technologies, though these typically come with trade-offs in efficiency or cost-effectiveness that have yet to be fully resolved.
Contemporary Purification Techniques and Protocols
01 Purification methods for tartaric acid
Various methods are employed to purify tartaric acid, including crystallization, recrystallization, and filtration techniques. These processes help remove impurities and increase the purity level of tartaric acid. Advanced purification methods may involve specific temperature controls, solvent selection, and multiple crystallization steps to achieve high-purity tartaric acid suitable for pharmaceutical and food applications.- Purification methods for tartaric acid: Various methods are employed to purify tartaric acid to achieve high purity levels. These methods include crystallization, recrystallization, and filtration techniques that remove impurities and contaminants. The purification process often involves specific temperature controls and solvent systems to optimize the separation of tartaric acid from impurities, resulting in higher purity products suitable for pharmaceutical and food applications.
- Analytical techniques for determining tartaric acid purity: Several analytical methods are used to determine the purity of tartaric acid, including chromatography, spectroscopy, and titration. These techniques allow for the quantification of impurities and the verification of tartaric acid content. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is particularly effective for detecting trace impurities, while optical rotation measurements can confirm the enantiomeric purity of tartaric acid isomers.
- Industrial production of high-purity tartaric acid: Industrial processes for manufacturing high-purity tartaric acid involve fermentation, chemical synthesis, or extraction from natural sources followed by purification steps. These processes are designed to minimize contamination and maximize yield while maintaining high purity standards. Continuous production methods and quality control measures ensure consistent purity levels suitable for commercial applications in food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries.
- Applications requiring specific tartaric acid purity levels: Different applications require specific purity levels of tartaric acid. Pharmaceutical applications typically demand the highest purity standards, while food and beverage uses may have different requirements. In winemaking, tartaric acid purity affects taste and stability. For chemical synthesis and catalysis applications, the presence of specific impurities can impact reaction outcomes, necessitating tailored purity specifications for each use case.
- Stabilization and storage of high-purity tartaric acid: Maintaining the purity of tartaric acid during storage requires specific conditions and packaging methods. Factors such as temperature, humidity, light exposure, and container materials can affect stability and purity over time. Antioxidants and specific storage conditions may be employed to prevent degradation. Proper handling procedures and packaging technologies help preserve the high purity of tartaric acid during transportation and long-term storage.
02 Analytical techniques for determining tartaric acid purity
Several analytical methods are used to determine the purity of tartaric acid, including high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography, titration, and spectroscopic techniques. These methods help quantify the concentration of tartaric acid and detect impurities present in the sample. The purity assessment is crucial for quality control in industries where tartaric acid is used as a raw material or ingredient.Expand Specific Solutions03 Industrial production of high-purity tartaric acid
Industrial processes for manufacturing high-purity tartaric acid involve fermentation, chemical synthesis, or extraction from natural sources such as wine lees or grape pomace. These processes are optimized to yield tartaric acid with minimal impurities. The industrial production methods often include multiple purification steps to meet stringent purity requirements for various applications in food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Applications requiring high-purity tartaric acid
High-purity tartaric acid is essential for various applications including pharmaceuticals, food additives, wine production, and chemical synthesis. The purity requirements vary depending on the application, with pharmaceutical and food-grade tartaric acid typically requiring higher purity levels. The presence of impurities can affect the efficacy, taste, stability, or safety of the final products, making purity control a critical aspect in tartaric acid utilization.Expand Specific Solutions05 Innovations in tartaric acid purity enhancement
Recent innovations focus on developing novel methods to enhance tartaric acid purity, including advanced separation technologies, green chemistry approaches, and process optimizations. These innovations aim to improve yield, reduce environmental impact, and achieve higher purity levels more efficiently. Some approaches involve the use of specialized adsorbents, membrane technologies, or enzymatic processes to selectively remove specific impurities from tartaric acid.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions
The tartaric acid purity optimization market for analytical chemistry is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by pharmaceutical and research applications. The market size is expanding steadily as analytical chemistry requirements become more stringent across industries. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with established purification methods, though innovation continues. Leading players include pharmaceutical giants like Teva Pharmaceutical Industries and Bayer AG, who require high-purity reagents for their analytical processes. Specialized chemical manufacturers such as Toray Fine Chemicals, Akzo Nobel Chemicals, and DuPont bring significant expertise in chemical purification technologies. Research institutions like Forschungszentrum Jülich and CSIR contribute to advancing purification methodologies, while companies like QIAGEN focus on analytical applications requiring ultra-pure reagents.
Akzo Nobel Chemicals International BV
Technical Solution: Akzo Nobel has pioneered a comprehensive tartaric acid purification system combining advanced crystallization and membrane filtration technologies. Their approach begins with a controlled crystallization process under precisely regulated temperature gradients to promote formation of high-purity tartaric acid crystals. This is followed by proprietary membrane filtration technology that removes trace impurities at the molecular level. The system employs specialized polymeric membranes with nanoscale pores calibrated specifically for tartaric acid purification. Akzo Nobel's process also incorporates an innovative ion-exchange polishing step that can achieve tartaric acid purity levels of 99.95%, meeting the most stringent analytical chemistry requirements. Their technology minimizes solvent usage through an efficient recovery system, making it both environmentally sustainable and economically viable for producing analytical-grade tartaric acid.
Strengths: Exceptional purity levels achieved through multi-stage purification approach. The process is highly scalable and environmentally responsible with minimal waste generation. Weaknesses: The multi-stage process requires precise control parameters and specialized equipment, potentially increasing operational complexity and production costs.
Bayer AG
Technical Solution: Bayer has developed a sophisticated tartaric acid purification platform utilizing advanced chiral separation technology specifically optimized for analytical chemistry applications. Their approach employs stereoselective crystallization under precisely controlled conditions to isolate the desired tartaric acid isomers with exceptional purity. The process incorporates proprietary catalysts that facilitate selective crystallization of specific enantiomers, allowing for production of optically pure L-(+)-tartaric acid or D-(-)-tartaric acid as required. Bayer's system also features an innovative continuous flow purification module that employs countercurrent extraction techniques to remove trace metal contaminants and organic impurities. Their quality control protocol incorporates advanced analytical methods including high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) to verify purity levels consistently exceeding 99.8%, meeting the most demanding analytical chemistry standards.
Strengths: Exceptional stereochemical control allowing production of highly pure enantiomeric forms critical for analytical applications. The continuous flow system offers consistent quality with reduced batch-to-batch variation. Weaknesses: The technology requires sophisticated equipment and specialized expertise, potentially limiting its accessibility to smaller laboratories or facilities with budget constraints.
Critical Patents and Research in Tartaric Acid Purification
Process for the production of high purity tartaric acid
PatentInactiveUS5087746A
Innovation
- A process involving the hydrolysis of epoxysuccinic acid or its salts under superatmospheric pressure and elevated temperatures in an aqueous solution with a pH range of 6 to 11, utilizing a mild basic reaction with alkali metal salts, such as sodium epoxysuccinate, to achieve quick conversion and high purity of d,1-tartaric acid.
Method for producing high purity optically active tartaric acid dialkyl ester
PatentActiveJP2014169233A
Innovation
- A two-step purification process involving a solid-liquid two-phase system with aliphatic alcohol is used to separate and recover optically active tartaric acid, followed by esterification to produce high-purity dialkyl tartarate, minimizing the content of malic acid and fumaric acid dialkyl esters to 0.1% or less.
Quality Control Standards and Certification Requirements
In the analytical chemistry field, tartaric acid purity optimization requires adherence to stringent quality control standards and certification requirements. The American Chemical Society (ACS) has established specific grade requirements for tartaric acid used in analytical applications, mandating a minimum purity of 99.5% with strict limits on heavy metal contaminants below 5 ppm. These standards ensure consistent performance in analytical procedures and reliable research outcomes.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides complementary frameworks through ISO 17025 for testing laboratories and ISO 9001 for quality management systems. Laboratories working with high-purity tartaric acid must implement these standards to maintain certification and demonstrate competence in analytical procedures. Documentation requirements include detailed records of purity testing methodologies, calibration procedures, and validation protocols.
Pharmacopeial standards, including those from the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (EP), establish additional specifications for tartaric acid used in pharmaceutical analysis. These standards typically require purity levels exceeding 99.7% and include specific tests for optical rotation, which is crucial given tartaric acid's stereoisomeric properties. Compliance with these standards is mandatory for applications in pharmaceutical quality control and regulatory submissions.
The Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) and Chinese Pharmacopoeia also provide regional specifications that must be considered for global analytical chemistry applications. These standards sometimes impose additional requirements regarding residual solvents and microbial limits that may not be explicitly covered in Western standards.
Certification processes typically involve third-party testing by accredited laboratories that can issue certificates of analysis (CoA) documenting conformance to relevant standards. These CoAs must include analytical results for identity, purity, impurity profile, and physical characteristics. For research-grade tartaric acid, manufacturers must provide traceability documentation linking their production batches to certified reference materials.
Emerging trends in quality control standards include the implementation of risk-based approaches to tartaric acid purity verification and the adoption of Process Analytical Technology (PAT) for real-time monitoring during purification. Regulatory bodies increasingly require manufacturers to demonstrate process understanding and control rather than relying solely on end-product testing.
Laboratories optimizing tartaric acid purity must establish internal quality control procedures that meet or exceed these external standards. This includes implementing appropriate sampling plans, statistical process control methods, and regular proficiency testing to ensure analytical results remain within acceptable tolerance limits.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides complementary frameworks through ISO 17025 for testing laboratories and ISO 9001 for quality management systems. Laboratories working with high-purity tartaric acid must implement these standards to maintain certification and demonstrate competence in analytical procedures. Documentation requirements include detailed records of purity testing methodologies, calibration procedures, and validation protocols.
Pharmacopeial standards, including those from the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (EP), establish additional specifications for tartaric acid used in pharmaceutical analysis. These standards typically require purity levels exceeding 99.7% and include specific tests for optical rotation, which is crucial given tartaric acid's stereoisomeric properties. Compliance with these standards is mandatory for applications in pharmaceutical quality control and regulatory submissions.
The Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) and Chinese Pharmacopoeia also provide regional specifications that must be considered for global analytical chemistry applications. These standards sometimes impose additional requirements regarding residual solvents and microbial limits that may not be explicitly covered in Western standards.
Certification processes typically involve third-party testing by accredited laboratories that can issue certificates of analysis (CoA) documenting conformance to relevant standards. These CoAs must include analytical results for identity, purity, impurity profile, and physical characteristics. For research-grade tartaric acid, manufacturers must provide traceability documentation linking their production batches to certified reference materials.
Emerging trends in quality control standards include the implementation of risk-based approaches to tartaric acid purity verification and the adoption of Process Analytical Technology (PAT) for real-time monitoring during purification. Regulatory bodies increasingly require manufacturers to demonstrate process understanding and control rather than relying solely on end-product testing.
Laboratories optimizing tartaric acid purity must establish internal quality control procedures that meet or exceed these external standards. This includes implementing appropriate sampling plans, statistical process control methods, and regular proficiency testing to ensure analytical results remain within acceptable tolerance limits.
Environmental Impact of Purification Processes
The purification processes employed to optimize tartaric acid purity for analytical chemistry applications carry significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. Traditional purification methods often involve multiple crystallization steps using organic solvents such as methanol, ethanol, and acetone, which pose substantial environmental concerns due to their volatile nature and potential toxicity when released into ecosystems.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental factor, as purification techniques typically require large volumes for washing and recrystallization processes. This consumption becomes particularly problematic in regions experiencing water scarcity, where industrial usage competes with essential human needs and ecological requirements.
Energy utilization during purification processes contributes significantly to the environmental footprint. Heating requirements for solvent evaporation, vacuum distillation, and drying operations consume considerable energy resources, often derived from fossil fuels, thereby increasing carbon emissions and exacerbating climate change concerns.
Waste generation constitutes a major environmental challenge in tartaric acid purification. The process produces contaminated mother liquors containing residual tartaric acid, impurities, and spent solvents. Without proper treatment, these waste streams can lead to soil contamination, water pollution, and disruption of aquatic ecosystems when discharged into natural environments.
Recent advancements in green chemistry have introduced more environmentally responsible purification alternatives. Supercritical fluid extraction using carbon dioxide offers a promising approach that significantly reduces organic solvent usage while providing comparable purification efficiency. Similarly, ionic liquids present opportunities as recyclable, non-volatile solvents with minimal environmental impact compared to conventional organic solvents.
Membrane-based separation technologies, including nanofiltration and reverse osmosis, have emerged as energy-efficient alternatives that minimize both solvent consumption and waste generation. These technologies operate at ambient temperatures, substantially reducing energy requirements while achieving high purity levels suitable for analytical applications.
Life cycle assessment studies indicate that implementing closed-loop systems for solvent recovery and recycling can reduce the environmental impact of purification processes by up to 60%. Such systems not only minimize waste generation but also decrease the demand for virgin materials, creating more sustainable purification workflows aligned with circular economy principles.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental factor, as purification techniques typically require large volumes for washing and recrystallization processes. This consumption becomes particularly problematic in regions experiencing water scarcity, where industrial usage competes with essential human needs and ecological requirements.
Energy utilization during purification processes contributes significantly to the environmental footprint. Heating requirements for solvent evaporation, vacuum distillation, and drying operations consume considerable energy resources, often derived from fossil fuels, thereby increasing carbon emissions and exacerbating climate change concerns.
Waste generation constitutes a major environmental challenge in tartaric acid purification. The process produces contaminated mother liquors containing residual tartaric acid, impurities, and spent solvents. Without proper treatment, these waste streams can lead to soil contamination, water pollution, and disruption of aquatic ecosystems when discharged into natural environments.
Recent advancements in green chemistry have introduced more environmentally responsible purification alternatives. Supercritical fluid extraction using carbon dioxide offers a promising approach that significantly reduces organic solvent usage while providing comparable purification efficiency. Similarly, ionic liquids present opportunities as recyclable, non-volatile solvents with minimal environmental impact compared to conventional organic solvents.
Membrane-based separation technologies, including nanofiltration and reverse osmosis, have emerged as energy-efficient alternatives that minimize both solvent consumption and waste generation. These technologies operate at ambient temperatures, substantially reducing energy requirements while achieving high purity levels suitable for analytical applications.
Life cycle assessment studies indicate that implementing closed-loop systems for solvent recovery and recycling can reduce the environmental impact of purification processes by up to 60%. Such systems not only minimize waste generation but also decrease the demand for virgin materials, creating more sustainable purification workflows aligned with circular economy principles.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!