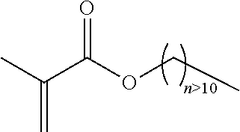
How to Reduce Acrylic Resin VOC Emissions in Paint Formulations
OCT 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Acrylic Resin VOC Emission Reduction Background and Objectives
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) have been a significant environmental concern in the paint and coating industry for decades. Acrylic resins, widely used in paint formulations due to their excellent durability, weather resistance, and aesthetic properties, have traditionally been major contributors to VOC emissions. The evolution of regulations governing VOC emissions began in the 1970s with the Clean Air Act in the United States, followed by increasingly stringent standards worldwide, driving the technical evolution in this field.
The paint industry has undergone a transformative journey from solvent-based formulations with VOC contents exceeding 300-400 g/L to modern low-VOC alternatives with less than 50 g/L. This transition reflects both regulatory pressure and growing market demand for environmentally responsible products. The European Union's implementation of the Paints Directive (2004/42/EC) and similar regulations in North America and Asia have established clear VOC reduction targets, accelerating innovation in acrylic resin technology.
Recent technological advancements have focused on water-based acrylic emulsions, high-solids formulations, and powder coatings as alternatives to traditional solvent-based systems. The development of novel polymerization techniques and the incorporation of bio-based raw materials represent emerging trends in sustainable acrylic resin technology. These innovations aim to maintain or enhance performance characteristics while significantly reducing environmental impact.
The primary objective of VOC reduction in acrylic resin paint formulations is to minimize the release of harmful compounds into the atmosphere while maintaining or improving product performance. This includes developing formulations that meet or exceed current regulatory standards while anticipating future restrictions. Additionally, there is a focus on addressing consumer concerns regarding indoor air quality and health impacts associated with traditional paint products.
Technical goals in this domain include the development of zero-VOC acrylic resins that maintain excellent adhesion, durability, and application properties. Research efforts are directed toward understanding the fundamental chemistry of acrylic polymerization and film formation without volatile components. This involves exploring alternative crosslinking mechanisms, novel monomer compositions, and innovative additives that can facilitate film formation without traditional coalescing solvents.
The industry is also pursuing cost-effective manufacturing processes for low-VOC acrylic resins to ensure market competitiveness. This economic consideration is crucial for widespread adoption, as environmentally friendly alternatives must remain financially viable compared to conventional technologies. The convergence of environmental sustainability, regulatory compliance, and market demands is driving unprecedented innovation in acrylic resin technology for paint applications.
The paint industry has undergone a transformative journey from solvent-based formulations with VOC contents exceeding 300-400 g/L to modern low-VOC alternatives with less than 50 g/L. This transition reflects both regulatory pressure and growing market demand for environmentally responsible products. The European Union's implementation of the Paints Directive (2004/42/EC) and similar regulations in North America and Asia have established clear VOC reduction targets, accelerating innovation in acrylic resin technology.
Recent technological advancements have focused on water-based acrylic emulsions, high-solids formulations, and powder coatings as alternatives to traditional solvent-based systems. The development of novel polymerization techniques and the incorporation of bio-based raw materials represent emerging trends in sustainable acrylic resin technology. These innovations aim to maintain or enhance performance characteristics while significantly reducing environmental impact.
The primary objective of VOC reduction in acrylic resin paint formulations is to minimize the release of harmful compounds into the atmosphere while maintaining or improving product performance. This includes developing formulations that meet or exceed current regulatory standards while anticipating future restrictions. Additionally, there is a focus on addressing consumer concerns regarding indoor air quality and health impacts associated with traditional paint products.
Technical goals in this domain include the development of zero-VOC acrylic resins that maintain excellent adhesion, durability, and application properties. Research efforts are directed toward understanding the fundamental chemistry of acrylic polymerization and film formation without volatile components. This involves exploring alternative crosslinking mechanisms, novel monomer compositions, and innovative additives that can facilitate film formation without traditional coalescing solvents.
The industry is also pursuing cost-effective manufacturing processes for low-VOC acrylic resins to ensure market competitiveness. This economic consideration is crucial for widespread adoption, as environmentally friendly alternatives must remain financially viable compared to conventional technologies. The convergence of environmental sustainability, regulatory compliance, and market demands is driving unprecedented innovation in acrylic resin technology for paint applications.
Market Demand for Low-VOC Paint Products
The global market for low-VOC paint products has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven primarily by increasing environmental regulations and growing consumer awareness about indoor air quality. The architectural coatings segment, which includes residential and commercial applications, represents the largest market share for low-VOC paints, with an estimated annual growth rate exceeding the overall paint industry average.
Regulatory frameworks across major markets have become increasingly stringent regarding VOC emissions. The European Union's Paints Directive (2004/42/EC) has established strict VOC content limits for various coating categories, while the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency continues to tighten regulations through the Clean Air Act. Similarly, countries like China and Japan have implemented their own standards to reduce VOC emissions, creating a global push toward environmentally friendly paint formulations.
Consumer preferences have shifted dramatically toward eco-friendly products, with health-conscious consumers willing to pay premium prices for paints that ensure better indoor air quality. This trend is particularly pronounced in residential applications, where homeowners are increasingly concerned about the potential health impacts of traditional solvent-based paints on family members, especially children and the elderly.
The commercial and institutional sectors represent another significant market driver, with green building certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method) incentivizing the use of low-VOC materials. These certification programs have become important market differentiators for commercial properties, further stimulating demand for environmentally responsible coating solutions.
Market research indicates that the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market for low-VOC paints, fueled by rapid urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and strengthening environmental regulations. North America and Europe continue to represent mature markets with steady growth, primarily driven by renovation and remodeling activities rather than new construction.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated consumer interest in healthier living environments, creating additional momentum for low-VOC paint products. With more people spending time at home and becoming increasingly conscious of their immediate environment, manufacturers have reported significant increases in demand for paints that contribute to better indoor air quality.
Industry analysts project that the market for low-VOC acrylic paint formulations will continue to expand at a compound annual growth rate significantly above the industry average through 2030, presenting substantial opportunities for manufacturers who can effectively address both environmental compliance and performance requirements in their product development strategies.
Regulatory frameworks across major markets have become increasingly stringent regarding VOC emissions. The European Union's Paints Directive (2004/42/EC) has established strict VOC content limits for various coating categories, while the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency continues to tighten regulations through the Clean Air Act. Similarly, countries like China and Japan have implemented their own standards to reduce VOC emissions, creating a global push toward environmentally friendly paint formulations.
Consumer preferences have shifted dramatically toward eco-friendly products, with health-conscious consumers willing to pay premium prices for paints that ensure better indoor air quality. This trend is particularly pronounced in residential applications, where homeowners are increasingly concerned about the potential health impacts of traditional solvent-based paints on family members, especially children and the elderly.
The commercial and institutional sectors represent another significant market driver, with green building certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method) incentivizing the use of low-VOC materials. These certification programs have become important market differentiators for commercial properties, further stimulating demand for environmentally responsible coating solutions.
Market research indicates that the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market for low-VOC paints, fueled by rapid urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and strengthening environmental regulations. North America and Europe continue to represent mature markets with steady growth, primarily driven by renovation and remodeling activities rather than new construction.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated consumer interest in healthier living environments, creating additional momentum for low-VOC paint products. With more people spending time at home and becoming increasingly conscious of their immediate environment, manufacturers have reported significant increases in demand for paints that contribute to better indoor air quality.
Industry analysts project that the market for low-VOC acrylic paint formulations will continue to expand at a compound annual growth rate significantly above the industry average through 2030, presenting substantial opportunities for manufacturers who can effectively address both environmental compliance and performance requirements in their product development strategies.
Current VOC Emission Challenges in Acrylic Paint Formulations
Acrylic resin-based paints have become increasingly popular in various industries due to their durability, versatility, and aesthetic appeal. However, these formulations face significant challenges regarding Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) emissions, which have become a critical environmental and regulatory concern worldwide. Traditional acrylic paint formulations typically contain between 250-400 g/L of VOCs, substantially exceeding the increasingly stringent regulatory limits being implemented globally.
The primary sources of VOC emissions in acrylic paint formulations include solvents used for resin dissolution, coalescents that facilitate film formation, and various additives that enhance performance characteristics. Conventional acrylic resins often require substantial amounts of organic solvents to maintain proper viscosity and application properties, contributing significantly to overall VOC content. Additionally, the coalescence process, essential for proper film formation at ambient temperatures, typically relies on slow-evaporating solvents that eventually release into the atmosphere.
Regulatory pressures have intensified globally, with the European Union's VOC Solvents Emissions Directive limiting VOC content to 130 g/L for interior architectural coatings and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency establishing similar restrictions through various Clean Air Act provisions. California's South Coast Air Quality Management District has implemented even more stringent regulations, with some categories restricted to as low as 50 g/L VOC content.
Technical challenges in reducing VOC emissions while maintaining performance include the difficulty of achieving proper film formation without traditional coalescents, maintaining freeze-thaw stability without glycols, and preserving application properties like flow, leveling, and open time without conventional solvents. Furthermore, low-VOC formulations often exhibit compromised durability, adhesion, and scrub resistance, creating a significant technical barrier to widespread adoption.
Market demands for high-performance coatings with specific application characteristics further complicate VOC reduction efforts. Consumers and professional applicators expect consistent performance regardless of environmental considerations, creating tension between regulatory compliance and market expectations. This has led to a fragmented approach where different regions and market segments operate under varying VOC compliance standards.
Manufacturing infrastructure presents another significant challenge, as many production facilities are designed around solvent-based technologies and require substantial capital investment to transition to low-VOC alternatives. The cost implications of reformulation, combined with potential performance trade-offs, create economic barriers that slow industry-wide adoption of low-VOC technologies.
The primary sources of VOC emissions in acrylic paint formulations include solvents used for resin dissolution, coalescents that facilitate film formation, and various additives that enhance performance characteristics. Conventional acrylic resins often require substantial amounts of organic solvents to maintain proper viscosity and application properties, contributing significantly to overall VOC content. Additionally, the coalescence process, essential for proper film formation at ambient temperatures, typically relies on slow-evaporating solvents that eventually release into the atmosphere.
Regulatory pressures have intensified globally, with the European Union's VOC Solvents Emissions Directive limiting VOC content to 130 g/L for interior architectural coatings and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency establishing similar restrictions through various Clean Air Act provisions. California's South Coast Air Quality Management District has implemented even more stringent regulations, with some categories restricted to as low as 50 g/L VOC content.
Technical challenges in reducing VOC emissions while maintaining performance include the difficulty of achieving proper film formation without traditional coalescents, maintaining freeze-thaw stability without glycols, and preserving application properties like flow, leveling, and open time without conventional solvents. Furthermore, low-VOC formulations often exhibit compromised durability, adhesion, and scrub resistance, creating a significant technical barrier to widespread adoption.
Market demands for high-performance coatings with specific application characteristics further complicate VOC reduction efforts. Consumers and professional applicators expect consistent performance regardless of environmental considerations, creating tension between regulatory compliance and market expectations. This has led to a fragmented approach where different regions and market segments operate under varying VOC compliance standards.
Manufacturing infrastructure presents another significant challenge, as many production facilities are designed around solvent-based technologies and require substantial capital investment to transition to low-VOC alternatives. The cost implications of reformulation, combined with potential performance trade-offs, create economic barriers that slow industry-wide adoption of low-VOC technologies.
Current VOC Reduction Methodologies in Paint Formulations
01 Low VOC acrylic resin formulations
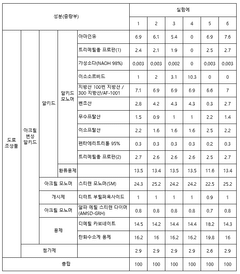
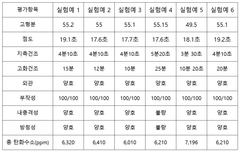
Formulations of acrylic resins with reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) content have been developed to meet environmental regulations. These formulations typically involve modified acrylic polymers, water-based systems, or high-solids compositions that maintain performance properties while minimizing harmful emissions. These environmentally friendly alternatives help manufacturers comply with increasingly stringent air quality standards while providing comparable coating performance.- Low VOC acrylic resin formulations: Formulations of acrylic resins with reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) content have been developed to meet environmental regulations. These formulations typically involve modified acrylic polymers, water-based systems, or high-solids compositions that maintain performance properties while minimizing harmful emissions. These environmentally friendly alternatives help manufacturers comply with increasingly stringent air quality standards while providing comparable coating performance.
- VOC capture and treatment systems: Various systems and methods have been developed to capture and treat VOC emissions from acrylic resin manufacturing and application processes. These include adsorption systems using activated carbon, catalytic oxidation units, and thermal oxidizers that can effectively reduce emissions. Such systems are designed to be integrated into production lines to ensure that VOCs are properly managed before being released into the atmosphere.
- Water-based acrylic alternatives: Water-based acrylic resin systems have been developed as alternatives to traditional solvent-based formulations. These systems use water as the primary carrier instead of organic solvents, significantly reducing VOC emissions. Innovations in emulsion polymerization and dispersion technology have improved the performance of water-based acrylics, making them viable options for many applications where solvent-based systems were previously required.
- Bio-based and sustainable acrylic resins: Research has focused on developing bio-based and sustainable acrylic resins that inherently produce fewer VOC emissions. These formulations incorporate renewable raw materials and bio-derived monomers that can replace petroleum-based components. The resulting resins not only reduce VOC emissions but also decrease the overall carbon footprint of acrylic products, addressing both air quality and climate change concerns.
- Testing and monitoring methods for VOC emissions: Advanced testing and monitoring methods have been developed to accurately measure VOC emissions from acrylic resins. These include gas chromatography techniques, real-time monitoring systems, and standardized testing protocols that help manufacturers assess and verify compliance with emission standards. Continuous monitoring solutions enable production facilities to make immediate adjustments to processes when emission levels approach regulatory limits.
02 VOC capture and treatment systems
Various systems and methods have been developed to capture and treat VOC emissions from acrylic resin manufacturing and application processes. These include adsorption systems using activated carbon, catalytic oxidation units, thermal oxidizers, and condensation technologies. Such systems can significantly reduce the amount of VOCs released into the atmosphere, helping facilities meet environmental compliance requirements.Expand Specific Solutions03 Water-based acrylic alternatives
Water-based acrylic resin systems have been developed as alternatives to traditional solvent-based formulations to reduce VOC emissions. These systems use water as the primary carrier instead of organic solvents, significantly reducing the release of harmful compounds during application and curing. Advances in water-based technology have improved performance characteristics such as durability, adhesion, and drying time, making them viable alternatives in many applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 High-solids acrylic formulations
High-solids acrylic resin formulations contain a greater percentage of non-volatile components, thereby reducing the amount of solvents needed and consequently lowering VOC emissions. These formulations typically utilize lower molecular weight resins with reactive functional groups that crosslink during curing. The technology allows for maintaining application properties and film performance while significantly reducing environmental impact through decreased solvent usage.Expand Specific Solutions05 Testing and measurement of VOC emissions
Various methods and equipment have been developed for accurately testing and measuring VOC emissions from acrylic resins. These include gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, and specialized chambers for capturing and analyzing emissions under controlled conditions. Standardized testing protocols help manufacturers assess compliance with regulations and develop formulations with reduced environmental impact. These measurement techniques are crucial for product development and regulatory certification.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in Low-VOC Paint Technology
The VOC emissions reduction in acrylic resin paint formulations market is in a growth phase, driven by stringent environmental regulations and increasing sustainability demands. The market is expanding at a significant rate as industries shift toward eco-friendly coatings. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with ongoing innovation. Leading players include Sherwin-Williams, BASF SE, and Nippon Paint, who are developing water-based formulations, bio-based alternatives, and advanced VOC-capturing technologies. Sika Technology AG and SINOPEC Beijing Research Institute are making notable advancements in polymer chemistry for low-emission resins. Kansai Paint and PPG Industries are focusing on high-performance, low-VOC industrial coatings, while academic partnerships with institutions like Drexel University are accelerating research into novel emission reduction methodologies.
The Sherwin-Williams Co.
Technical Solution: Sherwin-Williams has developed waterborne acrylic resin technologies that significantly reduce VOC emissions while maintaining performance characteristics. Their approach includes the use of high-solid acrylic formulations with VOC content as low as 50 g/L, compared to traditional solvent-based systems that typically contain 250-400 g/L. The company has pioneered reactive diluent technology where low-molecular-weight acrylic monomers replace conventional solvents, becoming part of the polymer matrix during curing rather than evaporating. Additionally, they've implemented innovative crosslinking mechanisms using carbodiimide chemistry that enables lower-temperature curing, further reducing energy consumption and VOC emissions during application. Their ProMar 200 Zero VOC interior latex paint line demonstrates commercial implementation of these technologies.
Strengths: Maintains excellent adhesion and durability comparable to traditional solvent-based systems while achieving regulatory compliance. Their formulations offer improved application properties and reduced environmental impact. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional systems and potential limitations in certain high-performance industrial applications requiring chemical resistance.
Sika Technology AG
Technical Solution: Sika has developed innovative acrylic resin technologies for VOC reduction through their Sikalastic® and Sikagard® product lines. Their approach centers on advanced emulsion polymerization techniques that produce high-molecular-weight acrylic polymers with optimized particle size distribution, enabling high-solids content (up to 60%) while maintaining workable application viscosity. Sika has pioneered the use of silane-functional acrylic polymers that crosslink through moisture-cure mechanisms rather than requiring conventional solvents for film formation. Their technology incorporates specialized rheology modifiers derived from renewable resources that provide application stability without contributing to VOC content. Additionally, Sika has developed proprietary acrylic-silicone hybrid technologies that combine the environmental benefits of waterborne systems with enhanced weathering resistance. Their EcoPrime® system demonstrates commercial implementation, achieving VOC reductions of approximately 80% compared to conventional solvent-based primers while maintaining excellent adhesion properties.
Strengths: Superior weathering resistance and durability in exterior applications. Their technologies offer excellent substrate adhesion across diverse materials including concrete, metal, and plastics. Weaknesses: Higher production costs and potential limitations in low-temperature application environments compared to solvent-based alternatives.
Key Innovations in Low-VOC Acrylic Resin Technology
Bio-based, high-solid low viscosity acrylic resin and preparation method thereof
PatentInactiveUS20250263510A1
Innovation
- A bio-based, high-solid, low-viscosity acrylic resin is developed using bio-based acrylates, low-toxic solvents, and specific initiators, with a formulation and preparation method that ensures a solid content above 70% and viscosity below 20,000 cP, enhancing weather resistance, chemical resistance, and corrosion resistance.
Acrylic-modified alkyd resin and paint composition comprising same
PatentWO2025159417A1
Innovation
- An acrylic-modified alkyd resin is developed using linseed oil, isosorbide, and specific acrylic and styrene monomers to reduce viscosity and molecular weight, enhancing rust prevention and curing properties while minimizing solvent use.
Environmental Regulations Impacting Paint VOC Emissions
The regulatory landscape governing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions in paint formulations has evolved significantly over the past decades, becoming increasingly stringent across global markets. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) established the National Volatile Organic Compound Emission Standards for Architectural Coatings under the Clean Air Act, which sets specific VOC content limits for various coating categories. These regulations have undergone several revisions, with the most recent updates further reducing allowable VOC content in acrylic paint formulations.
The European Union has implemented even more restrictive measures through the VOC Solvents Emissions Directive (1999/13/EC) and the Paints Directive (2004/42/EC), which established harmonized limitations on the VOC content of decorative paints and varnishes. These directives have been instrumental in driving innovation toward low-VOC and zero-VOC acrylic resin technologies across the European market.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have developed their own regulatory frameworks. China's national standard GB 18582-2008 regulates VOC content in architectural wall coatings, while Japan's Air Pollution Control Law includes specific provisions for VOC emissions from paint manufacturing and application processes. These regulations continue to tighten as air quality concerns grow in densely populated urban centers.
California's South Coast Air Quality Management District (SCAQMD) Rule 1113 represents one of the most stringent regional regulations globally, often serving as a bellwether for future national standards. The rule has progressively lowered VOC limits for architectural coatings, pushing manufacturers toward advanced acrylic resin technologies that maintain performance while reducing emissions.
Compliance mechanisms vary across jurisdictions but typically include mandatory product labeling, certification processes, and reporting requirements. Many regulations incorporate phase-in periods to allow industry adaptation, though these timelines have generally shortened as low-VOC technologies have matured.
The economic implications of these regulations have been substantial, with manufacturers investing significantly in research and development to reformulate products. However, studies indicate that regulatory pressure has accelerated innovation, resulting in new acrylic resin technologies that often outperform their higher-VOC predecessors while reducing environmental impact.
Future regulatory trends point toward further restrictions, with several jurisdictions announcing roadmaps to progressively lower VOC limits over the next decade. This regulatory momentum continues to drive the paint industry toward waterborne formulations, high-solids systems, and novel acrylic resin chemistries designed specifically to minimize volatile organic compounds while maintaining application properties and durability.
The European Union has implemented even more restrictive measures through the VOC Solvents Emissions Directive (1999/13/EC) and the Paints Directive (2004/42/EC), which established harmonized limitations on the VOC content of decorative paints and varnishes. These directives have been instrumental in driving innovation toward low-VOC and zero-VOC acrylic resin technologies across the European market.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have developed their own regulatory frameworks. China's national standard GB 18582-2008 regulates VOC content in architectural wall coatings, while Japan's Air Pollution Control Law includes specific provisions for VOC emissions from paint manufacturing and application processes. These regulations continue to tighten as air quality concerns grow in densely populated urban centers.
California's South Coast Air Quality Management District (SCAQMD) Rule 1113 represents one of the most stringent regional regulations globally, often serving as a bellwether for future national standards. The rule has progressively lowered VOC limits for architectural coatings, pushing manufacturers toward advanced acrylic resin technologies that maintain performance while reducing emissions.
Compliance mechanisms vary across jurisdictions but typically include mandatory product labeling, certification processes, and reporting requirements. Many regulations incorporate phase-in periods to allow industry adaptation, though these timelines have generally shortened as low-VOC technologies have matured.
The economic implications of these regulations have been substantial, with manufacturers investing significantly in research and development to reformulate products. However, studies indicate that regulatory pressure has accelerated innovation, resulting in new acrylic resin technologies that often outperform their higher-VOC predecessors while reducing environmental impact.
Future regulatory trends point toward further restrictions, with several jurisdictions announcing roadmaps to progressively lower VOC limits over the next decade. This regulatory momentum continues to drive the paint industry toward waterborne formulations, high-solids systems, and novel acrylic resin chemistries designed specifically to minimize volatile organic compounds while maintaining application properties and durability.
Lifecycle Assessment of Low-VOC Paint Technologies
Lifecycle assessment (LCA) of low-VOC paint technologies reveals significant environmental advantages compared to traditional high-VOC formulations. The assessment encompasses raw material extraction, manufacturing, application, use phase, and end-of-life disposal, providing a comprehensive environmental impact evaluation. Studies indicate that water-based acrylic paints with reduced VOC content demonstrate 30-45% lower global warming potential across their lifecycle compared to solvent-based alternatives.
Manufacturing processes for low-VOC acrylic resins consume approximately 25% less energy than conventional methods, primarily due to reduced solvent processing requirements. The elimination of petroleum-derived solvents in water-based formulations further decreases the carbon footprint associated with raw material extraction and processing phases.
During the application phase, low-VOC paints release significantly fewer harmful emissions. Quantitative measurements show that conventional solvent-based paints can emit 250-400 g/L of VOCs during application and curing, while advanced low-VOC formulations reduce this to below 50 g/L, with ultra-low options achieving less than 10 g/L.
The use phase analysis demonstrates additional benefits beyond reduced emissions. Low-VOC acrylic paints typically maintain their protective and aesthetic properties for 7-10 years, comparable to or exceeding traditional formulations. This extended durability translates to reduced maintenance requirements and fewer reapplication cycles over a building's lifetime.
End-of-life considerations reveal that water-based acrylic paints generally pose fewer disposal challenges. They contain fewer hazardous components requiring special treatment, though proper disposal remains important for all paint products. Several lifecycle studies indicate that the waste management burden is approximately 35% lower for low-VOC formulations.
Economic lifecycle assessment shows that while low-VOC technologies may carry 10-15% higher initial costs, the total lifecycle cost often proves competitive or advantageous when accounting for reduced health impacts, regulatory compliance, and potential extended durability. Healthcare cost savings from reduced respiratory issues and other VOC-related health problems represent significant externalized benefits not typically captured in traditional pricing models.
Recent advancements in bio-based acrylic resins show promise for further improving the lifecycle profile of low-VOC paints. Preliminary assessments indicate potential reductions in fossil resource depletion by up to 60% compared to petroleum-derived acrylic resins, though these technologies remain in early commercialization stages and require further optimization to achieve performance parity.
Manufacturing processes for low-VOC acrylic resins consume approximately 25% less energy than conventional methods, primarily due to reduced solvent processing requirements. The elimination of petroleum-derived solvents in water-based formulations further decreases the carbon footprint associated with raw material extraction and processing phases.
During the application phase, low-VOC paints release significantly fewer harmful emissions. Quantitative measurements show that conventional solvent-based paints can emit 250-400 g/L of VOCs during application and curing, while advanced low-VOC formulations reduce this to below 50 g/L, with ultra-low options achieving less than 10 g/L.
The use phase analysis demonstrates additional benefits beyond reduced emissions. Low-VOC acrylic paints typically maintain their protective and aesthetic properties for 7-10 years, comparable to or exceeding traditional formulations. This extended durability translates to reduced maintenance requirements and fewer reapplication cycles over a building's lifetime.
End-of-life considerations reveal that water-based acrylic paints generally pose fewer disposal challenges. They contain fewer hazardous components requiring special treatment, though proper disposal remains important for all paint products. Several lifecycle studies indicate that the waste management burden is approximately 35% lower for low-VOC formulations.
Economic lifecycle assessment shows that while low-VOC technologies may carry 10-15% higher initial costs, the total lifecycle cost often proves competitive or advantageous when accounting for reduced health impacts, regulatory compliance, and potential extended durability. Healthcare cost savings from reduced respiratory issues and other VOC-related health problems represent significant externalized benefits not typically captured in traditional pricing models.
Recent advancements in bio-based acrylic resins show promise for further improving the lifecycle profile of low-VOC paints. Preliminary assessments indicate potential reductions in fossil resource depletion by up to 60% compared to petroleum-derived acrylic resins, though these technologies remain in early commercialization stages and require further optimization to achieve performance parity.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!