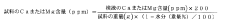How to Reduce Costs with Cellulose Acetate Production Methods?
Cellulose Acetate Production Background and Objectives
Cellulose acetate production has a rich history dating back to the early 20th century when it was first developed as a more stable alternative to cellulose nitrate. Over the decades, this versatile material has found applications in various industries, including textiles, films, and plastics. The evolution of cellulose acetate production methods has been driven by the need for improved efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and cost-effectiveness.
The primary objective in cellulose acetate production is to convert cellulose, typically derived from wood pulp or cotton linters, into a soluble form through acetylation. This process involves the reaction of cellulose with acetic anhydride in the presence of a catalyst, usually sulfuric acid. The resulting cellulose acetate can then be further processed into various forms, such as fibers, films, or molded products.
In recent years, the focus of technological advancements in cellulose acetate production has shifted towards sustainability and cost reduction. This shift is driven by increasing environmental concerns and the need to maintain competitiveness in a global market. Key areas of development include improving raw material utilization, optimizing reaction conditions, and enhancing recovery and recycling of solvents and byproducts.
One significant trend in cellulose acetate production is the exploration of alternative raw materials. While wood pulp remains the primary source of cellulose, research is being conducted on utilizing agricultural residues and other cellulosic waste materials. This approach not only addresses sustainability concerns but also has the potential to reduce raw material costs significantly.
Another important aspect of cellulose acetate production technology is the development of more efficient catalysts. Traditional sulfuric acid catalysts are being replaced or supplemented with heterogeneous catalysts that offer improved selectivity and easier separation from the reaction mixture. These advancements contribute to both cost reduction and environmental sustainability by minimizing waste and improving product quality.
Process intensification techniques are also being explored to enhance the efficiency of cellulose acetate production. This includes the use of microreactors and continuous flow processes, which can lead to better control over reaction conditions, reduced energy consumption, and improved product consistency. Such innovations have the potential to significantly reduce production costs while maintaining or even improving product quality.
As we look towards the future of cellulose acetate production, the industry faces both challenges and opportunities. The primary goal remains to develop more cost-effective and environmentally friendly production methods while maintaining the material's desirable properties. This requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining advances in chemistry, materials science, and engineering to create innovative solutions that address the evolving needs of the market and society.
Market Analysis for Cost-Effective Cellulose Acetate
The global cellulose acetate market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand in various industries such as textiles, cigarette filters, and packaging. The market size was valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $4.3 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 3.5% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising consumption of cellulose acetate in cigarette filters and the expanding textile industry in developing countries.
The demand for cost-effective cellulose acetate production methods has become increasingly crucial due to the competitive nature of the market and the pressure to maintain profit margins. Key factors influencing the market include raw material prices, energy costs, and environmental regulations. The primary raw materials for cellulose acetate production, such as wood pulp and acetic anhydride, have shown price volatility in recent years, impacting production costs significantly.
Asia-Pacific region dominates the cellulose acetate market, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This is largely due to the presence of major textile manufacturing hubs in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow, with a significant market share driven by the demand for cigarette filters and packaging materials.
The market is characterized by the presence of several large-scale manufacturers and a number of small to medium-sized players. Key market players include Eastman Chemical Company, Celanese Corporation, Daicel Corporation, and Solvay. These companies are actively investing in research and development to improve production efficiency and reduce costs.
Cost-effective production methods are becoming a key differentiator in the market. Companies are focusing on developing innovative processes to optimize raw material usage, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste generation. For instance, some manufacturers are exploring the use of alternative raw materials, such as agricultural waste, to produce cellulose acetate more economically.
The market also faces challenges from increasing environmental concerns and regulations. Stricter policies regarding plastic waste and the push for biodegradable alternatives are influencing market dynamics. This has led to increased research into bio-based and more environmentally friendly production methods for cellulose acetate.
In conclusion, the market analysis for cost-effective cellulose acetate production methods reveals a growing demand driven by various industries. The focus on cost reduction and efficiency improvement is crucial for maintaining competitiveness in this evolving market landscape. Companies that can successfully develop and implement innovative, cost-effective production methods while addressing environmental concerns are likely to gain a significant advantage in the global cellulose acetate market.
Current Challenges in Cellulose Acetate Manufacturing
Cellulose acetate manufacturing faces several significant challenges in today's industrial landscape. One of the primary issues is the high cost of raw materials, particularly cellulose and acetic anhydride. The fluctuating prices of these inputs can significantly impact production costs, making it difficult for manufacturers to maintain consistent profit margins.
Energy consumption is another major concern in cellulose acetate production. The process requires substantial amounts of energy for various stages, including acetylation, hydrolysis, and drying. As energy prices continue to rise globally, this aspect of production becomes increasingly expensive, putting pressure on manufacturers to find more energy-efficient methods.
Environmental regulations pose a growing challenge for the industry. The production of cellulose acetate involves the use of potentially harmful chemicals and generates waste that requires careful management. Stricter environmental standards are forcing manufacturers to invest in costly pollution control measures and waste treatment systems, further adding to production expenses.
The complexity of the manufacturing process itself presents ongoing challenges. The multi-step nature of cellulose acetate production, involving acetylation, hydrolysis, and precipitation, requires precise control and optimization at each stage. Any inefficiencies or inconsistencies in these processes can lead to quality issues and increased production costs.
Labor costs and skilled workforce availability are also significant concerns. The production of cellulose acetate requires specialized knowledge and expertise, and attracting and retaining skilled workers can be challenging and expensive, particularly in regions with competitive labor markets.
Additionally, the industry faces challenges related to product quality and consistency. Maintaining uniform properties across batches of cellulose acetate is crucial for meeting customer specifications, especially in high-value applications such as film and fiber production. Achieving this consistency while simultaneously trying to reduce costs can be a delicate balancing act.
Lastly, the cellulose acetate industry is grappling with increasing competition from alternative materials, particularly in certain applications. This market pressure necessitates continuous innovation and cost reduction efforts to maintain competitiveness, adding another layer of complexity to the manufacturing challenges.
Existing Cost Reduction Strategies in Production
01 Production methods affecting costs
Various production methods can significantly impact the cost of cellulose acetate. These include improvements in acetylation processes, solvent recovery systems, and the use of alternative raw materials. Optimizing these processes can lead to more cost-effective production of cellulose acetate.- Production methods affecting costs: Various production methods can significantly impact the cost of cellulose acetate. These include improvements in acetylation processes, solvent recovery systems, and optimization of reaction conditions. Advanced manufacturing techniques can lead to increased efficiency and reduced production costs.
- Raw material sourcing and alternatives: The cost of cellulose acetate is heavily influenced by raw material sourcing. Exploring alternative sources of cellulose, such as agricultural waste or non-wood plants, can potentially reduce costs. Additionally, developing processes to use lower-grade cellulose sources may lead to more economical production.
- Recycling and waste reduction: Implementing effective recycling processes and waste reduction strategies can significantly lower the overall cost of cellulose acetate production. This includes recovering and reusing solvents, minimizing byproducts, and developing closed-loop manufacturing systems.
- Energy efficiency in production: Improving energy efficiency in cellulose acetate production can lead to substantial cost reductions. This may involve optimizing reaction temperatures, implementing heat recovery systems, and utilizing more energy-efficient equipment throughout the manufacturing process.
- Scale and automation in manufacturing: Increasing production scale and implementing automation in cellulose acetate manufacturing can help reduce costs. This includes developing continuous production processes, integrating advanced control systems, and optimizing plant layouts for improved efficiency and reduced labor costs.
02 Raw material sourcing and costs
The cost of cellulose acetate is heavily influenced by the sourcing and pricing of raw materials, particularly cellulose. Exploring alternative sources of cellulose, such as agricultural waste or non-wood plants, can potentially reduce production costs. Additionally, fluctuations in the global market for raw materials can impact the overall cost of cellulose acetate.Expand Specific Solutions03 Energy efficiency in production
Improving energy efficiency in the production process can significantly reduce the costs associated with cellulose acetate manufacturing. This includes optimizing reaction conditions, implementing heat recovery systems, and utilizing more efficient equipment. Energy-saving measures can lead to lower production costs and improved sustainability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Recycling and waste reduction
Implementing effective recycling and waste reduction strategies can help lower the overall costs of cellulose acetate production. This includes recovering and reusing solvents, minimizing byproduct formation, and finding applications for production waste. Such measures can reduce raw material costs and improve process efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Market demand and economies of scale
The cost of cellulose acetate is influenced by market demand and production scale. Increased demand can lead to economies of scale, potentially reducing production costs. Conversely, fluctuations in demand or oversupply can impact pricing. Understanding market trends and adjusting production accordingly can help optimize costs.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Cellulose Acetate Industry
The cellulose acetate production market is in a mature stage, with established players like Daicel Corp., Eastman Chemical Co., and Cerdia Produktions GmbH dominating the industry. The global market size is estimated to be around $3.5 billion, with steady growth projected. Technological maturity varies among companies, with industry leaders focusing on cost reduction and sustainability. Emerging players such as Nantong Cellulose Fibers Co. Ltd. and Jiangsu Ruichen Chemical Co. Ltd. are investing in innovative production methods to gain market share. Research institutions like the Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and universities are contributing to advancements in production efficiency and environmental sustainability, driving the industry towards more cost-effective and eco-friendly solutions.
Daicel Corp.
BASF Corp.
Innovative Technologies for Cellulose Acetate Synthesis
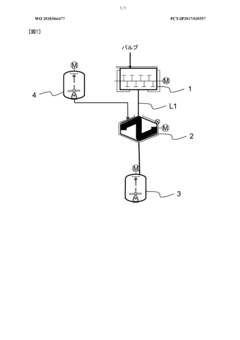
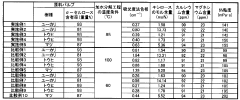
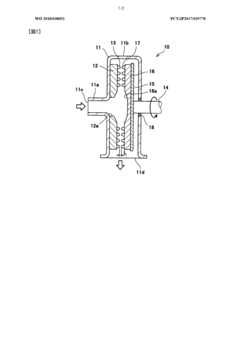
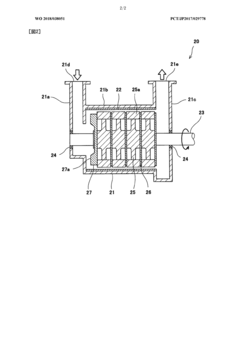
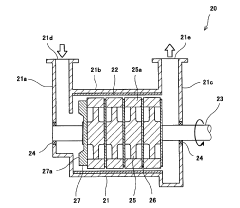
- A method involving crushing wood pulp, pretreating it with acetic acid, reacting with acetic anhydride, and adjusting the degree of acetyl substitution through hydrolysis at specific temperature conditions to produce cellulose acetate with improved hue and moldability, while utilizing low-grade pulp with low α-cellulose content.
- A method involving the crushing of linter pulp using a disc refiner and air flow crusher, followed by acetylation with controlled acetic acid and sulfuric acid treatment, to produce cellulose acetate with specific sugar chain component ratios and filtration characteristics, reducing insoluble foreign substances and improving production efficiency.
Raw Material Sourcing and Supply Chain Optimization
Optimizing raw material sourcing and supply chain management is crucial for reducing costs in cellulose acetate production. The primary raw materials for cellulose acetate include cellulose, typically derived from wood pulp or cotton linters, and acetic anhydride. Establishing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers of these materials can lead to more stable pricing and consistent quality.
Diversifying the sources of raw materials can help mitigate supply chain risks and potentially reduce costs. For instance, exploring alternative sources of cellulose, such as agricultural waste or bamboo, may offer cost advantages in certain regions. Additionally, implementing just-in-time inventory management can minimize storage costs and reduce the risk of material obsolescence.
Vertical integration strategies, such as investing in wood pulp production facilities or partnering with forestry companies, can provide greater control over raw material costs and quality. This approach may also offer opportunities for process optimization across the entire value chain, from raw material extraction to final product manufacturing.
Leveraging advanced analytics and artificial intelligence in supply chain management can lead to more accurate demand forecasting, optimized inventory levels, and improved logistics planning. These technologies can help identify cost-saving opportunities throughout the supply chain, from procurement to distribution.
Implementing sustainable sourcing practices can not only improve the environmental footprint of cellulose acetate production but also potentially reduce costs in the long term. For example, utilizing recycled materials or investing in more efficient extraction processes can lead to both cost savings and improved sustainability credentials.
Exploring regional sourcing strategies can help minimize transportation costs and reduce the carbon footprint of the supply chain. This may involve establishing production facilities closer to raw material sources or key markets, or collaborating with local suppliers to develop more efficient supply networks.
Continuous improvement initiatives focused on reducing waste and improving yield in raw material processing can significantly impact overall production costs. This may include investing in more efficient equipment, optimizing process parameters, or implementing lean manufacturing principles throughout the supply chain.
By addressing these aspects of raw material sourcing and supply chain optimization, cellulose acetate producers can achieve substantial cost reductions while maintaining product quality and meeting market demands.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The production of cellulose acetate has significant environmental implications that must be carefully considered in the pursuit of cost reduction. Traditional manufacturing processes often involve the use of hazardous chemicals and generate substantial waste, posing risks to both human health and the environment. However, recent advancements in production methods have opened up opportunities for more sustainable practices.
One key area of focus is the reduction of solvent usage in the acetylation process. By implementing more efficient solvent recovery systems and exploring alternative, less toxic solvents, manufacturers can minimize environmental impact while simultaneously lowering production costs. Additionally, the development of closed-loop systems for chemical recycling has shown promise in reducing waste and improving resource efficiency.
Water consumption is another critical factor in cellulose acetate production. Innovative water management techniques, such as advanced filtration and purification systems, can significantly reduce water usage and wastewater generation. This not only lessens the environmental footprint but also contributes to cost savings through reduced water treatment and disposal expenses.
Energy efficiency improvements present another avenue for both cost reduction and environmental benefit. The adoption of more energy-efficient equipment, process optimization, and the integration of renewable energy sources can lead to substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and energy costs. Some manufacturers have successfully implemented combined heat and power systems, further enhancing overall energy efficiency.
Biodegradability and end-of-life considerations are increasingly important aspects of cellulose acetate production. Research into enhancing the biodegradability of cellulose acetate products without compromising performance characteristics is ongoing. This focus on product lifecycle management not only addresses environmental concerns but also aligns with growing consumer demand for sustainable materials.
Raw material sourcing plays a crucial role in the sustainability of cellulose acetate production. The use of sustainably harvested wood pulp or alternative cellulose sources, such as agricultural waste, can significantly reduce the environmental impact of raw material procurement. Some producers are exploring the potential of genetically modified trees with higher cellulose content to increase yield and reduce land use.
Lastly, the implementation of green chemistry principles in cellulose acetate production offers promising pathways for environmental improvement. This includes the development of catalysts that enable milder reaction conditions, the use of bio-based chemicals, and the design of processes that minimize the generation of hazardous byproducts. These approaches not only enhance sustainability but also often lead to more efficient and cost-effective production methods.