How V8 Engines Advance High-Performance Motorcycles?
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V8 Engine Evolution in Motorcycles
The evolution of V8 engines in motorcycles represents a significant milestone in the pursuit of high-performance two-wheeled machines. This journey began in the early 20th century when motorcycle manufacturers first experimented with multi-cylinder engines to increase power output. However, it wasn't until the late 1990s that the first production V8 motorcycle engine emerged, marking a new era in motorcycle engineering.
The initial attempts to incorporate V8 engines into motorcycles were largely custom projects or concept vehicles. These early designs faced numerous challenges, including weight distribution, cooling efficiency, and power delivery. As technology advanced, engineers found innovative solutions to these problems, paving the way for more refined V8 motorcycle engines.
A pivotal moment in V8 motorcycle history came with the introduction of the Boss Hoss motorcycles in 1990. These machines, powered by small-block Chevrolet V8 engines, demonstrated the feasibility of integrating large-displacement automotive engines into motorcycle frames. While not traditional motorcycle engines, they set the stage for future developments in high-performance V8 motorcycles.
The true breakthrough in purpose-built V8 motorcycle engines arrived with the Morbidelli V8 in 1994. This 847cc engine was specifically designed for motorcycle use, featuring a compact 90-degree V configuration and producing an impressive 120 horsepower. Although the Morbidelli never reached mass production, it proved that a dedicated V8 motorcycle engine was not only possible but could offer exceptional performance.
Following these pioneering efforts, other manufacturers began exploring V8 motorcycle designs. Notable examples include the Millyard Viper V10, a custom-built motorcycle using a Dodge Viper engine, and the MTT Turbine Superbike, which utilized a Rolls-Royce turboshaft engine. While not V8s, these projects further pushed the boundaries of what was possible in high-performance motorcycle engineering.
In recent years, advancements in materials science, computer-aided design, and manufacturing techniques have allowed for the development of more compact and efficient V8 motorcycle engines. Modern V8 motorcycles, such as the PGM V8, showcase the potential of these powerplants, offering unparalleled power-to-weight ratios and exhilarating performance.
The evolution of V8 engines in motorcycles continues to this day, with ongoing research into areas such as weight reduction, improved fuel efficiency, and enhanced power delivery. As motorcycle enthusiasts and engineers push the limits of what's possible, the V8 engine remains a symbol of ultimate performance in the two-wheeled world.
The initial attempts to incorporate V8 engines into motorcycles were largely custom projects or concept vehicles. These early designs faced numerous challenges, including weight distribution, cooling efficiency, and power delivery. As technology advanced, engineers found innovative solutions to these problems, paving the way for more refined V8 motorcycle engines.
A pivotal moment in V8 motorcycle history came with the introduction of the Boss Hoss motorcycles in 1990. These machines, powered by small-block Chevrolet V8 engines, demonstrated the feasibility of integrating large-displacement automotive engines into motorcycle frames. While not traditional motorcycle engines, they set the stage for future developments in high-performance V8 motorcycles.
The true breakthrough in purpose-built V8 motorcycle engines arrived with the Morbidelli V8 in 1994. This 847cc engine was specifically designed for motorcycle use, featuring a compact 90-degree V configuration and producing an impressive 120 horsepower. Although the Morbidelli never reached mass production, it proved that a dedicated V8 motorcycle engine was not only possible but could offer exceptional performance.
Following these pioneering efforts, other manufacturers began exploring V8 motorcycle designs. Notable examples include the Millyard Viper V10, a custom-built motorcycle using a Dodge Viper engine, and the MTT Turbine Superbike, which utilized a Rolls-Royce turboshaft engine. While not V8s, these projects further pushed the boundaries of what was possible in high-performance motorcycle engineering.
In recent years, advancements in materials science, computer-aided design, and manufacturing techniques have allowed for the development of more compact and efficient V8 motorcycle engines. Modern V8 motorcycles, such as the PGM V8, showcase the potential of these powerplants, offering unparalleled power-to-weight ratios and exhilarating performance.
The evolution of V8 engines in motorcycles continues to this day, with ongoing research into areas such as weight reduction, improved fuel efficiency, and enhanced power delivery. As motorcycle enthusiasts and engineers push the limits of what's possible, the V8 engine remains a symbol of ultimate performance in the two-wheeled world.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for high-performance motorcycles equipped with V8 engines has been steadily growing, driven by enthusiasts seeking unparalleled power, sound, and riding experience. This niche segment of the motorcycle industry caters to a specific demographic of riders who prioritize performance and exclusivity over practicality and fuel efficiency.
The global high-performance motorcycle market has shown consistent growth, with a significant portion attributed to V8-powered bikes. These motorcycles appeal to affluent consumers, collectors, and racing enthusiasts who are willing to invest in premium, high-end machines. The unique characteristics of V8 engines, such as their distinctive sound and smooth power delivery, contribute to their desirability among motorcycle aficionados.
In recent years, there has been an increased interest in track-focused motorcycles, where V8 engines excel due to their power output and torque characteristics. This trend has led to a rise in demand for V8-powered motorcycles designed for both road and track use, blurring the lines between street-legal bikes and race-oriented machines.
The market for V8 motorcycles is not limited to traditional motorcycle manufacturers. Custom builders and boutique manufacturers have also entered this space, offering bespoke V8-powered motorcycles to cater to the most discerning customers. This diversification has expanded the market and created new opportunities for innovation and design in the high-performance motorcycle segment.
Environmental regulations and a global shift towards sustainability have posed challenges to the V8 motorcycle market. However, manufacturers are responding by developing more efficient V8 engines and exploring hybrid technologies to meet emissions standards while maintaining performance. This adaptation is crucial for the continued growth and relevance of V8 motorcycles in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
The tourism and leisure sectors have also contributed to the demand for V8 motorcycles. High-end motorcycle touring and rental services have emerged, offering enthusiasts the opportunity to experience these powerful machines without the commitment of ownership. This has broadened the market reach and introduced V8 motorcycles to a wider audience of potential buyers.
While the overall motorcycle market has faced fluctuations, the high-performance segment, including V8-powered bikes, has shown resilience. The exclusivity and premium nature of these motorcycles have insulated them to some extent from broader market downturns, as their target consumers are less affected by economic fluctuations.
Looking ahead, the market for V8 motorcycles is expected to continue its growth trajectory, albeit at a measured pace. Innovations in engine technology, materials science, and aerodynamics are likely to drive future demand, as manufacturers strive to push the boundaries of performance while addressing environmental concerns. The integration of advanced electronics and rider aids is also anticipated to enhance the appeal of V8 motorcycles, making them more accessible to a broader range of skilled riders.
The global high-performance motorcycle market has shown consistent growth, with a significant portion attributed to V8-powered bikes. These motorcycles appeal to affluent consumers, collectors, and racing enthusiasts who are willing to invest in premium, high-end machines. The unique characteristics of V8 engines, such as their distinctive sound and smooth power delivery, contribute to their desirability among motorcycle aficionados.
In recent years, there has been an increased interest in track-focused motorcycles, where V8 engines excel due to their power output and torque characteristics. This trend has led to a rise in demand for V8-powered motorcycles designed for both road and track use, blurring the lines between street-legal bikes and race-oriented machines.
The market for V8 motorcycles is not limited to traditional motorcycle manufacturers. Custom builders and boutique manufacturers have also entered this space, offering bespoke V8-powered motorcycles to cater to the most discerning customers. This diversification has expanded the market and created new opportunities for innovation and design in the high-performance motorcycle segment.
Environmental regulations and a global shift towards sustainability have posed challenges to the V8 motorcycle market. However, manufacturers are responding by developing more efficient V8 engines and exploring hybrid technologies to meet emissions standards while maintaining performance. This adaptation is crucial for the continued growth and relevance of V8 motorcycles in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
The tourism and leisure sectors have also contributed to the demand for V8 motorcycles. High-end motorcycle touring and rental services have emerged, offering enthusiasts the opportunity to experience these powerful machines without the commitment of ownership. This has broadened the market reach and introduced V8 motorcycles to a wider audience of potential buyers.
While the overall motorcycle market has faced fluctuations, the high-performance segment, including V8-powered bikes, has shown resilience. The exclusivity and premium nature of these motorcycles have insulated them to some extent from broader market downturns, as their target consumers are less affected by economic fluctuations.
Looking ahead, the market for V8 motorcycles is expected to continue its growth trajectory, albeit at a measured pace. Innovations in engine technology, materials science, and aerodynamics are likely to drive future demand, as manufacturers strive to push the boundaries of performance while addressing environmental concerns. The integration of advanced electronics and rider aids is also anticipated to enhance the appeal of V8 motorcycles, making them more accessible to a broader range of skilled riders.
Current V8 Motorcycle Tech Challenges
The integration of V8 engines into high-performance motorcycles presents several significant technical challenges that manufacturers and engineers must overcome. One of the primary obstacles is the sheer size and weight of V8 engines, which are traditionally designed for automobiles. Adapting these powerplants to fit within the compact frame of a motorcycle requires extensive redesign and innovative engineering solutions to maintain balance, handling, and overall performance.
Heat management poses another critical challenge. V8 engines generate substantial heat, which can be problematic in the confined spaces of a motorcycle chassis. Effective cooling systems must be developed to prevent overheating and ensure optimal engine performance, particularly during high-speed or prolonged riding conditions. This often necessitates the implementation of advanced liquid cooling systems and carefully designed airflow management.
Power delivery and transmission present unique hurdles in V8 motorcycle applications. The immense torque produced by these engines can overwhelm traditional motorcycle drivetrains, requiring the development of robust transmission systems and reinforced final drive components. Engineers must also address the challenge of smoothly transferring power to the rear wheel while maintaining traction and stability across various riding conditions.
Fuel efficiency and emissions control are increasingly important considerations in modern motorcycle design. V8 engines, known for their high fuel consumption, must be optimized to meet stringent environmental regulations without sacrificing performance. This involves the implementation of advanced fuel injection systems, exhaust gas recirculation, and catalytic converters tailored for motorcycle applications.
Vibration management is another significant technical challenge. The inherent characteristics of V8 engines can produce substantial vibrations, which can lead to rider fatigue and potentially compromise the structural integrity of the motorcycle over time. Innovative mounting systems and vibration damping technologies must be employed to ensure a smooth and comfortable riding experience.
The complexity of V8 engines also presents challenges in terms of maintenance and serviceability. Motorcycle manufacturers must develop designs that allow for relatively easy access to critical components, despite the compact nature of motorcycle frames. This requires careful consideration of component placement and the development of specialized tools and maintenance procedures.
Lastly, the integration of modern electronics and rider aids with V8 motorcycle engines presents its own set of challenges. Developing engine management systems, traction control, and other electronic assists that can effectively harness and control the power of a V8 engine in a motorcycle application requires sophisticated software and hardware solutions. These systems must be seamlessly integrated to enhance performance and safety without compromising the raw, visceral experience that attracts riders to V8-powered motorcycles.
Heat management poses another critical challenge. V8 engines generate substantial heat, which can be problematic in the confined spaces of a motorcycle chassis. Effective cooling systems must be developed to prevent overheating and ensure optimal engine performance, particularly during high-speed or prolonged riding conditions. This often necessitates the implementation of advanced liquid cooling systems and carefully designed airflow management.
Power delivery and transmission present unique hurdles in V8 motorcycle applications. The immense torque produced by these engines can overwhelm traditional motorcycle drivetrains, requiring the development of robust transmission systems and reinforced final drive components. Engineers must also address the challenge of smoothly transferring power to the rear wheel while maintaining traction and stability across various riding conditions.
Fuel efficiency and emissions control are increasingly important considerations in modern motorcycle design. V8 engines, known for their high fuel consumption, must be optimized to meet stringent environmental regulations without sacrificing performance. This involves the implementation of advanced fuel injection systems, exhaust gas recirculation, and catalytic converters tailored for motorcycle applications.
Vibration management is another significant technical challenge. The inherent characteristics of V8 engines can produce substantial vibrations, which can lead to rider fatigue and potentially compromise the structural integrity of the motorcycle over time. Innovative mounting systems and vibration damping technologies must be employed to ensure a smooth and comfortable riding experience.
The complexity of V8 engines also presents challenges in terms of maintenance and serviceability. Motorcycle manufacturers must develop designs that allow for relatively easy access to critical components, despite the compact nature of motorcycle frames. This requires careful consideration of component placement and the development of specialized tools and maintenance procedures.
Lastly, the integration of modern electronics and rider aids with V8 motorcycle engines presents its own set of challenges. Developing engine management systems, traction control, and other electronic assists that can effectively harness and control the power of a V8 engine in a motorcycle application requires sophisticated software and hardware solutions. These systems must be seamlessly integrated to enhance performance and safety without compromising the raw, visceral experience that attracts riders to V8-powered motorcycles.
V8 Motorcycle Engine Design Solutions
01 Cylinder configuration and design
V8 engine performance can be enhanced through optimized cylinder configuration and design. This includes improvements in cylinder head geometry, valve arrangement, and combustion chamber design to increase efficiency and power output.- Cylinder configuration optimization: Optimizing the cylinder configuration in V8 engines can significantly improve performance. This includes adjusting the angle between cylinder banks, optimizing firing order, and implementing variable valve timing systems. These modifications can enhance combustion efficiency, reduce vibration, and increase power output.
- Fuel injection and combustion improvements: Advanced fuel injection systems and combustion chamber designs can boost V8 engine performance. Direct injection technology, optimized fuel spray patterns, and improved air-fuel mixture formation contribute to better fuel efficiency and increased power. Additionally, implementing variable compression ratio technology can further enhance engine performance across different operating conditions.
- Turbocharging and supercharging systems: Forced induction systems, such as turbochargers and superchargers, can significantly increase the power output of V8 engines. These systems compress the intake air, allowing for more fuel to be burned and resulting in higher power output. Advanced designs, including twin-turbo setups or electric superchargers, can further improve engine response and overall performance.
- Lightweight materials and design: Utilizing lightweight materials and innovative design techniques can improve V8 engine performance by reducing overall weight and enhancing thermal efficiency. This includes the use of aluminum alloys, composite materials, and advanced manufacturing processes to create lighter engine components without compromising strength or durability.
- Engine management and control systems: Advanced engine management and control systems play a crucial role in optimizing V8 engine performance. These systems include sophisticated ECUs, adaptive engine mapping, and real-time monitoring of various engine parameters. By precisely controlling fuel injection, ignition timing, and other variables, these systems can maximize power output while maintaining fuel efficiency and emissions compliance.
02 Fuel injection and combustion optimization
Advanced fuel injection systems and combustion optimization techniques are employed to improve V8 engine performance. This involves precise fuel delivery, improved atomization, and enhanced mixture formation for better combustion efficiency and power generation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Turbocharging and supercharging
Forced induction systems, such as turbochargers and superchargers, are utilized to boost V8 engine performance. These systems increase air intake, allowing for more fuel combustion and resulting in higher power output and improved efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Variable valve timing and lift
Implementation of variable valve timing and lift mechanisms in V8 engines allows for optimized air intake and exhaust flow across different engine speeds. This technology enhances performance, fuel efficiency, and reduces emissions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Engine management and control systems
Advanced engine management and control systems are employed to optimize V8 engine performance. These systems monitor and adjust various parameters in real-time, such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and air-fuel ratio, to maximize power output and efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key V8 Motorcycle Manufacturers
The V8 engine technology in high-performance motorcycles is at a mature stage, with established players dominating the market. Industry leaders like Honda, Yamaha, and BMW have been refining V8 designs for decades, achieving high power outputs and reliability. The market for V8 motorcycles remains niche but stable, catering to enthusiasts seeking extreme performance. While not as widespread as other engine configurations, V8 motorcycles represent the pinnacle of engineering in the industry. Emerging companies like Zhejiang Qianjiang and CF Moto are also entering this space, potentially disrupting the market with innovative approaches to V8 technology.
Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honda's V8 engine advancements for high-performance motorcycles focus on optimizing power-to-weight ratios and enhancing overall performance. Their latest V8 design incorporates a compact, lightweight architecture with a 90-degree V-angle for optimal balance[1]. The engine features direct fuel injection and variable valve timing, allowing for precise control over fuel delivery and combustion efficiency[2]. Honda has also implemented advanced materials such as titanium connecting rods and forged aluminum pistons to reduce reciprocating mass and improve high-RPM performance[3]. Additionally, their V8 engines utilize a dry-sump lubrication system, which lowers the engine's center of gravity and ensures consistent oil pressure during high-G cornering and acceleration[4].
Strengths: Excellent power-to-weight ratio, advanced materials for durability, and innovative lubrication system. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs due to advanced materials and complexity, which may impact affordability for consumers.
Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Yamaha's approach to V8 engine technology in high-performance motorcycles emphasizes a balance between power output and rider control. Their V8 design features a crossplane crankshaft configuration, which provides a linear power delivery and improved traction[1]. Yamaha has integrated ride-by-wire throttle technology, allowing for multiple riding modes and traction control settings to suit various riding conditions[2]. The engine also incorporates a sophisticated engine management system that optimizes fuel injection and ignition timing based on real-time data from multiple sensors[3]. To address heat management, Yamaha has developed an efficient liquid cooling system with strategically placed radiators to maintain optimal operating temperatures even under extreme conditions[4].
Strengths: Linear power delivery, advanced rider aids, and efficient heat management. Weaknesses: Potential complexity in maintenance and higher initial cost due to advanced electronic systems.
Innovative V8 Motorcycle Technologies
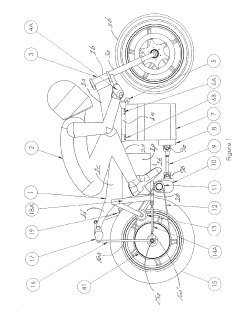
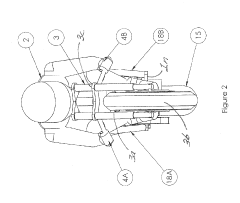
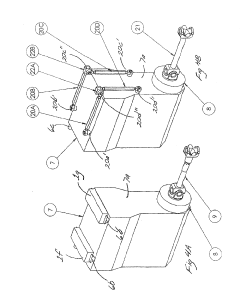
V8 engine and outboard motor
PatentActiveUS20160341097A1
Innovation
- A V8 engine design with a simple construction featuring aggregated exhaust pathways and adjustable exhaust cams, where the central angle of exhaust cams for each cylinder is optimized to minimize valve overlap and reduce exhaust interference, allowing for even firing intervals and improved exhaust gas management.
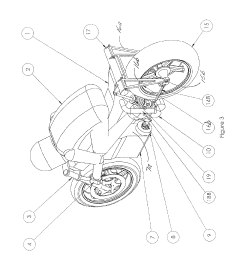
High performance motorcycle
PatentActiveUS20190092422A1
Innovation
- A high-performance motorcycle design featuring a monocoque frame with a lowered rider position, engine suspension system for damping oscillations, and a rear suspension system that maintains constant belt tension and anti-squat characteristics through innovative pulley positioning and adjustable linkages, along with a lightweight and unified frame configuration.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact of V8 engines in high-performance motorcycles is a critical consideration in today's eco-conscious world. These powerful engines, while delivering exceptional performance, also contribute significantly to environmental concerns.
V8 engines in motorcycles typically consume more fuel than their smaller counterparts, leading to increased carbon dioxide emissions. This higher fuel consumption directly correlates with a larger carbon footprint, contributing to global warming and climate change. The increased emissions also contribute to local air pollution, particularly in urban areas where motorcycles are frequently used.
Noise pollution is another environmental concern associated with V8-powered motorcycles. These engines generally produce higher noise levels compared to smaller engines, potentially disturbing wildlife and affecting urban soundscapes. This can lead to stress and behavioral changes in animals, as well as negatively impact human health in densely populated areas.
The manufacturing process of V8 engines for motorcycles also has environmental implications. The production of larger, more complex engines requires more raw materials and energy, increasing the overall environmental impact before the motorcycle even hits the road. Additionally, the disposal of these engines at the end of their lifecycle presents challenges in terms of waste management and recycling.
However, advancements in engine technology have led to improvements in fuel efficiency and emissions control for V8 engines. Modern V8 motorcycle engines often incorporate technologies such as direct fuel injection, variable valve timing, and advanced engine management systems. These innovations help to optimize fuel consumption and reduce emissions, mitigating some of the environmental concerns.
Furthermore, the development of cleaner fuels and the potential for hybrid or electric V8 systems could further reduce the environmental impact of these high-performance engines. Some manufacturers are exploring ways to combine the power of V8 engines with electric motors, creating hybrid systems that offer both performance and improved fuel efficiency.
In conclusion, while V8 engines in high-performance motorcycles do have significant environmental impacts, ongoing technological advancements are working to address these concerns. The challenge lies in balancing the desire for high performance with the need for environmental responsibility, a task that continues to drive innovation in the motorcycle industry.
V8 engines in motorcycles typically consume more fuel than their smaller counterparts, leading to increased carbon dioxide emissions. This higher fuel consumption directly correlates with a larger carbon footprint, contributing to global warming and climate change. The increased emissions also contribute to local air pollution, particularly in urban areas where motorcycles are frequently used.
Noise pollution is another environmental concern associated with V8-powered motorcycles. These engines generally produce higher noise levels compared to smaller engines, potentially disturbing wildlife and affecting urban soundscapes. This can lead to stress and behavioral changes in animals, as well as negatively impact human health in densely populated areas.
The manufacturing process of V8 engines for motorcycles also has environmental implications. The production of larger, more complex engines requires more raw materials and energy, increasing the overall environmental impact before the motorcycle even hits the road. Additionally, the disposal of these engines at the end of their lifecycle presents challenges in terms of waste management and recycling.
However, advancements in engine technology have led to improvements in fuel efficiency and emissions control for V8 engines. Modern V8 motorcycle engines often incorporate technologies such as direct fuel injection, variable valve timing, and advanced engine management systems. These innovations help to optimize fuel consumption and reduce emissions, mitigating some of the environmental concerns.
Furthermore, the development of cleaner fuels and the potential for hybrid or electric V8 systems could further reduce the environmental impact of these high-performance engines. Some manufacturers are exploring ways to combine the power of V8 engines with electric motors, creating hybrid systems that offer both performance and improved fuel efficiency.
In conclusion, while V8 engines in high-performance motorcycles do have significant environmental impacts, ongoing technological advancements are working to address these concerns. The challenge lies in balancing the desire for high performance with the need for environmental responsibility, a task that continues to drive innovation in the motorcycle industry.
Performance Benchmarking
Performance benchmarking is a critical aspect of evaluating how V8 engines advance high-performance motorcycles. This process involves rigorous testing and comparison of various performance metrics to assess the capabilities of V8-powered motorcycles against other engine configurations and industry standards.
One key area of focus in performance benchmarking is acceleration. V8 engines typically provide exceptional power-to-weight ratios, enabling rapid acceleration from a standstill. Metrics such as 0-60 mph times and quarter-mile speeds are commonly used to quantify this aspect of performance. High-performance V8 motorcycles often achieve 0-60 mph times in the range of 2.5 to 3.5 seconds, showcasing their impressive acceleration capabilities.
Top speed is another crucial benchmark for V8-powered motorcycles. These machines are capable of reaching extreme velocities, often exceeding 200 mph under controlled conditions. Such high-speed performance is a testament to the power output and aerodynamic efficiency of V8-equipped motorcycles.
Handling characteristics are also essential in performance benchmarking. Despite the increased weight of V8 engines compared to smaller configurations, advanced chassis design and weight distribution techniques allow these motorcycles to maintain exceptional cornering abilities. Metrics such as lateral g-forces during cornering and slalom times are used to evaluate handling performance.
Braking performance is equally important in benchmarking V8 motorcycles. The increased power and speed capabilities necessitate superior braking systems. Stopping distances from various speeds, such as 60-0 mph and 100-0 mph, are measured to assess braking efficiency.
Fuel efficiency, while not typically a primary concern for high-performance motorcycles, is still considered in benchmarking. V8 engines are known for their higher fuel consumption, but advancements in engine management systems and materials technology have led to improvements in this area.
Durability and reliability testing form a crucial part of performance benchmarking for V8 motorcycles. These engines are subjected to extended high-speed runs and endurance tests to ensure they can withstand the extreme conditions encountered during high-performance riding.
Comparative analysis against motorcycles with different engine configurations, such as inline-four or V-twin engines, provides valuable insights into the unique advantages of V8 engines. This comparison often highlights the V8's superior torque output and linear power delivery across a wide RPM range.
In conclusion, performance benchmarking of V8-powered motorcycles encompasses a wide range of metrics, from acceleration and top speed to handling, braking, and durability. These comprehensive evaluations demonstrate the significant advancements that V8 engines bring to high-performance motorcycles, setting new standards in the industry.
One key area of focus in performance benchmarking is acceleration. V8 engines typically provide exceptional power-to-weight ratios, enabling rapid acceleration from a standstill. Metrics such as 0-60 mph times and quarter-mile speeds are commonly used to quantify this aspect of performance. High-performance V8 motorcycles often achieve 0-60 mph times in the range of 2.5 to 3.5 seconds, showcasing their impressive acceleration capabilities.
Top speed is another crucial benchmark for V8-powered motorcycles. These machines are capable of reaching extreme velocities, often exceeding 200 mph under controlled conditions. Such high-speed performance is a testament to the power output and aerodynamic efficiency of V8-equipped motorcycles.
Handling characteristics are also essential in performance benchmarking. Despite the increased weight of V8 engines compared to smaller configurations, advanced chassis design and weight distribution techniques allow these motorcycles to maintain exceptional cornering abilities. Metrics such as lateral g-forces during cornering and slalom times are used to evaluate handling performance.
Braking performance is equally important in benchmarking V8 motorcycles. The increased power and speed capabilities necessitate superior braking systems. Stopping distances from various speeds, such as 60-0 mph and 100-0 mph, are measured to assess braking efficiency.
Fuel efficiency, while not typically a primary concern for high-performance motorcycles, is still considered in benchmarking. V8 engines are known for their higher fuel consumption, but advancements in engine management systems and materials technology have led to improvements in this area.
Durability and reliability testing form a crucial part of performance benchmarking for V8 motorcycles. These engines are subjected to extended high-speed runs and endurance tests to ensure they can withstand the extreme conditions encountered during high-performance riding.
Comparative analysis against motorcycles with different engine configurations, such as inline-four or V-twin engines, provides valuable insights into the unique advantages of V8 engines. This comparison often highlights the V8's superior torque output and linear power delivery across a wide RPM range.
In conclusion, performance benchmarking of V8-powered motorcycles encompasses a wide range of metrics, from acceleration and top speed to handling, braking, and durability. These comprehensive evaluations demonstrate the significant advancements that V8 engines bring to high-performance motorcycles, setting new standards in the industry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!