HPLC Stability Studies: Ensuring Consistent Data
SEP 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HPLC Stability Testing Background and Objectives
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1960s, becoming a cornerstone analytical technique in pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and chemical industries. The development trajectory of HPLC stability testing has been shaped by increasingly stringent regulatory requirements and technological advancements in chromatographic systems, column technology, and detection methods.
The evolution of HPLC stability testing can be traced through several key milestones: from basic isocratic systems to sophisticated gradient capabilities, from manual injection to automated sample handling, and from simple UV detection to multi-detector arrays including mass spectrometry integration. These advancements have dramatically improved the precision, sensitivity, and reproducibility of stability data generation.
Regulatory frameworks have played a pivotal role in shaping HPLC stability testing protocols. The International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines, particularly ICH Q1A through Q1E, established in the 1990s and continuously updated, provide comprehensive frameworks for stability testing across different climatic zones and storage conditions. These guidelines have standardized approaches to stability data collection and interpretation globally.
The primary technical objective of HPLC stability studies is to generate reliable, reproducible data that accurately reflects the chemical stability profile of pharmaceutical products and active ingredients over time. This includes detecting and quantifying degradation products, monitoring potency changes, and ensuring that product quality remains within acceptable limits throughout the shelf life.
Current technological trends in HPLC stability testing include the integration of Quality by Design (QbD) principles, implementation of ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) for faster analysis, and adoption of automated stability chambers with integrated sampling systems. These innovations aim to enhance data integrity while reducing analysis time and resource requirements.
The convergence of HPLC with other analytical techniques, such as mass spectrometry and spectroscopic methods, represents another significant trend, enabling more comprehensive characterization of degradation pathways and unknown impurities. This multi-modal approach provides deeper insights into stability mechanisms and supports more robust formulation development.
Looking forward, the field is moving toward predictive stability modeling, where accelerated testing combined with advanced algorithms can potentially predict long-term stability with greater accuracy. Additionally, continuous monitoring approaches using Process Analytical Technology (PAT) principles are gaining traction, potentially transforming how stability data is collected and interpreted in real-time manufacturing environments.
The evolution of HPLC stability testing can be traced through several key milestones: from basic isocratic systems to sophisticated gradient capabilities, from manual injection to automated sample handling, and from simple UV detection to multi-detector arrays including mass spectrometry integration. These advancements have dramatically improved the precision, sensitivity, and reproducibility of stability data generation.
Regulatory frameworks have played a pivotal role in shaping HPLC stability testing protocols. The International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines, particularly ICH Q1A through Q1E, established in the 1990s and continuously updated, provide comprehensive frameworks for stability testing across different climatic zones and storage conditions. These guidelines have standardized approaches to stability data collection and interpretation globally.
The primary technical objective of HPLC stability studies is to generate reliable, reproducible data that accurately reflects the chemical stability profile of pharmaceutical products and active ingredients over time. This includes detecting and quantifying degradation products, monitoring potency changes, and ensuring that product quality remains within acceptable limits throughout the shelf life.
Current technological trends in HPLC stability testing include the integration of Quality by Design (QbD) principles, implementation of ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) for faster analysis, and adoption of automated stability chambers with integrated sampling systems. These innovations aim to enhance data integrity while reducing analysis time and resource requirements.
The convergence of HPLC with other analytical techniques, such as mass spectrometry and spectroscopic methods, represents another significant trend, enabling more comprehensive characterization of degradation pathways and unknown impurities. This multi-modal approach provides deeper insights into stability mechanisms and supports more robust formulation development.
Looking forward, the field is moving toward predictive stability modeling, where accelerated testing combined with advanced algorithms can potentially predict long-term stability with greater accuracy. Additionally, continuous monitoring approaches using Process Analytical Technology (PAT) principles are gaining traction, potentially transforming how stability data is collected and interpreted in real-time manufacturing environments.
Market Demand for Reliable Pharmaceutical Stability Data
The pharmaceutical industry's demand for reliable stability data has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven primarily by increasingly stringent regulatory requirements and the expanding global pharmaceutical market. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) stability studies represent a critical component in drug development and quality control processes, with market research indicating that pharmaceutical companies allocate substantial resources to ensure data integrity and consistency in stability testing.
Recent market analyses reveal that the global pharmaceutical analytical testing outsourcing market, which includes stability testing services, was valued at approximately $5.6 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8.3% through 2028. Within this segment, HPLC-based stability testing services account for a substantial portion due to the technique's versatility and reliability in detecting chemical degradation.
The demand is particularly pronounced in regions with established pharmaceutical manufacturing bases, including North America, Europe, and increasingly in emerging markets across Asia-Pacific. China and India have shown remarkable growth rates in demand for advanced analytical testing capabilities, reflecting their expanding pharmaceutical production capacities and increasing focus on meeting international quality standards.
Key market drivers include the rising number of biopharmaceutical products entering development pipelines, which often present complex stability challenges requiring sophisticated analytical approaches. Additionally, the growing trend toward personalized medicine has increased the diversity of pharmaceutical products requiring stability assessment, further expanding market demand for reliable HPLC stability testing methodologies.
Regulatory bodies worldwide, including the FDA, EMA, and ICH, have intensified their focus on data integrity in stability studies, creating substantial market pressure for solutions that ensure consistent and reliable stability data. This regulatory emphasis has translated into increased investment in advanced HPLC systems, automated data processing software, and specialized consulting services focused on stability study design and execution.
Contract Research Organizations (CROs) and Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) have responded to this market demand by expanding their stability testing capabilities, with many investing in state-of-the-art HPLC equipment and developing specialized expertise in stability-indicating method development and validation.
Industry surveys indicate that pharmaceutical companies increasingly prioritize vendors and partners who can demonstrate robust data integrity practices and consistent stability testing results. This preference has created a premium market segment for analytical service providers who can offer comprehensive stability study packages with guaranteed data reliability and regulatory compliance.
Recent market analyses reveal that the global pharmaceutical analytical testing outsourcing market, which includes stability testing services, was valued at approximately $5.6 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8.3% through 2028. Within this segment, HPLC-based stability testing services account for a substantial portion due to the technique's versatility and reliability in detecting chemical degradation.
The demand is particularly pronounced in regions with established pharmaceutical manufacturing bases, including North America, Europe, and increasingly in emerging markets across Asia-Pacific. China and India have shown remarkable growth rates in demand for advanced analytical testing capabilities, reflecting their expanding pharmaceutical production capacities and increasing focus on meeting international quality standards.
Key market drivers include the rising number of biopharmaceutical products entering development pipelines, which often present complex stability challenges requiring sophisticated analytical approaches. Additionally, the growing trend toward personalized medicine has increased the diversity of pharmaceutical products requiring stability assessment, further expanding market demand for reliable HPLC stability testing methodologies.
Regulatory bodies worldwide, including the FDA, EMA, and ICH, have intensified their focus on data integrity in stability studies, creating substantial market pressure for solutions that ensure consistent and reliable stability data. This regulatory emphasis has translated into increased investment in advanced HPLC systems, automated data processing software, and specialized consulting services focused on stability study design and execution.
Contract Research Organizations (CROs) and Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) have responded to this market demand by expanding their stability testing capabilities, with many investing in state-of-the-art HPLC equipment and developing specialized expertise in stability-indicating method development and validation.
Industry surveys indicate that pharmaceutical companies increasingly prioritize vendors and partners who can demonstrate robust data integrity practices and consistent stability testing results. This preference has created a premium market segment for analytical service providers who can offer comprehensive stability study packages with guaranteed data reliability and regulatory compliance.
Current Challenges in HPLC Stability Analysis
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) stability studies face numerous technical challenges that impact data consistency and reliability. One of the primary obstacles is instrument variability, where differences between HPLC systems, even those of identical make and model, can produce divergent results. This variability stems from subtle differences in detector sensitivity, pump precision, and column performance characteristics that accumulate over time through normal wear and usage patterns.
Sample preparation inconsistencies represent another significant challenge, with variations in extraction efficiency, sample handling procedures, and storage conditions introducing bias into stability measurements. Even minor deviations in preparation protocols can lead to substantial differences in analyte recovery rates, particularly for complex pharmaceutical formulations or biological samples.
Method transfer difficulties persist across laboratories and organizations, with seemingly identical methods yielding different results when implemented at different sites. These discrepancies often arise from undocumented nuances in method execution, differences in reagent sources, or variations in environmental conditions that are not adequately controlled or reported in standard operating procedures.
Environmental factors, including temperature fluctuations, humidity variations, and laboratory vibrations, can significantly impact chromatographic performance. Modern HPLC systems, despite technological advances, remain sensitive to these environmental variables, which can alter retention times, peak shapes, and integration parameters during long-term stability studies.
Reference standard degradation presents a particularly insidious challenge, as the very standards used to calibrate instruments and validate methods may themselves undergo subtle changes during storage. This degradation can introduce systematic errors that accumulate over time, potentially masking or exaggerating actual stability trends in test samples.
Data integration and interpretation inconsistencies further complicate stability assessments. Analyst-to-analyst variations in peak integration decisions, baseline determinations, and outlier handling can introduce subjective elements into what should be an objective analytical process. These human factors become especially problematic in multi-site studies or when personnel changes occur during long-term stability monitoring programs.
Regulatory compliance requirements add another layer of complexity, with different regions imposing varying standards for stability data collection, validation, and reporting. Meeting these diverse requirements while maintaining scientific consistency presents significant challenges for global pharmaceutical organizations conducting stability studies across multiple markets.
Emerging challenges include the integration of automation and artificial intelligence into stability testing workflows, which promises efficiency gains but introduces new validation requirements and potential sources of variability that must be carefully managed to ensure data integrity throughout the stability assessment lifecycle.
Sample preparation inconsistencies represent another significant challenge, with variations in extraction efficiency, sample handling procedures, and storage conditions introducing bias into stability measurements. Even minor deviations in preparation protocols can lead to substantial differences in analyte recovery rates, particularly for complex pharmaceutical formulations or biological samples.
Method transfer difficulties persist across laboratories and organizations, with seemingly identical methods yielding different results when implemented at different sites. These discrepancies often arise from undocumented nuances in method execution, differences in reagent sources, or variations in environmental conditions that are not adequately controlled or reported in standard operating procedures.
Environmental factors, including temperature fluctuations, humidity variations, and laboratory vibrations, can significantly impact chromatographic performance. Modern HPLC systems, despite technological advances, remain sensitive to these environmental variables, which can alter retention times, peak shapes, and integration parameters during long-term stability studies.
Reference standard degradation presents a particularly insidious challenge, as the very standards used to calibrate instruments and validate methods may themselves undergo subtle changes during storage. This degradation can introduce systematic errors that accumulate over time, potentially masking or exaggerating actual stability trends in test samples.
Data integration and interpretation inconsistencies further complicate stability assessments. Analyst-to-analyst variations in peak integration decisions, baseline determinations, and outlier handling can introduce subjective elements into what should be an objective analytical process. These human factors become especially problematic in multi-site studies or when personnel changes occur during long-term stability monitoring programs.
Regulatory compliance requirements add another layer of complexity, with different regions imposing varying standards for stability data collection, validation, and reporting. Meeting these diverse requirements while maintaining scientific consistency presents significant challenges for global pharmaceutical organizations conducting stability studies across multiple markets.
Emerging challenges include the integration of automation and artificial intelligence into stability testing workflows, which promises efficiency gains but introduces new validation requirements and potential sources of variability that must be carefully managed to ensure data integrity throughout the stability assessment lifecycle.
Current HPLC Method Validation Approaches
01 HPLC method validation for stability studies
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) methods require thorough validation to ensure reliable stability data. This includes establishing parameters such as specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, and robustness. Validated HPLC methods are essential for generating consistent stability data that accurately reflects the degradation profile of pharmaceutical products over time. Proper method validation ensures that stability-indicating assays can reliably detect and quantify both the active ingredient and potential degradation products.- HPLC method validation for stability studies: High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) methods require thorough validation to ensure reliable stability data. This includes establishing parameters such as specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, and robustness. Validated HPLC methods provide consistent results across different testing conditions and time points, which is crucial for pharmaceutical stability studies. Proper method validation ensures that any changes observed in drug formulations during stability testing are genuine degradation effects rather than analytical variations.
- Data integrity in stability testing: Maintaining data integrity throughout stability studies is essential for regulatory compliance. This involves implementing proper controls for data acquisition, processing, and storage systems to prevent unauthorized modifications. Electronic data management systems with audit trails, appropriate access controls, and backup procedures help ensure the consistency and reliability of stability data. Compliance with good laboratory practices (GLP) and data integrity guidelines is necessary to generate trustworthy stability study results that can withstand regulatory scrutiny.
- Statistical approaches for stability data analysis: Statistical methods play a crucial role in analyzing HPLC stability data to identify trends, outliers, and establish shelf-life determinations. Techniques such as regression analysis, analysis of variance (ANOVA), and trend analysis help in interpreting stability data consistently. Statistical tools can be used to establish acceptance criteria, determine degradation rates, and predict product shelf life with appropriate confidence intervals. Proper statistical evaluation ensures that conclusions drawn from stability studies are scientifically sound and defensible.
- Automation and computerized systems in stability testing: Automated HPLC systems and computerized data management solutions enhance consistency in stability studies by reducing human error and standardizing analytical procedures. These systems can automatically schedule sample analysis, control chromatographic conditions, and generate reports according to predefined protocols. Integration of laboratory information management systems (LIMS) with HPLC instruments ensures seamless data transfer and consistent documentation. Automation improves efficiency, reduces variability, and enhances the overall reliability of stability data.
- Stability-indicating HPLC method development: Developing stability-indicating HPLC methods is critical for accurately monitoring product degradation over time. These methods must be capable of separating and quantifying the active pharmaceutical ingredient from its degradation products, impurities, and excipients. Forced degradation studies help in identifying potential degradation pathways and ensuring method specificity. Optimizing chromatographic parameters such as mobile phase composition, column selection, and detection techniques is essential for developing robust stability-indicating methods that provide consistent results throughout the product's shelf life.
02 Data integrity in stability testing
Maintaining data integrity throughout stability studies is crucial for regulatory compliance and product quality assurance. This involves implementing proper data management systems, audit trails, electronic signatures, and access controls to prevent unauthorized data manipulation. Consistent documentation practices, calibration of instruments, and adherence to standard operating procedures help ensure that stability data remains reliable and traceable. Regular system audits and validation of data handling processes further strengthen data integrity in stability testing programs.Expand Specific Solutions03 Automated systems for stability data management
Automated laboratory information management systems (LIMS) and specialized software solutions help maintain consistency in stability data collection, storage, and analysis. These systems can automatically flag out-of-specification results, track sample storage conditions, and generate regulatory-compliant reports. Integration of HPLC instruments with data management systems reduces manual data entry errors and provides real-time monitoring capabilities. Automated stability chambers with continuous monitoring ensure consistent environmental conditions throughout the study period, further enhancing data reliability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Statistical approaches for stability data analysis
Statistical methods play a critical role in evaluating stability data consistency and establishing product shelf life. Techniques such as regression analysis, trend analysis, and statistical tolerance intervals help identify significant changes in product quality over time. Statistical tools can detect outliers, evaluate batch-to-batch variability, and determine the significance of observed changes in stability parameters. Proper statistical analysis ensures that conclusions about product stability are scientifically sound and that shelf-life determinations are based on reliable data interpretation.Expand Specific Solutions05 Stability-indicating HPLC method development
Developing stability-indicating HPLC methods involves careful selection of chromatographic conditions that can effectively separate the active ingredient from potential degradation products. This includes optimization of mobile phase composition, column selection, detection parameters, and sample preparation techniques. Forced degradation studies are conducted to generate degradation products and verify the method's ability to detect them. The stability-indicating method must be capable of accurately quantifying the active ingredient throughout the shelf life while providing consistent results across different analysts and laboratories.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Pharmaceutical Analysis Equipment Providers
The HPLC stability studies market is currently in a growth phase, driven by increasing regulatory requirements for pharmaceutical quality control. The global market size is estimated to exceed $1.2 billion, with a CAGR of approximately 8-10% through 2025. Technologically, the field is mature but continuously evolving with innovations in automation and data integrity. Leading players include Agilent Technologies, which dominates with comprehensive analytical solutions, followed by Hitachi and Siemens offering integrated stability testing platforms. IBM and Pure Storage are emerging with data management innovations, while pharmaceutical service providers like Fujitsu and NEC are developing specialized HPLC stability protocols. The competitive landscape shows established instrumentation manufacturers competing with emerging IT-focused companies to address data consistency challenges.
Agilent Technologies, Inc.
Technical Solution: Agilent Technologies has developed comprehensive HPLC stability study solutions centered around their OpenLab CDS (Chromatography Data System) platform. Their approach integrates hardware precision with advanced software analytics to ensure data consistency in pharmaceutical stability testing. The OpenLab CDS incorporates automated system suitability tests that continuously monitor critical parameters like retention time drift, peak area reproducibility, and baseline stability[1]. Agilent's 1290 Infinity II LC systems feature temperature-controlled column compartments with precision of ±0.05°C, significantly reducing thermal variation effects on chromatographic separations[2]. Their patented Intelligent System Emulation Technology (ISET) allows method transfer between different HPLC instruments while maintaining consistent results, addressing a major challenge in multi-site stability studies[3]. Additionally, Agilent has implemented compliance-ready data integrity features including audit trails, electronic signatures, and data encryption that meet FDA 21 CFR Part 11 requirements for stability testing protocols.
Strengths: Industry-leading precision in temperature control and gradient formation; comprehensive data integrity features; seamless method transfer capabilities between instruments. Weaknesses: Higher initial investment compared to competitors; complex software may require extensive training; proprietary consumables can increase operational costs over time.
Hitachi Ltd.
Technical Solution: Hitachi's approach to HPLC stability studies centers on their Chromaster and LaChrom Elite HPLC systems with specialized stability-indicating method development tools. Their technology incorporates advanced pump designs with active damping mechanisms that achieve flow precision of ±0.1% RSD, critical for maintaining consistent retention times across long-term stability studies[1]. Hitachi's systems feature proprietary thermal management technology that maintains column temperatures within ±0.1°C even during ambient fluctuations, ensuring reproducible chromatographic separations over extended stability timepoints[2]. Their EZChrom Elite software includes stability-specific data processing algorithms that automatically flag out-of-specification trends and apply statistical process control methods to detect subtle changes in chromatographic profiles before they become critical deviations. Hitachi has also developed specialized validation protocols specifically for pharmaceutical stability studies that include automated system suitability testing, calibration verification, and instrument performance qualification to ensure data reliability throughout the product lifecycle.
Strengths: Exceptional flow rate precision; robust thermal management system; specialized stability-indicating method development tools; comprehensive validation protocols. Weaknesses: More limited global service network compared to some competitors; software interface considered less intuitive by some users; fewer integration options with third-party laboratory information management systems.
Key Innovations in Chromatographic Data Consistency
Systems, materials, and methods for reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) for monitoring formation of multi-specific molecules
PatentWO2021209953A1
Innovation
- The implementation of reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) using a polar aqueous mobile phase with an ion-pairing agent and an organic non-polar mobile phase to elute and monitor the formation of multi-specific molecules, allowing for gradient elution and detection of multi-specific antibody formation.
Improvements in or relating to high performance liquid chromatography systems
PatentInactiveGB2174016A
Innovation
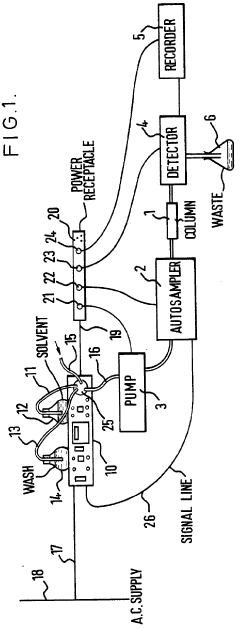
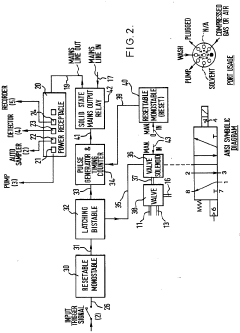
- An ancillary apparatus that includes a valve system for selecting between mobile phase and wash liquid sources, a timing mechanism initiated by a trigger pulse from the HPLC system, and an electric switch to disconnect power to the HPLC system units after a predetermined wash liquid supply, ensuring a controlled shutdown and washout process.
Regulatory Compliance in Stability Studies
Regulatory compliance forms the cornerstone of stability studies in pharmaceutical development and quality control processes. The FDA, EMA, ICH, and other global regulatory bodies have established stringent guidelines that govern how HPLC stability studies must be conducted to ensure data integrity and product safety. These regulations are not static but evolve continuously to address emerging challenges and incorporate technological advancements.
ICH Q1A(R2) provides the fundamental framework for stability testing of new drug substances and products, detailing requirements for storage conditions, testing frequencies, and data evaluation. For HPLC methods specifically, ICH Q2(R1) outlines validation parameters including specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, and robustness that must be demonstrated to ensure reliable stability data generation.
The FDA's 21 CFR Part 11 regulations govern electronic records and signatures, which is particularly relevant for modern HPLC systems that generate digital data. Compliance requires implementation of audit trails, secure user access controls, and validated data processing software to prevent unauthorized alterations to stability data.
Data integrity principles encapsulated in ALCOA+ (Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate, plus Complete, Consistent, Enduring, and Available) must be rigorously applied throughout stability studies. Recent regulatory inspections have increasingly focused on data governance practices, with particular scrutiny on laboratory controls and data management systems.
Method transfer considerations present additional regulatory challenges when stability studies span multiple testing sites or contract laboratories. Regulatory agencies expect robust transfer protocols that demonstrate equivalent performance across different instruments, analysts, and laboratory environments to maintain data consistency throughout the product lifecycle.
Stability-indicating methods require particular regulatory attention, as they must demonstrate the ability to separate and quantify degradation products. Current regulatory expectations include forced degradation studies to challenge the method's specificity and establish its stability-indicating power.
Out-of-specification (OOS) results in stability studies trigger specific regulatory requirements for investigation and documentation. Regulatory bodies expect thorough root cause analysis and scientifically justified conclusions before accepting or rejecting stability data, with clear documentation of all decisions made during the investigation process.
The global harmonization of stability requirements continues to evolve, with initiatives aimed at reducing redundant testing while maintaining high quality standards. Understanding regional variations in stability requirements remains essential for products intended for global markets, as differences in climatic zone classifications and reporting expectations persist despite harmonization efforts.
ICH Q1A(R2) provides the fundamental framework for stability testing of new drug substances and products, detailing requirements for storage conditions, testing frequencies, and data evaluation. For HPLC methods specifically, ICH Q2(R1) outlines validation parameters including specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, and robustness that must be demonstrated to ensure reliable stability data generation.
The FDA's 21 CFR Part 11 regulations govern electronic records and signatures, which is particularly relevant for modern HPLC systems that generate digital data. Compliance requires implementation of audit trails, secure user access controls, and validated data processing software to prevent unauthorized alterations to stability data.
Data integrity principles encapsulated in ALCOA+ (Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate, plus Complete, Consistent, Enduring, and Available) must be rigorously applied throughout stability studies. Recent regulatory inspections have increasingly focused on data governance practices, with particular scrutiny on laboratory controls and data management systems.
Method transfer considerations present additional regulatory challenges when stability studies span multiple testing sites or contract laboratories. Regulatory agencies expect robust transfer protocols that demonstrate equivalent performance across different instruments, analysts, and laboratory environments to maintain data consistency throughout the product lifecycle.
Stability-indicating methods require particular regulatory attention, as they must demonstrate the ability to separate and quantify degradation products. Current regulatory expectations include forced degradation studies to challenge the method's specificity and establish its stability-indicating power.
Out-of-specification (OOS) results in stability studies trigger specific regulatory requirements for investigation and documentation. Regulatory bodies expect thorough root cause analysis and scientifically justified conclusions before accepting or rejecting stability data, with clear documentation of all decisions made during the investigation process.
The global harmonization of stability requirements continues to evolve, with initiatives aimed at reducing redundant testing while maintaining high quality standards. Understanding regional variations in stability requirements remains essential for products intended for global markets, as differences in climatic zone classifications and reporting expectations persist despite harmonization efforts.
Data Integrity Management Systems
Data Integrity Management Systems for HPLC stability studies represent a critical infrastructure component that ensures the reliability, traceability, and compliance of analytical data throughout its lifecycle. These systems incorporate both technological solutions and procedural frameworks designed to maintain data integrity according to ALCOA+ principles (Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate, plus Complete, Consistent, Enduring, and Available).
Modern data integrity management systems for HPLC stability testing typically feature automated audit trails that capture all data modifications, including who made changes, when they occurred, and the justification behind them. This chronological record provides transparency and accountability, essential elements for regulatory compliance in pharmaceutical environments where stability data directly impacts product quality decisions.
Access control mechanisms constitute another fundamental aspect of these systems, implementing role-based permissions that restrict data manipulation capabilities based on user credentials. This hierarchical approach prevents unauthorized alterations while maintaining appropriate workflow efficiency, with system administrators configuring permissions aligned with organizational responsibilities and regulatory requirements.
Electronic signatures integrated within these platforms serve as legally binding equivalents to handwritten signatures, authenticating critical actions such as data approval or method validation. The implementation follows regulations like 21 CFR Part 11 and EU Annex 11, ensuring that electronic approvals maintain the same level of accountability as traditional documentation processes.
Data backup and archiving functionalities provide protection against data loss through automated, validated processes that create secure, retrievable copies of stability study information. These systems typically employ redundant storage solutions with encryption technologies to safeguard sensitive analytical data against both technical failures and security breaches.
Metadata management capabilities track contextual information surrounding stability data, including instrument parameters, column specifications, mobile phase compositions, and environmental conditions. This comprehensive documentation enables complete reconstruction of analytical conditions, supporting investigation of anomalies and ensuring scientific validity of stability determinations.
Integration with laboratory information management systems (LIMS) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms creates a cohesive data ecosystem that eliminates transcription errors and facilitates seamless information flow across organizational boundaries. This interconnectivity supports trend analysis across multiple stability batches, enhancing the organization's ability to identify patterns that might indicate formulation or manufacturing issues.
Modern data integrity management systems for HPLC stability testing typically feature automated audit trails that capture all data modifications, including who made changes, when they occurred, and the justification behind them. This chronological record provides transparency and accountability, essential elements for regulatory compliance in pharmaceutical environments where stability data directly impacts product quality decisions.
Access control mechanisms constitute another fundamental aspect of these systems, implementing role-based permissions that restrict data manipulation capabilities based on user credentials. This hierarchical approach prevents unauthorized alterations while maintaining appropriate workflow efficiency, with system administrators configuring permissions aligned with organizational responsibilities and regulatory requirements.
Electronic signatures integrated within these platforms serve as legally binding equivalents to handwritten signatures, authenticating critical actions such as data approval or method validation. The implementation follows regulations like 21 CFR Part 11 and EU Annex 11, ensuring that electronic approvals maintain the same level of accountability as traditional documentation processes.
Data backup and archiving functionalities provide protection against data loss through automated, validated processes that create secure, retrievable copies of stability study information. These systems typically employ redundant storage solutions with encryption technologies to safeguard sensitive analytical data against both technical failures and security breaches.
Metadata management capabilities track contextual information surrounding stability data, including instrument parameters, column specifications, mobile phase compositions, and environmental conditions. This comprehensive documentation enables complete reconstruction of analytical conditions, supporting investigation of anomalies and ensuring scientific validity of stability determinations.
Integration with laboratory information management systems (LIMS) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms creates a cohesive data ecosystem that eliminates transcription errors and facilitates seamless information flow across organizational boundaries. This interconnectivity supports trend analysis across multiple stability batches, enhancing the organization's ability to identify patterns that might indicate formulation or manufacturing issues.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!