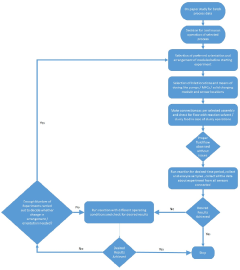
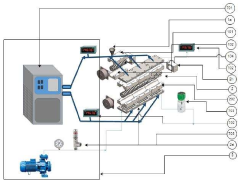
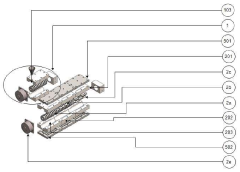
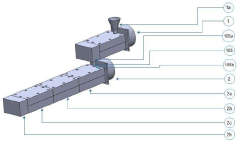
Microreactors in Energy Storage Materials Synthesis and Optimization
SEP 24, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Microreactor Technology Background and Objectives
Microreactor technology has evolved significantly over the past three decades, transforming from laboratory curiosities to practical tools for chemical synthesis and materials processing. Initially developed in the 1990s for pharmaceutical applications, microreactors have gradually expanded into various industrial sectors including energy storage materials synthesis. The fundamental principle behind microreactors—utilizing channels with dimensions in the micrometer range to enhance heat and mass transfer—has remained consistent, while fabrication techniques and integration capabilities have advanced dramatically.
The evolution of microreactor technology has been driven by several key factors: miniaturization of process equipment, enhanced control over reaction parameters, improved safety profiles for hazardous reactions, and significant reductions in reagent consumption. Recent developments have focused on integrating advanced monitoring capabilities, enabling real-time process analytics and feedback control systems that optimize reaction conditions dynamically.
In the context of energy storage materials synthesis, microreactors offer unprecedented precision in controlling crystallization processes, particle size distribution, and morphology—all critical parameters that directly influence electrochemical performance. Traditional batch synthesis methods often struggle with reproducibility and scalability issues that microreactor technology can potentially overcome.
The primary technical objectives for microreactor implementation in energy storage materials synthesis include achieving consistent nanomaterial production with precisely controlled properties, reducing synthesis time from hours to minutes, minimizing energy consumption during production processes, and enabling continuous manufacturing paradigms that can scale without compromising material quality.
Current research aims to develop microreactor platforms capable of synthesizing next-generation battery materials such as silicon anodes, solid-state electrolytes, and high-capacity cathode materials with tailored interfaces and architectures. These objectives align with broader industry goals of increasing energy density, improving cycling stability, and reducing production costs of energy storage systems.
Looking forward, the technology roadmap for microreactors in energy storage applications includes developing multi-stage reactor systems capable of performing sequential synthesis steps, integrating in-situ characterization techniques for real-time quality control, and creating modular designs that can be rapidly reconfigured for different material systems. The ultimate goal is establishing microreactor technology as the standard manufacturing approach for precision-engineered energy storage materials.
Achieving these objectives would represent a paradigm shift in how advanced materials for batteries and supercapacitors are developed and produced, potentially accelerating the transition to renewable energy systems through more efficient and effective energy storage solutions.
The evolution of microreactor technology has been driven by several key factors: miniaturization of process equipment, enhanced control over reaction parameters, improved safety profiles for hazardous reactions, and significant reductions in reagent consumption. Recent developments have focused on integrating advanced monitoring capabilities, enabling real-time process analytics and feedback control systems that optimize reaction conditions dynamically.
In the context of energy storage materials synthesis, microreactors offer unprecedented precision in controlling crystallization processes, particle size distribution, and morphology—all critical parameters that directly influence electrochemical performance. Traditional batch synthesis methods often struggle with reproducibility and scalability issues that microreactor technology can potentially overcome.
The primary technical objectives for microreactor implementation in energy storage materials synthesis include achieving consistent nanomaterial production with precisely controlled properties, reducing synthesis time from hours to minutes, minimizing energy consumption during production processes, and enabling continuous manufacturing paradigms that can scale without compromising material quality.
Current research aims to develop microreactor platforms capable of synthesizing next-generation battery materials such as silicon anodes, solid-state electrolytes, and high-capacity cathode materials with tailored interfaces and architectures. These objectives align with broader industry goals of increasing energy density, improving cycling stability, and reducing production costs of energy storage systems.
Looking forward, the technology roadmap for microreactors in energy storage applications includes developing multi-stage reactor systems capable of performing sequential synthesis steps, integrating in-situ characterization techniques for real-time quality control, and creating modular designs that can be rapidly reconfigured for different material systems. The ultimate goal is establishing microreactor technology as the standard manufacturing approach for precision-engineered energy storage materials.
Achieving these objectives would represent a paradigm shift in how advanced materials for batteries and supercapacitors are developed and produced, potentially accelerating the transition to renewable energy systems through more efficient and effective energy storage solutions.
Market Analysis for Microreactor-Based Energy Storage Solutions
The global market for microreactor-based energy storage solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for efficient and sustainable energy storage technologies. Current market valuation stands at approximately $3.2 billion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 18.7% through 2030, potentially reaching $12.5 billion by the end of the decade. This growth trajectory is supported by substantial investments in renewable energy infrastructure and the pressing need for advanced energy storage solutions.
The market segmentation reveals distinct application sectors, with grid-scale energy storage representing the largest share at 42%, followed by electric vehicle applications at 31%, consumer electronics at 18%, and emerging applications accounting for the remaining 9%. Geographically, North America currently leads with 38% market share, followed by Europe (29%), Asia-Pacific (27%), and other regions (6%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the fastest growth rate at 22.3% annually, primarily driven by China's aggressive investments in renewable energy technologies.
Key market drivers include the global push toward decarbonization, increasing integration of renewable energy sources into power grids, and growing demand for high-performance batteries with improved safety profiles. The microreactor approach offers significant advantages in terms of process intensification, precise control over material properties, and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional batch processing methods.
Customer demand patterns indicate a strong preference for energy storage solutions with higher energy density, faster charging capabilities, longer cycle life, and enhanced safety features. Microreactor technology directly addresses these requirements by enabling the synthesis of advanced materials with precisely controlled properties and consistent quality.
Market challenges include high initial capital investment requirements, technical complexity in scaling up microreactor systems, and regulatory uncertainties regarding novel materials and manufacturing processes. Additionally, competition from established manufacturing methods presents a significant barrier to market penetration.
Emerging opportunities include the development of specialized microreactor systems for next-generation battery chemistries such as solid-state batteries, lithium-sulfur, and metal-air technologies. The market also shows potential for integrated manufacturing platforms that combine microreactor synthesis with downstream processing and assembly operations.
Industry partnerships between technology developers, material suppliers, and end-users are becoming increasingly common, creating valuable ecosystem collaborations that accelerate commercialization timelines. Notable recent strategic alliances include joint ventures between chemical companies and battery manufacturers focused specifically on microreactor-based material synthesis technologies.
The market segmentation reveals distinct application sectors, with grid-scale energy storage representing the largest share at 42%, followed by electric vehicle applications at 31%, consumer electronics at 18%, and emerging applications accounting for the remaining 9%. Geographically, North America currently leads with 38% market share, followed by Europe (29%), Asia-Pacific (27%), and other regions (6%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the fastest growth rate at 22.3% annually, primarily driven by China's aggressive investments in renewable energy technologies.
Key market drivers include the global push toward decarbonization, increasing integration of renewable energy sources into power grids, and growing demand for high-performance batteries with improved safety profiles. The microreactor approach offers significant advantages in terms of process intensification, precise control over material properties, and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional batch processing methods.
Customer demand patterns indicate a strong preference for energy storage solutions with higher energy density, faster charging capabilities, longer cycle life, and enhanced safety features. Microreactor technology directly addresses these requirements by enabling the synthesis of advanced materials with precisely controlled properties and consistent quality.
Market challenges include high initial capital investment requirements, technical complexity in scaling up microreactor systems, and regulatory uncertainties regarding novel materials and manufacturing processes. Additionally, competition from established manufacturing methods presents a significant barrier to market penetration.
Emerging opportunities include the development of specialized microreactor systems for next-generation battery chemistries such as solid-state batteries, lithium-sulfur, and metal-air technologies. The market also shows potential for integrated manufacturing platforms that combine microreactor synthesis with downstream processing and assembly operations.
Industry partnerships between technology developers, material suppliers, and end-users are becoming increasingly common, creating valuable ecosystem collaborations that accelerate commercialization timelines. Notable recent strategic alliances include joint ventures between chemical companies and battery manufacturers focused specifically on microreactor-based material synthesis technologies.
Current Challenges in Microreactor Synthesis Technologies
Despite significant advancements in microreactor technology for energy storage materials synthesis, several critical challenges continue to impede widespread industrial adoption and optimization. The primary obstacle remains scalability, as most successful microreactor systems operate effectively at laboratory scale but encounter significant engineering difficulties when scaled to industrial production volumes. This scale-up challenge is particularly pronounced for energy storage materials that require precise control over crystallization processes and morphology development.
Material deposition and clogging represent another persistent challenge, especially when synthesizing high-viscosity precursors or materials that undergo phase transitions within the microchannels. These issues not only disrupt continuous flow operations but also compromise the long-term reliability of microreactor systems, necessitating frequent maintenance and reducing overall production efficiency.
Heat and mass transfer limitations emerge as significant barriers when synthesizing complex energy storage materials that require precise temperature control or rapid mixing of reactants with disparate properties. While microreactors generally excel at heat transfer due to high surface-to-volume ratios, certain energy storage material syntheses involve highly exothermic reactions that can create localized hotspots, potentially leading to product inconsistencies or safety concerns.
Process control and monitoring capabilities present ongoing challenges, particularly for real-time quality assessment during continuous synthesis. Current sensor technologies often struggle to provide accurate, non-invasive measurements within the confined spaces of microreactor channels, limiting the ability to implement advanced control strategies for optimizing material properties.
Materials compatibility issues arise when working with corrosive precursors common in battery material synthesis, requiring specialized construction materials that can significantly increase manufacturing costs. Additionally, the high-pressure conditions sometimes necessary for supercritical fluid processing in advanced energy storage material synthesis place extreme demands on microreactor structural integrity.
Integration challenges persist when attempting to combine multiple synthesis steps into continuous flow processes. Many energy storage materials require sequential reactions with intermediate separation or purification steps that are difficult to implement in continuous microreactor systems without compromising material quality or process efficiency.
Economic barriers remain significant, as the capital investment required for specialized microreactor equipment must be justified against traditional batch processing methods. The cost-benefit analysis becomes particularly challenging for materials with moderate production volumes or those requiring frequent process modifications to accommodate evolving energy storage material formulations.
Material deposition and clogging represent another persistent challenge, especially when synthesizing high-viscosity precursors or materials that undergo phase transitions within the microchannels. These issues not only disrupt continuous flow operations but also compromise the long-term reliability of microreactor systems, necessitating frequent maintenance and reducing overall production efficiency.
Heat and mass transfer limitations emerge as significant barriers when synthesizing complex energy storage materials that require precise temperature control or rapid mixing of reactants with disparate properties. While microreactors generally excel at heat transfer due to high surface-to-volume ratios, certain energy storage material syntheses involve highly exothermic reactions that can create localized hotspots, potentially leading to product inconsistencies or safety concerns.
Process control and monitoring capabilities present ongoing challenges, particularly for real-time quality assessment during continuous synthesis. Current sensor technologies often struggle to provide accurate, non-invasive measurements within the confined spaces of microreactor channels, limiting the ability to implement advanced control strategies for optimizing material properties.
Materials compatibility issues arise when working with corrosive precursors common in battery material synthesis, requiring specialized construction materials that can significantly increase manufacturing costs. Additionally, the high-pressure conditions sometimes necessary for supercritical fluid processing in advanced energy storage material synthesis place extreme demands on microreactor structural integrity.
Integration challenges persist when attempting to combine multiple synthesis steps into continuous flow processes. Many energy storage materials require sequential reactions with intermediate separation or purification steps that are difficult to implement in continuous microreactor systems without compromising material quality or process efficiency.
Economic barriers remain significant, as the capital investment required for specialized microreactor equipment must be justified against traditional batch processing methods. The cost-benefit analysis becomes particularly challenging for materials with moderate production volumes or those requiring frequent process modifications to accommodate evolving energy storage material formulations.
Current Microreactor Approaches for Energy Storage Materials
01 Microreactor design and fabrication techniques
Various approaches to designing and fabricating microreactors for chemical synthesis applications. These include specialized materials selection, channel geometry optimization, and integration of multiple functional components. Advanced fabrication techniques enable precise control over reaction parameters and improved heat and mass transfer characteristics, which are critical for efficient chemical synthesis at microscale.- Microreactor design and fabrication techniques: Various methods and technologies for designing and fabricating microreactors are disclosed, including materials selection, channel geometry optimization, and integration of functional components. These techniques enable the creation of efficient microreactor systems with enhanced heat and mass transfer capabilities, improved reaction control, and scalability for different applications. The designs incorporate features that optimize flow patterns, residence time distribution, and mixing efficiency.
- Process optimization and control in microreactors: Methods for optimizing and controlling chemical processes in microreactors, including parameter adjustment, real-time monitoring, and feedback control systems. These approaches enable precise regulation of reaction conditions such as temperature, pressure, residence time, and reagent concentrations to maximize yield, selectivity, and product quality. Advanced control algorithms and modeling techniques are employed to achieve optimal process performance and consistency.
- Computational methods for microreactor simulation and design: Computational tools and methodologies for simulating, designing, and optimizing microreactor systems. These include computational fluid dynamics (CFD), kinetic modeling, and machine learning approaches to predict and enhance microreactor performance. The computational methods enable virtual prototyping, parameter sensitivity analysis, and multi-objective optimization to accelerate the development cycle and improve design outcomes without extensive physical experimentation.
- Novel catalytic systems for microreactor applications: Development of specialized catalytic systems designed specifically for microreactor environments, including immobilized catalysts, catalyst coatings, and structured catalytic materials. These innovations enhance reaction efficiency, selectivity, and catalyst lifetime in confined microreactor spaces. The catalytic systems are engineered to maximize active surface area, minimize pressure drop, and enable continuous operation with improved stability and performance.
- Integrated microreactor systems for multi-step synthesis: Integrated microreactor platforms that combine multiple reaction steps, separation processes, and analytical capabilities in a single system. These integrated approaches enable continuous flow synthesis of complex molecules with in-line purification, analysis, and process control. The systems incorporate various functional modules such as mixers, heat exchangers, extractors, and sensors to create complete synthesis solutions with enhanced efficiency and reduced footprint compared to conventional batch processes.
02 Process optimization in microreactor systems
Methods for optimizing chemical processes in microreactor environments, including parameter tuning, reaction condition monitoring, and feedback control systems. These optimization techniques focus on enhancing reaction yields, selectivity, and efficiency through precise control of temperature, pressure, residence time, and reagent concentrations. Computational models and algorithms are employed to predict optimal operating conditions and process parameters.Expand Specific Solutions03 Computational modeling and simulation for microreactor development
Application of computational tools for modeling fluid dynamics, heat transfer, and chemical kinetics in microreactor systems. These simulation approaches enable virtual prototyping and performance prediction before physical implementation. Advanced algorithms and software frameworks support the design optimization process by identifying critical parameters and potential bottlenecks in microreactor operation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Continuous flow synthesis methodologies
Implementation of continuous flow processes in microreactors for improved synthesis efficiency compared to batch methods. These approaches enable precise control over reaction time, mixing efficiency, and scale-up potential. Continuous flow methodologies in microreactors offer advantages including enhanced safety for hazardous reactions, improved product quality, and reduced waste generation through more efficient reagent utilization.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of monitoring and control systems
Incorporation of real-time monitoring sensors and automated control systems in microreactor platforms to enable precise reaction management. These integrated systems allow for continuous monitoring of reaction parameters, automated adjustment of process conditions, and quality control during synthesis operations. Advanced sensor technologies and feedback mechanisms help maintain optimal reaction conditions and enable rapid response to process deviations.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Organizations in Microreactor and Energy Storage Research
Microreactors in energy storage materials synthesis are gaining momentum in a rapidly evolving market characterized by significant growth potential and increasing technological maturity. The industry is transitioning from early-stage research to commercial applications, with the global market expected to expand substantially as energy storage demands increase. Leading players like Corning, Sony Group, and Hitachi Plant Services are advancing microreactor technologies for precise material synthesis, while academic institutions including ETH Zurich, Nanyang Technological University, and Drexel University contribute fundamental research innovations. Companies such as Enphase Energy and Saudi Aramco are exploring applications in renewable energy integration, while chemical industry leaders like thyssenkrupp and Kemira focus on process optimization. This competitive landscape reflects a technology approaching commercial viability with diverse applications across energy sectors.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (Sinopec) has developed industrial-scale microreactor technology for energy storage materials synthesis focused on practical implementation and commercialization. Their approach utilizes numbering-up strategies with parallel microreactor arrays rather than traditional scale-up, maintaining the advantages of microscale processing while achieving production volumes of several kilograms per day. Sinopec's system incorporates static micromixers with characteristic dimensions of 100-500μm fabricated using advanced manufacturing techniques including 3D metal printing. Their technology enables continuous hydrothermal synthesis of cathode materials under precisely controlled temperature and pressure conditions (up to 350°C and 250 bar), with residence times optimized to millisecond precision. This approach has demonstrated particular success in producing lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) and lithium titanate (Li4Ti5O12) materials with uniform particle size distribution and excellent rate capability. Sinopec has integrated their microreactor technology with downstream processing including continuous separation and surface modification steps, creating an end-to-end manufacturing solution that reduces production costs by approximately 15-20% compared to conventional batch processes while improving product consistency.
Strengths: Proven industrial implementation with demonstrated cost advantages; integrated end-to-end processing capability from synthesis to final product formulation. Weaknesses: Less flexibility for rapid prototyping compared to academic systems; primarily optimized for established materials rather than novel chemistry exploration.
The Regents of the University of California
Technical Solution: The University of California system has developed comprehensive microreactor technologies for energy storage materials synthesis through multiple campuses. Their approach integrates microfluidic reactors with advanced in-situ characterization techniques including synchrotron X-ray scattering and absorption spectroscopy to monitor crystallization processes in real-time. UC researchers have pioneered silicon-based microreactors with integrated heating elements capable of operating under high pressure (up to 200 bar) and temperature (up to 400°C) conditions, enabling supercritical fluid synthesis routes for nanomaterials. Their platform incorporates automated precursor delivery systems with mixing times under 10ms, allowing precise control over nucleation and growth kinetics. This technology has been successfully applied to synthesize various electrode materials including silicon/carbon composites for anodes with capacity exceeding 1000 mAh/g and nickel-rich layered oxides (NCM811) with improved thermal stability. UC researchers have demonstrated throughput capabilities of producing gram-scale quantities of tailored nanomaterials per day while maintaining precise control over particle size distribution (coefficient of variation <5%).
Strengths: Exceptional fundamental understanding of nucleation and growth mechanisms through advanced in-situ characterization; ability to operate under extreme conditions enabling novel synthesis pathways. Weaknesses: Complex system integration requiring specialized expertise; higher implementation costs compared to conventional batch processes limiting industrial adoption.
Key Technical Innovations in Microreactor Synthesis Methods
A multiphase continuous flow microreactor for process intensification with clean technology and a process thereof
PatentActiveIN202121031526A
Innovation
- A modular, multiphase continuous flow microreactor with microchannel technology that allows for active or passive mixing, featuring a reactant charging module, 3D splitting-remixing module, and wall scraping module, enabling flexible configuration and efficient mixing through spiral flow paths, serrated blades, and temperature control for scalable and efficient chemical processes.
Novel renewable energy storage reactor and application thereof
PatentActiveCN113322483A
Innovation
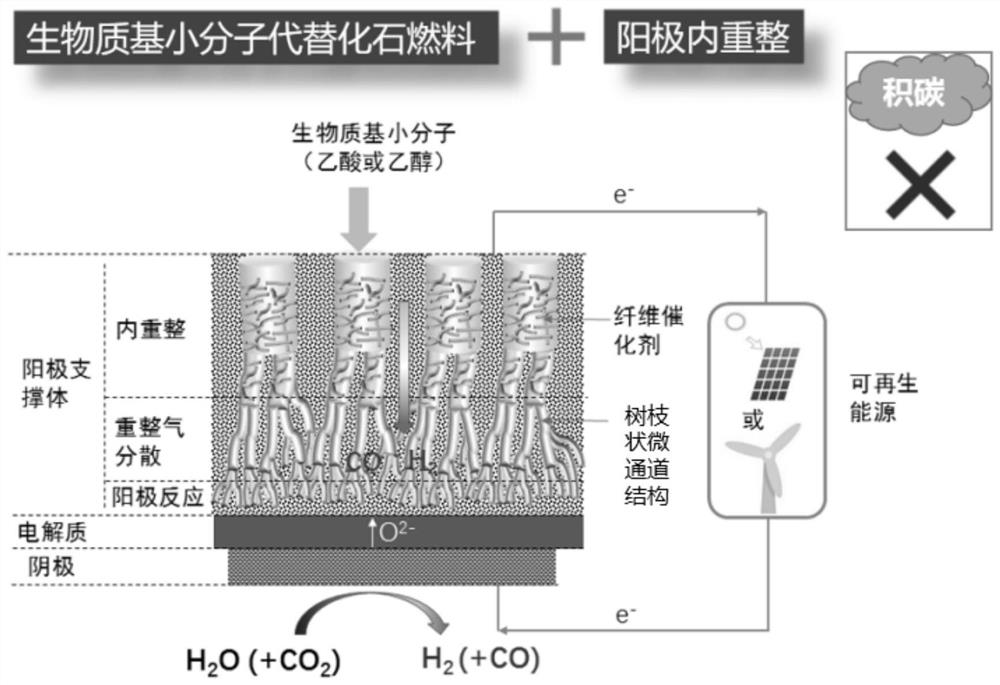
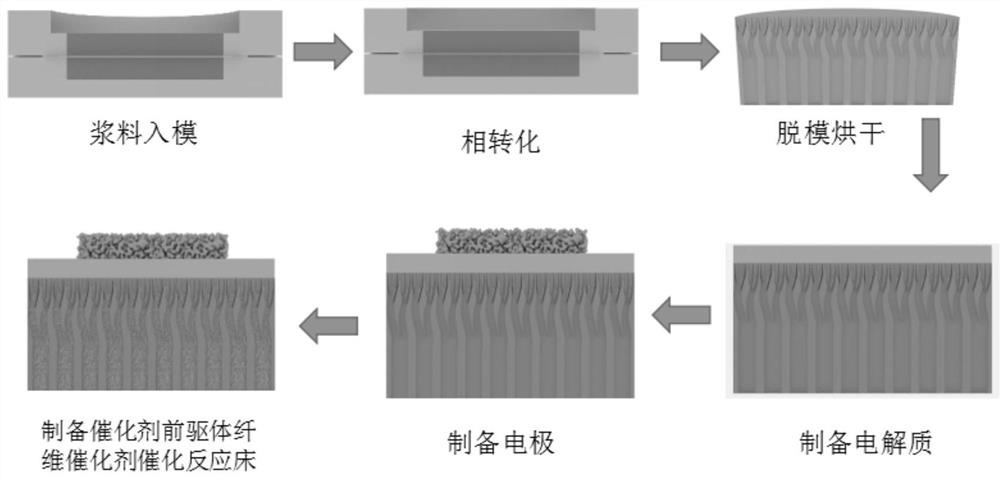
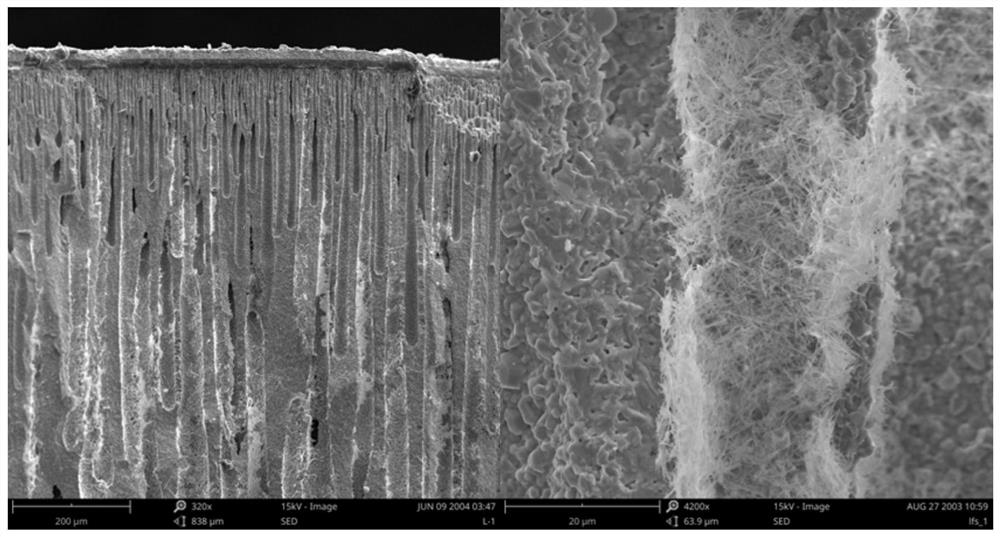
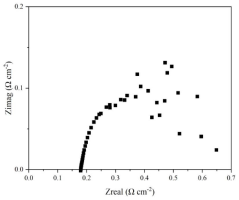
- An anode support with a microchannel structure and a porous cathode layer are used, with catalysts loaded inside. The catalyst is added with the assistance of negative pressure to form dendritic microchannels, which are used to reform biomass small molecules and achieve biomass-based small molecule-assisted electrolysis of water.
Scalability and Industrial Implementation Considerations
The scalability of microreactor technology represents a critical factor in determining its commercial viability for energy storage materials synthesis. Current laboratory-scale microreactor systems demonstrate excellent control over reaction parameters, but transitioning to industrial production volumes presents significant engineering challenges. The primary obstacle involves maintaining the precise reaction conditions and mixing efficiency that make microreactors advantageous when scaling up throughput by several orders of magnitude.
Parallel processing approaches offer promising solutions for industrial implementation. By employing multiple microreactor units in parallel configurations rather than increasing individual reactor dimensions, manufacturers can preserve the beneficial heat and mass transfer characteristics while increasing production capacity. This "numbering-up" strategy has been successfully demonstrated in pilot projects for lithium-ion battery cathode material synthesis, achieving production rates of 10-50 kg/day while maintaining nanoscale morphological control.
Material considerations become increasingly important at industrial scales. While laboratory microreactors often utilize glass, silicon, or PDMS construction, industrial implementations require more robust materials such as stainless steel, ceramic, or specialized corrosion-resistant alloys. These materials must withstand continuous operation under harsh chemical environments while maintaining precise dimensional tolerances critical for reaction control.
Process integration presents another implementation challenge. Microreactor systems must be effectively incorporated into existing manufacturing workflows, including upstream precursor preparation and downstream separation, purification, and post-processing operations. Continuous flow approaches that connect multiple process steps show particular promise for energy storage materials, as demonstrated by recent implementations for solid-state electrolyte synthesis that integrate mixing, reaction, and initial crystallization stages.
Economic considerations ultimately determine industrial adoption. Capital expenditure for microreactor systems currently exceeds conventional batch reactors, with specialized equipment costs ranging from $500,000 to several million dollars for production-scale systems. However, operational expenditure advantages—including reduced energy consumption (typically 30-45% lower), decreased solvent usage, higher yield (often 10-15% improvement), and reduced waste generation—can offset initial investments with payback periods of 2-4 years for high-value energy storage materials.
Regulatory frameworks and quality control systems must also evolve to accommodate continuous manufacturing paradigms. Real-time monitoring capabilities inherent to microreactor designs offer advantages for process analytical technology implementation, potentially streamlining regulatory approval for energy storage materials where consistent quality is paramount for performance and safety.
Parallel processing approaches offer promising solutions for industrial implementation. By employing multiple microreactor units in parallel configurations rather than increasing individual reactor dimensions, manufacturers can preserve the beneficial heat and mass transfer characteristics while increasing production capacity. This "numbering-up" strategy has been successfully demonstrated in pilot projects for lithium-ion battery cathode material synthesis, achieving production rates of 10-50 kg/day while maintaining nanoscale morphological control.
Material considerations become increasingly important at industrial scales. While laboratory microreactors often utilize glass, silicon, or PDMS construction, industrial implementations require more robust materials such as stainless steel, ceramic, or specialized corrosion-resistant alloys. These materials must withstand continuous operation under harsh chemical environments while maintaining precise dimensional tolerances critical for reaction control.
Process integration presents another implementation challenge. Microreactor systems must be effectively incorporated into existing manufacturing workflows, including upstream precursor preparation and downstream separation, purification, and post-processing operations. Continuous flow approaches that connect multiple process steps show particular promise for energy storage materials, as demonstrated by recent implementations for solid-state electrolyte synthesis that integrate mixing, reaction, and initial crystallization stages.
Economic considerations ultimately determine industrial adoption. Capital expenditure for microreactor systems currently exceeds conventional batch reactors, with specialized equipment costs ranging from $500,000 to several million dollars for production-scale systems. However, operational expenditure advantages—including reduced energy consumption (typically 30-45% lower), decreased solvent usage, higher yield (often 10-15% improvement), and reduced waste generation—can offset initial investments with payback periods of 2-4 years for high-value energy storage materials.
Regulatory frameworks and quality control systems must also evolve to accommodate continuous manufacturing paradigms. Real-time monitoring capabilities inherent to microreactor designs offer advantages for process analytical technology implementation, potentially streamlining regulatory approval for energy storage materials where consistent quality is paramount for performance and safety.
Sustainability Impact of Microreactor-Based Synthesis Methods
The adoption of microreactor technology in energy storage materials synthesis represents a significant advancement in sustainable manufacturing practices. Compared to conventional batch processes, microreactor-based synthesis methods demonstrate substantial environmental benefits through reduced energy consumption, with studies indicating energy efficiency improvements of 30-50% across various material synthesis applications. This efficiency stems from precise temperature control, enhanced heat transfer capabilities, and the elimination of energy-intensive heating and cooling cycles typical in batch processing.
Water usage reduction constitutes another critical sustainability advantage, with microreactor systems requiring up to 80% less water than traditional methods. The continuous flow nature of microreactors minimizes cleaning requirements between production runs and reduces cooling water needs, addressing growing concerns about water scarcity in industrial operations.
Chemical waste reduction represents perhaps the most significant environmental contribution of microreactor technology. The precise reaction control enables higher conversion rates and selectivity, reducing byproduct formation by 40-70% compared to conventional methods. Additionally, the ability to operate with smaller reagent volumes and achieve higher yields directly translates to less chemical waste per unit of product.
Carbon footprint assessments of microreactor-based synthesis reveal 25-60% reductions in greenhouse gas emissions compared to batch processes when producing equivalent quantities of energy storage materials. This improvement derives from both direct energy savings and reduced waste treatment requirements. Life cycle analyses further demonstrate that microreactor-manufactured materials often exhibit lower embodied carbon, enhancing the overall sustainability profile of resulting energy storage devices.
The space efficiency of microreactor systems also contributes to sustainability through reduced facility footprints. Compact microreactor installations require 50-75% less manufacturing floor space than equivalent batch production facilities, allowing for more efficient land use and potentially reducing construction material requirements and associated environmental impacts.
From a circular economy perspective, microreactor technology enables more efficient use of critical raw materials through precise dosing and higher conversion rates. This aspect is particularly relevant for energy storage materials that often rely on scarce resources like lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements. The technology's ability to process recycled feedstocks with variable compositions also supports closed-loop material systems, further enhancing sustainability credentials.
Water usage reduction constitutes another critical sustainability advantage, with microreactor systems requiring up to 80% less water than traditional methods. The continuous flow nature of microreactors minimizes cleaning requirements between production runs and reduces cooling water needs, addressing growing concerns about water scarcity in industrial operations.
Chemical waste reduction represents perhaps the most significant environmental contribution of microreactor technology. The precise reaction control enables higher conversion rates and selectivity, reducing byproduct formation by 40-70% compared to conventional methods. Additionally, the ability to operate with smaller reagent volumes and achieve higher yields directly translates to less chemical waste per unit of product.
Carbon footprint assessments of microreactor-based synthesis reveal 25-60% reductions in greenhouse gas emissions compared to batch processes when producing equivalent quantities of energy storage materials. This improvement derives from both direct energy savings and reduced waste treatment requirements. Life cycle analyses further demonstrate that microreactor-manufactured materials often exhibit lower embodied carbon, enhancing the overall sustainability profile of resulting energy storage devices.
The space efficiency of microreactor systems also contributes to sustainability through reduced facility footprints. Compact microreactor installations require 50-75% less manufacturing floor space than equivalent batch production facilities, allowing for more efficient land use and potentially reducing construction material requirements and associated environmental impacts.
From a circular economy perspective, microreactor technology enables more efficient use of critical raw materials through precise dosing and higher conversion rates. This aspect is particularly relevant for energy storage materials that often rely on scarce resources like lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements. The technology's ability to process recycled feedstocks with variable compositions also supports closed-loop material systems, further enhancing sustainability credentials.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!