Pilot-To-Commercial: Lessons Learned From Recent Demonstrations
SEP 1, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Pilot Project Background and Commercialization Goals
The transition from pilot demonstrations to commercial-scale operations represents a critical phase in technology development across various industries. Recent years have witnessed numerous pilot projects aimed at validating emerging technologies, with varying degrees of success in their commercialization journeys. These demonstrations serve as crucial proving grounds where theoretical concepts meet real-world constraints, providing invaluable insights for full-scale implementation.
Historically, pilot demonstrations have evolved from simple proof-of-concept exercises to sophisticated multi-stakeholder initiatives that closely mimic commercial conditions. This evolution reflects the growing recognition that technical feasibility alone does not guarantee commercial success. The technology landscape has increasingly emphasized the importance of scalability, cost-effectiveness, and market alignment from the earliest stages of development.
Current pilot projects typically aim to achieve multiple objectives simultaneously: technical validation, operational optimization, regulatory compliance, and business model verification. Recent demonstrations across renewable energy, advanced manufacturing, biotechnology, and digital infrastructure sectors have highlighted the need for comprehensive approaches that address both technical and non-technical barriers to commercialization.
The commercialization goals driving these pilot demonstrations have become more nuanced and multifaceted. Beyond proving technical performance, modern pilots seek to establish supply chain readiness, develop workforce capabilities, refine customer value propositions, and create pathways for financing full-scale deployment. This expanded scope reflects a deeper understanding of the complex ecosystem factors that influence successful technology adoption.
Analysis of recent demonstration projects reveals several emerging trends in commercialization strategies. First, there is increasing emphasis on modular and phased approaches that allow for iterative scaling rather than binary "pilot-to-commercial" transitions. Second, successful projects typically incorporate early engagement with end-users and regulatory stakeholders to anticipate adoption challenges. Third, there is growing recognition of the importance of developing parallel innovations in business models alongside technical advancements.
The technology adoption curve has also influenced pilot demonstration design, with greater attention to crossing the "valley of death" between early adopters and mainstream markets. Recent successful commercialization efforts have strategically positioned pilot demonstrations to generate evidence specifically addressing the concerns of pragmatic mainstream customers rather than focusing exclusively on technical enthusiasts.
Looking forward, the trajectory of pilot-to-commercial transitions suggests an accelerating pace of technology adoption, driven by digital tools that enable more rapid iteration and knowledge transfer between demonstration phases. However, this acceleration also creates new challenges in ensuring that lessons from pilot demonstrations are thoroughly incorporated before premature scaling occurs.
Historically, pilot demonstrations have evolved from simple proof-of-concept exercises to sophisticated multi-stakeholder initiatives that closely mimic commercial conditions. This evolution reflects the growing recognition that technical feasibility alone does not guarantee commercial success. The technology landscape has increasingly emphasized the importance of scalability, cost-effectiveness, and market alignment from the earliest stages of development.
Current pilot projects typically aim to achieve multiple objectives simultaneously: technical validation, operational optimization, regulatory compliance, and business model verification. Recent demonstrations across renewable energy, advanced manufacturing, biotechnology, and digital infrastructure sectors have highlighted the need for comprehensive approaches that address both technical and non-technical barriers to commercialization.
The commercialization goals driving these pilot demonstrations have become more nuanced and multifaceted. Beyond proving technical performance, modern pilots seek to establish supply chain readiness, develop workforce capabilities, refine customer value propositions, and create pathways for financing full-scale deployment. This expanded scope reflects a deeper understanding of the complex ecosystem factors that influence successful technology adoption.
Analysis of recent demonstration projects reveals several emerging trends in commercialization strategies. First, there is increasing emphasis on modular and phased approaches that allow for iterative scaling rather than binary "pilot-to-commercial" transitions. Second, successful projects typically incorporate early engagement with end-users and regulatory stakeholders to anticipate adoption challenges. Third, there is growing recognition of the importance of developing parallel innovations in business models alongside technical advancements.
The technology adoption curve has also influenced pilot demonstration design, with greater attention to crossing the "valley of death" between early adopters and mainstream markets. Recent successful commercialization efforts have strategically positioned pilot demonstrations to generate evidence specifically addressing the concerns of pragmatic mainstream customers rather than focusing exclusively on technical enthusiasts.
Looking forward, the trajectory of pilot-to-commercial transitions suggests an accelerating pace of technology adoption, driven by digital tools that enable more rapid iteration and knowledge transfer between demonstration phases. However, this acceleration also creates new challenges in ensuring that lessons from pilot demonstrations are thoroughly incorporated before premature scaling occurs.
Market Demand Analysis for Pilot Technologies
The market for pilot technologies has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for innovative solutions across various industries. Analysis of market trends reveals that companies are increasingly investing in pilot projects as a strategic approach to test new technologies before full-scale implementation. This shift represents a fundamental change in how organizations approach innovation, with pilot demonstrations serving as critical proof points for commercial viability.
Recent market research indicates that industries including healthcare, manufacturing, energy, and transportation are leading adopters of pilot technology demonstrations. These sectors collectively represent substantial market potential for technologies that successfully transition from pilot to commercial scale. The healthcare sector, in particular, has shown remarkable receptivity to pilot technologies, especially those addressing efficiency challenges, patient care improvement, and cost reduction.
Market demand for pilot technologies is further characterized by regional variations. North American and European markets typically prioritize innovations that demonstrate clear regulatory compliance and return on investment, while emerging markets in Asia and Africa often focus on scalability and adaptability to local infrastructure constraints. This geographical diversity in market requirements necessitates tailored approaches to pilot demonstrations.
Financial analysis of the pilot technology market reveals significant investment growth, with venture capital and corporate innovation funds increasingly allocating resources to promising pilot projects. This funding trend reflects growing confidence in the pilot-to-commercial pathway as a de-risking strategy for technology investment. Companies that can demonstrate successful pilot implementations are securing follow-on funding at higher valuations, indicating strong market validation.
Customer demand patterns show evolving expectations regarding pilot technologies. End-users increasingly expect shorter demonstration periods with more definitive outcomes, placing pressure on technology developers to design more efficient pilot programs. Additionally, there is growing demand for pilot technologies that integrate seamlessly with existing systems and processes, minimizing disruption during implementation phases.
Market feedback from recent pilot demonstrations highlights several critical success factors that drive commercial adoption. These include demonstrable cost savings, measurable performance improvements, ease of integration, and scalability potential. Technologies that address multiple pain points simultaneously are experiencing particularly strong market pull, as organizations seek comprehensive solutions rather than incremental improvements.
Competitive analysis reveals that the market for pilot technologies is becoming increasingly crowded, with both established companies and startups vying for demonstration opportunities. This competitive landscape is driving innovation in how pilot projects are structured and executed, with greater emphasis on rapid iteration and customer involvement throughout the demonstration process.
Recent market research indicates that industries including healthcare, manufacturing, energy, and transportation are leading adopters of pilot technology demonstrations. These sectors collectively represent substantial market potential for technologies that successfully transition from pilot to commercial scale. The healthcare sector, in particular, has shown remarkable receptivity to pilot technologies, especially those addressing efficiency challenges, patient care improvement, and cost reduction.
Market demand for pilot technologies is further characterized by regional variations. North American and European markets typically prioritize innovations that demonstrate clear regulatory compliance and return on investment, while emerging markets in Asia and Africa often focus on scalability and adaptability to local infrastructure constraints. This geographical diversity in market requirements necessitates tailored approaches to pilot demonstrations.
Financial analysis of the pilot technology market reveals significant investment growth, with venture capital and corporate innovation funds increasingly allocating resources to promising pilot projects. This funding trend reflects growing confidence in the pilot-to-commercial pathway as a de-risking strategy for technology investment. Companies that can demonstrate successful pilot implementations are securing follow-on funding at higher valuations, indicating strong market validation.
Customer demand patterns show evolving expectations regarding pilot technologies. End-users increasingly expect shorter demonstration periods with more definitive outcomes, placing pressure on technology developers to design more efficient pilot programs. Additionally, there is growing demand for pilot technologies that integrate seamlessly with existing systems and processes, minimizing disruption during implementation phases.
Market feedback from recent pilot demonstrations highlights several critical success factors that drive commercial adoption. These include demonstrable cost savings, measurable performance improvements, ease of integration, and scalability potential. Technologies that address multiple pain points simultaneously are experiencing particularly strong market pull, as organizations seek comprehensive solutions rather than incremental improvements.
Competitive analysis reveals that the market for pilot technologies is becoming increasingly crowded, with both established companies and startups vying for demonstration opportunities. This competitive landscape is driving innovation in how pilot projects are structured and executed, with greater emphasis on rapid iteration and customer involvement throughout the demonstration process.
Current Challenges in Pilot-to-Commercial Transition
The transition from pilot demonstrations to commercial-scale operations represents one of the most challenging phases in technology development cycles. Recent demonstrations across various industries have highlighted several persistent barriers that impede successful commercialization. Technical scalability remains a primary concern, as solutions that function effectively in controlled pilot environments often encounter unforeseen complications when scaled to commercial operations. These complications frequently manifest as performance degradation, reliability issues, or efficiency losses that weren't apparent at smaller scales.
Economic viability constitutes another significant hurdle. The financial models that appear promising during pilot phases can deteriorate when confronted with real-world market conditions. Many demonstrations fail to accurately account for economies of scale, overlooking how unit economics change dramatically between pilot and commercial implementation. Additionally, pilot projects often benefit from subsidies, grants, or other financial support mechanisms that mask true operational costs, creating unrealistic expectations for commercial viability.
Regulatory compliance frameworks present evolving challenges as technologies move toward commercialization. Pilot demonstrations frequently operate under regulatory exemptions or in sandbox environments that don't reflect the full compliance burden of commercial operations. The regulatory landscape may also shift during the transition period, introducing new requirements that weren't considered during the pilot phase.
Market acceptance and customer adoption represent critical yet frequently underestimated challenges. Technical success in pilot demonstrations doesn't guarantee market readiness or customer willingness to adopt new solutions. Recent demonstrations have shown that insufficient attention to user experience, integration requirements, and change management can severely impede commercial success despite technical merit.
Supply chain and manufacturing readiness issues have emerged as particularly problematic in recent years. Many pilot demonstrations utilize custom-built components or rely on manufacturing processes that cannot be easily replicated at commercial scale. The transition often reveals supply chain vulnerabilities, manufacturing bottlenecks, or quality control challenges that weren't apparent during limited production runs.
Talent and organizational capability gaps frequently surface during commercialization efforts. The skill sets required to execute successful pilots differ significantly from those needed to operate commercial-scale enterprises. Recent demonstrations have highlighted how organizational structures, processes, and capabilities must evolve substantially to support commercial operations.
Intellectual property protection and competitive positioning also present complex challenges during the transition phase. As technologies move toward commercialization, IP strategies must evolve from protecting core innovations to establishing defensible market positions against emerging competitors who may have observed the pilot's success.
Economic viability constitutes another significant hurdle. The financial models that appear promising during pilot phases can deteriorate when confronted with real-world market conditions. Many demonstrations fail to accurately account for economies of scale, overlooking how unit economics change dramatically between pilot and commercial implementation. Additionally, pilot projects often benefit from subsidies, grants, or other financial support mechanisms that mask true operational costs, creating unrealistic expectations for commercial viability.
Regulatory compliance frameworks present evolving challenges as technologies move toward commercialization. Pilot demonstrations frequently operate under regulatory exemptions or in sandbox environments that don't reflect the full compliance burden of commercial operations. The regulatory landscape may also shift during the transition period, introducing new requirements that weren't considered during the pilot phase.
Market acceptance and customer adoption represent critical yet frequently underestimated challenges. Technical success in pilot demonstrations doesn't guarantee market readiness or customer willingness to adopt new solutions. Recent demonstrations have shown that insufficient attention to user experience, integration requirements, and change management can severely impede commercial success despite technical merit.
Supply chain and manufacturing readiness issues have emerged as particularly problematic in recent years. Many pilot demonstrations utilize custom-built components or rely on manufacturing processes that cannot be easily replicated at commercial scale. The transition often reveals supply chain vulnerabilities, manufacturing bottlenecks, or quality control challenges that weren't apparent during limited production runs.
Talent and organizational capability gaps frequently surface during commercialization efforts. The skill sets required to execute successful pilots differ significantly from those needed to operate commercial-scale enterprises. Recent demonstrations have highlighted how organizational structures, processes, and capabilities must evolve substantially to support commercial operations.
Intellectual property protection and competitive positioning also present complex challenges during the transition phase. As technologies move toward commercialization, IP strategies must evolve from protecting core innovations to establishing defensible market positions against emerging competitors who may have observed the pilot's success.
Successful Demonstration Methodologies and Frameworks
01 Process optimization and scale-up strategies
When transitioning from pilot to commercial scale, optimizing manufacturing processes is crucial. This includes identifying bottlenecks, streamlining workflows, and implementing efficient scale-up methodologies. Lessons learned emphasize the importance of thorough process validation, equipment qualification, and establishing robust control parameters to ensure consistent product quality during scale-up. Successful transitions require systematic approaches to address challenges related to increased production volumes while maintaining product specifications.- Risk management and quality control in scale-up processes: Transitioning from pilot to commercial scale requires robust risk management strategies and quality control measures. Lessons learned emphasize the importance of identifying potential failure points early, implementing comprehensive testing protocols, and establishing quality control checkpoints throughout the scale-up process. Maintaining consistent product quality while increasing production volume presents significant challenges that must be addressed through systematic approaches and continuous monitoring systems.
- Knowledge transfer and documentation practices: Effective knowledge transfer between research, development, and manufacturing teams is critical during pilot-to-commercial transitions. Documentation of processes, parameters, and problem-solving approaches ensures that valuable insights are preserved and accessible. Lessons learned highlight the importance of creating comprehensive technical transfer packages, maintaining detailed records of process modifications, and establishing clear communication channels between different functional teams to facilitate smooth transitions.
- Equipment and technology scaling considerations: Scaling up equipment and technology from pilot to commercial production presents unique challenges. Key lessons include the importance of understanding how process parameters change with scale, accounting for differences in equipment design and capabilities, and conducting thorough validation of technology transfer. Successful transitions require careful selection of commercial equipment that can replicate critical process conditions established during pilot production while accommodating larger volumes and continuous operation requirements.
- Training and workforce development strategies: Preparing the workforce for commercial production is essential for successful scale-up. Lessons learned emphasize the need for comprehensive training programs that address both technical skills and operational procedures. Simulation-based training, hands-on experience with pilot equipment, and gradual transition of responsibilities help build operator confidence and competence. Establishing mentorship programs between experienced staff and new operators facilitates knowledge transfer and helps maintain operational continuity during the transition phase.
- Project management and timeline optimization: Effective project management is crucial for successful pilot-to-commercial transitions. Lessons learned highlight the importance of realistic timeline planning, resource allocation, and milestone-based progress tracking. Parallel development paths, early engagement with regulatory authorities, and anticipation of potential bottlenecks can significantly reduce time-to-market. Implementing stage-gate processes with clear decision criteria helps manage risks and ensures that critical issues are addressed before proceeding to full commercial production.
02 Knowledge transfer and training systems
Effective knowledge transfer between pilot and commercial teams is essential for successful transitions. This includes comprehensive documentation of procedures, training programs for commercial staff, and systems to capture and apply lessons learned. Establishing standardized training protocols ensures operational consistency and minimizes errors during the transition. Creating feedback mechanisms between research, development, and production teams facilitates continuous improvement and helps address unforeseen challenges that arise during commercial implementation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quality control and regulatory compliance
Maintaining quality standards and regulatory compliance during the transition from pilot to commercial scale presents significant challenges. Lessons learned highlight the importance of establishing robust quality management systems, conducting thorough risk assessments, and implementing appropriate control strategies. Successful transitions require early engagement with regulatory authorities, comprehensive validation protocols, and systems to monitor and address quality deviations. Ensuring consistent product quality across different production scales is critical for commercial success.Expand Specific Solutions04 Technology integration and automation
Integrating advanced technologies and automation systems is crucial when scaling from pilot to commercial production. Lessons learned emphasize the importance of selecting appropriate technologies that can scale effectively, implementing robust control systems, and ensuring compatibility between different equipment and software platforms. Successful transitions often involve phased implementation of automation, thorough testing of integrated systems, and contingency planning for technology-related disruptions. Balancing automation with operational flexibility is essential for addressing unforeseen challenges during commercial implementation.Expand Specific Solutions05 Supply chain and logistics management
Effective supply chain and logistics management is critical during the pilot-to-commercial transition. Lessons learned highlight the importance of securing reliable raw material suppliers, establishing robust inventory management systems, and developing efficient distribution networks. Successful transitions require thorough assessment of supplier capabilities, implementation of quality agreements, and contingency planning for supply disruptions. Coordinating production schedules with market demand and distribution capabilities helps ensure smooth commercial operations and customer satisfaction.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Demonstration Projects
The pilot-to-commercial transition landscape is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market adoption across multiple sectors. The global market for pilot-to-commercial technology implementations is expanding rapidly, driven by organizations seeking to scale successful demonstrations into viable business operations. Technology maturity varies significantly among key players, with IBM, ExxonMobil Chemical, and Honeywell International demonstrating advanced capabilities in transitioning pilots to commercial applications. Companies like Wing Aviation and Baidu are making significant strides in autonomous systems commercialization, while Proov Systems specializes in streamlining the pilot-to-commercial process. Financial institutions such as BNY Mellon are increasingly investing in fintech pilot programs, indicating the technology's growing cross-industry relevance and economic potential.
International Business Machines Corp.
Technical Solution: IBM's approach to pilot-to-commercial transition leverages their Enterprise Design Thinking framework, which emphasizes user-centered design principles throughout the development process. Their methodology includes three distinct phases: 1) Pilot Design & Implementation - utilizing small-scale deployments with carefully selected clients to validate technology in real-world environments; 2) Scaling Framework - employing a structured approach to identify technical, operational, and business challenges that emerge during scaling; and 3) Continuous Feedback Loop - implementing systems that capture user experiences and operational metrics to refine solutions iteratively. IBM's recent demonstrations in quantum computing commercialization showcase this approach, where they've moved from limited-access experimental platforms to their IBM Quantum System One, making quantum computing accessible to enterprise clients through cloud services while continuously incorporating feedback to improve system stability and usability.
Strengths: IBM's enterprise-scale infrastructure and established client relationships enable smooth transitions from pilot to commercial deployment. Their extensive experience with complex technology implementations provides valuable insights for scaling. Weaknesses: The company's size can sometimes lead to slower adaptation to rapidly changing market conditions, and their solutions often require significant customization for different industry verticals.
Honeywell International Technologies Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honeywell has developed a comprehensive Pilot-to-Commercial (P2C) methodology that focuses on industrial technology deployment. Their approach centers on what they call "Controlled Environment Scaling," where technologies are first deployed in highly controlled settings before gradually expanding to more variable environments. Honeywell's P2C process includes rigorous stage-gate reviews at critical transition points, with clearly defined technical and business metrics that must be achieved before advancing. A key component of their strategy is the "Digital Twin" approach, where they create virtual replicas of physical systems to simulate performance at scale before full deployment. This allows them to identify potential issues and optimize operations without disrupting existing systems. Honeywell has successfully applied this methodology in their recent quantum computing initiatives and industrial automation solutions, where they've demonstrated the ability to move from laboratory demonstrations to commercially viable products with predictable performance characteristics.
Strengths: Honeywell's strong engineering culture and deep domain expertise in industrial systems enable them to effectively anticipate scaling challenges. Their methodical approach minimizes risks during commercialization. Weaknesses: Their focus on rigorous testing and validation can extend time-to-market compared to more agile competitors, and their solutions sometimes prioritize reliability over cutting-edge innovation.
Critical Case Studies and Technical Insights
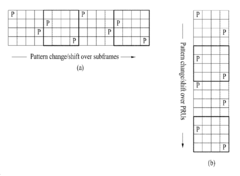
Method for transmitting pilot signal for machine to machine communication in wireless communication system and apparatus thereof
PatentInactiveUS9001779B2
Innovation
- A method for transmitting pilot signals in M2M communication that configures basic units with pilot and data resource elements, allocates pilot signals to specific resource elements, and transmits these units in subframes excluding control channel subframes, using a previously defined rule, allowing for efficient resource usage and reduced pilot overhead.
Risk Management Strategies for Commercial Implementation
Effective risk management is paramount when transitioning from pilot demonstrations to full commercial implementation. Based on recent technology demonstrations across various industries, several key risk management strategies have emerged as critical success factors. These strategies form a comprehensive framework that organizations can adopt to mitigate potential pitfalls during commercialization.
Financial risk management requires a multi-layered approach, beginning with phased investment structures that allow for strategic capital allocation based on milestone achievements. Companies that have successfully commercialized pilot technologies typically establish contingency funds representing 15-20% of the total project budget to address unforeseen challenges. Additionally, implementing robust financial monitoring systems with real-time analytics capabilities enables early detection of cost overruns or resource allocation inefficiencies.
Technical risk mitigation strategies focus on maintaining scalability without compromising performance. Successful commercial implementations often employ modular design approaches that allow for incremental scaling and targeted troubleshooting. Establishing comprehensive testing protocols that simulate various operational scenarios and stress conditions has proven essential for identifying potential failure points before full-scale deployment. Furthermore, developing redundancy systems for critical components ensures operational continuity even when technical issues arise.
Market-related risks require careful navigation through strategic partnerships and customer engagement models. Early adopter programs with tiered pricing structures have demonstrated effectiveness in building market traction while gathering valuable feedback. Developing flexible product configurations that can adapt to varying customer requirements without significant redesign has emerged as a competitive advantage in rapidly evolving markets.
Regulatory compliance represents another critical risk domain that demands proactive management. Creating cross-functional compliance teams that continuously monitor regulatory developments across target markets helps prevent costly delays or redesigns. Engaging with regulatory bodies early in the commercialization process and participating in industry standardization efforts can significantly reduce compliance uncertainties.
Operational risk management strategies focus on knowledge transfer and organizational readiness. Structured documentation of pilot learnings, including both successes and failures, provides valuable institutional knowledge. Implementing formal transition protocols between R&D and operations teams ensures critical insights aren't lost during handover. Additionally, developing specialized training programs for operational staff has proven essential for maintaining performance metrics during scaling.
Financial risk management requires a multi-layered approach, beginning with phased investment structures that allow for strategic capital allocation based on milestone achievements. Companies that have successfully commercialized pilot technologies typically establish contingency funds representing 15-20% of the total project budget to address unforeseen challenges. Additionally, implementing robust financial monitoring systems with real-time analytics capabilities enables early detection of cost overruns or resource allocation inefficiencies.
Technical risk mitigation strategies focus on maintaining scalability without compromising performance. Successful commercial implementations often employ modular design approaches that allow for incremental scaling and targeted troubleshooting. Establishing comprehensive testing protocols that simulate various operational scenarios and stress conditions has proven essential for identifying potential failure points before full-scale deployment. Furthermore, developing redundancy systems for critical components ensures operational continuity even when technical issues arise.
Market-related risks require careful navigation through strategic partnerships and customer engagement models. Early adopter programs with tiered pricing structures have demonstrated effectiveness in building market traction while gathering valuable feedback. Developing flexible product configurations that can adapt to varying customer requirements without significant redesign has emerged as a competitive advantage in rapidly evolving markets.
Regulatory compliance represents another critical risk domain that demands proactive management. Creating cross-functional compliance teams that continuously monitor regulatory developments across target markets helps prevent costly delays or redesigns. Engaging with regulatory bodies early in the commercialization process and participating in industry standardization efforts can significantly reduce compliance uncertainties.
Operational risk management strategies focus on knowledge transfer and organizational readiness. Structured documentation of pilot learnings, including both successes and failures, provides valuable institutional knowledge. Implementing formal transition protocols between R&D and operations teams ensures critical insights aren't lost during handover. Additionally, developing specialized training programs for operational staff has proven essential for maintaining performance metrics during scaling.
Financial Models for Pilot-to-Commercial Transition
Financial modeling for the transition from pilot to commercial scale represents a critical component in the successful deployment of new technologies. Recent demonstrations have highlighted the importance of robust financial frameworks that can accurately predict and manage the economic challenges of scaling up. Traditional models often fail to account for the non-linear cost relationships that emerge when moving from demonstration to full-scale implementation.
The most effective financial models incorporate multiple funding scenarios, recognizing that capital requirements typically increase by factors of 10-50x when transitioning from pilot to commercial operations. Analysis of recent case studies reveals that successful transitions often employ phased investment approaches, with clear milestone-based funding triggers that help manage investor risk while maintaining operational momentum.
Risk assessment methodologies have evolved significantly, with leading organizations now implementing Monte Carlo simulations to account for market volatility, regulatory changes, and technical uncertainties. These probabilistic approaches provide stakeholders with more realistic projections compared to traditional deterministic models, particularly when dealing with emerging technologies where historical data may be limited.
Cost estimation techniques for commercial scale operations require careful consideration of economies of scale, which often don't follow linear projections from pilot demonstrations. Recent demonstrations have shown that while certain costs decrease proportionally with scale (materials, energy inputs), others may increase disproportionately (regulatory compliance, quality control, specialized labor). Successful financial models disaggregate these cost categories and apply appropriate scaling factors to each.
Revenue forecasting represents another critical dimension, with the most effective models incorporating market adoption curves specific to the technology sector. Early-stage commercial deployments frequently experience slower-than-anticipated market penetration, creating cash flow challenges that must be anticipated in financial planning. Leading organizations now incorporate sensitivity analyses around adoption timelines, pricing strategies, and competitive responses.
Return on investment calculations have also evolved, with sophisticated models now considering multiple value creation pathways beyond direct product sales, including intellectual property licensing, data monetization, and ecosystem development. This holistic approach to value capture has proven essential for technologies that create benefits across multiple stakeholders or industry segments.
The most effective financial models incorporate multiple funding scenarios, recognizing that capital requirements typically increase by factors of 10-50x when transitioning from pilot to commercial operations. Analysis of recent case studies reveals that successful transitions often employ phased investment approaches, with clear milestone-based funding triggers that help manage investor risk while maintaining operational momentum.
Risk assessment methodologies have evolved significantly, with leading organizations now implementing Monte Carlo simulations to account for market volatility, regulatory changes, and technical uncertainties. These probabilistic approaches provide stakeholders with more realistic projections compared to traditional deterministic models, particularly when dealing with emerging technologies where historical data may be limited.
Cost estimation techniques for commercial scale operations require careful consideration of economies of scale, which often don't follow linear projections from pilot demonstrations. Recent demonstrations have shown that while certain costs decrease proportionally with scale (materials, energy inputs), others may increase disproportionately (regulatory compliance, quality control, specialized labor). Successful financial models disaggregate these cost categories and apply appropriate scaling factors to each.
Revenue forecasting represents another critical dimension, with the most effective models incorporating market adoption curves specific to the technology sector. Early-stage commercial deployments frequently experience slower-than-anticipated market penetration, creating cash flow challenges that must be anticipated in financial planning. Leading organizations now incorporate sensitivity analyses around adoption timelines, pricing strategies, and competitive responses.
Return on investment calculations have also evolved, with sophisticated models now considering multiple value creation pathways beyond direct product sales, including intellectual property licensing, data monetization, and ecosystem development. This holistic approach to value capture has proven essential for technologies that create benefits across multiple stakeholders or industry segments.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!