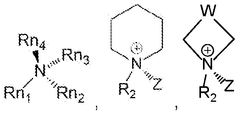
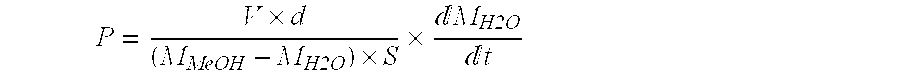Crosslinked quaternary ammonium membranes for improved durability
OCT 27, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Quaternary Ammonium Membrane Development History and Objectives
Quaternary ammonium membranes (QAMs) have emerged as a significant technology in various applications, particularly in fuel cells, water purification, and ion exchange processes. The development of these membranes can be traced back to the 1950s when researchers first began exploring ion exchange membranes for electrochemical applications. Initially, these membranes suffered from poor stability and limited functionality, restricting their practical applications.
The 1970s marked a turning point with the introduction of perfluorinated membranes like Nafion, which demonstrated superior chemical stability. However, these materials were expensive and had limitations in alkaline environments. This gap prompted research into alternative membrane technologies, leading to increased interest in quaternary ammonium functionalized membranes in the 1990s.
Early QAMs faced significant durability challenges, particularly in harsh chemical environments and at elevated temperatures. The quaternary ammonium functional groups, while excellent for ion conductivity, were prone to degradation through several mechanisms including Hofmann elimination, nucleophilic substitution, and oxidative degradation. These limitations severely restricted the operational lifetime of devices utilizing these membranes.
The 2000s witnessed significant advancements in polymer chemistry and membrane fabrication techniques, enabling the development of more stable QAM architectures. Researchers began exploring various polymer backbones including polysulfones, polyethersulfones, and polyphenylene oxides as platforms for quaternary ammonium functionalization. Despite these improvements, durability remained a persistent challenge.
A paradigm shift occurred in the 2010s with the introduction of crosslinking strategies to enhance membrane stability. Crosslinking provided structural reinforcement and reduced swelling, addressing key degradation pathways. Various approaches including thermal, chemical, and radiation-induced crosslinking were explored, each offering unique advantages for specific applications.
The current research landscape focuses on developing advanced crosslinked QAMs with enhanced durability while maintaining high ionic conductivity. The primary objectives include extending operational lifetime beyond 5,000 hours under practical conditions, improving mechanical stability under hydration-dehydration cycles, and developing membranes capable of withstanding temperatures above 80°C in alkaline environments.
Future research aims to establish fundamental structure-property relationships governing membrane durability, develop novel crosslinking chemistries that can be precisely controlled at the molecular level, and create manufacturing processes suitable for commercial-scale production of these advanced materials. The ultimate goal is to enable widespread adoption of QAM technology in clean energy applications, particularly in alkaline fuel cells and electrolyzers, where durability remains a critical barrier to commercialization.
The 1970s marked a turning point with the introduction of perfluorinated membranes like Nafion, which demonstrated superior chemical stability. However, these materials were expensive and had limitations in alkaline environments. This gap prompted research into alternative membrane technologies, leading to increased interest in quaternary ammonium functionalized membranes in the 1990s.
Early QAMs faced significant durability challenges, particularly in harsh chemical environments and at elevated temperatures. The quaternary ammonium functional groups, while excellent for ion conductivity, were prone to degradation through several mechanisms including Hofmann elimination, nucleophilic substitution, and oxidative degradation. These limitations severely restricted the operational lifetime of devices utilizing these membranes.
The 2000s witnessed significant advancements in polymer chemistry and membrane fabrication techniques, enabling the development of more stable QAM architectures. Researchers began exploring various polymer backbones including polysulfones, polyethersulfones, and polyphenylene oxides as platforms for quaternary ammonium functionalization. Despite these improvements, durability remained a persistent challenge.
A paradigm shift occurred in the 2010s with the introduction of crosslinking strategies to enhance membrane stability. Crosslinking provided structural reinforcement and reduced swelling, addressing key degradation pathways. Various approaches including thermal, chemical, and radiation-induced crosslinking were explored, each offering unique advantages for specific applications.
The current research landscape focuses on developing advanced crosslinked QAMs with enhanced durability while maintaining high ionic conductivity. The primary objectives include extending operational lifetime beyond 5,000 hours under practical conditions, improving mechanical stability under hydration-dehydration cycles, and developing membranes capable of withstanding temperatures above 80°C in alkaline environments.
Future research aims to establish fundamental structure-property relationships governing membrane durability, develop novel crosslinking chemistries that can be precisely controlled at the molecular level, and create manufacturing processes suitable for commercial-scale production of these advanced materials. The ultimate goal is to enable widespread adoption of QAM technology in clean energy applications, particularly in alkaline fuel cells and electrolyzers, where durability remains a critical barrier to commercialization.
Market Analysis for Durable Ion Exchange Membranes
The global ion exchange membrane market is experiencing robust growth, driven primarily by increasing applications in water treatment, energy storage, and chemical processing industries. The market for durable ion exchange membranes, particularly crosslinked quaternary ammonium membranes, is projected to reach significant market value by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding the broader membrane technology sector.
Water treatment represents the largest application segment for ion exchange membranes, accounting for approximately one-third of the total market share. The growing global water scarcity issues and stringent regulations regarding water quality have substantially increased demand for advanced water purification technologies. Industrial wastewater treatment, specifically in sectors like mining, pharmaceuticals, and electronics manufacturing, presents a particularly promising growth avenue for durable anion exchange membranes.
Energy applications constitute the fastest-growing segment for these membranes. The expanding renewable energy sector has intensified the need for efficient energy storage solutions, with flow batteries and fuel cells emerging as critical technologies. Crosslinked quaternary ammonium membranes with enhanced durability are especially valuable in these applications, where membrane degradation has historically been a significant performance limitation.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for high-performance ion exchange membranes, collectively accounting for over half of global consumption. However, the Asia-Pacific region is witnessing the highest growth rate, driven by rapid industrialization in China, India, and Southeast Asian countries, coupled with increasing environmental regulations and water treatment infrastructure development.
Customer demand patterns reveal a clear shift toward membranes with extended operational lifespans. End-users across industries are increasingly prioritizing total cost of ownership over initial acquisition costs, creating market pull for more durable membrane technologies. This trend is particularly evident in industrial applications where system downtime for membrane replacement results in substantial operational losses.
Price sensitivity varies significantly across application segments. While municipal water treatment remains highly cost-conscious, specialized industrial applications and advanced energy storage systems demonstrate greater willingness to pay premium prices for membranes offering superior durability and performance characteristics.
The competitive landscape features both established membrane manufacturers expanding their product portfolios and specialized startups focusing exclusively on next-generation membrane technologies. Strategic partnerships between membrane developers and system integrators are becoming increasingly common, creating more comprehensive solution offerings and accelerating market adoption of advanced membrane technologies.
Water treatment represents the largest application segment for ion exchange membranes, accounting for approximately one-third of the total market share. The growing global water scarcity issues and stringent regulations regarding water quality have substantially increased demand for advanced water purification technologies. Industrial wastewater treatment, specifically in sectors like mining, pharmaceuticals, and electronics manufacturing, presents a particularly promising growth avenue for durable anion exchange membranes.
Energy applications constitute the fastest-growing segment for these membranes. The expanding renewable energy sector has intensified the need for efficient energy storage solutions, with flow batteries and fuel cells emerging as critical technologies. Crosslinked quaternary ammonium membranes with enhanced durability are especially valuable in these applications, where membrane degradation has historically been a significant performance limitation.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for high-performance ion exchange membranes, collectively accounting for over half of global consumption. However, the Asia-Pacific region is witnessing the highest growth rate, driven by rapid industrialization in China, India, and Southeast Asian countries, coupled with increasing environmental regulations and water treatment infrastructure development.
Customer demand patterns reveal a clear shift toward membranes with extended operational lifespans. End-users across industries are increasingly prioritizing total cost of ownership over initial acquisition costs, creating market pull for more durable membrane technologies. This trend is particularly evident in industrial applications where system downtime for membrane replacement results in substantial operational losses.
Price sensitivity varies significantly across application segments. While municipal water treatment remains highly cost-conscious, specialized industrial applications and advanced energy storage systems demonstrate greater willingness to pay premium prices for membranes offering superior durability and performance characteristics.
The competitive landscape features both established membrane manufacturers expanding their product portfolios and specialized startups focusing exclusively on next-generation membrane technologies. Strategic partnerships between membrane developers and system integrators are becoming increasingly common, creating more comprehensive solution offerings and accelerating market adoption of advanced membrane technologies.
Current Challenges in Crosslinked QA Membrane Technology
Despite significant advancements in crosslinked quaternary ammonium (QA) membrane technology, several critical challenges continue to impede their widespread commercial adoption and long-term performance. The most persistent issue remains the chemical and mechanical stability of these membranes under operating conditions. When exposed to alkaline environments, QA membranes often undergo degradation through Hofmann elimination and nucleophilic substitution reactions, leading to progressive loss of ion exchange capacity and conductivity over time.
The hydroxide counterions in anion exchange membranes (AEMs) are particularly aggressive, attacking the β-hydrogen atoms adjacent to the quaternary ammonium groups. This results in the elimination of trimethylamine and formation of alkenes, compromising the membrane's structural integrity. Current crosslinking strategies have shown limited success in fully mitigating this degradation pathway, especially at elevated temperatures above 60°C.
Mechanical durability presents another significant challenge. The dimensional changes during hydration/dehydration cycles create internal stresses that can lead to microcracking and eventual membrane failure. While crosslinking improves dimensional stability, it often results in increased brittleness, creating a difficult balance between mechanical strength and flexibility that has not been optimally resolved.
Water management within crosslinked QA membranes remains problematic. The hydrophilic quaternary ammonium groups promote water uptake necessary for ion transport, but excessive swelling compromises mechanical properties. Conversely, highly crosslinked membranes may restrict water content below optimal levels for efficient ion conductivity, creating a performance trade-off that limits practical applications.
Manufacturing scalability presents additional hurdles. Laboratory-scale synthesis methods for crosslinked QA membranes often involve complex multi-step processes that are difficult to translate to industrial production. The crosslinking reactions must be precisely controlled to ensure uniform distribution throughout the membrane, a requirement that becomes increasingly challenging at larger scales.
Cost factors further complicate commercial viability. Current synthesis routes for crosslinked QA membranes typically involve expensive precursors and complex processing steps. The specialized monomers containing quaternary ammonium groups or their precursors are significantly more costly than conventional hydrocarbon polymers, driving up the overall membrane production costs.
Lastly, characterization and standardization of crosslinked QA membranes remain underdeveloped. The lack of standardized testing protocols specifically designed for these materials makes it difficult to compare results across different research groups and establish reliable performance benchmarks, hindering systematic improvement efforts and technology transfer to industrial applications.
The hydroxide counterions in anion exchange membranes (AEMs) are particularly aggressive, attacking the β-hydrogen atoms adjacent to the quaternary ammonium groups. This results in the elimination of trimethylamine and formation of alkenes, compromising the membrane's structural integrity. Current crosslinking strategies have shown limited success in fully mitigating this degradation pathway, especially at elevated temperatures above 60°C.
Mechanical durability presents another significant challenge. The dimensional changes during hydration/dehydration cycles create internal stresses that can lead to microcracking and eventual membrane failure. While crosslinking improves dimensional stability, it often results in increased brittleness, creating a difficult balance between mechanical strength and flexibility that has not been optimally resolved.
Water management within crosslinked QA membranes remains problematic. The hydrophilic quaternary ammonium groups promote water uptake necessary for ion transport, but excessive swelling compromises mechanical properties. Conversely, highly crosslinked membranes may restrict water content below optimal levels for efficient ion conductivity, creating a performance trade-off that limits practical applications.
Manufacturing scalability presents additional hurdles. Laboratory-scale synthesis methods for crosslinked QA membranes often involve complex multi-step processes that are difficult to translate to industrial production. The crosslinking reactions must be precisely controlled to ensure uniform distribution throughout the membrane, a requirement that becomes increasingly challenging at larger scales.
Cost factors further complicate commercial viability. Current synthesis routes for crosslinked QA membranes typically involve expensive precursors and complex processing steps. The specialized monomers containing quaternary ammonium groups or their precursors are significantly more costly than conventional hydrocarbon polymers, driving up the overall membrane production costs.
Lastly, characterization and standardization of crosslinked QA membranes remain underdeveloped. The lack of standardized testing protocols specifically designed for these materials makes it difficult to compare results across different research groups and establish reliable performance benchmarks, hindering systematic improvement efforts and technology transfer to industrial applications.
State-of-the-Art Crosslinking Methods for Enhanced Durability
01 Crosslinking methods for enhanced durability
Various crosslinking methods can be employed to enhance the durability of quaternary ammonium membranes. These methods include chemical crosslinking with specific agents, thermal crosslinking processes, and radiation-induced crosslinking. The crosslinking creates a three-dimensional network structure that improves mechanical strength, chemical stability, and overall durability of the membranes, making them more resistant to degradation during long-term operation in harsh environments.- Crosslinking methods for enhanced durability: Various crosslinking methods can be employed to enhance the durability of quaternary ammonium membranes. These methods include thermal crosslinking, chemical crosslinking with specific agents, and radiation-induced crosslinking. The crosslinking process creates a three-dimensional network structure that improves mechanical strength, chemical stability, and overall durability of the membranes, making them more resistant to degradation during long-term operation in harsh environments.
- Chemical modifications to improve stability: Chemical modifications of quaternary ammonium membranes can significantly improve their stability and durability. These modifications include incorporating specific functional groups, optimizing the degree of quaternization, and introducing stabilizing additives. By carefully controlling the chemical composition and structure of the membrane, properties such as alkaline stability, thermal resistance, and mechanical strength can be enhanced, leading to improved durability and extended service life.
- Composite membrane structures: Composite structures combining quaternary ammonium membranes with reinforcing materials can significantly enhance durability. These composites often incorporate support layers, nanoparticles, or fiber reinforcements that provide mechanical strength while maintaining ion conductivity. The synergistic effect of different materials in these composite membranes results in improved dimensional stability, reduced swelling, and enhanced resistance to physical degradation, making them suitable for demanding applications.
- Testing and evaluation methods for durability: Specific testing and evaluation methods have been developed to assess the durability of crosslinked quaternary ammonium membranes. These include accelerated aging tests, mechanical stress testing, chemical resistance evaluations, and long-term performance studies. By subjecting membranes to controlled stress conditions and monitoring changes in their properties, researchers can predict service life and identify failure mechanisms, enabling the development of more durable membrane formulations.
- Application-specific durability enhancements: Durability enhancements tailored to specific applications of quaternary ammonium membranes have been developed. These include specialized formulations for fuel cells, water treatment systems, and electrochemical devices. By optimizing the membrane composition and structure according to the specific operating conditions and requirements of each application, such as pH range, temperature, pressure, and exposure to contaminants, the durability and performance of the membranes can be significantly improved for their intended use.
02 Chemical modification strategies
Chemical modification strategies can significantly improve the durability of crosslinked quaternary ammonium membranes. These strategies include incorporating specific functional groups, using reinforcing additives, and optimizing the quaternization process. By carefully selecting chemical modifiers and reaction conditions, the membrane's resistance to chemical degradation, alkaline stability, and mechanical properties can be enhanced, leading to extended service life and improved performance in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Composite membrane structures
Developing composite membrane structures is an effective approach to improve the durability of quaternary ammonium membranes. These structures typically combine the quaternary ammonium functional layer with supporting materials such as polymer substrates, inorganic reinforcements, or hybrid organic-inorganic components. The composite design distributes mechanical stress, prevents swelling, and provides additional barriers against degradation factors, resulting in membranes with superior durability and operational stability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Testing and characterization of membrane durability
Comprehensive testing and characterization methods are essential for evaluating the durability of crosslinked quaternary ammonium membranes. These methods include accelerated aging tests, mechanical strength measurements, chemical stability assessments, and long-term performance evaluations under operational conditions. Advanced analytical techniques such as spectroscopy, microscopy, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy provide insights into degradation mechanisms and help optimize membrane formulations for enhanced durability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Application-specific durability enhancements
Tailoring durability enhancements based on specific applications is crucial for optimizing crosslinked quaternary ammonium membranes. For fuel cells, emphasis is placed on oxidative stability and conductivity retention. In water treatment applications, resistance to fouling and chlorine exposure is prioritized. For electrodialysis, mechanical stability under pressure differentials is enhanced. These application-specific approaches involve customized formulations, specialized additives, and targeted crosslinking strategies to address the unique durability challenges in each operational environment.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in QA Membranes
The research on crosslinked quaternary ammonium membranes for improved durability is in a growth phase, with an expanding market driven by increasing demand for sustainable ion exchange technologies. The global market is projected to reach significant scale as applications in water treatment, fuel cells, and energy storage continue to develop. Leading companies like Tokuyama Corp., Ionomr Innovations, and Nitto Denko are advancing the technology's maturity through innovative approaches to enhance durability and performance. Academic institutions including Zhejiang University and Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics collaborate with industrial players such as Fujifilm, 3M, and Chemours to overcome key technical challenges of membrane degradation and stability. The competitive landscape features both established chemical corporations and specialized startups focusing on environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional fluorinated membranes.
Tokuyama Corp.
Technical Solution: Tokuyama Corporation has developed advanced crosslinked quaternary ammonium membranes utilizing a proprietary multi-stage polymerization process. Their technology incorporates a fluoropolymer backbone with strategically positioned quaternary ammonium functional groups that are subsequently crosslinked using bifunctional agents. This creates a three-dimensional network structure that significantly enhances mechanical stability while maintaining high hydroxide conductivity. The company's latest generation membranes employ a core-shell morphology where hydrophobic domains provide structural integrity while hydrophilic channels facilitate ion transport. Tokuyama has implemented a post-polymerization treatment that reduces susceptibility to nucleophilic attack, addressing one of the primary degradation mechanisms in quaternary ammonium membranes. Their membranes demonstrate stability at temperatures up to 80°C for over 1000 hours in alkaline conditions, representing a substantial improvement over conventional anion exchange membranes.
Strengths: Superior alkaline stability due to proprietary crosslinking chemistry; excellent mechanical durability under hydration/dehydration cycles; maintains conductivity while improving dimensional stability. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to non-crosslinked alternatives; some reduction in ionic conductivity due to crosslinking constraints; limited flexibility which can impact certain applications requiring membrane conformability.
Ionomr Innovations, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ionomr Innovations has pioneered the development of Aemion+™, a revolutionary hydrocarbon-based anion exchange membrane featuring highly crosslinked quaternary ammonium functional groups. Their proprietary technology utilizes a sterically hindered molecular architecture that shields the quaternary ammonium sites from hydroxide attack, significantly enhancing chemical stability. The membrane employs a multi-block copolymer structure with hydrophobic and hydrophilic domains that self-assemble into well-defined ion transport channels. The crosslinking is achieved through a controlled radical polymerization process that creates covalent bonds between polymer chains without sacrificing ion conductivity. Independent testing has demonstrated that Aemion+™ membranes maintain over 90% of their initial conductivity after 1000 hours in 1M KOH at 80°C, outperforming most commercial alternatives. The company has also developed specialized coating techniques that improve the membrane-electrode interface in electrochemical applications, reducing contact resistance and enhancing overall system performance.
Strengths: Exceptional chemical stability in highly alkaline environments; maintains mechanical integrity during repeated hydration cycles; environmentally friendly hydrocarbon chemistry without fluorinated compounds. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost compared to traditional membranes; requires specialized handling during device assembly; limited production scale currently constrains widespread adoption in large-scale applications.
Key Patents and Scientific Breakthroughs in QA Membrane Chemistry
Crosslinked polymer electrolyte fuel cell membranes and their producing process
PatentInactiveUS20060281824A1
Innovation
- A polymer electrolyte membrane with a crosslinking structure is developed through irradiation and multiplex graft polymerization of specific vinyl monomers, including those with halogens, followed by sulfonation and heat treatment to introduce crosslinking in the graft chains, enhancing dimensional stability and preventing gas crossover.
Membrane electrode assembly
PatentWO2025042990A1
Innovation
- Development of novel anion-exchange polymers that can be cross-linked with or without organic or metalorganic moieties, functionalized to form quaternary ammonium groups, enabling their use as membranes or ionomers in electrolyzers. These polymers achieve high current density, durability, and operation at low electrolyte concentrations, while minimizing gas leakage.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of crosslinked quaternary ammonium membranes (QAMs) represents a critical consideration in their development and application. These membranes, while offering superior durability for various separation processes, must be evaluated within a comprehensive sustainability framework. Current manufacturing processes for QAMs often involve petroleum-derived precursors and energy-intensive synthesis methods, raising concerns about their carbon footprint and overall environmental sustainability.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that the environmental burden of QAMs primarily stems from three phases: raw material extraction, membrane fabrication, and end-of-life disposal. The crosslinking agents commonly employed, such as dibromoalkanes and epoxides, may present toxicity concerns if released into aquatic environments. However, the enhanced durability of crosslinked QAMs potentially offsets these impacts by reducing replacement frequency and associated waste generation.
Recent innovations have focused on developing greener synthesis routes for QAMs, including the utilization of bio-based precursors derived from renewable resources. For instance, quaternary ammonium groups can now be incorporated into cellulose-based materials, offering a more sustainable alternative to conventional petroleum-based polymers. Additionally, water-based processing techniques are gradually replacing solvent-intensive methods, significantly reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during manufacturing.
The end-of-life management of QAMs presents both challenges and opportunities. While these membranes are not readily biodegradable due to their crosslinked structure, research into chemical recycling methods shows promise for recovering valuable components. Thermal recovery processes can potentially harness energy from spent membranes, though careful management of potential toxic emissions is essential.
Water purification applications of crosslinked QAMs deliver substantial environmental benefits through improved access to clean water and reduced chemical usage compared to conventional treatment methods. The antimicrobial properties of these membranes can minimize biofouling without requiring additional biocides, further enhancing their environmental profile in water treatment scenarios.
Energy efficiency considerations also factor prominently in sustainability assessments. The improved ion selectivity and conductivity of crosslinked QAMs can enhance the efficiency of electrochemical processes, potentially reducing energy consumption in applications such as fuel cells and electrodialysis systems. This energy savings must be balanced against the energy requirements for membrane production when calculating net environmental impact.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly emphasizing the importance of sustainable materials in water treatment and energy technologies. Future development of crosslinked QAMs will likely be shaped by these evolving standards, driving innovation toward greener synthesis methods, reduced toxicity, and improved recyclability while maintaining the enhanced durability that makes these membranes valuable in the first place.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that the environmental burden of QAMs primarily stems from three phases: raw material extraction, membrane fabrication, and end-of-life disposal. The crosslinking agents commonly employed, such as dibromoalkanes and epoxides, may present toxicity concerns if released into aquatic environments. However, the enhanced durability of crosslinked QAMs potentially offsets these impacts by reducing replacement frequency and associated waste generation.
Recent innovations have focused on developing greener synthesis routes for QAMs, including the utilization of bio-based precursors derived from renewable resources. For instance, quaternary ammonium groups can now be incorporated into cellulose-based materials, offering a more sustainable alternative to conventional petroleum-based polymers. Additionally, water-based processing techniques are gradually replacing solvent-intensive methods, significantly reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during manufacturing.
The end-of-life management of QAMs presents both challenges and opportunities. While these membranes are not readily biodegradable due to their crosslinked structure, research into chemical recycling methods shows promise for recovering valuable components. Thermal recovery processes can potentially harness energy from spent membranes, though careful management of potential toxic emissions is essential.
Water purification applications of crosslinked QAMs deliver substantial environmental benefits through improved access to clean water and reduced chemical usage compared to conventional treatment methods. The antimicrobial properties of these membranes can minimize biofouling without requiring additional biocides, further enhancing their environmental profile in water treatment scenarios.
Energy efficiency considerations also factor prominently in sustainability assessments. The improved ion selectivity and conductivity of crosslinked QAMs can enhance the efficiency of electrochemical processes, potentially reducing energy consumption in applications such as fuel cells and electrodialysis systems. This energy savings must be balanced against the energy requirements for membrane production when calculating net environmental impact.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly emphasizing the importance of sustainable materials in water treatment and energy technologies. Future development of crosslinked QAMs will likely be shaped by these evolving standards, driving innovation toward greener synthesis methods, reduced toxicity, and improved recyclability while maintaining the enhanced durability that makes these membranes valuable in the first place.
Standardization and Testing Protocols for Membrane Durability
The standardization of testing protocols for membrane durability represents a critical challenge in the advancement of crosslinked quaternary ammonium membranes. Currently, the field suffers from inconsistent methodologies across research institutions and industrial laboratories, making direct comparisons between different membrane formulations problematic. Establishing universal testing standards would significantly accelerate development cycles and enable more meaningful benchmarking of membrane performance.
Key durability parameters requiring standardized testing include chemical stability, mechanical integrity, and ion conductivity retention over time. Chemical stability tests should incorporate accelerated aging protocols using standardized concentrations of oxidizing agents such as hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radicals, simulating the harsh conditions these membranes encounter in fuel cell and electrolysis applications. These protocols should specify precise temperature conditions, exposure durations, and analytical methods for quantifying degradation.
Mechanical durability testing requires standardization of hydration-dehydration cycling procedures, as dimensional changes during these cycles represent a primary failure mode for quaternary ammonium membranes. Protocols should define cycle frequency, humidity ranges, and temperature conditions that accurately reflect real-world operating environments. Tensile strength, elongation at break, and tear resistance measurements should follow consistent methodologies to enable reliable comparison between different membrane formulations.
Ion conductivity retention testing presents particular challenges due to the complex interplay between membrane degradation and performance loss. Standardized protocols should include in-situ conductivity measurements during accelerated stress tests, with clearly defined measurement conditions including temperature, humidity, and applied current density. Long-term stability testing should follow consistent timeframes, with measurements taken at regular intervals using calibrated equipment.
International standards organizations including ISO, ASTM, and IEC have begun preliminary work on developing these protocols, but significant gaps remain. Industry consortia involving membrane manufacturers, device integrators, and academic institutions are increasingly collaborating to establish consensus-based testing methodologies. These efforts should prioritize protocols that balance scientific rigor with practical implementation considerations.
The development of reference materials represents another crucial aspect of standardization efforts. Well-characterized benchmark membranes with documented durability profiles would provide valuable calibration points for new testing facilities and methodologies. These reference materials should span a range of performance characteristics to enable meaningful comparisons across the spectrum of membrane technologies under development.
Key durability parameters requiring standardized testing include chemical stability, mechanical integrity, and ion conductivity retention over time. Chemical stability tests should incorporate accelerated aging protocols using standardized concentrations of oxidizing agents such as hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radicals, simulating the harsh conditions these membranes encounter in fuel cell and electrolysis applications. These protocols should specify precise temperature conditions, exposure durations, and analytical methods for quantifying degradation.
Mechanical durability testing requires standardization of hydration-dehydration cycling procedures, as dimensional changes during these cycles represent a primary failure mode for quaternary ammonium membranes. Protocols should define cycle frequency, humidity ranges, and temperature conditions that accurately reflect real-world operating environments. Tensile strength, elongation at break, and tear resistance measurements should follow consistent methodologies to enable reliable comparison between different membrane formulations.
Ion conductivity retention testing presents particular challenges due to the complex interplay between membrane degradation and performance loss. Standardized protocols should include in-situ conductivity measurements during accelerated stress tests, with clearly defined measurement conditions including temperature, humidity, and applied current density. Long-term stability testing should follow consistent timeframes, with measurements taken at regular intervals using calibrated equipment.
International standards organizations including ISO, ASTM, and IEC have begun preliminary work on developing these protocols, but significant gaps remain. Industry consortia involving membrane manufacturers, device integrators, and academic institutions are increasingly collaborating to establish consensus-based testing methodologies. These efforts should prioritize protocols that balance scientific rigor with practical implementation considerations.
The development of reference materials represents another crucial aspect of standardization efforts. Well-characterized benchmark membranes with documented durability profiles would provide valuable calibration points for new testing facilities and methodologies. These reference materials should span a range of performance characteristics to enable meaningful comparisons across the spectrum of membrane technologies under development.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!