Hypochlorous Acid in Advanced Disinfection Technologies
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCl Tech Background
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a key player in advanced disinfection technologies, marking a significant evolution in the field of sanitization and sterilization. This naturally occurring molecule, produced by the human immune system to fight infections, has gained prominence due to its potent antimicrobial properties and environmental friendliness.
The journey of HOCl in disinfection technology began in the early 20th century when it was first recognized for its bactericidal properties. However, its widespread adoption was initially hindered by stability issues and production challenges. The technological breakthrough came in the late 1990s with the development of electrolyzed water systems, which enabled the on-site generation of stable HOCl solutions.
Over the past two decades, research into HOCl has intensified, driven by the growing demand for safer, more effective disinfection methods. This surge in interest has been further accelerated by global health crises, including the recent COVID-19 pandemic, which highlighted the critical need for advanced disinfection technologies.
The evolution of HOCl technology has been marked by several key milestones. These include the refinement of electrolysis techniques to produce higher concentrations of HOCl, the development of stabilization methods to extend shelf life, and the creation of delivery systems that optimize its application across various settings.
Current research in HOCl technology focuses on enhancing its efficacy against a broader spectrum of pathogens, improving its stability for long-term storage, and developing novel application methods. Scientists are exploring the synergistic effects of combining HOCl with other disinfection technologies, such as UV light or nanoparticles, to create more robust sanitization solutions.
The environmental implications of HOCl technology have also become a focal point of research. As a chlorine-based disinfectant that breaks down into simple salt and water, HOCl presents a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional chemical disinfectants. This aspect aligns with the growing global emphasis on sustainable and green technologies.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of HOCl in advanced disinfection technologies appears promising. Researchers are investigating its potential applications beyond traditional disinfection, including wound care, food safety, and water treatment. The goal is to leverage HOCl's unique properties to address complex sanitization challenges across various industries and sectors.
The journey of HOCl in disinfection technology began in the early 20th century when it was first recognized for its bactericidal properties. However, its widespread adoption was initially hindered by stability issues and production challenges. The technological breakthrough came in the late 1990s with the development of electrolyzed water systems, which enabled the on-site generation of stable HOCl solutions.
Over the past two decades, research into HOCl has intensified, driven by the growing demand for safer, more effective disinfection methods. This surge in interest has been further accelerated by global health crises, including the recent COVID-19 pandemic, which highlighted the critical need for advanced disinfection technologies.
The evolution of HOCl technology has been marked by several key milestones. These include the refinement of electrolysis techniques to produce higher concentrations of HOCl, the development of stabilization methods to extend shelf life, and the creation of delivery systems that optimize its application across various settings.
Current research in HOCl technology focuses on enhancing its efficacy against a broader spectrum of pathogens, improving its stability for long-term storage, and developing novel application methods. Scientists are exploring the synergistic effects of combining HOCl with other disinfection technologies, such as UV light or nanoparticles, to create more robust sanitization solutions.
The environmental implications of HOCl technology have also become a focal point of research. As a chlorine-based disinfectant that breaks down into simple salt and water, HOCl presents a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional chemical disinfectants. This aspect aligns with the growing global emphasis on sustainable and green technologies.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of HOCl in advanced disinfection technologies appears promising. Researchers are investigating its potential applications beyond traditional disinfection, including wound care, food safety, and water treatment. The goal is to leverage HOCl's unique properties to address complex sanitization challenges across various industries and sectors.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for advanced disinfection technologies utilizing hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has been experiencing significant growth in recent years. This surge is primarily driven by increasing awareness of the importance of effective disinfection in various sectors, including healthcare, food processing, water treatment, and public spaces.
In the healthcare sector, there is a growing need for powerful yet safe disinfectants to combat hospital-acquired infections and antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Hypochlorous acid-based solutions have gained traction due to their broad-spectrum antimicrobial efficacy and low toxicity profile. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the adoption of advanced disinfection technologies, with HOCl emerging as a preferred choice for surface and air disinfection in healthcare facilities.
The food processing industry is another key market for HOCl-based disinfection technologies. Stringent food safety regulations and consumer demand for chemical-free food preservation methods have led to increased interest in natural, non-toxic disinfectants. Hypochlorous acid's ability to effectively eliminate foodborne pathogens without leaving harmful residues aligns well with these industry requirements.
Water treatment applications represent a substantial market opportunity for HOCl technologies. Municipal water suppliers and industrial users are seeking alternatives to traditional chlorine-based disinfection methods that can address concerns about disinfection by-products and environmental impact. Hypochlorous acid offers a promising solution, providing effective microbial control with fewer harmful by-products.
The hospitality and travel industries have also shown growing interest in advanced disinfection technologies. Hotels, airlines, and public transportation systems are implementing enhanced cleaning protocols to reassure customers and prevent disease transmission. HOCl-based systems are being adopted for their rapid action, ease of application, and compatibility with various surfaces.
Consumer demand for household disinfection products has surged, particularly in the wake of global health crises. This has opened up new market opportunities for HOCl-based products in the form of ready-to-use sprays, wipes, and portable disinfection devices. The non-toxic nature of hypochlorous acid makes it an attractive option for households with children and pets.
As environmental concerns continue to shape consumer preferences and regulatory landscapes, the market for eco-friendly disinfection solutions is expanding. Hypochlorous acid's biodegradability and low environmental impact position it favorably in this growing segment. Industries and consumers alike are increasingly seeking sustainable alternatives to traditional chemical disinfectants, driving further demand for HOCl-based technologies.
In the healthcare sector, there is a growing need for powerful yet safe disinfectants to combat hospital-acquired infections and antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Hypochlorous acid-based solutions have gained traction due to their broad-spectrum antimicrobial efficacy and low toxicity profile. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the adoption of advanced disinfection technologies, with HOCl emerging as a preferred choice for surface and air disinfection in healthcare facilities.
The food processing industry is another key market for HOCl-based disinfection technologies. Stringent food safety regulations and consumer demand for chemical-free food preservation methods have led to increased interest in natural, non-toxic disinfectants. Hypochlorous acid's ability to effectively eliminate foodborne pathogens without leaving harmful residues aligns well with these industry requirements.
Water treatment applications represent a substantial market opportunity for HOCl technologies. Municipal water suppliers and industrial users are seeking alternatives to traditional chlorine-based disinfection methods that can address concerns about disinfection by-products and environmental impact. Hypochlorous acid offers a promising solution, providing effective microbial control with fewer harmful by-products.
The hospitality and travel industries have also shown growing interest in advanced disinfection technologies. Hotels, airlines, and public transportation systems are implementing enhanced cleaning protocols to reassure customers and prevent disease transmission. HOCl-based systems are being adopted for their rapid action, ease of application, and compatibility with various surfaces.
Consumer demand for household disinfection products has surged, particularly in the wake of global health crises. This has opened up new market opportunities for HOCl-based products in the form of ready-to-use sprays, wipes, and portable disinfection devices. The non-toxic nature of hypochlorous acid makes it an attractive option for households with children and pets.
As environmental concerns continue to shape consumer preferences and regulatory landscapes, the market for eco-friendly disinfection solutions is expanding. Hypochlorous acid's biodegradability and low environmental impact position it favorably in this growing segment. Industries and consumers alike are increasingly seeking sustainable alternatives to traditional chemical disinfectants, driving further demand for HOCl-based technologies.
Current Challenges
Despite the promising potential of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in advanced disinfection technologies, several challenges currently hinder its widespread adoption and optimal utilization. One of the primary obstacles is the stability of HOCl solutions. The compound is known to be highly reactive and can quickly degrade, especially when exposed to light, heat, or organic matter. This instability poses significant challenges for storage, transportation, and long-term effectiveness in various applications.
Another critical challenge lies in the production and standardization of HOCl solutions. The concentration and pH of HOCl solutions are crucial factors that determine their efficacy and safety. However, maintaining consistent quality across different production batches and ensuring precise control over these parameters remains a technical hurdle. This variability can lead to inconsistent disinfection results and potential safety concerns in sensitive applications such as healthcare settings or food processing industries.
The scalability of HOCl production for large-scale industrial applications presents another significant challenge. While small-scale electrolysis systems for on-site generation are available, scaling up these processes to meet the demands of large facilities or municipal water treatment plants requires further technological advancements and cost-effective solutions.
Moreover, the lack of comprehensive regulatory guidelines and standardized testing protocols for HOCl-based disinfection systems poses challenges for manufacturers and end-users alike. This regulatory gap can lead to uncertainty in product claims, efficacy comparisons, and safety assessments, potentially slowing down market adoption and innovation in the field.
The environmental impact of HOCl production and use is another area of concern. While HOCl is generally considered environmentally friendly due to its rapid breakdown into harmless byproducts, the energy consumption and potential chemical waste associated with its production process need to be carefully evaluated and optimized to ensure true sustainability.
Additionally, there is a need for more extensive research on the long-term effects of HOCl exposure on various materials and surfaces. While HOCl is known for its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, its potential corrosive effects on certain materials, especially at higher concentrations or with prolonged exposure, require further investigation to develop appropriate application guidelines and material compatibility recommendations.
Lastly, public perception and education about HOCl technology present a challenge. Despite its effectiveness and potential benefits, there is still limited awareness and understanding of HOCl among the general public and even some industry professionals. Overcoming misconceptions and effectively communicating the science behind HOCl disinfection is crucial for wider acceptance and implementation of this technology in various sectors.
Another critical challenge lies in the production and standardization of HOCl solutions. The concentration and pH of HOCl solutions are crucial factors that determine their efficacy and safety. However, maintaining consistent quality across different production batches and ensuring precise control over these parameters remains a technical hurdle. This variability can lead to inconsistent disinfection results and potential safety concerns in sensitive applications such as healthcare settings or food processing industries.
The scalability of HOCl production for large-scale industrial applications presents another significant challenge. While small-scale electrolysis systems for on-site generation are available, scaling up these processes to meet the demands of large facilities or municipal water treatment plants requires further technological advancements and cost-effective solutions.
Moreover, the lack of comprehensive regulatory guidelines and standardized testing protocols for HOCl-based disinfection systems poses challenges for manufacturers and end-users alike. This regulatory gap can lead to uncertainty in product claims, efficacy comparisons, and safety assessments, potentially slowing down market adoption and innovation in the field.
The environmental impact of HOCl production and use is another area of concern. While HOCl is generally considered environmentally friendly due to its rapid breakdown into harmless byproducts, the energy consumption and potential chemical waste associated with its production process need to be carefully evaluated and optimized to ensure true sustainability.
Additionally, there is a need for more extensive research on the long-term effects of HOCl exposure on various materials and surfaces. While HOCl is known for its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, its potential corrosive effects on certain materials, especially at higher concentrations or with prolonged exposure, require further investigation to develop appropriate application guidelines and material compatibility recommendations.
Lastly, public perception and education about HOCl technology present a challenge. Despite its effectiveness and potential benefits, there is still limited awareness and understanding of HOCl among the general public and even some industry professionals. Overcoming misconceptions and effectively communicating the science behind HOCl disinfection is crucial for wider acceptance and implementation of this technology in various sectors.
Existing HOCl Solutions
01 Hypochlorous acid generation and application methods
Various methods for generating and applying hypochlorous acid for disinfection purposes are described. These include electrolytic generation, on-site production systems, and specialized application devices. The techniques aim to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of hypochlorous acid as a disinfectant in different settings.- Hypochlorous acid generation and application methods: Various methods for generating and applying hypochlorous acid for disinfection purposes are described. These include electrolytic generation, on-site production systems, and specialized application devices. The techniques aim to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of hypochlorous acid as a disinfectant in different settings.
- Hypochlorous acid-based disinfection systems: Innovative disinfection systems utilizing hypochlorous acid are presented. These systems incorporate features such as automated dispensing, misting capabilities, and portable designs. They are engineered to provide efficient and widespread disinfection in various environments, including public spaces, healthcare facilities, and industrial settings.
- Hypochlorous acid formulations and compositions: Specific formulations and compositions of hypochlorous acid for enhanced disinfection properties are detailed. These may include stabilized forms of hypochlorous acid, combinations with other disinfecting agents, or specialized additives to improve efficacy or longevity. The formulations are designed to maximize the disinfecting power while maintaining safety and stability.
- Hypochlorous acid disinfection in specific applications: The use of hypochlorous acid for disinfection in targeted applications is explored. This includes specialized equipment for disinfecting medical devices, food processing facilities, water treatment systems, and personal care products. The applications focus on leveraging the unique properties of hypochlorous acid for specific disinfection needs.
- Monitoring and control systems for hypochlorous acid disinfection: Advanced monitoring and control systems for hypochlorous acid disinfection processes are presented. These systems may include sensors for concentration measurement, automated dosing mechanisms, and feedback loops for maintaining optimal disinfection levels. The focus is on ensuring consistent and effective disinfection while optimizing resource usage.
02 Hypochlorous acid-based disinfection systems
Innovative disinfection systems utilizing hypochlorous acid are developed for various applications. These systems may include specialized equipment for producing, storing, and dispensing the disinfectant solution. They are designed to enhance the practicality and effectiveness of hypochlorous acid disinfection in different environments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Hypochlorous acid formulations and compositions
Specific formulations and compositions of hypochlorous acid for disinfection are developed. These may include stabilized solutions, combinations with other active ingredients, or specialized preparations for specific applications. The formulations aim to enhance the stability, efficacy, or targeted use of hypochlorous acid as a disinfectant.Expand Specific Solutions04 Hypochlorous acid disinfection in specific industries
Applications of hypochlorous acid disinfection in specific industries or sectors are explored. This includes use in healthcare facilities, food processing, agriculture, and water treatment. The adaptations and methods for using hypochlorous acid in these specific contexts are described, addressing unique challenges and requirements of each industry.Expand Specific Solutions05 Hypochlorous acid disinfection devices and equipment
Various devices and equipment designed specifically for hypochlorous acid disinfection are developed. These may include sprayers, foggers, automated dispensing systems, or portable disinfection units. The equipment is designed to optimize the application and effectiveness of hypochlorous acid in different settings and for various disinfection needs.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The research on hypochlorous acid in advanced disinfection technologies is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global market for disinfection technologies is expanding, driven by heightened awareness of hygiene and sanitation. Companies like Annihilare Medical Systems, Parasol Medical, and PCT Ltd. are at the forefront, developing innovative applications for hypochlorous acid in medical and commercial settings. Established players such as Fresenius Medical Care and Kao Corp. are also investing in this technology. The field is seeing a blend of specialized startups and diversified conglomerates, indicating a maturing but still evolving technological landscape with significant potential for further innovation and market expansion.
Guangzhou Taidaoan Medical Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Guangzhou Taidaoan Medical Technology has focused on developing HOCl-based disinfection solutions for healthcare settings. Their research has led to the creation of a stabilized HOCl formulation that maintains its efficacy for up to 12 months. The company's HOCl products are produced using a controlled electrolysis process that ensures consistent quality and purity. Taidaoan has also developed specialized application methods for their HOCl solutions, including fine mist sprayers and foggers designed for use in hospitals and other medical facilities[10]. Their technology has been shown to be effective against a wide range of pathogens, including antibiotic-resistant bacteria and viruses[11].
Strengths: Specialized solutions for healthcare settings; extended shelf life; diverse application methods. Weaknesses: May have limited applications outside of healthcare; potential regulatory challenges in different markets.
ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS, INC.
Technical Solution: Annihilare Medical Systems has developed a patented HOCl generation system that produces a highly pure and stable form of HOCl called Annihilyte®. Their technology utilizes a proprietary electrolysis process that minimizes the formation of byproducts, resulting in a HOCl solution with superior antimicrobial efficacy and safety profile. The Annihilyte® system can produce HOCl solutions with concentrations ranging from 100-500 ppm, suitable for various medical and industrial applications[8]. Annihilare has also developed a unique delivery system that maintains the stability of HOCl during application, ensuring consistent efficacy even in challenging environments[9].
Strengths: High purity HOCl production; versatile concentration range; specialized delivery systems. Weaknesses: May have higher initial costs due to proprietary technology; requires specific training for optimal use.
Core HOCl Innovations
Technology for producing a disinfectant for neutralizing viruses, bacteria and other microorganisms
PatentWO2020019047A1
Innovation
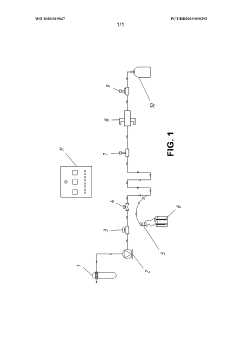
- The production of hypochlorous acid through electrochemical synthesis in a saline solution under neutral pH, utilizing a reactor system that allows for controlled and reproducible biocidal solution production, which effectively penetrates cell membranes to eliminate biofilms and microorganisms without resistance development.
System and method for effective cleaning and disinfecting protocol
PatentInactiveGB2594696A
Innovation
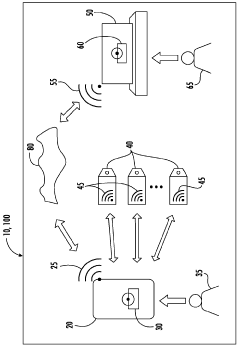
- A system and method utilizing a portable computing device with RFID/NFC technology to track and verify adherence to cleaning protocols, ensuring the use of effective disinfectants within their lifecycle, including Hypochlorous acid, through authentication, data management, and reporting functionalities.
Safety Regulations
The safety regulations surrounding the use of hypochlorous acid in advanced disinfection technologies are crucial for ensuring public health and environmental protection. These regulations typically cover various aspects, including production, storage, handling, application, and disposal of hypochlorous acid solutions.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a key role in regulating hypochlorous acid as a disinfectant. The EPA requires that hypochlorous acid products used for disinfection purposes be registered under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). This registration process involves rigorous testing to evaluate the product's efficacy and safety profile.
Occupational safety is another important aspect of hypochlorous acid regulations. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established guidelines for workplace exposure limits to ensure worker safety. These guidelines include permissible exposure limits (PELs) and recommended exposure limits (RELs) for chlorine compounds, which are relevant to hypochlorous acid production and handling.
Transportation of hypochlorous acid solutions is regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOT) in the United States. The DOT classifies hypochlorous acid solutions based on their concentration and potential hazards, determining specific packaging, labeling, and shipping requirements to minimize risks during transport.
Internationally, the use of hypochlorous acid in disinfection technologies is subject to varying regulations across different countries and regions. The European Union, for instance, regulates hypochlorous acid under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), which requires thorough assessment of the substance's safety and efficacy before market authorization.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the use of hypochlorous acid. Many countries have established guidelines for the discharge of chlorine-containing compounds into water bodies to protect aquatic ecosystems. These regulations often specify maximum allowable concentrations and require treatment of wastewater containing hypochlorous acid before release into the environment.
As the use of hypochlorous acid in advanced disinfection technologies continues to grow, regulatory bodies are adapting their frameworks to address emerging concerns and new applications. This includes ongoing research into potential long-term effects of hypochlorous acid exposure and the development of more precise testing methods for residual chlorine compounds in various environments.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a key role in regulating hypochlorous acid as a disinfectant. The EPA requires that hypochlorous acid products used for disinfection purposes be registered under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). This registration process involves rigorous testing to evaluate the product's efficacy and safety profile.
Occupational safety is another important aspect of hypochlorous acid regulations. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established guidelines for workplace exposure limits to ensure worker safety. These guidelines include permissible exposure limits (PELs) and recommended exposure limits (RELs) for chlorine compounds, which are relevant to hypochlorous acid production and handling.
Transportation of hypochlorous acid solutions is regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOT) in the United States. The DOT classifies hypochlorous acid solutions based on their concentration and potential hazards, determining specific packaging, labeling, and shipping requirements to minimize risks during transport.
Internationally, the use of hypochlorous acid in disinfection technologies is subject to varying regulations across different countries and regions. The European Union, for instance, regulates hypochlorous acid under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), which requires thorough assessment of the substance's safety and efficacy before market authorization.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the use of hypochlorous acid. Many countries have established guidelines for the discharge of chlorine-containing compounds into water bodies to protect aquatic ecosystems. These regulations often specify maximum allowable concentrations and require treatment of wastewater containing hypochlorous acid before release into the environment.
As the use of hypochlorous acid in advanced disinfection technologies continues to grow, regulatory bodies are adapting their frameworks to address emerging concerns and new applications. This includes ongoing research into potential long-term effects of hypochlorous acid exposure and the development of more precise testing methods for residual chlorine compounds in various environments.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in advanced disinfection technologies is a critical consideration for its widespread adoption. HOCl is generally regarded as an environmentally friendly disinfectant due to its natural occurrence in biological systems and its rapid breakdown into harmless components.
One of the primary environmental advantages of HOCl is its decomposition process. When released into the environment, HOCl quickly breaks down into water, oxygen, and salt, leaving no harmful residues or by-products. This characteristic makes it significantly less harmful to ecosystems compared to traditional chlorine-based disinfectants, which can form toxic chlorinated organic compounds.
The production of HOCl through electrolysis of salt water is another environmentally beneficial aspect. This process requires only salt, water, and electricity, reducing the need for transportation and storage of hazardous chemicals. Furthermore, on-site generation of HOCl minimizes packaging waste and carbon emissions associated with the distribution of pre-made disinfectants.
In aquatic environments, HOCl demonstrates a lower impact on marine life compared to other disinfectants. Its rapid degradation means that it does not persist in water bodies, reducing the risk of long-term ecological damage. This property is particularly important for applications in water treatment facilities and aquaculture.
However, it is essential to note that while HOCl is less harmful than many alternatives, its use still requires careful management. Overuse or improper application can lead to temporary pH changes in water systems, potentially affecting sensitive aquatic organisms. Therefore, proper dosing and monitoring are crucial to minimize any negative environmental impacts.
The use of HOCl in agriculture presents both benefits and challenges from an environmental perspective. As a natural disinfectant, it can reduce the reliance on synthetic pesticides and fungicides, supporting more sustainable farming practices. However, large-scale application must be carefully controlled to prevent soil pH imbalances or disruption of beneficial microbial communities.
In indoor environments, HOCl contributes to improved air quality by effectively eliminating airborne pathogens without introducing harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other pollutants. This makes it an attractive option for use in hospitals, schools, and other public spaces where air quality is a significant concern.
As research continues, the full scope of HOCl's environmental impact is still being explored. Current studies suggest that its widespread adoption in disinfection technologies could lead to a significant reduction in the environmental footprint of sanitation practices across various industries. However, ongoing monitoring and assessment are necessary to ensure that its use remains aligned with sustainable environmental practices.
One of the primary environmental advantages of HOCl is its decomposition process. When released into the environment, HOCl quickly breaks down into water, oxygen, and salt, leaving no harmful residues or by-products. This characteristic makes it significantly less harmful to ecosystems compared to traditional chlorine-based disinfectants, which can form toxic chlorinated organic compounds.
The production of HOCl through electrolysis of salt water is another environmentally beneficial aspect. This process requires only salt, water, and electricity, reducing the need for transportation and storage of hazardous chemicals. Furthermore, on-site generation of HOCl minimizes packaging waste and carbon emissions associated with the distribution of pre-made disinfectants.
In aquatic environments, HOCl demonstrates a lower impact on marine life compared to other disinfectants. Its rapid degradation means that it does not persist in water bodies, reducing the risk of long-term ecological damage. This property is particularly important for applications in water treatment facilities and aquaculture.
However, it is essential to note that while HOCl is less harmful than many alternatives, its use still requires careful management. Overuse or improper application can lead to temporary pH changes in water systems, potentially affecting sensitive aquatic organisms. Therefore, proper dosing and monitoring are crucial to minimize any negative environmental impacts.
The use of HOCl in agriculture presents both benefits and challenges from an environmental perspective. As a natural disinfectant, it can reduce the reliance on synthetic pesticides and fungicides, supporting more sustainable farming practices. However, large-scale application must be carefully controlled to prevent soil pH imbalances or disruption of beneficial microbial communities.
In indoor environments, HOCl contributes to improved air quality by effectively eliminating airborne pathogens without introducing harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other pollutants. This makes it an attractive option for use in hospitals, schools, and other public spaces where air quality is a significant concern.
As research continues, the full scope of HOCl's environmental impact is still being explored. Current studies suggest that its widespread adoption in disinfection technologies could lead to a significant reduction in the environmental footprint of sanitation practices across various industries. However, ongoing monitoring and assessment are necessary to ensure that its use remains aligned with sustainable environmental practices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!