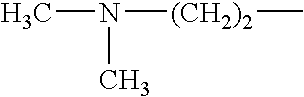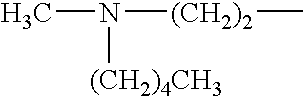Sodium Bisulfate Benefits for Organic Compound Processing
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
NaHSO4 in Organic Synthesis: Background and Objectives
Sodium bisulfate (NaHSO4) has emerged as a versatile and efficient reagent in organic synthesis, attracting significant attention from researchers and industry professionals alike. This compound, also known as sodium hydrogen sulfate or sodium acid sulfate, has a rich history dating back to its discovery in the early 19th century. Initially utilized primarily in industrial applications, NaHSO4 has gradually found its way into the realm of organic chemistry, where its unique properties have proven invaluable in various synthetic processes.
The evolution of NaHSO4 in organic synthesis can be traced through several key milestones. In the mid-20th century, researchers began to explore its potential as a catalyst and reagent in organic reactions. The compound's ability to act as both a Brønsted acid and a mild oxidizing agent opened up new possibilities for selective transformations. As synthetic methodologies advanced, NaHSO4 found applications in areas such as esterification, protection-deprotection sequences, and rearrangement reactions.
The growing interest in green chemistry and sustainable processes has further propelled the use of NaHSO4 in recent years. Its relatively low toxicity, ease of handling, and potential for recycling align well with the principles of environmentally friendly synthesis. This has led to increased research efforts aimed at expanding the scope of NaHSO4-mediated reactions and optimizing its use in various organic transformations.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to provide a comprehensive overview of the benefits and applications of sodium bisulfate in organic compound processing. By examining the current state of the art and identifying emerging trends, we aim to elucidate the full potential of NaHSO4 as a versatile tool in organic synthesis. This includes assessing its advantages over traditional reagents, exploring novel reaction pathways, and evaluating its role in addressing challenges in modern organic chemistry.
Furthermore, this report seeks to highlight the technological advancements that have enhanced the utility of NaHSO4 in organic synthesis. From improved formulations and delivery methods to innovative reactor designs, we will explore how these developments have contributed to the compound's growing prominence in both academic and industrial settings. By analyzing these aspects, we aim to provide valuable insights that can guide future research directions and inform strategic decisions in the field of organic synthesis.
The evolution of NaHSO4 in organic synthesis can be traced through several key milestones. In the mid-20th century, researchers began to explore its potential as a catalyst and reagent in organic reactions. The compound's ability to act as both a Brønsted acid and a mild oxidizing agent opened up new possibilities for selective transformations. As synthetic methodologies advanced, NaHSO4 found applications in areas such as esterification, protection-deprotection sequences, and rearrangement reactions.
The growing interest in green chemistry and sustainable processes has further propelled the use of NaHSO4 in recent years. Its relatively low toxicity, ease of handling, and potential for recycling align well with the principles of environmentally friendly synthesis. This has led to increased research efforts aimed at expanding the scope of NaHSO4-mediated reactions and optimizing its use in various organic transformations.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to provide a comprehensive overview of the benefits and applications of sodium bisulfate in organic compound processing. By examining the current state of the art and identifying emerging trends, we aim to elucidate the full potential of NaHSO4 as a versatile tool in organic synthesis. This includes assessing its advantages over traditional reagents, exploring novel reaction pathways, and evaluating its role in addressing challenges in modern organic chemistry.
Furthermore, this report seeks to highlight the technological advancements that have enhanced the utility of NaHSO4 in organic synthesis. From improved formulations and delivery methods to innovative reactor designs, we will explore how these developments have contributed to the compound's growing prominence in both academic and industrial settings. By analyzing these aspects, we aim to provide valuable insights that can guide future research directions and inform strategic decisions in the field of organic synthesis.
Market Analysis for NaHSO4 in Chemical Industry
The global market for sodium bisulfate (NaHSO4) in the chemical industry has been experiencing steady growth, driven by its versatile applications in organic compound processing and other sectors. The compound's unique properties as an acidic salt make it valuable for pH adjustment, cleaning, and as a reagent in various chemical processes.
In recent years, the demand for sodium bisulfate has been particularly strong in the water treatment sector, where it is used for pH control and as a disinfectant. The growing emphasis on water quality and environmental regulations has contributed to increased adoption of NaHSO4 in municipal water treatment facilities and industrial wastewater management systems.
The food and beverage industry represents another significant market for sodium bisulfate. Its use as a preservative and pH regulator in food products has seen consistent demand, especially in regions with stringent food safety regulations. The compound's effectiveness in controlling microbial growth while maintaining product quality has made it a preferred choice for many food manufacturers.
In the realm of organic compound processing, sodium bisulfate has gained traction due to its ability to catalyze certain reactions and serve as an acidifying agent. This has led to increased usage in the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and specialty chemicals. The pharmaceutical industry, in particular, has shown a growing interest in NaHSO4 for its role in drug synthesis and formulation processes.
The market for sodium bisulfate is geographically diverse, with significant consumption in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific regions. Developing economies in Asia, particularly China and India, have emerged as key growth markets due to rapid industrialization and increasing investments in chemical manufacturing and water treatment infrastructure.
Despite positive growth trends, the sodium bisulfate market faces challenges from alternative products and environmental concerns. Substitutes such as sulfuric acid and other acidic compounds compete in certain applications, while environmental regulations regarding sulfur emissions and waste disposal impact the production and use of NaHSO4 in some regions.
Looking ahead, the market for sodium bisulfate in the chemical industry is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Innovations in production processes, development of high-purity grades for specialized applications, and expansion into new geographical markets are likely to drive future demand. Additionally, the increasing focus on sustainable and eco-friendly chemical processes may create opportunities for sodium bisulfate as a less hazardous alternative to stronger acids in certain applications.
In recent years, the demand for sodium bisulfate has been particularly strong in the water treatment sector, where it is used for pH control and as a disinfectant. The growing emphasis on water quality and environmental regulations has contributed to increased adoption of NaHSO4 in municipal water treatment facilities and industrial wastewater management systems.
The food and beverage industry represents another significant market for sodium bisulfate. Its use as a preservative and pH regulator in food products has seen consistent demand, especially in regions with stringent food safety regulations. The compound's effectiveness in controlling microbial growth while maintaining product quality has made it a preferred choice for many food manufacturers.
In the realm of organic compound processing, sodium bisulfate has gained traction due to its ability to catalyze certain reactions and serve as an acidifying agent. This has led to increased usage in the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and specialty chemicals. The pharmaceutical industry, in particular, has shown a growing interest in NaHSO4 for its role in drug synthesis and formulation processes.
The market for sodium bisulfate is geographically diverse, with significant consumption in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific regions. Developing economies in Asia, particularly China and India, have emerged as key growth markets due to rapid industrialization and increasing investments in chemical manufacturing and water treatment infrastructure.
Despite positive growth trends, the sodium bisulfate market faces challenges from alternative products and environmental concerns. Substitutes such as sulfuric acid and other acidic compounds compete in certain applications, while environmental regulations regarding sulfur emissions and waste disposal impact the production and use of NaHSO4 in some regions.
Looking ahead, the market for sodium bisulfate in the chemical industry is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Innovations in production processes, development of high-purity grades for specialized applications, and expansion into new geographical markets are likely to drive future demand. Additionally, the increasing focus on sustainable and eco-friendly chemical processes may create opportunities for sodium bisulfate as a less hazardous alternative to stronger acids in certain applications.
Current Applications and Challenges in Organic Processing
Sodium bisulfate has emerged as a versatile compound in organic processing, finding applications across various industries. In the food sector, it serves as an effective acidulant and preservative, enhancing flavor profiles while extending shelf life. The pharmaceutical industry utilizes sodium bisulfate for pH adjustment in drug formulations and as a cleaning agent in equipment sterilization. In water treatment, it acts as a pH reducer and helps control algae growth in swimming pools and industrial water systems.
The textile industry employs sodium bisulfate in dyeing processes, where it aids in color fixation and fabric treatment. In the chemical manufacturing sector, it plays a crucial role as a reducing agent and catalyst in numerous organic reactions. Additionally, sodium bisulfate finds use in personal care products as a pH adjuster and in the mining industry for mineral processing.
Despite its widespread applications, several challenges persist in the use of sodium bisulfate for organic processing. One primary concern is its corrosive nature, which necessitates careful handling and storage. This property can lead to equipment degradation over time, increasing maintenance costs and potential safety hazards. The compound's high acidity also poses environmental concerns, requiring proper waste management and disposal protocols to prevent ecological damage.
Another challenge lies in achieving precise pH control in various applications. While sodium bisulfate is effective in lowering pH, maintaining consistent levels across different batches or processes can be difficult due to variations in raw materials and environmental conditions. This inconsistency can affect product quality and process efficiency, particularly in industries with stringent quality control requirements.
The hygroscopic nature of sodium bisulfate presents storage and handling challenges. Exposure to moisture can lead to caking and reduced effectiveness, necessitating specialized storage facilities and handling procedures. This characteristic also complicates its use in certain formulations, particularly in the food and pharmaceutical industries, where moisture control is critical.
In the realm of organic synthesis, while sodium bisulfate offers advantages as a catalyst and reducing agent, optimizing reaction conditions to maximize yield and selectivity remains a challenge. Researchers continue to explore novel methodologies to enhance its catalytic efficiency and broaden its applicability in complex organic transformations.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, industries face the challenge of developing more sustainable practices in sodium bisulfate usage. This includes finding ways to reduce its environmental footprint, improve recovery and recycling processes, and explore eco-friendly alternatives where possible. Balancing these environmental concerns with the compound's beneficial properties presents an ongoing challenge for researchers and industry professionals alike.
The textile industry employs sodium bisulfate in dyeing processes, where it aids in color fixation and fabric treatment. In the chemical manufacturing sector, it plays a crucial role as a reducing agent and catalyst in numerous organic reactions. Additionally, sodium bisulfate finds use in personal care products as a pH adjuster and in the mining industry for mineral processing.
Despite its widespread applications, several challenges persist in the use of sodium bisulfate for organic processing. One primary concern is its corrosive nature, which necessitates careful handling and storage. This property can lead to equipment degradation over time, increasing maintenance costs and potential safety hazards. The compound's high acidity also poses environmental concerns, requiring proper waste management and disposal protocols to prevent ecological damage.
Another challenge lies in achieving precise pH control in various applications. While sodium bisulfate is effective in lowering pH, maintaining consistent levels across different batches or processes can be difficult due to variations in raw materials and environmental conditions. This inconsistency can affect product quality and process efficiency, particularly in industries with stringent quality control requirements.
The hygroscopic nature of sodium bisulfate presents storage and handling challenges. Exposure to moisture can lead to caking and reduced effectiveness, necessitating specialized storage facilities and handling procedures. This characteristic also complicates its use in certain formulations, particularly in the food and pharmaceutical industries, where moisture control is critical.
In the realm of organic synthesis, while sodium bisulfate offers advantages as a catalyst and reducing agent, optimizing reaction conditions to maximize yield and selectivity remains a challenge. Researchers continue to explore novel methodologies to enhance its catalytic efficiency and broaden its applicability in complex organic transformations.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, industries face the challenge of developing more sustainable practices in sodium bisulfate usage. This includes finding ways to reduce its environmental footprint, improve recovery and recycling processes, and explore eco-friendly alternatives where possible. Balancing these environmental concerns with the compound's beneficial properties presents an ongoing challenge for researchers and industry professionals alike.
Existing Methodologies for NaHSO4 Application
01 pH adjustment and acidity control
Sodium bisulfate is widely used as a pH adjuster and acidity control agent in various industries. It effectively lowers the pH of solutions, making it useful in water treatment, food processing, and industrial cleaning applications. Its ability to control acidity helps in preserving products and maintaining desired chemical properties.- pH adjustment and acidity control: Sodium bisulfate is widely used as a pH adjuster and acidity control agent in various industries. It effectively lowers the pH of solutions, making it useful in water treatment, food processing, and industrial cleaning applications. Its ability to control acidity helps in preserving products and maintaining desired chemical properties.
- Cleaning and disinfection: Sodium bisulfate serves as an effective cleaning and disinfecting agent. It is used in household and industrial cleaning products, swimming pool treatments, and sanitizers. Its acidic properties help in removing mineral deposits, scale, and stains, while also providing antimicrobial effects.
- Food preservation and processing: In the food industry, sodium bisulfate is utilized as a preservative and processing aid. It helps prevent microbial growth, maintains color, and extends shelf life in various food products. Additionally, it can be used as a leavening agent in baking applications and for pH adjustment in beverage production.
- Water treatment and purification: Sodium bisulfate is beneficial in water treatment processes. It is used for pH adjustment in drinking water and wastewater treatment, helps in the removal of chlorine from water, and aids in the precipitation of heavy metals. Its application in swimming pool maintenance helps balance water chemistry and improve water quality.
- Industrial and agricultural applications: Sodium bisulfate finds various applications in industrial processes and agriculture. It is used in metal surface treatment, as a flux in metallurgy, and as a reducing agent in chemical reactions. In agriculture, it can be used for soil pH adjustment and as a component in fertilizers. Its versatility makes it valuable in diverse industrial sectors.
02 Cleaning and disinfection
Sodium bisulfate serves as an effective cleaning and disinfecting agent. It is used in household and industrial cleaning products, swimming pool treatments, and sanitation systems. Its acidic nature helps in removing mineral deposits, scale, and stains, while also providing antimicrobial properties that aid in disinfection.Expand Specific Solutions03 Food preservation and flavor enhancement
In the food industry, sodium bisulfate is utilized as a preservative and flavor enhancer. It helps extend the shelf life of various food products by inhibiting microbial growth. Additionally, it can be used to adjust the acidity of foods, enhancing their flavor profile and improving overall taste.Expand Specific Solutions04 Water treatment and purification
Sodium bisulfate plays a crucial role in water treatment and purification processes. It is used to adjust the pH of water, remove alkalinity, and control the growth of algae and bacteria in swimming pools and industrial water systems. Its application helps maintain water quality and prevents scale formation in pipes and equipment.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial and agricultural applications
Sodium bisulfate finds various applications in industrial and agricultural sectors. It is used in metal processing, textile manufacturing, and as a soil amendment in agriculture. Its acidic properties make it useful for metal etching, dye-setting in textiles, and adjusting soil pH for optimal plant growth.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers and Suppliers of NaHSO4
The research on sodium bisulfate benefits for organic compound processing is in a developing stage, with the market showing potential for growth. The technology's maturity varies across different applications, with some areas more advanced than others. Key players like Kemira Oyj, China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., and Applied Biosystems LLC are driving innovation in this field. The market size is expanding as industries recognize the versatility of sodium bisulfate in organic processing. Companies such as BASF Corp. and Procter & Gamble Co. are exploring new applications, while research institutions like MIT and Central South University are contributing to the scientific understanding of sodium bisulfate's properties and potential uses in organic compound processing.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an innovative approach for using sodium bisulfate in organic compound processing. Their method involves a two-step process: first, sodium bisulfate is used as a catalyst in the esterification of organic acids, significantly improving reaction rates and yields[1]. Second, they employ sodium bisulfate in a novel extraction technique for separating aromatic compounds from aliphatic mixtures, enhancing the purity of final products[3]. Sinopec has also implemented a regeneration system for sodium bisulfate, allowing for its repeated use in industrial processes, thereby reducing waste and operational costs[5]. Their research has shown that sodium bisulfate can effectively remove sulfur compounds from petroleum products, leading to cleaner fuels and reduced environmental impact[7].
Strengths: Cost-effective catalyst, improved reaction efficiency, and environmentally friendly approach to sulfur removal. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for handling and regeneration of sodium bisulfate, potential corrosion issues in certain process conditions.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has made significant strides in utilizing sodium bisulfate for organic compound processing. They have developed a novel approach for using sodium bisulfate as a catalyst in the production of biodegradable plastics from renewable resources[2]. This process not only improves the efficiency of polymerization but also enhances the biodegradability of the final product[4]. BASF has also implemented sodium bisulfate in their water treatment solutions, where it acts as a pH adjuster and helps in the removal of organic contaminants through coagulation and flocculation processes[6]. In the field of organic synthesis, BASF researchers have discovered that sodium bisulfate can serve as an effective desulfurizing agent for certain organosulfur compounds, leading to cleaner and more efficient production of fine chemicals[8]. Additionally, they have explored the use of sodium bisulfate in the modification of cellulose-based materials, improving their properties for various industrial applications[10].
Strengths: Sustainable solutions, improved process efficiency, and versatile applications in multiple industries. Weaknesses: May require optimization for specific organic compounds, potential for increased salt content in some processes.
Innovative NaHSO4-based Organic Reactions
Novel process
PatentInactiveUS20090198062A1
Innovation
- A process involving the phosphorylation of carboxylic acids with phosphorous acid and a phosphorous halide in the presence of a polar organic solvent, followed by recrystallization using water and a polar organic solvent, which avoids the use of methane sulfonic acid, sulfolane, and other restricted solvents, allowing for a single-pot reaction and efficient production of bisphosphonic acid monosodium salts with high yield and purity.
Method of making sulfide compounds
PatentActiveUS20150246928A1
Innovation
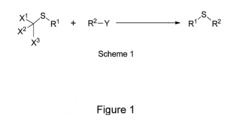
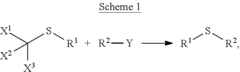
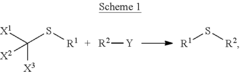
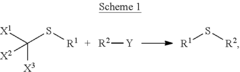
- A method involving Scheme 1, where X1, X2, and X3 are selected from F, Cl, Br, and I, and R1 and R2 from alkyl, cycloalkyl, alkenyl, etc., with optional covalent linking and potentially no catalyst, allows for the formation of sulfide compounds with improved flexibility and yield.
Environmental Impact of NaHSO4 in Chemical Processes
The use of sodium bisulfate (NaHSO4) in chemical processes has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. As an acidic salt, NaHSO4 can contribute to the acidification of aquatic ecosystems if released into water bodies without proper treatment. This can lead to changes in pH levels, potentially harming aquatic life and disrupting ecosystem balance.
However, when used appropriately in organic compound processing, NaHSO4 can offer environmental benefits. Its ability to act as a pH regulator and catalyst in various chemical reactions can lead to more efficient processes, potentially reducing the overall environmental footprint of industrial operations. By enhancing reaction rates and yields, NaHSO4 can minimize waste production and energy consumption, aligning with principles of green chemistry.
In wastewater treatment applications, NaHSO4 has shown promise in removing heavy metals and other contaminants. This capability can contribute to improved water quality and reduced environmental pollution. Additionally, its use in certain desulfurization processes can help mitigate sulfur dioxide emissions, a significant contributor to air pollution and acid rain.
The production of NaHSO4 itself has environmental considerations. It is typically manufactured as a by-product of other industrial processes, such as the production of sodium hydroxide. This dual-use nature can be viewed as an efficient use of resources, reducing waste from other chemical manufacturing processes.
However, the transportation and storage of NaHSO4 present potential environmental risks. Accidental spills or improper handling can lead to localized soil and water contamination. Proper safety measures and handling protocols are essential to mitigate these risks and prevent environmental damage.
In terms of lifecycle assessment, the environmental impact of NaHSO4 in chemical processes must be evaluated holistically. This includes considering its production, transportation, use, and disposal. While it offers benefits in certain applications, its overall environmental footprint depends on the specific context of its use and the efficiency of the processes it facilitates.
As industries strive for more sustainable practices, the role of NaHSO4 in chemical processes continues to evolve. Research into greener alternatives and optimized usage strategies is ongoing, aiming to maximize the benefits of NaHSO4 while minimizing its potential negative environmental impacts. This balanced approach is crucial for ensuring that the use of NaHSO4 aligns with broader environmental sustainability goals in the chemical industry.
However, when used appropriately in organic compound processing, NaHSO4 can offer environmental benefits. Its ability to act as a pH regulator and catalyst in various chemical reactions can lead to more efficient processes, potentially reducing the overall environmental footprint of industrial operations. By enhancing reaction rates and yields, NaHSO4 can minimize waste production and energy consumption, aligning with principles of green chemistry.
In wastewater treatment applications, NaHSO4 has shown promise in removing heavy metals and other contaminants. This capability can contribute to improved water quality and reduced environmental pollution. Additionally, its use in certain desulfurization processes can help mitigate sulfur dioxide emissions, a significant contributor to air pollution and acid rain.
The production of NaHSO4 itself has environmental considerations. It is typically manufactured as a by-product of other industrial processes, such as the production of sodium hydroxide. This dual-use nature can be viewed as an efficient use of resources, reducing waste from other chemical manufacturing processes.
However, the transportation and storage of NaHSO4 present potential environmental risks. Accidental spills or improper handling can lead to localized soil and water contamination. Proper safety measures and handling protocols are essential to mitigate these risks and prevent environmental damage.
In terms of lifecycle assessment, the environmental impact of NaHSO4 in chemical processes must be evaluated holistically. This includes considering its production, transportation, use, and disposal. While it offers benefits in certain applications, its overall environmental footprint depends on the specific context of its use and the efficiency of the processes it facilitates.
As industries strive for more sustainable practices, the role of NaHSO4 in chemical processes continues to evolve. Research into greener alternatives and optimized usage strategies is ongoing, aiming to maximize the benefits of NaHSO4 while minimizing its potential negative environmental impacts. This balanced approach is crucial for ensuring that the use of NaHSO4 aligns with broader environmental sustainability goals in the chemical industry.
Safety Protocols for Handling NaHSO4 in Labs
Handling sodium bisulfate (NaHSO4) in laboratory settings requires strict adherence to safety protocols to minimize risks associated with its corrosive and acidic properties. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential when working with NaHSO4. This includes wearing chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles or a face shield, and a lab coat or chemical-resistant apron. Closed-toe shoes are also mandatory to protect against accidental spills.
Adequate ventilation is crucial when handling NaHSO4. All operations involving this compound should be conducted in a fume hood to prevent inhalation of any vapors or dust particles. If a fume hood is not available, respiratory protection may be necessary, especially when dealing with large quantities or in poorly ventilated areas.
Storage of NaHSO4 requires careful consideration. It should be kept in tightly sealed containers made of compatible materials, such as polyethylene or polypropylene, and stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Segregation from incompatible substances, particularly strong bases, oxidizing agents, and metals, is essential to prevent dangerous reactions.
Proper labeling of all containers containing NaHSO4 is critical. Labels should clearly indicate the chemical name, concentration, hazard warnings, and date of preparation or receipt. This ensures that all laboratory personnel are aware of the contents and associated risks.
Spill response procedures must be established and communicated to all lab workers. Small spills can be neutralized with sodium bicarbonate or other suitable bases, followed by absorption with an inert material. Larger spills may require professional hazardous waste disposal services. Eye wash stations and safety showers should be readily accessible in case of accidental exposure.
Training is a fundamental aspect of safety protocols. All personnel working with NaHSO4 should receive comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, proper handling techniques, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher courses and safety drills can help maintain awareness and preparedness.
Documentation of safety procedures, including Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for NaHSO4, must be readily available to all laboratory staff. These documents should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect any changes in regulations or best practices.
Waste disposal of NaHSO4 and its solutions requires careful management. Neutralization before disposal is often necessary, and compliance with local, state, and federal regulations for hazardous waste disposal is mandatory. Proper documentation of waste generation and disposal is essential for regulatory compliance and environmental protection.
By implementing and strictly adhering to these safety protocols, laboratories can significantly reduce the risks associated with handling sodium bisulfate, ensuring a safer working environment for all personnel involved in organic compound processing research and applications.
Adequate ventilation is crucial when handling NaHSO4. All operations involving this compound should be conducted in a fume hood to prevent inhalation of any vapors or dust particles. If a fume hood is not available, respiratory protection may be necessary, especially when dealing with large quantities or in poorly ventilated areas.
Storage of NaHSO4 requires careful consideration. It should be kept in tightly sealed containers made of compatible materials, such as polyethylene or polypropylene, and stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Segregation from incompatible substances, particularly strong bases, oxidizing agents, and metals, is essential to prevent dangerous reactions.
Proper labeling of all containers containing NaHSO4 is critical. Labels should clearly indicate the chemical name, concentration, hazard warnings, and date of preparation or receipt. This ensures that all laboratory personnel are aware of the contents and associated risks.
Spill response procedures must be established and communicated to all lab workers. Small spills can be neutralized with sodium bicarbonate or other suitable bases, followed by absorption with an inert material. Larger spills may require professional hazardous waste disposal services. Eye wash stations and safety showers should be readily accessible in case of accidental exposure.
Training is a fundamental aspect of safety protocols. All personnel working with NaHSO4 should receive comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, proper handling techniques, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher courses and safety drills can help maintain awareness and preparedness.
Documentation of safety procedures, including Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for NaHSO4, must be readily available to all laboratory staff. These documents should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect any changes in regulations or best practices.
Waste disposal of NaHSO4 and its solutions requires careful management. Neutralization before disposal is often necessary, and compliance with local, state, and federal regulations for hazardous waste disposal is mandatory. Proper documentation of waste generation and disposal is essential for regulatory compliance and environmental protection.
By implementing and strictly adhering to these safety protocols, laboratories can significantly reduce the risks associated with handling sodium bisulfate, ensuring a safer working environment for all personnel involved in organic compound processing research and applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!