Sulfamic Acid in Energy Storage Applications for Battery Systems
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfamic Acid in Energy Storage: Background and Objectives
Sulfamic acid, a compound with the chemical formula H3NSO3, has emerged as a promising candidate in the field of energy storage, particularly for battery systems. The exploration of sulfamic acid in this context stems from the growing demand for more efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective energy storage solutions. As global energy needs continue to rise and the push for renewable energy sources intensifies, the development of advanced battery technologies has become paramount.
The primary objective of researching sulfamic acid in energy storage applications is to harness its unique properties to enhance battery performance. Sulfamic acid's potential lies in its ability to act as an electrolyte additive or a key component in novel electrode materials. Its high stability, low toxicity, and favorable electrochemical properties make it an attractive option for improving various aspects of battery systems, including capacity, cycle life, and safety.
The evolution of battery technology has seen significant advancements over the past few decades, from lead-acid batteries to lithium-ion systems. However, current technologies face limitations in terms of energy density, charging speed, and long-term stability. The investigation of sulfamic acid aims to address these challenges by exploring its role in next-generation battery chemistries.
One of the key goals of this research is to understand how sulfamic acid can contribute to the development of more environmentally friendly battery systems. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in technological advancements, finding alternatives to toxic or scarce materials used in conventional batteries is crucial. Sulfamic acid's relatively benign nature and potential for improved recyclability align well with these environmental considerations.
Furthermore, the research seeks to elucidate the fundamental mechanisms by which sulfamic acid interacts with other battery components. This includes studying its behavior at electrode-electrolyte interfaces, its impact on solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation, and its potential to mitigate common battery degradation processes. By gaining a deeper understanding of these interactions, researchers aim to optimize battery designs and formulations that incorporate sulfamic acid.
The broader implications of this research extend beyond just improving existing battery technologies. It also aims to pave the way for entirely new energy storage concepts that could revolutionize how we store and utilize energy in various applications, from portable electronics to grid-scale storage systems. As such, the study of sulfamic acid in energy storage represents a critical step towards addressing the global challenges of energy sustainability and technological advancement in the 21st century.
The primary objective of researching sulfamic acid in energy storage applications is to harness its unique properties to enhance battery performance. Sulfamic acid's potential lies in its ability to act as an electrolyte additive or a key component in novel electrode materials. Its high stability, low toxicity, and favorable electrochemical properties make it an attractive option for improving various aspects of battery systems, including capacity, cycle life, and safety.
The evolution of battery technology has seen significant advancements over the past few decades, from lead-acid batteries to lithium-ion systems. However, current technologies face limitations in terms of energy density, charging speed, and long-term stability. The investigation of sulfamic acid aims to address these challenges by exploring its role in next-generation battery chemistries.
One of the key goals of this research is to understand how sulfamic acid can contribute to the development of more environmentally friendly battery systems. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in technological advancements, finding alternatives to toxic or scarce materials used in conventional batteries is crucial. Sulfamic acid's relatively benign nature and potential for improved recyclability align well with these environmental considerations.
Furthermore, the research seeks to elucidate the fundamental mechanisms by which sulfamic acid interacts with other battery components. This includes studying its behavior at electrode-electrolyte interfaces, its impact on solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation, and its potential to mitigate common battery degradation processes. By gaining a deeper understanding of these interactions, researchers aim to optimize battery designs and formulations that incorporate sulfamic acid.
The broader implications of this research extend beyond just improving existing battery technologies. It also aims to pave the way for entirely new energy storage concepts that could revolutionize how we store and utilize energy in various applications, from portable electronics to grid-scale storage systems. As such, the study of sulfamic acid in energy storage represents a critical step towards addressing the global challenges of energy sustainability and technological advancement in the 21st century.
Market Analysis for Sulfamic Acid-Based Battery Systems
The market for sulfamic acid-based battery systems is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for efficient and sustainable energy storage solutions. As the global energy landscape shifts towards renewable sources, the need for advanced battery technologies has become paramount. Sulfamic acid, traditionally used in industrial cleaning and water treatment, is emerging as a promising component in next-generation battery systems.
The potential market for sulfamic acid in energy storage applications is closely tied to the broader battery market, which is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of electric vehicles, the integration of renewable energy into power grids, and the proliferation of portable electronic devices. The unique properties of sulfamic acid, including its stability and high energy density, position it as a valuable alternative to conventional battery chemistries.
In the automotive sector, sulfamic acid-based batteries could offer advantages in terms of faster charging times and improved safety profiles compared to lithium-ion batteries. This potential has attracted the attention of major automotive manufacturers and battery producers, who are exploring sulfamic acid as a means to overcome current limitations in electric vehicle range and charging infrastructure.
The stationary energy storage market also presents significant opportunities for sulfamic acid-based systems. As renewable energy sources like solar and wind become more prevalent, the need for efficient, large-scale energy storage solutions grows. Sulfamic acid batteries could provide a cost-effective and durable option for grid-scale storage, helping to balance supply and demand in renewable energy systems.
Consumer electronics represent another key market segment for sulfamic acid battery technology. With the ever-increasing power demands of smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices, there is a constant search for battery chemistries that can deliver higher energy densities and longer lifespans. Sulfamic acid-based batteries could potentially meet these requirements, offering improved performance in a compact form factor.
However, the market for sulfamic acid in battery applications is not without challenges. Competition from established battery technologies, particularly lithium-ion, remains strong. Additionally, the development and scaling of new battery chemistries require significant investment in research, manufacturing infrastructure, and safety testing. Regulatory hurdles and the need for standardization across the industry could also impact market growth.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of sulfamic acid-based batteries are driving continued interest and investment. As research progresses and pilot projects demonstrate the viability of this technology, the market is expected to expand. Collaborations between academic institutions, battery manufacturers, and end-users are likely to accelerate the commercialization of sulfamic acid-based energy storage solutions, paving the way for broader market adoption in the coming years.
The potential market for sulfamic acid in energy storage applications is closely tied to the broader battery market, which is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of electric vehicles, the integration of renewable energy into power grids, and the proliferation of portable electronic devices. The unique properties of sulfamic acid, including its stability and high energy density, position it as a valuable alternative to conventional battery chemistries.
In the automotive sector, sulfamic acid-based batteries could offer advantages in terms of faster charging times and improved safety profiles compared to lithium-ion batteries. This potential has attracted the attention of major automotive manufacturers and battery producers, who are exploring sulfamic acid as a means to overcome current limitations in electric vehicle range and charging infrastructure.
The stationary energy storage market also presents significant opportunities for sulfamic acid-based systems. As renewable energy sources like solar and wind become more prevalent, the need for efficient, large-scale energy storage solutions grows. Sulfamic acid batteries could provide a cost-effective and durable option for grid-scale storage, helping to balance supply and demand in renewable energy systems.
Consumer electronics represent another key market segment for sulfamic acid battery technology. With the ever-increasing power demands of smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices, there is a constant search for battery chemistries that can deliver higher energy densities and longer lifespans. Sulfamic acid-based batteries could potentially meet these requirements, offering improved performance in a compact form factor.
However, the market for sulfamic acid in battery applications is not without challenges. Competition from established battery technologies, particularly lithium-ion, remains strong. Additionally, the development and scaling of new battery chemistries require significant investment in research, manufacturing infrastructure, and safety testing. Regulatory hurdles and the need for standardization across the industry could also impact market growth.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of sulfamic acid-based batteries are driving continued interest and investment. As research progresses and pilot projects demonstrate the viability of this technology, the market is expected to expand. Collaborations between academic institutions, battery manufacturers, and end-users are likely to accelerate the commercialization of sulfamic acid-based energy storage solutions, paving the way for broader market adoption in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Sulfamic Acid Energy Storage
Despite the promising potential of sulfamic acid in energy storage applications for battery systems, several significant challenges currently hinder its widespread adoption and optimal utilization. One of the primary obstacles is the limited understanding of sulfamic acid's long-term stability in battery environments. The acid's behavior under prolonged cycling and varying temperature conditions remains uncertain, raising concerns about its reliability in real-world applications.
Another critical challenge lies in the optimization of sulfamic acid's concentration and formulation for different battery chemistries. While sulfamic acid has shown promise in enhancing the performance of various battery types, finding the ideal balance between its beneficial effects and potential side reactions is a complex task. This optimization process requires extensive research and testing across different battery systems, which is both time-consuming and resource-intensive.
The integration of sulfamic acid into existing battery manufacturing processes presents another significant hurdle. Current production lines may require substantial modifications to accommodate the incorporation of sulfamic acid, potentially leading to increased manufacturing costs and complexity. Additionally, ensuring uniform distribution of sulfamic acid within battery components, particularly in large-scale production, remains a technical challenge that needs to be addressed.
Environmental and safety concerns also pose challenges to the widespread adoption of sulfamic acid in energy storage applications. While generally considered less corrosive than some alternatives, the long-term environmental impact of sulfamic acid in battery systems is not yet fully understood. Furthermore, proper handling and disposal protocols need to be established to mitigate any potential risks associated with its use in large-scale energy storage solutions.
The scalability of sulfamic acid production for battery applications is another area of concern. As demand for energy storage solutions continues to grow, ensuring a stable and cost-effective supply of high-purity sulfamic acid becomes crucial. Current production methods may need to be scaled up or optimized to meet the potential demand from the battery industry, which could impact the overall economic viability of sulfamic acid-based energy storage solutions.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding the use of sulfamic acid in battery systems remains uncertain in many jurisdictions. The lack of standardized testing protocols and safety regulations specific to sulfamic acid in energy storage applications could slow down its adoption and commercialization. Developing comprehensive regulatory frameworks and industry standards will be essential for building confidence among manufacturers, consumers, and regulatory bodies in the safety and reliability of sulfamic acid-based energy storage solutions.
Another critical challenge lies in the optimization of sulfamic acid's concentration and formulation for different battery chemistries. While sulfamic acid has shown promise in enhancing the performance of various battery types, finding the ideal balance between its beneficial effects and potential side reactions is a complex task. This optimization process requires extensive research and testing across different battery systems, which is both time-consuming and resource-intensive.
The integration of sulfamic acid into existing battery manufacturing processes presents another significant hurdle. Current production lines may require substantial modifications to accommodate the incorporation of sulfamic acid, potentially leading to increased manufacturing costs and complexity. Additionally, ensuring uniform distribution of sulfamic acid within battery components, particularly in large-scale production, remains a technical challenge that needs to be addressed.
Environmental and safety concerns also pose challenges to the widespread adoption of sulfamic acid in energy storage applications. While generally considered less corrosive than some alternatives, the long-term environmental impact of sulfamic acid in battery systems is not yet fully understood. Furthermore, proper handling and disposal protocols need to be established to mitigate any potential risks associated with its use in large-scale energy storage solutions.
The scalability of sulfamic acid production for battery applications is another area of concern. As demand for energy storage solutions continues to grow, ensuring a stable and cost-effective supply of high-purity sulfamic acid becomes crucial. Current production methods may need to be scaled up or optimized to meet the potential demand from the battery industry, which could impact the overall economic viability of sulfamic acid-based energy storage solutions.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding the use of sulfamic acid in battery systems remains uncertain in many jurisdictions. The lack of standardized testing protocols and safety regulations specific to sulfamic acid in energy storage applications could slow down its adoption and commercialization. Developing comprehensive regulatory frameworks and industry standards will be essential for building confidence among manufacturers, consumers, and regulatory bodies in the safety and reliability of sulfamic acid-based energy storage solutions.
Existing Sulfamic Acid Energy Storage Solutions
01 Synthesis and production of sulfamic acid
Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing sulfamic acid are described. These include reactions involving sulfur trioxide and ammonia, as well as other chemical precursors. The processes aim to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in the production of sulfamic acid.- Synthesis and production of sulfamic acid: Various methods for synthesizing and producing sulfamic acid are described. These processes often involve the reaction of sulfur trioxide with ammonia or urea under specific conditions. The production methods aim to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in industrial-scale manufacturing of sulfamic acid.
- Applications in cleaning and descaling: Sulfamic acid is widely used in cleaning and descaling formulations. It is effective in removing mineral deposits, rust, and scale from various surfaces and equipment. These applications include household cleaners, industrial descaling agents, and specialized cleaning products for specific industries.
- Use in water treatment and purification: Sulfamic acid plays a role in water treatment and purification processes. It is used for pH adjustment, scale prevention, and as a component in water treatment chemicals. The compound's properties make it suitable for various water-related applications in industrial and municipal settings.
- Agricultural and horticultural applications: Sulfamic acid finds use in agricultural and horticultural contexts. It is employed in fertilizer formulations, soil pH adjustment, and as a component in certain pesticides or herbicides. These applications leverage the compound's chemical properties to enhance plant growth or control unwanted vegetation.
- Industrial processes and chemical reactions: Sulfamic acid is utilized in various industrial processes and chemical reactions. It serves as a reagent, catalyst, or intermediate in the production of other chemicals. The compound's unique properties make it valuable in specific manufacturing processes across different industries.
02 Applications in cleaning and descaling
Sulfamic acid is widely used in cleaning and descaling formulations. It is effective in removing mineral deposits, rust, and other stubborn stains from various surfaces. The acid's properties make it suitable for use in household and industrial cleaning products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in water treatment
Sulfamic acid finds applications in water treatment processes. It is used for pH adjustment, scale removal in water systems, and as a component in water purification methods. The acid's properties make it effective in treating both industrial and municipal water supplies.Expand Specific Solutions04 Agricultural and horticultural applications
Sulfamic acid is utilized in various agricultural and horticultural products. It serves as a component in fertilizers, soil conditioners, and plant growth regulators. The acid's properties contribute to improved nutrient uptake and soil pH management.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial and chemical processing
Sulfamic acid plays a role in various industrial and chemical processes. It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis, as a catalyst in certain reactions, and as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals. The acid's versatility makes it valuable in diverse manufacturing applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sulfamic Acid Battery Research
The research on sulfamic acid in energy storage applications for battery systems is in an early developmental stage, with the market still emerging. The global energy storage market is projected to grow significantly, driven by increasing demand for renewable energy integration and grid stability. While the technology is not yet fully mature, several key players are actively involved in advancing this field. Companies like Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Arkema, Inc., and Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Ltd. are conducting research and development to explore the potential of sulfamic acid in battery systems. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established corporations and innovative startups contributing to technological advancements. As the technology progresses, we can expect increased collaboration between academic institutions and industry leaders to accelerate commercialization efforts.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Technical Solution: MIT has developed a novel approach using sulfamic acid as an electrolyte additive in lithium-ion batteries. Their research focuses on improving the stability of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer, which is crucial for battery performance and longevity. The team has found that adding small amounts of sulfamic acid (typically 0.5-2% by weight) to the electrolyte solution can significantly enhance the formation of a more stable and uniform SEI layer[1]. This modification results in improved cycling stability and increased capacity retention over extended charge-discharge cycles. Additionally, MIT researchers have explored the use of sulfamic acid in aqueous electrolytes for safer and more environmentally friendly energy storage systems[3].
Strengths: Improved battery stability and longevity, potential for safer and more eco-friendly energy storage. Weaknesses: May require modifications to existing battery manufacturing processes, potential long-term effects on battery materials need further study.
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: CATL has incorporated sulfamic acid-based additives in their advanced lithium-ion battery formulations. Their approach involves using sulfamic acid as a functional electrolyte additive to enhance the performance of high-nickel cathode materials, which are known for their high energy density but suffer from stability issues. CATL's research has shown that the addition of 0.1-0.5 wt% sulfamic acid can significantly improve the interfacial stability between the cathode and electrolyte[2]. This results in reduced capacity fading and improved cycle life, particularly at elevated temperatures. Furthermore, CATL has explored the synergistic effects of combining sulfamic acid with other additives to create a more comprehensive electrolyte optimization strategy[4].
Strengths: Enhanced performance of high-energy-density batteries, improved thermal stability. Weaknesses: Potential increase in production costs, may require fine-tuning for different battery chemistries.
Innovative Sulfamic Acid Battery Designs
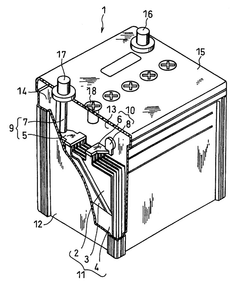
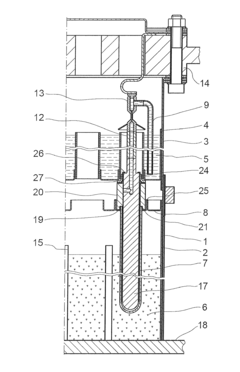
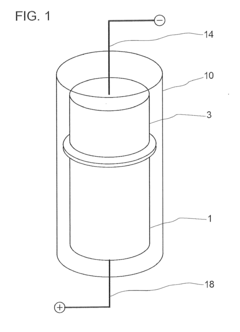
Lead acid storage battery
PatentWO2017110594A1
Innovation
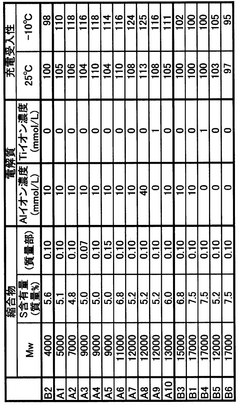
- Incorporating a condensate of bisphenols and aminobenzenesulfonic acids with formaldehyde into the negative electrode, with a weight average molecular weight of 5,000 to 13,000, and using an electrolyte containing aluminum or titanium ions to suppress sulfation and enhance charge acceptance by maintaining a larger effective surface area for lead sulfate and lead ions.
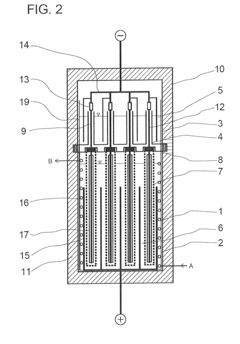
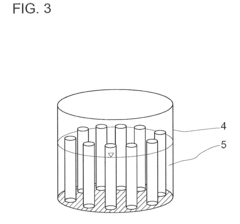
Industrial apparatus for the large-scale storage of electric energy
PatentInactiveUS20110311845A1
Innovation
- An electrochemical power station using a redox pair of alkali metals, such as sodium, and sulfur, where the materials are stored separately in containers connected by a solid electrolyte, allowing for efficient storage and release of electric energy through an electrochemical reactor, enabling scalable and efficient energy storage and transport.
Environmental Impact of Sulfamic Acid Batteries
The environmental impact of sulfamic acid batteries is a crucial consideration in the development and deployment of this emerging energy storage technology. As with any battery system, the production, use, and disposal of sulfamic acid batteries have potential environmental implications that must be carefully assessed and managed.
During the manufacturing process of sulfamic acid batteries, there are concerns regarding the extraction and processing of raw materials. The production of sulfamic acid itself involves the reaction of urea with sulfuric acid, which can generate emissions and waste products that require proper handling and treatment. Additionally, the synthesis of other battery components may contribute to energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
In terms of battery operation, sulfamic acid batteries generally exhibit lower environmental risks compared to some conventional battery technologies. The electrolyte used in these batteries is less corrosive and toxic than those found in lead-acid or certain lithium-ion batteries. This characteristic reduces the potential for harmful leaks or spills during use and transportation.
End-of-life management and recycling of sulfamic acid batteries present both challenges and opportunities. The recyclability of battery components, particularly the sulfamic acid electrolyte, is an area of ongoing research. Effective recycling processes could significantly reduce the environmental footprint of these batteries by recovering valuable materials and minimizing waste.
One of the potential environmental benefits of sulfamic acid batteries is their potential for improved energy density and longer cycle life compared to some existing battery technologies. This could lead to reduced material consumption and waste generation over the long term, as fewer batteries would be needed to meet energy storage demands.
Water consumption and potential impacts on aquatic ecosystems are also important considerations. While sulfamic acid is generally considered biodegradable, large-scale production and use of these batteries could potentially affect local water resources if not properly managed.
The carbon footprint associated with sulfamic acid batteries throughout their lifecycle is an area that requires further study. This includes assessing the emissions from raw material extraction, manufacturing, transportation, use, and end-of-life processing. Comparative analyses with other battery technologies will be crucial in determining the overall environmental sustainability of sulfamic acid batteries.
As research and development in this field progress, it is essential to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments (LCAs) to fully understand and quantify the environmental impacts of sulfamic acid batteries. These assessments should consider all stages of the battery lifecycle and compare the results with alternative energy storage solutions to inform decision-making and guide sustainable technology development.
During the manufacturing process of sulfamic acid batteries, there are concerns regarding the extraction and processing of raw materials. The production of sulfamic acid itself involves the reaction of urea with sulfuric acid, which can generate emissions and waste products that require proper handling and treatment. Additionally, the synthesis of other battery components may contribute to energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
In terms of battery operation, sulfamic acid batteries generally exhibit lower environmental risks compared to some conventional battery technologies. The electrolyte used in these batteries is less corrosive and toxic than those found in lead-acid or certain lithium-ion batteries. This characteristic reduces the potential for harmful leaks or spills during use and transportation.
End-of-life management and recycling of sulfamic acid batteries present both challenges and opportunities. The recyclability of battery components, particularly the sulfamic acid electrolyte, is an area of ongoing research. Effective recycling processes could significantly reduce the environmental footprint of these batteries by recovering valuable materials and minimizing waste.
One of the potential environmental benefits of sulfamic acid batteries is their potential for improved energy density and longer cycle life compared to some existing battery technologies. This could lead to reduced material consumption and waste generation over the long term, as fewer batteries would be needed to meet energy storage demands.
Water consumption and potential impacts on aquatic ecosystems are also important considerations. While sulfamic acid is generally considered biodegradable, large-scale production and use of these batteries could potentially affect local water resources if not properly managed.
The carbon footprint associated with sulfamic acid batteries throughout their lifecycle is an area that requires further study. This includes assessing the emissions from raw material extraction, manufacturing, transportation, use, and end-of-life processing. Comparative analyses with other battery technologies will be crucial in determining the overall environmental sustainability of sulfamic acid batteries.
As research and development in this field progress, it is essential to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments (LCAs) to fully understand and quantify the environmental impacts of sulfamic acid batteries. These assessments should consider all stages of the battery lifecycle and compare the results with alternative energy storage solutions to inform decision-making and guide sustainable technology development.
Safety Regulations for Sulfamic Acid in Energy Storage
The safety regulations for sulfamic acid in energy storage applications are crucial for ensuring the safe handling, storage, and use of this compound in battery systems. These regulations are designed to protect workers, the environment, and the integrity of energy storage facilities.
One of the primary safety concerns with sulfamic acid is its corrosive nature. As a result, regulations typically mandate the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling the substance. This includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing. In some cases, respiratory protection may also be required, especially in areas with poor ventilation or where there is a risk of dust or vapor inhalation.
Storage regulations for sulfamic acid in energy storage facilities often specify the need for cool, dry, and well-ventilated areas. The acid should be kept away from heat sources, direct sunlight, and incompatible materials such as strong oxidizing agents, chlorine, and nitric acid. Containers must be properly labeled and sealed to prevent accidental spills or exposure.
Emergency response procedures are another critical aspect of safety regulations. Facilities must have clearly defined protocols for dealing with spills, leaks, or accidental exposure. This includes the availability of eyewash stations, safety showers, and spill containment equipment. Staff should be trained in these procedures and regular drills conducted to ensure readiness.
Environmental protection is also a key consideration in safety regulations. Proper disposal methods for sulfamic acid and its waste products must be followed to prevent contamination of soil and water sources. This may involve neutralization processes or specialized waste treatment facilities.
In the context of battery systems, regulations often address the potential risks associated with the interaction between sulfamic acid and other battery components. This includes guidelines for the design and construction of battery casings to prevent acid leakage and measures to mitigate the risk of thermal runaway or other chemical reactions.
Workplace exposure limits are typically established to protect workers from the potential health effects of long-term exposure to sulfamic acid. These limits may vary depending on the jurisdiction but generally specify maximum allowable concentrations in the air over specific time periods.
Regular safety inspections and audits are often mandated to ensure ongoing compliance with these regulations. This may involve periodic testing of safety equipment, review of handling procedures, and assessment of storage conditions.
Transportation regulations for sulfamic acid used in energy storage applications are also important. These typically align with broader hazardous materials transportation guidelines, specifying requirements for packaging, labeling, and documentation during transit.
One of the primary safety concerns with sulfamic acid is its corrosive nature. As a result, regulations typically mandate the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling the substance. This includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing. In some cases, respiratory protection may also be required, especially in areas with poor ventilation or where there is a risk of dust or vapor inhalation.
Storage regulations for sulfamic acid in energy storage facilities often specify the need for cool, dry, and well-ventilated areas. The acid should be kept away from heat sources, direct sunlight, and incompatible materials such as strong oxidizing agents, chlorine, and nitric acid. Containers must be properly labeled and sealed to prevent accidental spills or exposure.
Emergency response procedures are another critical aspect of safety regulations. Facilities must have clearly defined protocols for dealing with spills, leaks, or accidental exposure. This includes the availability of eyewash stations, safety showers, and spill containment equipment. Staff should be trained in these procedures and regular drills conducted to ensure readiness.
Environmental protection is also a key consideration in safety regulations. Proper disposal methods for sulfamic acid and its waste products must be followed to prevent contamination of soil and water sources. This may involve neutralization processes or specialized waste treatment facilities.
In the context of battery systems, regulations often address the potential risks associated with the interaction between sulfamic acid and other battery components. This includes guidelines for the design and construction of battery casings to prevent acid leakage and measures to mitigate the risk of thermal runaway or other chemical reactions.
Workplace exposure limits are typically established to protect workers from the potential health effects of long-term exposure to sulfamic acid. These limits may vary depending on the jurisdiction but generally specify maximum allowable concentrations in the air over specific time periods.
Regular safety inspections and audits are often mandated to ensure ongoing compliance with these regulations. This may involve periodic testing of safety equipment, review of handling procedures, and assessment of storage conditions.
Transportation regulations for sulfamic acid used in energy storage applications are also important. These typically align with broader hazardous materials transportation guidelines, specifying requirements for packaging, labeling, and documentation during transit.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!