Acrylic Resin vs Melamine: Crosslinking Density Effects
OCT 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Crosslinking Density Background and Research Objectives
Crosslinking density represents a fundamental parameter in polymer science that significantly influences the physical, mechanical, and chemical properties of resinous materials. The concept emerged in the early 20th century with the development of synthetic polymers, gaining prominence as industries sought materials with tailored performance characteristics. Historically, the evolution of crosslinking technology has progressed from simple thermosetting resins to sophisticated systems with controllable network architectures.
In the specific context of acrylic resins versus melamine systems, crosslinking density exhibits distinct behavior patterns that warrant comprehensive investigation. Acrylic resins typically form crosslinks through free-radical polymerization mechanisms, while melamine systems predominantly utilize condensation reactions. This fundamental difference creates unique network structures that respond differently to environmental stressors, mechanical forces, and chemical exposures.
Recent technological advancements have enabled more precise control over crosslinking parameters, allowing for customized material properties. The relationship between crosslinking density and performance attributes such as glass transition temperature, solvent resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal stability represents a critical area for exploration, particularly in comparative analyses between these two resin systems.
The global shift toward sustainable materials and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes has further intensified interest in optimizing crosslinking density. Lower crosslinking densities often permit easier recycling and material recovery, while higher densities typically enhance durability and service life—creating an important sustainability trade-off that requires careful evaluation.
This research aims to systematically investigate how variations in crosslinking density affect the performance characteristics of acrylic and melamine resin systems across multiple application environments. Specifically, we seek to establish quantitative relationships between crosslinking parameters and key performance indicators including tensile strength, impact resistance, chemical resistance, weatherability, and thermal stability.
Additionally, this study will explore novel methodologies for precisely measuring and controlling crosslinking density during manufacturing processes, addressing a significant gap in current industrial practice. By developing predictive models that correlate crosslinking density with material performance, we aim to enable more efficient material selection and formulation processes for specific applications.
The ultimate objective is to create a comprehensive technical framework that allows for intelligent design of crosslinked polymer systems with optimized property profiles, potentially leading to new material formulations that combine the advantageous properties of both acrylic and melamine chemistries through controlled crosslinking architectures.
In the specific context of acrylic resins versus melamine systems, crosslinking density exhibits distinct behavior patterns that warrant comprehensive investigation. Acrylic resins typically form crosslinks through free-radical polymerization mechanisms, while melamine systems predominantly utilize condensation reactions. This fundamental difference creates unique network structures that respond differently to environmental stressors, mechanical forces, and chemical exposures.
Recent technological advancements have enabled more precise control over crosslinking parameters, allowing for customized material properties. The relationship between crosslinking density and performance attributes such as glass transition temperature, solvent resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal stability represents a critical area for exploration, particularly in comparative analyses between these two resin systems.
The global shift toward sustainable materials and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes has further intensified interest in optimizing crosslinking density. Lower crosslinking densities often permit easier recycling and material recovery, while higher densities typically enhance durability and service life—creating an important sustainability trade-off that requires careful evaluation.
This research aims to systematically investigate how variations in crosslinking density affect the performance characteristics of acrylic and melamine resin systems across multiple application environments. Specifically, we seek to establish quantitative relationships between crosslinking parameters and key performance indicators including tensile strength, impact resistance, chemical resistance, weatherability, and thermal stability.
Additionally, this study will explore novel methodologies for precisely measuring and controlling crosslinking density during manufacturing processes, addressing a significant gap in current industrial practice. By developing predictive models that correlate crosslinking density with material performance, we aim to enable more efficient material selection and formulation processes for specific applications.
The ultimate objective is to create a comprehensive technical framework that allows for intelligent design of crosslinked polymer systems with optimized property profiles, potentially leading to new material formulations that combine the advantageous properties of both acrylic and melamine chemistries through controlled crosslinking architectures.
Market Applications and Demand Analysis for Crosslinked Resins
The global market for crosslinked resins has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across multiple industries including automotive, construction, electronics, and consumer goods. Acrylic and melamine resins, in particular, have gained prominence due to their versatile performance characteristics that can be tailored through crosslinking density manipulation.
In the coatings sector, which represents approximately 40% of the total crosslinked resin market, there is growing demand for high-performance protective finishes with enhanced durability and chemical resistance. The automotive industry specifically seeks coatings that can withstand harsh environmental conditions while maintaining aesthetic appeal, creating a premium segment where crosslinking density optimization is crucial for product differentiation.
The construction industry represents another major market driver, with demand for weather-resistant exterior coatings and durable interior finishes. Here, the balance between hardness and flexibility achieved through precise crosslinking density control directly addresses customer requirements for longevity and performance under varying conditions.
Electronics manufacturers increasingly require specialized encapsulation materials with tailored electrical properties, thermal stability, and moisture resistance - all characteristics directly influenced by crosslinking density. This segment has shown the fastest growth rate among all applications, expanding at over 7% annually as electronic components become more sophisticated and widespread.
Consumer preference shifts toward environmentally friendly products have created new market opportunities for water-based acrylic systems with optimized crosslinking. Regulatory pressures, particularly in Europe and North America, continue to drive innovation in low-VOC formulations where crosslinking chemistry plays a pivotal role in maintaining performance while reducing environmental impact.
The Asia-Pacific region currently leads market consumption, accounting for over 45% of global demand, with China and India showing the strongest growth trajectories. This regional dominance is expected to continue as manufacturing activities expand and living standards rise, increasing demand for higher-quality finished products.
Market analysis indicates a price premium of 15-30% for precisely engineered crosslinked systems compared to standard formulations, reflecting the value-added nature of optimized crosslinking technology. This premium pricing structure supports continued research investment in understanding fundamental structure-property relationships.
Industry forecasts suggest the global market for crosslinked acrylic and melamine resins will continue expanding at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 5-6% through 2028, with higher growth rates in specialized applications where performance requirements are most stringent and technical differentiation creates sustainable competitive advantages.
In the coatings sector, which represents approximately 40% of the total crosslinked resin market, there is growing demand for high-performance protective finishes with enhanced durability and chemical resistance. The automotive industry specifically seeks coatings that can withstand harsh environmental conditions while maintaining aesthetic appeal, creating a premium segment where crosslinking density optimization is crucial for product differentiation.
The construction industry represents another major market driver, with demand for weather-resistant exterior coatings and durable interior finishes. Here, the balance between hardness and flexibility achieved through precise crosslinking density control directly addresses customer requirements for longevity and performance under varying conditions.
Electronics manufacturers increasingly require specialized encapsulation materials with tailored electrical properties, thermal stability, and moisture resistance - all characteristics directly influenced by crosslinking density. This segment has shown the fastest growth rate among all applications, expanding at over 7% annually as electronic components become more sophisticated and widespread.
Consumer preference shifts toward environmentally friendly products have created new market opportunities for water-based acrylic systems with optimized crosslinking. Regulatory pressures, particularly in Europe and North America, continue to drive innovation in low-VOC formulations where crosslinking chemistry plays a pivotal role in maintaining performance while reducing environmental impact.
The Asia-Pacific region currently leads market consumption, accounting for over 45% of global demand, with China and India showing the strongest growth trajectories. This regional dominance is expected to continue as manufacturing activities expand and living standards rise, increasing demand for higher-quality finished products.
Market analysis indicates a price premium of 15-30% for precisely engineered crosslinked systems compared to standard formulations, reflecting the value-added nature of optimized crosslinking technology. This premium pricing structure supports continued research investment in understanding fundamental structure-property relationships.
Industry forecasts suggest the global market for crosslinked acrylic and melamine resins will continue expanding at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 5-6% through 2028, with higher growth rates in specialized applications where performance requirements are most stringent and technical differentiation creates sustainable competitive advantages.
Current Technical Challenges in Acrylic vs Melamine Crosslinking
The crosslinking density in polymer systems represents a critical parameter that significantly influences the physical, mechanical, and chemical properties of the resulting materials. When comparing acrylic resins and melamine systems, several technical challenges emerge that require sophisticated solutions and innovative approaches. Currently, one of the primary challenges involves achieving precise control over crosslinking density while maintaining consistent performance across different environmental conditions.
Acrylic resins typically employ free-radical polymerization mechanisms, which can be difficult to regulate with high precision. The exothermic nature of these reactions often leads to temperature gradients within the curing material, resulting in heterogeneous crosslinking density distributions. This heterogeneity manifests as inconsistent mechanical properties and can compromise the overall performance of the final product, particularly in applications requiring uniform stress distribution.
Melamine systems, conversely, utilize condensation reactions for crosslinking, which present different challenges. The reaction kinetics are highly sensitive to both temperature and humidity, making process control particularly demanding in variable manufacturing environments. Additionally, the release of small molecules (typically water or formaldehyde) during crosslinking can create voids or defects if not properly managed, affecting the structural integrity of the final product.
Another significant technical hurdle involves the trade-off between crosslinking density and material flexibility. Higher crosslinking densities generally improve chemical resistance and thermal stability but often at the expense of impact resistance and elongation properties. This balance is particularly challenging to optimize in applications requiring both chemical durability and mechanical resilience, such as automotive coatings or industrial protective finishes.
The characterization of crosslinking density presents its own set of challenges. Current analytical methods, including swelling tests, dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA), and solid-state NMR, each have limitations in accuracy, reproducibility, or accessibility. The development of more precise, non-destructive measurement techniques remains an active area of research and development.
Environmental and regulatory constraints further complicate the technical landscape. Traditional crosslinking agents, particularly in melamine systems, often contain or release formaldehyde, which faces increasing regulatory scrutiny worldwide. Developing high-performance, low-emission alternatives that maintain the desired crosslinking density profiles represents a significant challenge for materials scientists and formulators.
The stability of crosslinked networks over time (aging) presents another technical challenge. Both acrylic and melamine systems can experience degradation through various mechanisms including hydrolysis, photo-oxidation, and thermal stress. Understanding and mitigating these aging processes, particularly as they relate to crosslinking density changes, remains incompletely resolved despite extensive research efforts.
Acrylic resins typically employ free-radical polymerization mechanisms, which can be difficult to regulate with high precision. The exothermic nature of these reactions often leads to temperature gradients within the curing material, resulting in heterogeneous crosslinking density distributions. This heterogeneity manifests as inconsistent mechanical properties and can compromise the overall performance of the final product, particularly in applications requiring uniform stress distribution.
Melamine systems, conversely, utilize condensation reactions for crosslinking, which present different challenges. The reaction kinetics are highly sensitive to both temperature and humidity, making process control particularly demanding in variable manufacturing environments. Additionally, the release of small molecules (typically water or formaldehyde) during crosslinking can create voids or defects if not properly managed, affecting the structural integrity of the final product.
Another significant technical hurdle involves the trade-off between crosslinking density and material flexibility. Higher crosslinking densities generally improve chemical resistance and thermal stability but often at the expense of impact resistance and elongation properties. This balance is particularly challenging to optimize in applications requiring both chemical durability and mechanical resilience, such as automotive coatings or industrial protective finishes.
The characterization of crosslinking density presents its own set of challenges. Current analytical methods, including swelling tests, dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA), and solid-state NMR, each have limitations in accuracy, reproducibility, or accessibility. The development of more precise, non-destructive measurement techniques remains an active area of research and development.
Environmental and regulatory constraints further complicate the technical landscape. Traditional crosslinking agents, particularly in melamine systems, often contain or release formaldehyde, which faces increasing regulatory scrutiny worldwide. Developing high-performance, low-emission alternatives that maintain the desired crosslinking density profiles represents a significant challenge for materials scientists and formulators.
The stability of crosslinked networks over time (aging) presents another technical challenge. Both acrylic and melamine systems can experience degradation through various mechanisms including hydrolysis, photo-oxidation, and thermal stress. Understanding and mitigating these aging processes, particularly as they relate to crosslinking density changes, remains incompletely resolved despite extensive research efforts.
Comparative Analysis of Current Crosslinking Methods
01 Factors affecting crosslinking density in acrylic-melamine systems
Various factors influence the crosslinking density between acrylic resins and melamine, including the ratio of components, curing temperature, and catalyst concentration. Higher melamine content generally increases crosslinking density, while optimal curing temperatures ensure complete reaction without degradation. Catalyst type and concentration significantly impact the crosslinking reaction rate and final network structure, affecting mechanical properties and chemical resistance of the cured film.- Factors affecting crosslinking density in acrylic-melamine systems: Various factors influence the crosslinking density between acrylic resins and melamine, including the ratio of components, functional group concentration, curing temperature, and catalyst type. Higher functional group density in either component leads to increased crosslinking points. The molecular weight of the acrylic resin and the degree of alkylation in the melamine also significantly impact the final network structure and properties of the cured film.
- Measurement and characterization of crosslinking density: Crosslinking density in acrylic-melamine systems can be measured through various analytical techniques including solvent swelling tests, dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and infrared spectroscopy. These methods help quantify the degree of crosslinking by evaluating properties such as glass transition temperature, solvent resistance, and mechanical strength. Understanding these parameters allows for optimization of coating formulations for specific applications.
- Catalyst systems for controlling crosslinking reactions: Acid catalysts play a crucial role in controlling the crosslinking reaction between acrylic resins and melamine. Different catalyst types, concentrations, and activation temperatures can be used to manipulate the crosslinking density and reaction kinetics. Blocked catalysts that activate at specific temperatures allow for better control of the curing process, resulting in more uniform crosslinking throughout the coating. The selection of appropriate catalyst systems is essential for achieving desired film properties.
- Formulation strategies for optimized crosslinking: Specific formulation strategies can be employed to optimize the crosslinking density between acrylic resins and melamine. These include adjusting the hydroxyl value of the acrylic resin, selecting appropriate melamine types (fully or partially methylated), incorporating additional functional monomers, and using reactive diluents. The balance of these components affects not only crosslinking density but also properties such as flexibility, hardness, chemical resistance, and weatherability of the final coating.
- Advanced applications requiring controlled crosslinking density: Controlled crosslinking density in acrylic-melamine systems is critical for advanced applications such as automotive coatings, industrial finishes, and electronic materials. By precisely managing the crosslinking density, properties such as scratch resistance, chemical resistance, and durability can be enhanced while maintaining flexibility and adhesion. Recent innovations include self-healing coatings, low-temperature curing systems, and environmentally friendly formulations with reduced volatile organic compounds.
02 Measurement and characterization of crosslinking density
Crosslinking density in acrylic-melamine systems can be measured through various analytical techniques. These include solvent swelling tests, dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and infrared spectroscopy. These methods help quantify the degree of crosslinking by measuring properties such as glass transition temperature, modulus changes, solvent resistance, and chemical bond formation, providing insights into the network structure and performance characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Modified melamine resins for controlled crosslinking
Chemical modifications to melamine resins can provide better control over crosslinking density with acrylic polymers. These modifications include partial alkylation, introducing specific functional groups, or creating blocked reactive sites that activate under certain conditions. Such modified melamines allow for more precise control of reaction kinetics, resulting in coatings with tailored properties such as improved flexibility, weatherability, and controlled cure response.Expand Specific Solutions04 Acrylic resin design for optimal melamine crosslinking
The structure and functionality of acrylic resins significantly impact crosslinking density with melamine. Key design factors include the type and distribution of functional groups (hydroxyl, carboxyl), molecular weight, and glass transition temperature of the acrylic polymer. Acrylic resins with controlled placement of reactive sites and appropriate molecular architecture enable optimized crosslinking networks, resulting in coatings with enhanced durability, appearance, and performance properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications leveraging controlled crosslinking density
Controlled crosslinking density between acrylic and melamine resins enables specialized applications across multiple industries. In automotive coatings, precise crosslinking provides weather resistance and appearance retention. For industrial finishes, tailored networks deliver chemical and abrasion resistance. Electronic applications benefit from controlled dielectric properties, while architectural coatings achieve balance between hardness and flexibility. Advanced manufacturing techniques further optimize these systems for specific performance requirements.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Research Institutions
The crosslinking density research in Acrylic Resin versus Melamine is currently in a growth phase, with an estimated global market size of $15-20 billion. The technology is approaching maturity, with key players demonstrating varied levels of advancement. Companies like BASF, Allnex, and DuPont lead with comprehensive crosslinking technology portfolios, while Kansai Paint, Nippon Paint, and LG Chem have developed specialized applications in automotive and industrial coatings. Japanese firms including Toray Industries and Nippon Shokubai are focusing on high-performance applications, while emerging players like Chongqing Polycomp are expanding capabilities. The competitive landscape shows regional strengths with European companies emphasizing sustainability and Asian manufacturers focusing on cost-effective formulations.
Kansai Paint Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Kansai Paint has developed sophisticated approaches to controlling crosslinking density in acrylic-melamine systems, particularly for automotive and industrial coatings. Their research focuses on the relationship between crosslinking density and coating performance properties, demonstrating that precisely controlled networks significantly improve weatherability and chemical resistance. Kansai's proprietary "Controlled Network Architecture" technology utilizes specially designed acrylic resins with optimized hydroxyl functionality distribution and molecular weight profiles that interact predictably with melamine crosslinkers. Their studies show that increasing crosslinking density in acrylic-melamine systems improves solvent resistance by up to 200% but must be balanced against flexibility requirements. Kansai has also pioneered low-temperature curing systems that achieve high crosslinking density without requiring elevated temperatures, utilizing specialized catalyst packages that selectively accelerate the acrylic-melamine reaction while minimizing unwanted side reactions that could compromise coating performance.
Strengths: Excellent balance of hardness and flexibility through precise crosslinking control; superior weathering performance; innovative low-temperature curing technology. Weaknesses: Complex formulation requirements; potential for water sensitivity in highly crosslinked systems; may require specialized application techniques.
LG Chem Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Chem has conducted extensive research on crosslinking density effects in acrylic-melamine systems, developing proprietary technologies that optimize coating performance through controlled network formation. Their approach involves tailored acrylic resin designs with specific hydroxyl value distributions and molecular architectures engineered to interact optimally with various melamine crosslinkers. LG Chem's research demonstrates that controlled heterogeneity in crosslinking density can significantly enhance coating flexibility while maintaining excellent chemical resistance. Their "Adaptive Crosslink Technology" creates regions of varying crosslink density within the same coating, allowing for improved impact resistance without sacrificing hardness. LG Chem has also pioneered environmentally friendly acrylic-melamine systems with reduced formaldehyde emissions through innovative melamine derivatives that achieve high crosslinking efficiency at lower concentrations. Their studies show that optimized crosslinking density can improve coating durability by up to 35% in accelerated weathering tests while maintaining excellent appearance properties.
Strengths: Innovative heterogeneous crosslinking approach provides excellent mechanical properties; reduced formaldehyde emissions; superior weatherability in optimized systems. Weaknesses: More complex manufacturing process; potential for higher cost; may require specialized application parameters.
Critical Patents and Literature on Crosslinking Mechanisms
Acrylic pressure sensitive adhesive composition
PatentInactiveUS20070191517A1
Innovation
- Incorporating a room temperature eutectic salt composed of a metal salt with a perfluoroalkane group conjugate base of a super acid and an alkali metal cation with a compound having an amide group into the acrylic adhesive composition, which enhances electrical conductivity and antistatic properties without affecting transparency or causing whitening.
Non-woven fabric abrasive and manufacturing process thereof
PatentWO2005082576A1
Innovation
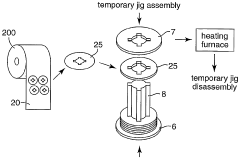
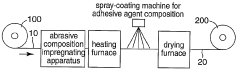
- A non-woven fabric abrasive is developed using a thermosetting aqueous adhesive agent precursor comprising isocyanate-terminated polymer with an anionic group, thermosetting acrylic polymer with hydroxyl groups, and melamine-based crosslinking agents, dispersed uniformly in water, to enhance grinding power and adhesion strength.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of crosslinking density in acrylic resin versus melamine systems represents a critical consideration in modern materials science. Higher crosslinking density typically results in more durable products with extended lifespans, potentially reducing waste generation and resource consumption over time. However, this environmental benefit comes with significant trade-offs that must be carefully evaluated.
Acrylic resins with increased crosslinking density often require higher energy inputs during manufacturing processes, contributing to greater carbon emissions compared to their lower-density counterparts. The curing temperatures and times necessary to achieve optimal crosslinking in high-density networks can increase the overall carbon footprint of production facilities significantly.
Melamine systems present different environmental challenges. While they can achieve comparable mechanical properties at potentially lower crosslinking densities than acrylics, they often incorporate formaldehyde-based components that pose serious environmental and health concerns. Emissions during production and potential leaching during product use or disposal represent significant environmental hazards that must be mitigated through careful formulation and processing controls.
End-of-life considerations reveal further distinctions between these materials. Highly crosslinked networks, regardless of whether acrylic or melamine-based, present substantial recycling challenges due to their thermoset nature. The irreversible chemical bonds that provide desirable performance characteristics simultaneously render these materials difficult to reprocess through conventional recycling methods, potentially increasing landfill burden.
Recent advances in degradable crosslinkers show promise for both resin systems. Incorporating strategically designed cleavable linkages can maintain performance during product use while enabling more environmentally friendly disposal options. Research indicates that acrylic systems may offer greater flexibility for incorporating such sustainable design elements compared to traditional melamine formulations.
Water-based formulations represent another sustainability frontier, with both resin types seeing development of reduced-VOC alternatives. Acrylic systems currently hold an advantage in this area, with more commercially viable water-based options available that maintain acceptable crosslinking density and performance characteristics. Melamine systems are advancing in this direction but face greater technical hurdles in achieving comparable performance without solvent carriers.
Lifecycle assessment studies comparing these materials indicate that the environmental impact balance depends heavily on specific application requirements and service conditions. When extended durability is paramount, the initial environmental costs of higher crosslinking density may be justified by reduced replacement frequency and associated resource conservation benefits over the complete product lifecycle.
Acrylic resins with increased crosslinking density often require higher energy inputs during manufacturing processes, contributing to greater carbon emissions compared to their lower-density counterparts. The curing temperatures and times necessary to achieve optimal crosslinking in high-density networks can increase the overall carbon footprint of production facilities significantly.
Melamine systems present different environmental challenges. While they can achieve comparable mechanical properties at potentially lower crosslinking densities than acrylics, they often incorporate formaldehyde-based components that pose serious environmental and health concerns. Emissions during production and potential leaching during product use or disposal represent significant environmental hazards that must be mitigated through careful formulation and processing controls.
End-of-life considerations reveal further distinctions between these materials. Highly crosslinked networks, regardless of whether acrylic or melamine-based, present substantial recycling challenges due to their thermoset nature. The irreversible chemical bonds that provide desirable performance characteristics simultaneously render these materials difficult to reprocess through conventional recycling methods, potentially increasing landfill burden.
Recent advances in degradable crosslinkers show promise for both resin systems. Incorporating strategically designed cleavable linkages can maintain performance during product use while enabling more environmentally friendly disposal options. Research indicates that acrylic systems may offer greater flexibility for incorporating such sustainable design elements compared to traditional melamine formulations.
Water-based formulations represent another sustainability frontier, with both resin types seeing development of reduced-VOC alternatives. Acrylic systems currently hold an advantage in this area, with more commercially viable water-based options available that maintain acceptable crosslinking density and performance characteristics. Melamine systems are advancing in this direction but face greater technical hurdles in achieving comparable performance without solvent carriers.
Lifecycle assessment studies comparing these materials indicate that the environmental impact balance depends heavily on specific application requirements and service conditions. When extended durability is paramount, the initial environmental costs of higher crosslinking density may be justified by reduced replacement frequency and associated resource conservation benefits over the complete product lifecycle.
Performance Testing Standards and Quality Control
Standardized testing protocols are essential for accurately evaluating the performance characteristics of crosslinked acrylic resins and melamine systems. The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provides several key standards applicable to these materials, including ASTM D1545 for viscosity determination, ASTM D2583 for hardness testing, and ASTM D638 for tensile properties. These standards ensure consistent measurement methodologies across different laboratory environments.
For crosslinking density evaluation specifically, gel fraction analysis has emerged as a critical quantitative method. This technique involves solvent extraction of uncrosslinked components, followed by gravimetric analysis to determine the percentage of insoluble (crosslinked) material. The swelling ratio test complements this approach by measuring dimensional changes when the cured resin is immersed in compatible solvents, with higher crosslinking density typically resulting in reduced swelling.
Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) provides valuable insights into viscoelastic properties as a function of temperature, with the glass transition temperature (Tg) and storage modulus serving as indirect indicators of crosslinking extent. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) further enables quantification of residual cure potential and thermal stability differences between acrylic and melamine systems at varying crosslinking densities.
Quality control in production environments necessitates in-process monitoring techniques. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) allows real-time tracking of functional group conversion during curing, while rheological measurements can detect the gel point that signals the formation of a three-dimensional network. Statistical Process Control (SPC) methodologies, including control charts for key parameters like viscosity and cure time, help maintain consistent crosslinking density across production batches.
Accelerated aging tests are particularly important for predicting long-term performance. These include QUV exposure (ASTM G154) for UV resistance, salt spray testing (ASTM B117) for corrosion protection, and thermal cycling to evaluate dimensional stability. The correlation between crosslinking density and these performance metrics must be established through comprehensive test matrices that systematically vary formulation parameters.
Industry-specific standards further refine testing requirements. For automotive coatings, specifications like GM9540P and SAE J2527 define rigorous testing protocols, while architectural applications follow AAMA 2605 guidelines. These standards often include specific performance thresholds that directly relate to optimal crosslinking density ranges for each application environment.
For crosslinking density evaluation specifically, gel fraction analysis has emerged as a critical quantitative method. This technique involves solvent extraction of uncrosslinked components, followed by gravimetric analysis to determine the percentage of insoluble (crosslinked) material. The swelling ratio test complements this approach by measuring dimensional changes when the cured resin is immersed in compatible solvents, with higher crosslinking density typically resulting in reduced swelling.
Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) provides valuable insights into viscoelastic properties as a function of temperature, with the glass transition temperature (Tg) and storage modulus serving as indirect indicators of crosslinking extent. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) further enables quantification of residual cure potential and thermal stability differences between acrylic and melamine systems at varying crosslinking densities.
Quality control in production environments necessitates in-process monitoring techniques. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) allows real-time tracking of functional group conversion during curing, while rheological measurements can detect the gel point that signals the formation of a three-dimensional network. Statistical Process Control (SPC) methodologies, including control charts for key parameters like viscosity and cure time, help maintain consistent crosslinking density across production batches.
Accelerated aging tests are particularly important for predicting long-term performance. These include QUV exposure (ASTM G154) for UV resistance, salt spray testing (ASTM B117) for corrosion protection, and thermal cycling to evaluate dimensional stability. The correlation between crosslinking density and these performance metrics must be established through comprehensive test matrices that systematically vary formulation parameters.
Industry-specific standards further refine testing requirements. For automotive coatings, specifications like GM9540P and SAE J2527 define rigorous testing protocols, while architectural applications follow AAMA 2605 guidelines. These standards often include specific performance thresholds that directly relate to optimal crosslinking density ranges for each application environment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!