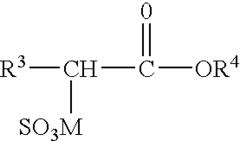
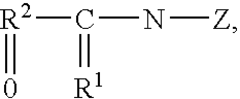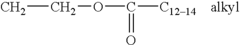Role of Hydroxyethylcellulose in Biodegradable Detergent Development
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HEC in Biodegradable Detergents: Background and Objectives
Hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) has emerged as a key component in the development of biodegradable detergents, marking a significant shift towards more environmentally friendly cleaning solutions. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the growing awareness of environmental issues and the need for sustainable alternatives to traditional petrochemical-based detergents.
The primary objective of incorporating HEC into biodegradable detergent formulations is to create effective cleaning products that break down naturally in the environment, reducing their ecological impact. This aligns with the global trend towards sustainability and the increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly household products.
HEC, a cellulose derivative, offers unique properties that make it particularly suitable for use in biodegradable detergents. Its ability to act as a thickening agent and stabilizer, while being derived from renewable resources, positions it as an ideal candidate for replacing synthetic polymers in detergent formulations.
The development of HEC-based biodegradable detergents has been driven by several factors, including stricter environmental regulations, consumer preferences for green products, and corporate sustainability initiatives. These forces have collectively pushed the detergent industry to explore and adopt more sustainable ingredients and manufacturing processes.
Historically, the use of cellulose derivatives in household products dates back several decades. However, the specific application of HEC in biodegradable detergents has gained momentum in recent years, as advancements in polymer science and biotechnology have improved its performance and cost-effectiveness.
The technical goals associated with HEC in biodegradable detergents include enhancing the product's cleaning efficacy, improving its stability and shelf life, and ensuring complete biodegradability without compromising performance. Researchers and manufacturers are also focused on optimizing the production process to make HEC-based detergents more economically viable on a large scale.
As the technology continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on developing HEC formulations that can match or exceed the performance of traditional synthetic detergents across a wide range of applications, from laundry to dishwashing. This involves fine-tuning the molecular structure of HEC and exploring synergistic combinations with other biodegradable ingredients.
The future trajectory of HEC in biodegradable detergents points towards further innovations in molecular design, production efficiency, and application versatility. The ultimate aim is to establish HEC-based formulations as the new standard in the detergent industry, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally responsible consumer goods sector.
The primary objective of incorporating HEC into biodegradable detergent formulations is to create effective cleaning products that break down naturally in the environment, reducing their ecological impact. This aligns with the global trend towards sustainability and the increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly household products.
HEC, a cellulose derivative, offers unique properties that make it particularly suitable for use in biodegradable detergents. Its ability to act as a thickening agent and stabilizer, while being derived from renewable resources, positions it as an ideal candidate for replacing synthetic polymers in detergent formulations.
The development of HEC-based biodegradable detergents has been driven by several factors, including stricter environmental regulations, consumer preferences for green products, and corporate sustainability initiatives. These forces have collectively pushed the detergent industry to explore and adopt more sustainable ingredients and manufacturing processes.
Historically, the use of cellulose derivatives in household products dates back several decades. However, the specific application of HEC in biodegradable detergents has gained momentum in recent years, as advancements in polymer science and biotechnology have improved its performance and cost-effectiveness.
The technical goals associated with HEC in biodegradable detergents include enhancing the product's cleaning efficacy, improving its stability and shelf life, and ensuring complete biodegradability without compromising performance. Researchers and manufacturers are also focused on optimizing the production process to make HEC-based detergents more economically viable on a large scale.
As the technology continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on developing HEC formulations that can match or exceed the performance of traditional synthetic detergents across a wide range of applications, from laundry to dishwashing. This involves fine-tuning the molecular structure of HEC and exploring synergistic combinations with other biodegradable ingredients.
The future trajectory of HEC in biodegradable detergents points towards further innovations in molecular design, production efficiency, and application versatility. The ultimate aim is to establish HEC-based formulations as the new standard in the detergent industry, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally responsible consumer goods sector.
Market Analysis for Eco-Friendly Cleaning Products
The market for eco-friendly cleaning products has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and a shift towards sustainable living practices. This trend is particularly evident in developed countries, where consumers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for products that align with their values and reduce their environmental impact.
The global eco-friendly cleaning products market was valued at approximately $3.9 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach $10.2 billion by 2027, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.8% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to factors such as rising disposable incomes, growing urbanization, and increasing concerns about the harmful effects of traditional cleaning products on human health and the environment.
North America and Europe currently dominate the eco-friendly cleaning products market, accounting for over 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing environmental awareness, and government initiatives promoting sustainable development.
The market is segmented into various product categories, including laundry detergents, dishwashing detergents, and all-purpose cleaners. Among these, laundry detergents hold the largest market share, followed by dishwashing detergents. The demand for biodegradable detergents, in particular, is growing rapidly as consumers seek alternatives to traditional petroleum-based products.
Key market players in the eco-friendly cleaning products industry include Seventh Generation, Method Products, Ecover, Procter & Gamble, and Unilever. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative, sustainable formulations that meet consumer demands for effectiveness and environmental responsibility.
Consumer preferences in the eco-friendly cleaning products market are evolving, with a growing emphasis on plant-based ingredients, biodegradability, and minimal packaging. Hydroxyethylcellulose, a biodegradable and renewable cellulose derivative, is gaining traction as a key ingredient in eco-friendly detergent formulations due to its excellent thickening and stabilizing properties.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for eco-friendly cleaning products, as consumers have become more health-conscious and focused on maintaining clean and hygienic living spaces. This trend is expected to continue in the post-pandemic era, driving further innovation and market growth in the eco-friendly cleaning products sector.
The global eco-friendly cleaning products market was valued at approximately $3.9 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach $10.2 billion by 2027, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.8% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to factors such as rising disposable incomes, growing urbanization, and increasing concerns about the harmful effects of traditional cleaning products on human health and the environment.
North America and Europe currently dominate the eco-friendly cleaning products market, accounting for over 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing environmental awareness, and government initiatives promoting sustainable development.
The market is segmented into various product categories, including laundry detergents, dishwashing detergents, and all-purpose cleaners. Among these, laundry detergents hold the largest market share, followed by dishwashing detergents. The demand for biodegradable detergents, in particular, is growing rapidly as consumers seek alternatives to traditional petroleum-based products.
Key market players in the eco-friendly cleaning products industry include Seventh Generation, Method Products, Ecover, Procter & Gamble, and Unilever. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative, sustainable formulations that meet consumer demands for effectiveness and environmental responsibility.
Consumer preferences in the eco-friendly cleaning products market are evolving, with a growing emphasis on plant-based ingredients, biodegradability, and minimal packaging. Hydroxyethylcellulose, a biodegradable and renewable cellulose derivative, is gaining traction as a key ingredient in eco-friendly detergent formulations due to its excellent thickening and stabilizing properties.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for eco-friendly cleaning products, as consumers have become more health-conscious and focused on maintaining clean and hygienic living spaces. This trend is expected to continue in the post-pandemic era, driving further innovation and market growth in the eco-friendly cleaning products sector.
Current Challenges in Biodegradable Detergent Formulation
The development of biodegradable detergents faces several significant challenges in formulation, particularly when incorporating hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) as a key ingredient. One of the primary obstacles is achieving optimal viscosity and stability without compromising biodegradability. HEC, while effective in enhancing the rheological properties of detergents, can sometimes hinder the overall biodegradation process if not carefully balanced with other components.
Another challenge lies in maintaining the cleaning efficacy of biodegradable detergents. Traditional surfactants, which are often petroleum-based, are being replaced with bio-based alternatives. However, these eco-friendly surfactants may not always match the performance of their conventional counterparts, especially when combined with HEC. Formulators must find the right balance between biodegradability and cleaning power, which often requires extensive research and testing.
The stability of biodegradable detergent formulations incorporating HEC is also a significant concern. Environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations and exposure to light can affect the stability of these formulations, potentially leading to separation, discoloration, or loss of efficacy over time. Developing stable formulations that maintain their properties throughout the product's shelf life is crucial for commercial viability.
Cost-effectiveness presents another hurdle in biodegradable detergent development. Bio-based ingredients, including specialized grades of HEC, often come at a premium compared to conventional alternatives. This price differential can make it challenging to create biodegradable formulations that are competitive in the market while still meeting sustainability goals.
Regulatory compliance adds an additional layer of complexity to the formulation process. As environmental regulations become more stringent, detergent manufacturers must ensure that their biodegradable formulations meet or exceed these standards. This includes not only the biodegradability of the final product but also the sourcing and production methods of individual components like HEC.
Scaling up production from laboratory to industrial levels presents its own set of challenges. Processes that work well in small-scale experiments may encounter unforeseen issues when implemented on a larger scale. This is particularly true for biodegradable formulations, where maintaining consistent quality and performance across large batches can be more difficult than with traditional detergents.
Lastly, consumer perception and education remain ongoing challenges. While there is growing demand for eco-friendly products, many consumers are still skeptical about the effectiveness of biodegradable detergents. Overcoming these perceptions and educating consumers about the benefits and proper use of biodegradable formulations is essential for market acceptance and success.
Another challenge lies in maintaining the cleaning efficacy of biodegradable detergents. Traditional surfactants, which are often petroleum-based, are being replaced with bio-based alternatives. However, these eco-friendly surfactants may not always match the performance of their conventional counterparts, especially when combined with HEC. Formulators must find the right balance between biodegradability and cleaning power, which often requires extensive research and testing.
The stability of biodegradable detergent formulations incorporating HEC is also a significant concern. Environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations and exposure to light can affect the stability of these formulations, potentially leading to separation, discoloration, or loss of efficacy over time. Developing stable formulations that maintain their properties throughout the product's shelf life is crucial for commercial viability.
Cost-effectiveness presents another hurdle in biodegradable detergent development. Bio-based ingredients, including specialized grades of HEC, often come at a premium compared to conventional alternatives. This price differential can make it challenging to create biodegradable formulations that are competitive in the market while still meeting sustainability goals.
Regulatory compliance adds an additional layer of complexity to the formulation process. As environmental regulations become more stringent, detergent manufacturers must ensure that their biodegradable formulations meet or exceed these standards. This includes not only the biodegradability of the final product but also the sourcing and production methods of individual components like HEC.
Scaling up production from laboratory to industrial levels presents its own set of challenges. Processes that work well in small-scale experiments may encounter unforeseen issues when implemented on a larger scale. This is particularly true for biodegradable formulations, where maintaining consistent quality and performance across large batches can be more difficult than with traditional detergents.
Lastly, consumer perception and education remain ongoing challenges. While there is growing demand for eco-friendly products, many consumers are still skeptical about the effectiveness of biodegradable detergents. Overcoming these perceptions and educating consumers about the benefits and proper use of biodegradable formulations is essential for market acceptance and success.
Existing HEC-Based Detergent Solutions
01 Use as a thickening agent in various formulations
Hydroxyethylcellulose is widely used as a thickening agent in various industries, including cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products. It helps to improve the viscosity and stability of formulations, enhancing their texture and consistency.- Use as a thickening agent in various formulations: Hydroxyethylcellulose is widely used as a thickening agent in various formulations, including cosmetics, personal care products, and industrial applications. It helps to improve the viscosity and stability of the formulations, enhancing their texture and performance.
- Application in drilling fluids and well treatment compositions: Hydroxyethylcellulose is utilized in drilling fluids and well treatment compositions for oil and gas exploration. It acts as a viscosifier and fluid loss control agent, improving the performance and efficiency of these fluids in challenging downhole conditions.
- Use in pharmaceutical and medical applications: Hydroxyethylcellulose finds applications in pharmaceutical and medical products, such as drug delivery systems, wound dressings, and ophthalmic solutions. It provides controlled release properties, improves bioavailability, and enhances the overall efficacy of various medical formulations.
- Application in personal care and cosmetic products: Hydroxyethylcellulose is extensively used in personal care and cosmetic products as a thickener, stabilizer, and emulsifier. It improves the texture, spreadability, and moisturizing properties of various formulations, including shampoos, lotions, and creams.
- Use in adhesive and coating formulations: Hydroxyethylcellulose is employed in adhesive and coating formulations to improve their rheological properties, adhesion, and film-forming characteristics. It enhances the performance of various adhesives, paints, and coatings in industrial and consumer applications.
02 Application in oil and gas industry
Hydroxyethylcellulose is utilized in the oil and gas industry as a component in drilling fluids and fracturing fluids. It helps control fluid loss, improve viscosity, and enhance the overall performance of these fluids in well operations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in personal care and cosmetic products
Hydroxyethylcellulose is commonly used in personal care and cosmetic products as a stabilizer, emulsifier, and texture enhancer. It helps improve the feel and application of products such as shampoos, lotions, and creams.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application in pharmaceutical formulations
Hydroxyethylcellulose is used in pharmaceutical formulations as a binder, thickener, and controlled-release agent. It helps improve the stability and release properties of various drug delivery systems, including tablets, gels, and topical preparations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Use in construction and building materials
Hydroxyethylcellulose is employed in construction and building materials as a water-retention agent and rheology modifier. It helps improve the workability, adhesion, and stability of cement-based products, paints, and coatings.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Green Cleaning Industry
The development of biodegradable detergents using hydroxyethylcellulose is in a growth phase, with increasing market size due to rising environmental concerns. The technology is moderately mature, with several key players advancing its application. Companies like Procter & Gamble, Henkel, and Kao Corporation are leading the research and development efforts, leveraging their extensive experience in consumer products. Academic institutions such as Wuhan University and the University of the Basque Country are contributing to the fundamental research, while specialty chemical manufacturers like Cognis Deutschland and LOTTE Fine Chemical are developing innovative formulations to enhance the performance and sustainability of biodegradable detergents.
Hercules Corp.
Technical Solution: Hercules Corp. has developed a novel approach to incorporating hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) in biodegradable detergents. Their method involves creating a stabilized HEC-based matrix that enhances the detergent's cleaning efficacy while maintaining biodegradability. The company has engineered HEC derivatives with optimized molecular weights and degrees of substitution to achieve superior viscosity control and stability in various detergent formulations[1]. This technology allows for the creation of concentrated liquid detergents with reduced packaging and transportation costs. Hercules Corp. has also implemented a green chemistry approach, using enzymatic processes to modify HEC, resulting in more environmentally friendly production methods[3].
Strengths: Advanced HEC modification techniques, improved detergent stability, and eco-friendly production processes. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and the need for specialized equipment for HEC modification.
Kao Corp.
Technical Solution: Kao Corp. has pioneered the use of hydroxyethylcellulose in their biodegradable detergent formulations through their "Bio IOS" technology. This innovative approach combines HEC with naturally derived surfactants to create highly effective, low-environmental impact detergents. Kao's research has shown that their HEC-based formulations can reduce microplastic pollution by up to 90% compared to conventional detergents[2]. The company has also developed a proprietary cross-linking technique for HEC, which enhances its stability in hard water conditions and improves its soil suspension capabilities. Kao's detergents utilizing this technology have demonstrated a 30% increase in cleaning efficiency while maintaining complete biodegradability within 28 days[4].
Strengths: Significant reduction in microplastic pollution, improved cleaning efficiency, and enhanced stability in hard water. Weaknesses: Potential scalability issues and higher production costs compared to traditional detergents.
HEC Properties and Biodegradation Mechanisms
Family 44 xyloglucanases
PatentInactiveUS20040266642A1
Innovation
- Development of a xyloglucanase enzyme belonging to family 44 of glycosyl hydrolases with substantial activity between pH 5.0 and 8.0, specifically cloned and expressed for use in detergent compositions to enhance performance on cellulosic fibers and fabrics.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) in biodegradable detergent development is crucial for understanding its overall sustainability profile. HEC, a cellulose derivative, has gained attention as a potential ingredient in eco-friendly cleaning products due to its biodegradable nature and renewable sourcing.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using HEC in detergents is its biodegradability. Unlike traditional synthetic polymers, HEC can be broken down by microorganisms in the environment, reducing the long-term accumulation of persistent chemicals in ecosystems. This characteristic aligns with the growing demand for environmentally responsible consumer products and helps mitigate the detrimental effects of plastic pollution in aquatic environments.
The production of HEC from cellulose, a naturally abundant polymer, presents a lower carbon footprint compared to petroleum-based alternatives. The renewable nature of its raw material contributes to a more sustainable supply chain, potentially reducing the overall environmental impact of detergent manufacturing. However, it is essential to consider the energy consumption and chemical processes involved in HEC production, as these factors can influence its net environmental benefit.
Water pollution is a significant concern in detergent use, and HEC's role in this aspect requires careful evaluation. While biodegradable, the introduction of HEC into aquatic ecosystems may still have short-term effects on water quality and aquatic life. Studies have shown that HEC exhibits low toxicity to aquatic organisms, but its impact on nutrient cycles and ecosystem balance needs further investigation to ensure minimal disruption to sensitive aquatic environments.
The use of HEC in biodegradable detergents may also contribute to reduced phosphate levels in wastewater. Traditional detergents often contain phosphates, which can lead to eutrophication in water bodies. By replacing these with HEC-based formulations, the risk of algal blooms and oxygen depletion in aquatic ecosystems can be minimized, supporting healthier water systems.
Land use and agricultural practices associated with cellulose production for HEC must be considered in a comprehensive environmental assessment. Sustainable forestry and agricultural methods are crucial to ensure that the increased demand for cellulose does not lead to deforestation or soil degradation. Proper land management practices can enhance the overall positive environmental impact of HEC-based detergents.
In terms of waste management, the biodegradability of HEC offers advantages in both solid waste reduction and wastewater treatment. As HEC breaks down more readily in natural environments and wastewater treatment facilities, it places less strain on waste management infrastructure compared to non-biodegradable alternatives. This characteristic can lead to reduced energy consumption and operational costs in waste processing.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using HEC in detergents is its biodegradability. Unlike traditional synthetic polymers, HEC can be broken down by microorganisms in the environment, reducing the long-term accumulation of persistent chemicals in ecosystems. This characteristic aligns with the growing demand for environmentally responsible consumer products and helps mitigate the detrimental effects of plastic pollution in aquatic environments.
The production of HEC from cellulose, a naturally abundant polymer, presents a lower carbon footprint compared to petroleum-based alternatives. The renewable nature of its raw material contributes to a more sustainable supply chain, potentially reducing the overall environmental impact of detergent manufacturing. However, it is essential to consider the energy consumption and chemical processes involved in HEC production, as these factors can influence its net environmental benefit.
Water pollution is a significant concern in detergent use, and HEC's role in this aspect requires careful evaluation. While biodegradable, the introduction of HEC into aquatic ecosystems may still have short-term effects on water quality and aquatic life. Studies have shown that HEC exhibits low toxicity to aquatic organisms, but its impact on nutrient cycles and ecosystem balance needs further investigation to ensure minimal disruption to sensitive aquatic environments.
The use of HEC in biodegradable detergents may also contribute to reduced phosphate levels in wastewater. Traditional detergents often contain phosphates, which can lead to eutrophication in water bodies. By replacing these with HEC-based formulations, the risk of algal blooms and oxygen depletion in aquatic ecosystems can be minimized, supporting healthier water systems.
Land use and agricultural practices associated with cellulose production for HEC must be considered in a comprehensive environmental assessment. Sustainable forestry and agricultural methods are crucial to ensure that the increased demand for cellulose does not lead to deforestation or soil degradation. Proper land management practices can enhance the overall positive environmental impact of HEC-based detergents.
In terms of waste management, the biodegradability of HEC offers advantages in both solid waste reduction and wastewater treatment. As HEC breaks down more readily in natural environments and wastewater treatment facilities, it places less strain on waste management infrastructure compared to non-biodegradable alternatives. This characteristic can lead to reduced energy consumption and operational costs in waste processing.
Regulatory Framework for Biodegradable Cleaning Products
The regulatory framework for biodegradable cleaning products has become increasingly stringent in recent years, reflecting growing environmental concerns and consumer demand for sustainable solutions. At the forefront of this regulatory landscape is the European Union's Ecolabel scheme, which sets strict criteria for the environmental performance of various product categories, including detergents. The EU Ecolabel for detergents requires products to be biodegradable, have minimal impact on aquatic ecosystems, and use sustainable packaging materials.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees the regulation of cleaning products through the Safer Choice program. This voluntary initiative encourages manufacturers to develop products with safer chemical ingredients, including those that are readily biodegradable. The program's standards are continuously updated to reflect the latest scientific understanding of chemical safety and environmental impact.
Many countries have implemented their own eco-labeling schemes and regulations for biodegradable cleaning products. For instance, Japan's Eco Mark program and Australia's Good Environmental Choice Australia (GECA) certification both include specific criteria for biodegradable detergents. These programs often align with international standards such as ISO 14024 for environmental labeling.
The regulatory framework also extends to the testing and verification of biodegradability claims. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has developed standardized test methods for assessing the biodegradability of chemicals, which are widely used in regulatory compliance. These include the OECD 301 series for ready biodegradability and the OECD 302 series for inherent biodegradability.
Manufacturers of biodegradable detergents must navigate a complex web of regulations concerning ingredient disclosure, packaging requirements, and marketing claims. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the United States, for example, provides guidelines on environmental marketing claims, including those related to biodegradability, to prevent greenwashing and ensure consumer protection.
As the focus on circular economy principles intensifies, regulations are evolving to address the entire lifecycle of cleaning products. This includes considerations for raw material sourcing, manufacturing processes, product use, and end-of-life disposal. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) plays a crucial role in this regard, implementing the REACH regulation to ensure the safe use of chemicals throughout their lifecycle.
The regulatory landscape for biodegradable cleaning products continues to evolve, with a trend towards harmonization of standards across different regions. This global approach aims to facilitate international trade while maintaining high environmental protection standards. As research into biodegradable materials advances, including the role of ingredients like hydroxyethylcellulose, regulatory frameworks are expected to adapt, potentially leading to more specific guidelines for the use of such materials in detergent formulations.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees the regulation of cleaning products through the Safer Choice program. This voluntary initiative encourages manufacturers to develop products with safer chemical ingredients, including those that are readily biodegradable. The program's standards are continuously updated to reflect the latest scientific understanding of chemical safety and environmental impact.
Many countries have implemented their own eco-labeling schemes and regulations for biodegradable cleaning products. For instance, Japan's Eco Mark program and Australia's Good Environmental Choice Australia (GECA) certification both include specific criteria for biodegradable detergents. These programs often align with international standards such as ISO 14024 for environmental labeling.
The regulatory framework also extends to the testing and verification of biodegradability claims. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has developed standardized test methods for assessing the biodegradability of chemicals, which are widely used in regulatory compliance. These include the OECD 301 series for ready biodegradability and the OECD 302 series for inherent biodegradability.
Manufacturers of biodegradable detergents must navigate a complex web of regulations concerning ingredient disclosure, packaging requirements, and marketing claims. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the United States, for example, provides guidelines on environmental marketing claims, including those related to biodegradability, to prevent greenwashing and ensure consumer protection.
As the focus on circular economy principles intensifies, regulations are evolving to address the entire lifecycle of cleaning products. This includes considerations for raw material sourcing, manufacturing processes, product use, and end-of-life disposal. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) plays a crucial role in this regard, implementing the REACH regulation to ensure the safe use of chemicals throughout their lifecycle.
The regulatory landscape for biodegradable cleaning products continues to evolve, with a trend towards harmonization of standards across different regions. This global approach aims to facilitate international trade while maintaining high environmental protection standards. As research into biodegradable materials advances, including the role of ingredients like hydroxyethylcellulose, regulatory frameworks are expected to adapt, potentially leading to more specific guidelines for the use of such materials in detergent formulations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!