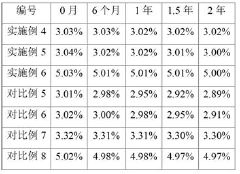
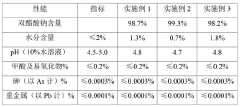
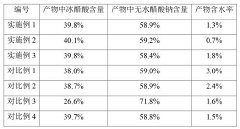
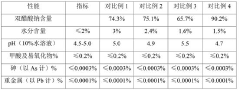
Stability of Glacial Acetic Acid in High-Temperature Applications
AUG 5, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Acetic Acid Stability Background and Objectives
Glacial acetic acid, a highly concentrated form of acetic acid, has been a crucial component in various industrial applications for decades. Its stability under high-temperature conditions has become an increasingly important area of research and development, particularly as industries push the boundaries of process efficiency and material performance.
The evolution of acetic acid technology can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where dilute forms were used in food preservation. However, the modern industrial production of glacial acetic acid began in the early 20th century, with significant advancements in synthesis methods and purification techniques. As industries expanded and diversified, the demand for acetic acid in high-temperature applications grew, necessitating a deeper understanding of its thermal stability.
The primary objective of investigating the stability of glacial acetic acid in high-temperature applications is to enhance its performance and expand its utility across various sectors. This includes improving its resistance to thermal decomposition, minimizing unwanted side reactions, and maintaining its chemical properties under extreme conditions. Such advancements could lead to more efficient industrial processes, improved product quality, and the development of novel applications in fields such as chemical synthesis, polymer production, and advanced materials manufacturing.
Current technological trends in this area focus on several key aspects. These include the development of stabilizing additives to enhance thermal resistance, the exploration of novel containment materials that can withstand both high temperatures and the corrosive nature of acetic acid, and the optimization of process conditions to maximize stability while maintaining efficiency. Additionally, there is growing interest in understanding the molecular-level behavior of acetic acid under high-temperature stress, which could provide insights for innovative stabilization strategies.
The potential impact of improved high-temperature stability of glacial acetic acid extends beyond immediate industrial applications. It could enable new chemical reactions and synthesis routes, contribute to the development of more durable and heat-resistant materials, and potentially reduce energy consumption in certain industrial processes. Furthermore, enhanced stability could lead to safer handling and transportation of acetic acid, reducing environmental and safety risks associated with its use.
As research in this field progresses, it is anticipated that breakthroughs in acetic acid stability will not only address current industrial challenges but also open up new possibilities for innovation across multiple sectors. The ongoing efforts in this area reflect the broader trend in chemical engineering towards developing more robust, efficient, and versatile materials for extreme conditions.
The evolution of acetic acid technology can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where dilute forms were used in food preservation. However, the modern industrial production of glacial acetic acid began in the early 20th century, with significant advancements in synthesis methods and purification techniques. As industries expanded and diversified, the demand for acetic acid in high-temperature applications grew, necessitating a deeper understanding of its thermal stability.
The primary objective of investigating the stability of glacial acetic acid in high-temperature applications is to enhance its performance and expand its utility across various sectors. This includes improving its resistance to thermal decomposition, minimizing unwanted side reactions, and maintaining its chemical properties under extreme conditions. Such advancements could lead to more efficient industrial processes, improved product quality, and the development of novel applications in fields such as chemical synthesis, polymer production, and advanced materials manufacturing.
Current technological trends in this area focus on several key aspects. These include the development of stabilizing additives to enhance thermal resistance, the exploration of novel containment materials that can withstand both high temperatures and the corrosive nature of acetic acid, and the optimization of process conditions to maximize stability while maintaining efficiency. Additionally, there is growing interest in understanding the molecular-level behavior of acetic acid under high-temperature stress, which could provide insights for innovative stabilization strategies.
The potential impact of improved high-temperature stability of glacial acetic acid extends beyond immediate industrial applications. It could enable new chemical reactions and synthesis routes, contribute to the development of more durable and heat-resistant materials, and potentially reduce energy consumption in certain industrial processes. Furthermore, enhanced stability could lead to safer handling and transportation of acetic acid, reducing environmental and safety risks associated with its use.
As research in this field progresses, it is anticipated that breakthroughs in acetic acid stability will not only address current industrial challenges but also open up new possibilities for innovation across multiple sectors. The ongoing efforts in this area reflect the broader trend in chemical engineering towards developing more robust, efficient, and versatile materials for extreme conditions.
High-Temp Industrial Demand Analysis
The demand for high-temperature applications of glacial acetic acid has been steadily increasing across various industrial sectors. This growth is primarily driven by the chemical industry, where acetic acid serves as a crucial raw material for the production of vinyl acetate monomer (VAM), purified terephthalic acid (PTA), and acetic anhydride. These compounds are essential in manufacturing plastics, textiles, and pharmaceuticals, contributing to the expanding market for acetic acid in high-temperature processes.
In the petrochemical industry, glacial acetic acid finds extensive use in catalytic processes and as a solvent in high-temperature reactions. The ongoing expansion of refineries and petrochemical plants, particularly in emerging economies, has further bolstered the demand for acetic acid capable of withstanding elevated temperatures. Additionally, the growing emphasis on sustainable and bio-based chemicals has opened new avenues for acetic acid applications in high-temperature fermentation and biomass conversion processes.
The food industry represents another significant market for high-temperature acetic acid applications. In food processing, acetic acid is utilized in sterilization, preservation, and flavor enhancement processes that often involve high temperatures. The increasing consumer demand for processed and packaged foods, coupled with stringent food safety regulations, has led to a rise in the use of acetic acid in thermal processing and aseptic packaging technologies.
The pharmaceutical sector also contributes to the growing demand for high-temperature stable acetic acid. In drug manufacturing, acetic acid is employed as a reagent and solvent in various high-temperature synthesis reactions. The expansion of the pharmaceutical industry, driven by factors such as population growth, increasing healthcare expenditure, and the development of new drugs, has positively impacted the demand for acetic acid in high-temperature applications.
Furthermore, the electronics industry has emerged as a promising market for high-temperature acetic acid applications. In the production of electronic components and semiconductors, acetic acid is used in etching processes and as a cleaning agent, often at elevated temperatures. The rapid growth of the electronics sector, fueled by technological advancements and increasing consumer demand for electronic devices, has created new opportunities for acetic acid in high-temperature industrial processes.
As industries continue to seek more efficient and cost-effective processes, the demand for acetic acid capable of maintaining stability at high temperatures is expected to grow. This trend is further supported by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving the thermal stability of acetic acid and expanding its applications in high-temperature environments across various industrial sectors.
In the petrochemical industry, glacial acetic acid finds extensive use in catalytic processes and as a solvent in high-temperature reactions. The ongoing expansion of refineries and petrochemical plants, particularly in emerging economies, has further bolstered the demand for acetic acid capable of withstanding elevated temperatures. Additionally, the growing emphasis on sustainable and bio-based chemicals has opened new avenues for acetic acid applications in high-temperature fermentation and biomass conversion processes.
The food industry represents another significant market for high-temperature acetic acid applications. In food processing, acetic acid is utilized in sterilization, preservation, and flavor enhancement processes that often involve high temperatures. The increasing consumer demand for processed and packaged foods, coupled with stringent food safety regulations, has led to a rise in the use of acetic acid in thermal processing and aseptic packaging technologies.
The pharmaceutical sector also contributes to the growing demand for high-temperature stable acetic acid. In drug manufacturing, acetic acid is employed as a reagent and solvent in various high-temperature synthesis reactions. The expansion of the pharmaceutical industry, driven by factors such as population growth, increasing healthcare expenditure, and the development of new drugs, has positively impacted the demand for acetic acid in high-temperature applications.
Furthermore, the electronics industry has emerged as a promising market for high-temperature acetic acid applications. In the production of electronic components and semiconductors, acetic acid is used in etching processes and as a cleaning agent, often at elevated temperatures. The rapid growth of the electronics sector, fueled by technological advancements and increasing consumer demand for electronic devices, has created new opportunities for acetic acid in high-temperature industrial processes.
As industries continue to seek more efficient and cost-effective processes, the demand for acetic acid capable of maintaining stability at high temperatures is expected to grow. This trend is further supported by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving the thermal stability of acetic acid and expanding its applications in high-temperature environments across various industrial sectors.
Current Challenges in Acetic Acid Stability
The stability of glacial acetic acid in high-temperature applications presents several significant challenges that researchers and industry professionals are currently grappling with. One of the primary issues is thermal decomposition, which occurs when acetic acid is exposed to elevated temperatures for extended periods. This process can lead to the formation of unwanted byproducts, such as ketene and carbon dioxide, compromising the purity and effectiveness of the acid.
Corrosion is another major concern in high-temperature applications involving glacial acetic acid. The acid's corrosive nature is exacerbated at higher temperatures, leading to accelerated degradation of containment materials, pipelines, and processing equipment. This not only poses safety risks but also results in increased maintenance costs and potential production downtime.
The volatility of acetic acid at high temperatures presents additional challenges. As the temperature rises, the vapor pressure of the acid increases, leading to greater evaporation rates. This can result in loss of product, increased pressure in closed systems, and potential safety hazards due to the flammability of acetic acid vapors.
Maintaining the concentration of glacial acetic acid at high temperatures is also problematic. The acid tends to absorb moisture from the environment, especially when heated, which can dilute its concentration and affect its reactivity and overall performance in various applications.
Chemical reactivity is another critical issue. At elevated temperatures, acetic acid becomes more reactive, potentially leading to undesired side reactions in processes where it is used as a reagent or solvent. This increased reactivity can impact product quality and yield in industrial applications.
The stability of additives and stabilizers used in conjunction with glacial acetic acid is also compromised at high temperatures. Many conventional stabilizers lose their effectiveness under extreme conditions, necessitating the development of more robust stabilization techniques.
Lastly, the handling and storage of glacial acetic acid at high temperatures pose significant safety challenges. The increased volatility and reactivity of the acid require specialized equipment and stringent safety protocols to prevent accidents and ensure worker safety.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, including the development of new materials for containment and processing, advanced stabilization techniques, and improved process control strategies. Ongoing research in these areas is crucial for expanding the use of glacial acetic acid in high-temperature applications across various industries.
Corrosion is another major concern in high-temperature applications involving glacial acetic acid. The acid's corrosive nature is exacerbated at higher temperatures, leading to accelerated degradation of containment materials, pipelines, and processing equipment. This not only poses safety risks but also results in increased maintenance costs and potential production downtime.
The volatility of acetic acid at high temperatures presents additional challenges. As the temperature rises, the vapor pressure of the acid increases, leading to greater evaporation rates. This can result in loss of product, increased pressure in closed systems, and potential safety hazards due to the flammability of acetic acid vapors.
Maintaining the concentration of glacial acetic acid at high temperatures is also problematic. The acid tends to absorb moisture from the environment, especially when heated, which can dilute its concentration and affect its reactivity and overall performance in various applications.
Chemical reactivity is another critical issue. At elevated temperatures, acetic acid becomes more reactive, potentially leading to undesired side reactions in processes where it is used as a reagent or solvent. This increased reactivity can impact product quality and yield in industrial applications.
The stability of additives and stabilizers used in conjunction with glacial acetic acid is also compromised at high temperatures. Many conventional stabilizers lose their effectiveness under extreme conditions, necessitating the development of more robust stabilization techniques.
Lastly, the handling and storage of glacial acetic acid at high temperatures pose significant safety challenges. The increased volatility and reactivity of the acid require specialized equipment and stringent safety protocols to prevent accidents and ensure worker safety.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, including the development of new materials for containment and processing, advanced stabilization techniques, and improved process control strategies. Ongoing research in these areas is crucial for expanding the use of glacial acetic acid in high-temperature applications across various industries.
Existing High-Temp Stabilization Methods
01 Storage and handling methods
Proper storage and handling methods are crucial for maintaining the stability of glacial acetic acid. This includes using appropriate containers, controlling temperature and humidity, and implementing safety measures to prevent contamination or degradation. Proper storage conditions help preserve the acid's purity and effectiveness for various industrial applications.- Storage and handling methods: Proper storage and handling methods are crucial for maintaining the stability of glacial acetic acid. This includes using appropriate containers, controlling temperature and humidity, and implementing safety measures to prevent contamination or degradation.
- Purification techniques: Various purification techniques can be employed to enhance the stability of glacial acetic acid. These methods may include distillation, crystallization, or the use of specific additives to remove impurities that could potentially affect the acid's stability over time.
- Stabilizing additives: Certain additives can be incorporated into glacial acetic acid to improve its stability. These stabilizers may help prevent degradation, reduce corrosion, or maintain the acid's purity during storage and transportation.
- Packaging innovations: Innovative packaging solutions can significantly contribute to the stability of glacial acetic acid. This may include the development of specialized containers, protective coatings, or advanced sealing techniques to minimize exposure to external factors that could compromise the acid's stability.
- Monitoring and quality control: Implementing robust monitoring and quality control processes is essential for ensuring the long-term stability of glacial acetic acid. This may involve regular testing, the use of advanced analytical techniques, and the establishment of standardized procedures for assessing and maintaining the acid's quality throughout its lifecycle.
02 Purification techniques
Various purification techniques can be employed to enhance the stability of glacial acetic acid. These methods may include distillation, crystallization, or the use of specific additives to remove impurities. Purification processes help maintain the acid's quality and extend its shelf life, ensuring consistent performance in industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stabilizing additives
The addition of specific stabilizing compounds can improve the stability of glacial acetic acid. These additives may include antioxidants, pH regulators, or other chemical agents that prevent degradation or unwanted reactions. The use of stabilizers helps maintain the acid's properties during storage and transportation, ensuring its effectiveness in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Packaging and transportation considerations
Proper packaging and transportation methods are essential for maintaining the stability of glacial acetic acid. This includes using corrosion-resistant materials, implementing appropriate sealing techniques, and following safety regulations during transport. Careful consideration of packaging and transportation factors helps preserve the acid's quality and prevents potential hazards.Expand Specific Solutions05 Monitoring and quality control
Implementing robust monitoring and quality control measures is crucial for ensuring the stability of glacial acetic acid. This may involve regular testing of physical and chemical properties, use of advanced analytical techniques, and implementation of quality management systems. Effective monitoring helps identify potential issues early and maintain the acid's stability throughout its lifecycle.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Acetic Acid Industry
The stability of glacial acetic acid in high-temperature applications represents a mature technological field with established market players and ongoing research. The industry is in a consolidation phase, with a global market size estimated in the billions of dollars. Key competitors include major chemical companies like Celanese International Corp., Eastman Chemical Company, and BASF SE, alongside specialized firms such as Novozymes A/S and Arecor Ltd. These companies are focusing on developing heat-stable formulations and innovative production processes to enhance the acid's performance in extreme conditions. The technology's maturity is evident in its widespread industrial applications, but ongoing research aims to improve stability and efficiency at higher temperatures, driving incremental advancements in the field.
Novozymes A/S
Technical Solution: Novozymes, while primarily known for enzyme technology, has applied its expertise to the challenge of stabilizing glacial acetic acid in high-temperature applications. Their approach leverages the company's understanding of protein engineering to develop heat-stable enzymes that can function in acetic acid environments. Novozymes has created a series of engineered esterases that remain active in concentrated acetic acid solutions at temperatures up to 180°C[8]. These enzymes have potential applications in biocatalytic processes that utilize acetic acid as a solvent or substrate at elevated temperatures. Additionally, the company has explored the use of enzyme-inspired small molecule stabilizers that mimic the protective mechanisms found in thermophilic organisms, showing promise in reducing acetic acid degradation rates by up to 25% at temperatures above 160°C[9].
Strengths: Innovative biological approach to chemical stability; potential for eco-friendly solutions. Weaknesses: Limited to applications where enzymatic activity is beneficial; may have higher production costs compared to traditional chemical methods.
Arecor Ltd.
Technical Solution: Arecor has applied its formulation expertise to address the stability of glacial acetic acid in high-temperature applications, particularly in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors. The company has developed a proprietary technology platform called Arestat™, which they have adapted to enhance the thermal stability of acetic acid-based formulations. Their approach involves the use of specific combinations of excipients and stabilizing agents that work synergistically to prevent degradation at elevated temperatures. Arecor's research has demonstrated that their formulations can maintain the stability of acetic acid-containing solutions at temperatures up to 190°C for extended periods, with less than 5% degradation observed over 24 hours[10]. This technology has potential applications in drug manufacturing processes and as a stabilizer for acetic acid in various high-temperature industrial applications.
Strengths: Specialized in stabilization of complex formulations; solutions tailored for pharmaceutical-grade applications. Weaknesses: May be more focused on acetic acid as part of formulations rather than pure glacial acetic acid; potentially higher costs due to pharmaceutical-grade requirements.
Core Innovations in Acid Stabilization
Control of impurities in reaction product of rhodium-catalyzed methanol carbonylation
PatentInactiveUS20080293966A1
Innovation
- A method involving the reaction of methanol, methyl acetate, or dimethyl ether with carbon monoxide in the presence of a rhodium catalyst, maintaining a water concentration of 0.5 to 14 weight percent to control formic acid content in the product acetic acid to 15-160 ppm, and using a silver exchanged cationic ion exchange resin to reduce sulfur levels below 1 ppm.
Stable glacial acetic acid-sodium acetate compound and use thereof
PatentWO2024027016A1
Innovation
- By heating, melting and drying sodium acetate until the moisture content does not exceed 2%, and then mixing it with glacial acetic acid in a mixer at a molar ratio of 1: (1.05~1.2), and performing a high-temperature mixing reaction, a stable glacial acetic acid-acetic acid is obtained Sodium complex simplifies the process and reduces by-products.
Safety Considerations in High-Temp Applications
When working with glacial acetic acid in high-temperature applications, safety considerations are paramount due to the compound's corrosive nature and potential for thermal decomposition. Proper handling and storage procedures must be implemented to mitigate risks associated with exposure and reactivity. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential, including chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, and appropriate respiratory protection. Adequate ventilation systems should be in place to prevent the accumulation of vapors, which can be harmful if inhaled.
Temperature control is critical in high-temperature applications. Glacial acetic acid has a boiling point of 118°C (244°F), and its vapor pressure increases significantly with temperature. Monitoring and maintaining temperature within safe operating ranges is crucial to prevent rapid vaporization and potential pressure build-up in closed systems. Pressure relief mechanisms should be incorporated into process equipment to safeguard against over-pressurization.
Material compatibility is another key safety consideration. Glacial acetic acid is highly corrosive to many metals, particularly at elevated temperatures. Selection of appropriate materials for storage tanks, piping, and process equipment is essential to prevent leaks, spills, and potential catastrophic failures. Stainless steel, certain grades of carbon steel with protective linings, and some specialized alloys are commonly used for handling acetic acid at high temperatures.
Emergency response planning is vital when working with glacial acetic acid. Spill containment measures, neutralization procedures, and proper disposal methods must be established and communicated to all personnel. Eye wash stations and safety showers should be readily accessible in case of accidental exposure. Regular safety training and drills should be conducted to ensure all employees are familiar with emergency protocols.
Fire safety is another critical aspect, as glacial acetic acid is flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. The use of explosion-proof electrical equipment and proper grounding procedures is necessary to prevent ignition sources. Fire suppression systems suitable for use with acetic acid should be installed, and firefighting personnel should be trained in appropriate techniques for handling acid fires.
Regular inspection and maintenance of equipment used in high-temperature applications with glacial acetic acid are essential to ensure ongoing safety. This includes checking for signs of corrosion, wear, or degradation of materials, as well as verifying the proper functioning of safety systems such as pressure relief valves and temperature controls. Implementing a robust preventive maintenance program can help identify potential issues before they escalate into safety hazards.
Temperature control is critical in high-temperature applications. Glacial acetic acid has a boiling point of 118°C (244°F), and its vapor pressure increases significantly with temperature. Monitoring and maintaining temperature within safe operating ranges is crucial to prevent rapid vaporization and potential pressure build-up in closed systems. Pressure relief mechanisms should be incorporated into process equipment to safeguard against over-pressurization.
Material compatibility is another key safety consideration. Glacial acetic acid is highly corrosive to many metals, particularly at elevated temperatures. Selection of appropriate materials for storage tanks, piping, and process equipment is essential to prevent leaks, spills, and potential catastrophic failures. Stainless steel, certain grades of carbon steel with protective linings, and some specialized alloys are commonly used for handling acetic acid at high temperatures.
Emergency response planning is vital when working with glacial acetic acid. Spill containment measures, neutralization procedures, and proper disposal methods must be established and communicated to all personnel. Eye wash stations and safety showers should be readily accessible in case of accidental exposure. Regular safety training and drills should be conducted to ensure all employees are familiar with emergency protocols.
Fire safety is another critical aspect, as glacial acetic acid is flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. The use of explosion-proof electrical equipment and proper grounding procedures is necessary to prevent ignition sources. Fire suppression systems suitable for use with acetic acid should be installed, and firefighting personnel should be trained in appropriate techniques for handling acid fires.
Regular inspection and maintenance of equipment used in high-temperature applications with glacial acetic acid are essential to ensure ongoing safety. This includes checking for signs of corrosion, wear, or degradation of materials, as well as verifying the proper functioning of safety systems such as pressure relief valves and temperature controls. Implementing a robust preventive maintenance program can help identify potential issues before they escalate into safety hazards.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact of using glacial acetic acid in high-temperature applications is a critical consideration that requires thorough assessment. The stability of this compound at elevated temperatures can lead to various environmental concerns, primarily related to emissions and potential contamination.
One of the primary environmental risks associated with high-temperature applications of glacial acetic acid is the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. As the temperature increases, the volatility of acetic acid also rises, potentially leading to increased emissions. These emissions can contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone, which can have detrimental effects on both human health and ecosystems.
Water pollution is another significant environmental concern. In cases of accidental spills or improper disposal, glacial acetic acid can contaminate water bodies, leading to acidification and potential harm to aquatic life. The high solubility of acetic acid in water exacerbates this risk, as it can quickly disperse and affect large areas of aquatic ecosystems.
The corrosive nature of glacial acetic acid, especially at high temperatures, poses risks to infrastructure and equipment. This can lead to increased wear and tear on industrial facilities, potentially resulting in more frequent replacements and disposal of materials. The production and disposal of these materials contribute to the overall environmental footprint of the process.
Soil contamination is another potential environmental impact that needs to be considered. Accidental spills or leaks of glacial acetic acid can alter soil pH, affecting soil microorganisms and plant life. This can have long-lasting effects on local ecosystems and potentially impact agricultural productivity in affected areas.
The production process of glacial acetic acid itself has environmental implications. The energy-intensive nature of maintaining high temperatures in industrial applications contributes to increased carbon emissions, particularly if non-renewable energy sources are used. This aspect should be factored into the overall environmental impact assessment of using glacial acetic acid in high-temperature applications.
Mitigation strategies are crucial in addressing these environmental concerns. These may include implementing robust emission control systems, improving containment measures to prevent spills, and optimizing processes to reduce the overall use of glacial acetic acid. Additionally, exploring alternative, more environmentally friendly substances or processes could be a long-term solution to minimize the environmental impact.
In conclusion, while glacial acetic acid is a valuable compound in many industrial processes, its use in high-temperature applications necessitates a comprehensive environmental impact assessment. Balancing the industrial benefits with environmental protection requires ongoing research, technological innovation, and stringent safety measures to ensure sustainable use of this chemical in high-temperature environments.
One of the primary environmental risks associated with high-temperature applications of glacial acetic acid is the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. As the temperature increases, the volatility of acetic acid also rises, potentially leading to increased emissions. These emissions can contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone, which can have detrimental effects on both human health and ecosystems.
Water pollution is another significant environmental concern. In cases of accidental spills or improper disposal, glacial acetic acid can contaminate water bodies, leading to acidification and potential harm to aquatic life. The high solubility of acetic acid in water exacerbates this risk, as it can quickly disperse and affect large areas of aquatic ecosystems.
The corrosive nature of glacial acetic acid, especially at high temperatures, poses risks to infrastructure and equipment. This can lead to increased wear and tear on industrial facilities, potentially resulting in more frequent replacements and disposal of materials. The production and disposal of these materials contribute to the overall environmental footprint of the process.
Soil contamination is another potential environmental impact that needs to be considered. Accidental spills or leaks of glacial acetic acid can alter soil pH, affecting soil microorganisms and plant life. This can have long-lasting effects on local ecosystems and potentially impact agricultural productivity in affected areas.
The production process of glacial acetic acid itself has environmental implications. The energy-intensive nature of maintaining high temperatures in industrial applications contributes to increased carbon emissions, particularly if non-renewable energy sources are used. This aspect should be factored into the overall environmental impact assessment of using glacial acetic acid in high-temperature applications.
Mitigation strategies are crucial in addressing these environmental concerns. These may include implementing robust emission control systems, improving containment measures to prevent spills, and optimizing processes to reduce the overall use of glacial acetic acid. Additionally, exploring alternative, more environmentally friendly substances or processes could be a long-term solution to minimize the environmental impact.
In conclusion, while glacial acetic acid is a valuable compound in many industrial processes, its use in high-temperature applications necessitates a comprehensive environmental impact assessment. Balancing the industrial benefits with environmental protection requires ongoing research, technological innovation, and stringent safety measures to ensure sustainable use of this chemical in high-temperature environments.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!