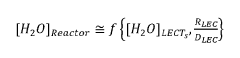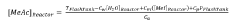Techniques for Monitoring Quality of Glacial Acetic Acid
AUG 5, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Glacial Acetic Acid Quality Monitoring: Background and Objectives
Glacial acetic acid, also known as anhydrous acetic acid, is a crucial chemical compound widely used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, textiles, and food processing. The quality monitoring of glacial acetic acid has become increasingly important due to its extensive applications and the stringent requirements for purity in many processes.
The development of techniques for monitoring the quality of glacial acetic acid has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, basic analytical methods such as titration and density measurements were the primary means of quality assessment. However, as industrial applications became more sophisticated, the need for more precise and comprehensive monitoring techniques emerged.
The primary objective of quality monitoring for glacial acetic acid is to ensure its purity, typically aiming for a concentration of 99.5% or higher. Impurities, even in minute quantities, can significantly affect the performance and safety of processes utilizing this compound. Common impurities include water, formic acid, and propionic acid, which can impact the acidity, reactivity, and overall effectiveness of the glacial acetic acid.
Recent technological advancements have led to the development of more advanced analytical techniques for quality monitoring. Spectroscopic methods, such as Near-Infrared (NIR) and Raman spectroscopy, have gained prominence due to their ability to provide rapid, non-destructive analysis. These techniques allow for real-time monitoring of acetic acid quality, enabling more efficient process control and quality assurance.
Chromatographic techniques, particularly Gas Chromatography (GC) and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), have also become essential tools in the quality monitoring arsenal. These methods offer high sensitivity and specificity, allowing for the detection and quantification of trace impurities that may not be easily identified by other means.
The trend in quality monitoring techniques is moving towards integrated systems that combine multiple analytical methods. This approach provides a more comprehensive assessment of glacial acetic acid quality, addressing various aspects such as purity, impurity profile, and physical properties simultaneously.
As industries continue to demand higher purity standards and more stringent quality control, the development of monitoring techniques is expected to focus on increasing sensitivity, improving real-time capabilities, and enhancing automation. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into quality monitoring systems is an emerging trend, promising to improve predictive capabilities and process optimization.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of glacial acetic acid quality monitoring reflect a dynamic field driven by industrial needs and technological advancements. The ongoing evolution of monitoring techniques aims to ensure the highest standards of purity and reliability in glacial acetic acid production and application across various industries.
The development of techniques for monitoring the quality of glacial acetic acid has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, basic analytical methods such as titration and density measurements were the primary means of quality assessment. However, as industrial applications became more sophisticated, the need for more precise and comprehensive monitoring techniques emerged.
The primary objective of quality monitoring for glacial acetic acid is to ensure its purity, typically aiming for a concentration of 99.5% or higher. Impurities, even in minute quantities, can significantly affect the performance and safety of processes utilizing this compound. Common impurities include water, formic acid, and propionic acid, which can impact the acidity, reactivity, and overall effectiveness of the glacial acetic acid.
Recent technological advancements have led to the development of more advanced analytical techniques for quality monitoring. Spectroscopic methods, such as Near-Infrared (NIR) and Raman spectroscopy, have gained prominence due to their ability to provide rapid, non-destructive analysis. These techniques allow for real-time monitoring of acetic acid quality, enabling more efficient process control and quality assurance.
Chromatographic techniques, particularly Gas Chromatography (GC) and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), have also become essential tools in the quality monitoring arsenal. These methods offer high sensitivity and specificity, allowing for the detection and quantification of trace impurities that may not be easily identified by other means.
The trend in quality monitoring techniques is moving towards integrated systems that combine multiple analytical methods. This approach provides a more comprehensive assessment of glacial acetic acid quality, addressing various aspects such as purity, impurity profile, and physical properties simultaneously.
As industries continue to demand higher purity standards and more stringent quality control, the development of monitoring techniques is expected to focus on increasing sensitivity, improving real-time capabilities, and enhancing automation. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into quality monitoring systems is an emerging trend, promising to improve predictive capabilities and process optimization.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of glacial acetic acid quality monitoring reflect a dynamic field driven by industrial needs and technological advancements. The ongoing evolution of monitoring techniques aims to ensure the highest standards of purity and reliability in glacial acetic acid production and application across various industries.
Market Demand Analysis for High-Purity Acetic Acid
The market demand for high-purity acetic acid, particularly glacial acetic acid, has been steadily increasing across various industries. This growth is primarily driven by the expanding applications in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, textiles, and electronics manufacturing. In the pharmaceutical industry, high-purity acetic acid is crucial for producing various medications and as a reagent in laboratory settings. The stringent quality requirements in this sector necessitate reliable monitoring techniques to ensure the purity of glacial acetic acid.
The food and beverage industry represents another significant market for high-purity acetic acid, where it is used as a food additive and preservative. With the growing consumer demand for processed and packaged foods, the need for high-quality acetic acid has surged. This trend is further amplified by the increasing popularity of organic and natural food products, which often rely on acetic acid as a natural preservative.
In the textile industry, glacial acetic acid plays a vital role in the production of synthetic fibers and dyes. The global expansion of the textile market, particularly in developing countries, has contributed to the increased demand for high-purity acetic acid. The electronics manufacturing sector also utilizes glacial acetic acid in the production of printed circuit boards and as a cleaning agent, further driving market growth.
The global market for high-purity acetic acid is expected to continue its upward trajectory in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the rising industrialization in emerging economies, technological advancements in manufacturing processes, and the increasing adoption of acetic acid-based products across various end-use industries. Additionally, the shift towards sustainable and bio-based acetic acid production methods is likely to create new opportunities in the market.
However, the market also faces challenges, such as fluctuating raw material prices and stringent environmental regulations. These factors underscore the importance of efficient monitoring techniques for glacial acetic acid quality, as manufacturers strive to optimize production processes and maintain high purity levels while managing costs. The development of advanced monitoring technologies is thus becoming increasingly critical to meet the growing market demand for high-quality acetic acid products.
The food and beverage industry represents another significant market for high-purity acetic acid, where it is used as a food additive and preservative. With the growing consumer demand for processed and packaged foods, the need for high-quality acetic acid has surged. This trend is further amplified by the increasing popularity of organic and natural food products, which often rely on acetic acid as a natural preservative.
In the textile industry, glacial acetic acid plays a vital role in the production of synthetic fibers and dyes. The global expansion of the textile market, particularly in developing countries, has contributed to the increased demand for high-purity acetic acid. The electronics manufacturing sector also utilizes glacial acetic acid in the production of printed circuit boards and as a cleaning agent, further driving market growth.
The global market for high-purity acetic acid is expected to continue its upward trajectory in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the rising industrialization in emerging economies, technological advancements in manufacturing processes, and the increasing adoption of acetic acid-based products across various end-use industries. Additionally, the shift towards sustainable and bio-based acetic acid production methods is likely to create new opportunities in the market.
However, the market also faces challenges, such as fluctuating raw material prices and stringent environmental regulations. These factors underscore the importance of efficient monitoring techniques for glacial acetic acid quality, as manufacturers strive to optimize production processes and maintain high purity levels while managing costs. The development of advanced monitoring technologies is thus becoming increasingly critical to meet the growing market demand for high-quality acetic acid products.
Current Challenges in Glacial Acetic Acid Quality Control
The quality control of glacial acetic acid faces several significant challenges in today's industrial landscape. One of the primary issues is the high purity requirement, typically 99.5% or higher, which demands extremely precise monitoring techniques. Traditional methods often struggle to detect minute impurities at these levels consistently.
Contamination during production and storage poses another major challenge. Glacial acetic acid is hygroscopic, readily absorbing moisture from the air, which can quickly compromise its purity. This necessitates stringent environmental controls and sophisticated monitoring systems to maintain quality throughout the production and storage processes.
The corrosive nature of glacial acetic acid presents additional complications for quality control. It can react with many common materials used in manufacturing and testing equipment, potentially introducing contaminants or causing equipment degradation. This reactivity limits the choice of materials for sensors and analytical instruments, often requiring specialized, costly equipment.
Temperature control during quality monitoring is crucial yet challenging. Glacial acetic acid's properties can change significantly with small temperature variations, affecting measurement accuracy. Maintaining consistent temperature conditions across production, storage, and testing environments is technically demanding and resource-intensive.
Another challenge lies in the real-time monitoring of quality parameters. Many current techniques involve batch testing or periodic sampling, which may not capture rapid quality fluctuations. Developing reliable, continuous monitoring systems that can withstand the harsh chemical environment remains a significant technical hurdle.
The detection and quantification of trace impurities, particularly organic compounds with similar properties to acetic acid, present ongoing difficulties. These impurities can significantly impact the acid's performance in various applications, yet they are often present at levels that push the limits of conventional analytical techniques.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in standardizing quality control methods across different production facilities and geographical locations. Variations in equipment, environmental conditions, and operator expertise can lead to inconsistencies in quality assessment, making it difficult to establish uniform quality standards and compare products from different sources.
Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research and development in analytical chemistry, materials science, and process engineering. Innovations in spectroscopic techniques, advanced sensor technologies, and data analytics are needed to enhance the accuracy, reliability, and efficiency of glacial acetic acid quality control processes.
Contamination during production and storage poses another major challenge. Glacial acetic acid is hygroscopic, readily absorbing moisture from the air, which can quickly compromise its purity. This necessitates stringent environmental controls and sophisticated monitoring systems to maintain quality throughout the production and storage processes.
The corrosive nature of glacial acetic acid presents additional complications for quality control. It can react with many common materials used in manufacturing and testing equipment, potentially introducing contaminants or causing equipment degradation. This reactivity limits the choice of materials for sensors and analytical instruments, often requiring specialized, costly equipment.
Temperature control during quality monitoring is crucial yet challenging. Glacial acetic acid's properties can change significantly with small temperature variations, affecting measurement accuracy. Maintaining consistent temperature conditions across production, storage, and testing environments is technically demanding and resource-intensive.
Another challenge lies in the real-time monitoring of quality parameters. Many current techniques involve batch testing or periodic sampling, which may not capture rapid quality fluctuations. Developing reliable, continuous monitoring systems that can withstand the harsh chemical environment remains a significant technical hurdle.
The detection and quantification of trace impurities, particularly organic compounds with similar properties to acetic acid, present ongoing difficulties. These impurities can significantly impact the acid's performance in various applications, yet they are often present at levels that push the limits of conventional analytical techniques.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in standardizing quality control methods across different production facilities and geographical locations. Variations in equipment, environmental conditions, and operator expertise can lead to inconsistencies in quality assessment, making it difficult to establish uniform quality standards and compare products from different sources.
Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research and development in analytical chemistry, materials science, and process engineering. Innovations in spectroscopic techniques, advanced sensor technologies, and data analytics are needed to enhance the accuracy, reliability, and efficiency of glacial acetic acid quality control processes.
Existing Quality Monitoring Techniques for Glacial Acetic Acid
01 Production methods for high-quality glacial acetic acid
Various production methods are employed to obtain high-quality glacial acetic acid. These include oxidation processes, fermentation techniques, and catalytic reactions. The focus is on optimizing reaction conditions, improving catalysts, and developing efficient separation and purification processes to achieve high purity and yield.- Purification methods for glacial acetic acid: Various purification techniques are employed to improve the quality of glacial acetic acid. These methods may include distillation, crystallization, and filtration processes to remove impurities and achieve high purity levels. Advanced purification methods can help in obtaining pharmaceutical or food-grade glacial acetic acid.
- Quality control and analysis techniques: Implementing rigorous quality control measures and utilizing advanced analytical techniques are crucial for ensuring the quality of glacial acetic acid. This may involve spectroscopic methods, chromatography, and other analytical tools to detect and quantify impurities, as well as to verify the concentration and purity of the final product.
- Production process optimization: Optimizing the production process of glacial acetic acid can significantly impact its quality. This includes refining reaction conditions, improving catalyst performance, and enhancing separation techniques. Continuous process monitoring and adjustments can lead to higher quality and more consistent glacial acetic acid production.
- Storage and handling considerations: Proper storage and handling of glacial acetic acid are essential for maintaining its quality. This involves using appropriate materials for containers and equipment, controlling temperature and humidity during storage, and implementing safety measures to prevent contamination or degradation of the product.
- Impurity reduction and removal: Developing methods to reduce and remove specific impurities in glacial acetic acid is crucial for improving its overall quality. This may include targeted approaches for eliminating trace metals, organic contaminants, or other unwanted compounds that can affect the acid's purity and performance in various applications.
02 Purification and quality control techniques
Advanced purification techniques are crucial for ensuring the quality of glacial acetic acid. These may include distillation, crystallization, and membrane separation processes. Quality control measures involve precise analytical methods to detect and remove impurities, ensuring the final product meets stringent purity standards.Expand Specific Solutions03 Storage and handling of glacial acetic acid
Proper storage and handling are essential for maintaining the quality of glacial acetic acid. This includes using appropriate materials for containers and equipment, controlling temperature and humidity, and implementing safety measures to prevent contamination and degradation during storage and transportation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Analytical methods for quality assessment
Various analytical techniques are employed to assess the quality of glacial acetic acid. These may include gas chromatography, high-performance liquid chromatography, spectroscopic methods, and titration techniques. These methods help in determining purity levels, identifying impurities, and ensuring compliance with quality standards.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications and quality requirements in different industries
The quality requirements for glacial acetic acid vary depending on its intended application. Different industries, such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical manufacturing, may have specific purity and quality standards. Understanding these requirements is crucial for producing glacial acetic acid that meets the needs of diverse industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Acetic Acid Production and Quality Monitoring
The market for monitoring techniques of glacial acetic acid quality is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for high-purity acetic acid in various industries. The global market size is expanding, with key players like LyondellBasell Acetyls LLC and BASF Plant Science LLC leading the way. Technological advancements are improving monitoring accuracy and efficiency, with companies such as Medtronic Monitoring, Inc. and Vista Precision Solutions, Inc. contributing to the field. Academic institutions like Jiangsu University and the University of Bremen are also actively researching and developing new monitoring techniques, indicating a moderate level of technological maturity with room for further innovation and refinement.
LyondellBasell Acetyls LLC
Technical Solution: LyondellBasell Acetyls LLC has developed advanced techniques for monitoring the quality of glacial acetic acid during production. Their approach involves the use of in-line Near-Infrared (NIR) spectroscopy for real-time analysis of acetic acid purity and water content[1]. This method allows for continuous monitoring without the need for sample extraction, significantly reducing the time between measurements. The company has also implemented a sophisticated data analytics system that uses machine learning algorithms to predict and prevent quality deviations based on historical production data and current process parameters[2]. Additionally, they have developed a novel catalytic distillation process that integrates quality monitoring directly into the purification step, ensuring high-purity glacial acetic acid production[3].
Strengths: Real-time monitoring capability, reduced quality control time, predictive analytics for quality assurance. Weaknesses: High initial investment for implementation, requires specialized training for operators, potential for system downtime during calibration or maintenance.
Endress+hauser Optical Analysis Inc
Technical Solution: Endress+hauser Optical Analysis Inc has pioneered the use of Raman spectroscopy for monitoring glacial acetic acid quality. Their system employs a fiber-optic probe that can be directly inserted into process streams or reactors, allowing for non-invasive, real-time measurements of acetic acid concentration and impurities[4]. The company has also developed proprietary algorithms that can compensate for temperature fluctuations and background interference, ensuring accurate readings across a wide range of process conditions[5]. Furthermore, their latest innovation includes a multi-point monitoring system that can simultaneously track acetic acid quality at various stages of production, from synthesis to purification and storage, providing a comprehensive quality assurance solution[6].
Strengths: Non-invasive monitoring, high accuracy across various process conditions, comprehensive multi-point monitoring capability. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to traditional methods, requires periodic recalibration, potential for fouling of optical components in harsh industrial environments.
Innovative Technologies for Acetic Acid Purity Analysis
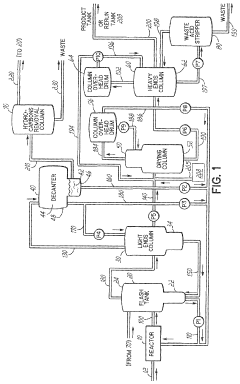
Methods for improved control of glacial acetic acid processes
PatentWO2023225077A1
Innovation
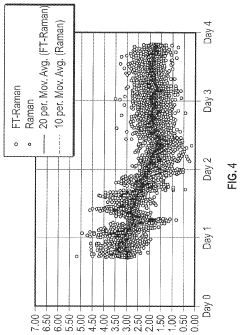
- The use of pseudo-analyzers or surrogate analyzers as a cross-check for FTIR and Raman data, or as an independent method for real-time calculation of reactor component concentrations, based on the concentrations of other components and temperature and pressure measurements downstream of the reactor.
Methods for improved control of glacial acetic acid processes
PatentPendingUS20230375478A1
Innovation
- The use of pseudo-analyzers or surrogate analyzers as cross-checks for FTIR and Raman data, or as independent methods for real-time calculation of reactor component concentrations, based on the concentrations of other components and temperature and pressure measurements in downstream apparatuses.
Environmental Impact of Acetic Acid Production and Monitoring
The production and monitoring of acetic acid, particularly glacial acetic acid, have significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The manufacturing process of acetic acid, primarily through methanol carbonylation or ethanol oxidation, generates various pollutants and greenhouse gases. These emissions, if not properly managed, can contribute to air and water pollution, as well as climate change.
One of the main environmental concerns is the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during production and handling. VOCs can react with nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight to form ground-level ozone, a major component of smog. This can lead to respiratory issues and damage to vegetation. Additionally, the production process often involves the use of metal catalysts, which can result in heavy metal contamination if not properly controlled and disposed of.
Water pollution is another critical issue associated with acetic acid production. Wastewater from the manufacturing process may contain high levels of organic compounds, including acetic acid itself, which can disrupt aquatic ecosystems if released untreated. Proper wastewater treatment systems are essential to mitigate this impact and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
The monitoring of glacial acetic acid quality is crucial not only for product consistency but also for environmental protection. Impurities in the acid can lead to increased waste and potentially more harmful byproducts during use. Advanced monitoring techniques, such as gas chromatography and spectroscopic methods, allow for precise detection of contaminants and ensure that the product meets stringent quality standards.
Implementing continuous monitoring systems in production facilities can help identify and address potential environmental issues promptly. Real-time data on emissions, energy consumption, and waste generation enables manufacturers to optimize their processes, reducing their environmental footprint. Moreover, life cycle assessments of acetic acid production can provide valuable insights into the overall environmental impact, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, acetic acid producers are increasingly adopting cleaner technologies and sustainable practices. This includes the use of renewable feedstocks, implementation of closed-loop systems to minimize waste, and investment in energy-efficient equipment. Some companies are exploring bio-based production methods, which have the potential to significantly reduce the carbon footprint of acetic acid manufacturing.
The environmental impact of acetic acid production and monitoring extends beyond the manufacturing site. Transportation and storage of the product also present potential risks, including accidental spills or leaks that can harm local ecosystems. Proper handling procedures, robust containment systems, and emergency response plans are essential components of responsible environmental management in the acetic acid industry.
One of the main environmental concerns is the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during production and handling. VOCs can react with nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight to form ground-level ozone, a major component of smog. This can lead to respiratory issues and damage to vegetation. Additionally, the production process often involves the use of metal catalysts, which can result in heavy metal contamination if not properly controlled and disposed of.
Water pollution is another critical issue associated with acetic acid production. Wastewater from the manufacturing process may contain high levels of organic compounds, including acetic acid itself, which can disrupt aquatic ecosystems if released untreated. Proper wastewater treatment systems are essential to mitigate this impact and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
The monitoring of glacial acetic acid quality is crucial not only for product consistency but also for environmental protection. Impurities in the acid can lead to increased waste and potentially more harmful byproducts during use. Advanced monitoring techniques, such as gas chromatography and spectroscopic methods, allow for precise detection of contaminants and ensure that the product meets stringent quality standards.
Implementing continuous monitoring systems in production facilities can help identify and address potential environmental issues promptly. Real-time data on emissions, energy consumption, and waste generation enables manufacturers to optimize their processes, reducing their environmental footprint. Moreover, life cycle assessments of acetic acid production can provide valuable insights into the overall environmental impact, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, acetic acid producers are increasingly adopting cleaner technologies and sustainable practices. This includes the use of renewable feedstocks, implementation of closed-loop systems to minimize waste, and investment in energy-efficient equipment. Some companies are exploring bio-based production methods, which have the potential to significantly reduce the carbon footprint of acetic acid manufacturing.
The environmental impact of acetic acid production and monitoring extends beyond the manufacturing site. Transportation and storage of the product also present potential risks, including accidental spills or leaks that can harm local ecosystems. Proper handling procedures, robust containment systems, and emergency response plans are essential components of responsible environmental management in the acetic acid industry.
Regulatory Standards for Glacial Acetic Acid Quality
Regulatory standards for glacial acetic acid quality are essential to ensure product safety, consistency, and compliance across industries. These standards are typically set by national and international regulatory bodies, such as the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Medicines Agency (EMA), and International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH). The primary focus of these regulations is to establish specifications for purity, impurity limits, and physical properties of glacial acetic acid.
One of the key regulatory standards for glacial acetic acid is the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) monograph, which outlines specific requirements for pharmaceutical-grade acetic acid. This includes specifications for assay (99.0% to 100.5% of CH3COOH), identification tests, and limits on impurities such as formic acid, sulfated ash, and heavy metals. Similarly, the European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) provides comparable standards for acetic acid used in pharmaceutical applications within the European Union.
For industrial applications, organizations like the American Chemical Society (ACS) and ASTM International have established guidelines for glacial acetic acid quality. These standards often focus on parameters such as acetic acid content, water content, color, and specific impurities relevant to industrial processes. The ACS grade, for instance, requires a minimum of 99.7% acetic acid content.
Regulatory bodies also mandate specific analytical methods for quality control and monitoring of glacial acetic acid. These methods typically include titration for assay determination, gas chromatography for impurity profiling, and spectrophotometric techniques for color assessment. The choice of analytical method often depends on the intended use of the acetic acid and the specific quality parameters being evaluated.
In recent years, there has been an increasing emphasis on the control of genotoxic impurities in pharmaceutical ingredients, including glacial acetic acid. Regulatory agencies have implemented stringent limits on potential genotoxic impurities, requiring manufacturers to develop and validate highly sensitive analytical methods for their detection and quantification. This has led to the adoption of advanced techniques such as liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) for trace impurity analysis in glacial acetic acid.
Compliance with these regulatory standards requires robust quality management systems and documentation practices. Manufacturers must maintain detailed records of production processes, analytical results, and any deviations from established specifications. Regular audits and inspections by regulatory authorities ensure ongoing compliance and may lead to updates in quality standards based on emerging scientific knowledge and technological advancements.
One of the key regulatory standards for glacial acetic acid is the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) monograph, which outlines specific requirements for pharmaceutical-grade acetic acid. This includes specifications for assay (99.0% to 100.5% of CH3COOH), identification tests, and limits on impurities such as formic acid, sulfated ash, and heavy metals. Similarly, the European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) provides comparable standards for acetic acid used in pharmaceutical applications within the European Union.
For industrial applications, organizations like the American Chemical Society (ACS) and ASTM International have established guidelines for glacial acetic acid quality. These standards often focus on parameters such as acetic acid content, water content, color, and specific impurities relevant to industrial processes. The ACS grade, for instance, requires a minimum of 99.7% acetic acid content.
Regulatory bodies also mandate specific analytical methods for quality control and monitoring of glacial acetic acid. These methods typically include titration for assay determination, gas chromatography for impurity profiling, and spectrophotometric techniques for color assessment. The choice of analytical method often depends on the intended use of the acetic acid and the specific quality parameters being evaluated.
In recent years, there has been an increasing emphasis on the control of genotoxic impurities in pharmaceutical ingredients, including glacial acetic acid. Regulatory agencies have implemented stringent limits on potential genotoxic impurities, requiring manufacturers to develop and validate highly sensitive analytical methods for their detection and quantification. This has led to the adoption of advanced techniques such as liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) for trace impurity analysis in glacial acetic acid.
Compliance with these regulatory standards requires robust quality management systems and documentation practices. Manufacturers must maintain detailed records of production processes, analytical results, and any deviations from established specifications. Regular audits and inspections by regulatory authorities ensure ongoing compliance and may lead to updates in quality standards based on emerging scientific knowledge and technological advancements.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!