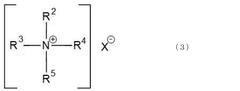
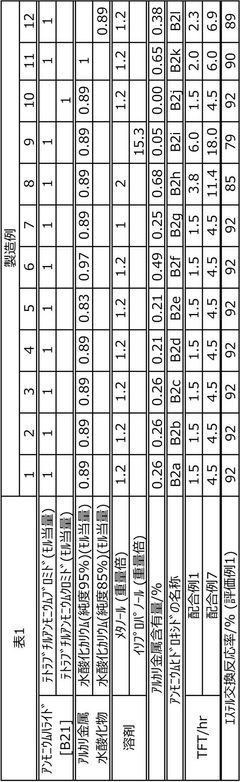
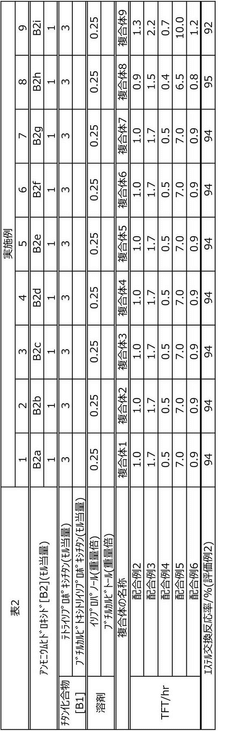
The use of ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing
AUG 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ammonium Hydroxide in Rubber: Background and Objectives
Ammonium hydroxide has played a significant role in rubber processing for over a century, with its use dating back to the early days of the rubber industry. This versatile compound, also known as aqueous ammonia, has been instrumental in various stages of rubber production, from raw material preparation to final product finishing. The evolution of ammonium hydroxide usage in rubber processing has been closely tied to the advancements in rubber technology and the growing demands of the automotive, construction, and consumer goods industries.
The primary objective of using ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing is to enhance the properties and performance of rubber compounds. It serves multiple purposes, including pH adjustment, coagulation of latex, and as a crucial component in the production of specialized rubber products. As the rubber industry has evolved, so too has the application of ammonium hydroxide, with ongoing research aimed at optimizing its use and exploring new potential benefits.
One of the key drivers behind the continued use and development of ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing is the need for improved sustainability and environmental compliance. As global regulations become more stringent, there is a growing emphasis on developing eco-friendly processing methods. Ammonium hydroxide, being a relatively benign chemical compared to some alternatives, has gained attention as a potential solution for more sustainable rubber production processes.
The rubber industry's technological trajectory has been shaped by the quest for enhanced material properties, such as increased durability, improved elasticity, and better resistance to environmental factors. Ammonium hydroxide has been at the forefront of many of these advancements, contributing to the development of rubber compounds with superior characteristics. Its role in modifying surface properties, controlling curing processes, and facilitating the incorporation of reinforcing agents has been crucial in meeting the ever-increasing performance standards demanded by various industries.
Looking ahead, the use of ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing faces both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, there is potential for further optimization of its application to achieve even better rubber properties and more efficient production processes. On the other hand, the industry must address concerns related to worker safety, environmental impact, and the development of alternative technologies. The future direction of ammonium hydroxide use in rubber processing will likely focus on balancing these factors while continuing to push the boundaries of rubber technology.
The primary objective of using ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing is to enhance the properties and performance of rubber compounds. It serves multiple purposes, including pH adjustment, coagulation of latex, and as a crucial component in the production of specialized rubber products. As the rubber industry has evolved, so too has the application of ammonium hydroxide, with ongoing research aimed at optimizing its use and exploring new potential benefits.
One of the key drivers behind the continued use and development of ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing is the need for improved sustainability and environmental compliance. As global regulations become more stringent, there is a growing emphasis on developing eco-friendly processing methods. Ammonium hydroxide, being a relatively benign chemical compared to some alternatives, has gained attention as a potential solution for more sustainable rubber production processes.
The rubber industry's technological trajectory has been shaped by the quest for enhanced material properties, such as increased durability, improved elasticity, and better resistance to environmental factors. Ammonium hydroxide has been at the forefront of many of these advancements, contributing to the development of rubber compounds with superior characteristics. Its role in modifying surface properties, controlling curing processes, and facilitating the incorporation of reinforcing agents has been crucial in meeting the ever-increasing performance standards demanded by various industries.
Looking ahead, the use of ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing faces both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, there is potential for further optimization of its application to achieve even better rubber properties and more efficient production processes. On the other hand, the industry must address concerns related to worker safety, environmental impact, and the development of alternative technologies. The future direction of ammonium hydroxide use in rubber processing will likely focus on balancing these factors while continuing to push the boundaries of rubber technology.
Market Analysis for Ammonium Hydroxide in Rubber Industry
The global market for ammonium hydroxide in the rubber industry has been experiencing steady growth, driven by the increasing demand for rubber products across various sectors. The automotive industry, in particular, has been a significant contributor to this growth, with the rising production of vehicles worldwide necessitating a higher consumption of rubber components. Additionally, the construction and industrial sectors have also played crucial roles in boosting the demand for rubber products, consequently impacting the market for ammonium hydroxide.
In recent years, the Asia-Pacific region has emerged as the dominant market for ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing. This can be attributed to the rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India, which have led to an increased demand for rubber products. The region's robust manufacturing sector, particularly in automotive and construction, has further fueled the growth of the ammonium hydroxide market.
North America and Europe have also maintained significant market shares, primarily due to their well-established automotive and industrial sectors. However, these regions are experiencing slower growth rates compared to Asia-Pacific, as manufacturing activities gradually shift towards emerging economies.
The market dynamics for ammonium hydroxide in the rubber industry are influenced by several factors. Environmental regulations play a crucial role, as governments worldwide are implementing stricter policies regarding chemical usage and emissions. This has led to increased research and development efforts to find more environmentally friendly alternatives or improve existing processes to reduce the environmental impact of ammonium hydroxide usage.
Price fluctuations of raw materials and energy costs also significantly impact the market. As ammonium hydroxide production is energy-intensive, changes in energy prices can affect its overall cost and, consequently, its demand in the rubber industry. Additionally, the availability and pricing of alternative chemicals used in rubber processing can influence the market share of ammonium hydroxide.
The rubber industry's ongoing focus on product innovation and quality improvement has been driving the demand for high-performance additives, including ammonium hydroxide. Manufacturers are continuously seeking ways to enhance the properties of rubber products, such as durability, flexibility, and resistance to various environmental factors. This trend is expected to sustain the growth of the ammonium hydroxide market in the rubber industry for the foreseeable future.
In recent years, the Asia-Pacific region has emerged as the dominant market for ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing. This can be attributed to the rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India, which have led to an increased demand for rubber products. The region's robust manufacturing sector, particularly in automotive and construction, has further fueled the growth of the ammonium hydroxide market.
North America and Europe have also maintained significant market shares, primarily due to their well-established automotive and industrial sectors. However, these regions are experiencing slower growth rates compared to Asia-Pacific, as manufacturing activities gradually shift towards emerging economies.
The market dynamics for ammonium hydroxide in the rubber industry are influenced by several factors. Environmental regulations play a crucial role, as governments worldwide are implementing stricter policies regarding chemical usage and emissions. This has led to increased research and development efforts to find more environmentally friendly alternatives or improve existing processes to reduce the environmental impact of ammonium hydroxide usage.
Price fluctuations of raw materials and energy costs also significantly impact the market. As ammonium hydroxide production is energy-intensive, changes in energy prices can affect its overall cost and, consequently, its demand in the rubber industry. Additionally, the availability and pricing of alternative chemicals used in rubber processing can influence the market share of ammonium hydroxide.
The rubber industry's ongoing focus on product innovation and quality improvement has been driving the demand for high-performance additives, including ammonium hydroxide. Manufacturers are continuously seeking ways to enhance the properties of rubber products, such as durability, flexibility, and resistance to various environmental factors. This trend is expected to sustain the growth of the ammonium hydroxide market in the rubber industry for the foreseeable future.
Current Applications and Challenges in Rubber Processing
Ammonium hydroxide plays a significant role in various stages of rubber processing, offering unique advantages and presenting certain challenges. In the compounding phase, it serves as an effective dispersing agent for fillers and pigments, enhancing the uniform distribution of these additives throughout the rubber matrix. This improved dispersion leads to better mechanical properties and appearance of the final product.
During vulcanization, ammonium hydroxide acts as a catalyst, accelerating the cross-linking process between rubber molecules and sulfur. This results in reduced curing times and improved efficiency in production. Additionally, it helps in controlling the scorch time, preventing premature vulcanization during processing.
In latex applications, ammonium hydroxide is widely used as a stabilizer. It maintains the colloidal stability of natural rubber latex by increasing the pH, which prevents coagulation during storage and processing. This is particularly crucial in the production of dipped goods such as gloves and balloons.
However, the use of ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing is not without challenges. One primary concern is its volatile nature, which can lead to emissions during processing. These emissions not only pose potential health risks to workers but also contribute to environmental pollution. Manufacturers must implement proper ventilation systems and safety protocols to mitigate these risks.
Another challenge lies in the precise control of ammonium hydroxide concentration. Excess amounts can lead to over-curing or scorching of the rubber, while insufficient quantities may result in inadequate vulcanization. This necessitates careful monitoring and adjustment of formulations to achieve optimal results.
The alkaline nature of ammonium hydroxide can also affect the stability of certain rubber additives, particularly antioxidants and some accelerators. This interaction may lead to reduced effectiveness of these additives, potentially impacting the long-term performance and aging characteristics of the rubber products.
Furthermore, the use of ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing faces increasing scrutiny due to environmental regulations. As industries move towards more sustainable practices, there is a growing need to find alternative, eco-friendly processing aids that can match the effectiveness of ammonium hydroxide while reducing environmental impact.
In response to these challenges, research is ongoing to develop improved formulations and processing techniques. This includes exploring synergistic combinations with other additives to enhance efficiency and reduce overall chemical usage, as well as investigating novel, less volatile alkaline compounds that could potentially replace ammonium hydroxide in certain applications.
During vulcanization, ammonium hydroxide acts as a catalyst, accelerating the cross-linking process between rubber molecules and sulfur. This results in reduced curing times and improved efficiency in production. Additionally, it helps in controlling the scorch time, preventing premature vulcanization during processing.
In latex applications, ammonium hydroxide is widely used as a stabilizer. It maintains the colloidal stability of natural rubber latex by increasing the pH, which prevents coagulation during storage and processing. This is particularly crucial in the production of dipped goods such as gloves and balloons.
However, the use of ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing is not without challenges. One primary concern is its volatile nature, which can lead to emissions during processing. These emissions not only pose potential health risks to workers but also contribute to environmental pollution. Manufacturers must implement proper ventilation systems and safety protocols to mitigate these risks.
Another challenge lies in the precise control of ammonium hydroxide concentration. Excess amounts can lead to over-curing or scorching of the rubber, while insufficient quantities may result in inadequate vulcanization. This necessitates careful monitoring and adjustment of formulations to achieve optimal results.
The alkaline nature of ammonium hydroxide can also affect the stability of certain rubber additives, particularly antioxidants and some accelerators. This interaction may lead to reduced effectiveness of these additives, potentially impacting the long-term performance and aging characteristics of the rubber products.
Furthermore, the use of ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing faces increasing scrutiny due to environmental regulations. As industries move towards more sustainable practices, there is a growing need to find alternative, eco-friendly processing aids that can match the effectiveness of ammonium hydroxide while reducing environmental impact.
In response to these challenges, research is ongoing to develop improved formulations and processing techniques. This includes exploring synergistic combinations with other additives to enhance efficiency and reduce overall chemical usage, as well as investigating novel, less volatile alkaline compounds that could potentially replace ammonium hydroxide in certain applications.
Existing Ammonium Hydroxide-based Rubber Processing Methods
01 Use in chemical processes
Ammonium hydroxide is widely used in various chemical processes, including as a reactant, pH adjuster, and neutralizing agent. It plays a crucial role in the production of certain chemicals and materials, and can be used to control the acidity or alkalinity of solutions in industrial applications.- Use of ammonium hydroxide in chemical processes: Ammonium hydroxide is widely used in various chemical processes as a reactant, catalyst, or pH regulator. It plays a crucial role in the synthesis of organic compounds, production of fertilizers, and treatment of industrial waste. Its alkaline properties make it suitable for neutralizing acids and controlling pH levels in different applications.
- Application in hair coloring and bleaching: Ammonium hydroxide is commonly used in hair coloring and bleaching products. It helps to open the hair cuticle, allowing the dye or bleaching agent to penetrate the hair shaft more effectively. This results in better color absorption and more uniform results. Additionally, it can help to adjust the pH of hair products for optimal performance.
- Role in cleaning and household products: Ammonium hydroxide is an effective cleaning agent used in various household and industrial cleaning products. It is particularly useful for removing grease, grime, and stubborn stains. Its alkaline nature helps to break down organic matter and dissolve oils. It is also used in glass cleaning solutions due to its ability to leave surfaces streak-free.
- Use in textile processing: In the textile industry, ammonium hydroxide is used for various purposes, including fabric treatment, dyeing, and finishing processes. It can help to improve the color fastness of dyes, neutralize acidic residues, and enhance the overall quality of textile products. It is also used in the production of certain synthetic fibers.
- Environmental and agricultural applications: Ammonium hydroxide has applications in environmental protection and agriculture. It is used in air pollution control systems to neutralize acidic gases and reduce emissions. In agriculture, it serves as a source of nitrogen for fertilizers and can be used to adjust soil pH. It also plays a role in the treatment of agricultural waste and the production of biofuels.
02 Application in cleaning and surface treatment
Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in cleaning formulations and surface treatment processes. It can effectively remove grease, oils, and other contaminants from surfaces. Additionally, it is used in etching and polishing processes for metals and semiconductors, as well as in the treatment of textiles and leather.Expand Specific Solutions03 Role in agricultural and fertilizer applications
Ammonium hydroxide serves as a source of nitrogen in fertilizers and is used in various agricultural applications. It can be directly applied to soil or used in the production of other nitrogen-containing fertilizers. The compound helps improve soil fertility and promotes plant growth.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use in wastewater treatment
Ammonium hydroxide is employed in wastewater treatment processes for pH adjustment and nitrogen removal. It can help neutralize acidic wastewater and assist in the precipitation of certain contaminants. The compound also plays a role in biological treatment systems for nitrogen reduction.Expand Specific Solutions05 Application in personal care and cosmetic products
Ammonium hydroxide finds use in various personal care and cosmetic formulations. It can act as a pH adjuster in hair dyes, skin care products, and other cosmetic preparations. The compound helps maintain the stability and effectiveness of certain ingredients in these products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Rubber Chemical Manufacturing
The use of ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing is a mature technology in a well-established industry. The global rubber processing chemicals market is expected to reach $5.31 billion by 2025, with a CAGR of 5.5%. Major players like Bridgestone, Yokohama Rubber, and Sumitomo Chemical dominate the market, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities and global presence. Emerging companies such as China Hainan Rubber Industry Group and UBE Corp. are also making significant strides in this field. The technology's maturity is evident from the involvement of academic institutions like South China University of Technology and Kyoto Institute of Technology, which continue to refine and improve existing processes.
Bridgestone Corp.
Technical Solution: Bridgestone has developed an innovative approach to using ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing, focusing on improving the overall quality and performance of their tire products. Their method involves a controlled application of ammonium hydroxide during the vulcanization process, which helps to neutralize acidic byproducts and enhance cross-linking between rubber molecules[1]. This results in improved tensile strength and reduced heat build-up in the final product. Additionally, Bridgestone has implemented a closed-loop system for ammonium hydroxide recovery and reuse, minimizing environmental impact and reducing production costs[3].
Strengths: Improved tire performance, reduced environmental impact, cost-effective production. Weaknesses: Requires specialized equipment and careful process control.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has pioneered a novel approach to incorporating ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing, particularly for silicone rubber applications. Their patented technology utilizes ammonium hydroxide as a catalyst in the condensation curing process of silicone rubbers[2]. This method allows for faster curing times and improved physical properties of the final product. Dow's process also includes a unique stabilization technique that prevents premature curing during storage and transportation, extending the shelf life of their rubber compounds[4]. The company has further developed eco-friendly formulations that reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during processing[5].
Strengths: Faster curing times, improved product stability, reduced VOC emissions. Weaknesses: Limited to specific types of rubber compounds, may require changes to existing manufacturing processes.
Innovative Approaches in Ammonium Hydroxide Utilization
Anti-scorch compositions, methods of making the same, and articles prepared from the same
PatentActiveUS20120178865A1
Innovation
- A composition comprising an interpolymer of ethylene, an α-olefin, and a nonconjugated polyene, combined with sulfur and a phase transfer catalyst, along with a primary accelerator, which balances cure rate and scorch resistance by optimizing the transferability of the curing agent.
Method for producing composite of titanium compound and ammonium hydroxide, method for producing composition, method for producing ester compound, and method for producing ammonium hydroxide
PatentWO2022004509A1
Innovation
- A method for producing a composite of a titanium compound and ammonium hydroxide, which acts as a highly active and safe catalyst, involving the reaction of a titanium compound with ammonium hydroxide to form a complex that can be used in moisture-curable compositions, urethane resin production, and ester compound synthesis.
Environmental Impact and Regulations
The use of ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing has significant environmental implications and is subject to various regulations. The primary environmental concern stems from the potential release of ammonia gas during the manufacturing process. Ammonia is a toxic substance that can cause respiratory irritation and damage to aquatic ecosystems if released into the environment in high concentrations.
Regulatory bodies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, have established strict guidelines for the handling and disposal of ammonium hydroxide in industrial settings. These regulations typically require proper ventilation systems, containment measures, and waste treatment protocols to minimize environmental impact. Companies engaged in rubber processing must adhere to air quality standards, which often include limits on ammonia emissions.
Water pollution is another critical aspect of environmental regulations concerning ammonium hydroxide use. Effluent from rubber processing facilities must be carefully monitored and treated to remove excess ammonia before discharge. Many jurisdictions have implemented stringent water quality standards that mandate the reduction of ammonia levels in wastewater to protect aquatic life and maintain the ecological balance of receiving water bodies.
Occupational health and safety regulations also play a crucial role in governing the use of ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing. Workers must be provided with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and trained in the safe handling of this chemical. Workplace exposure limits for ammonia are typically set by agencies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) to protect workers from harmful effects.
In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards more sustainable rubber processing methods. This has led to increased research into alternative compounds that can replace or reduce the use of ammonium hydroxide. Some companies have adopted closed-loop systems to recycle and reuse ammonium hydroxide, minimizing waste and environmental impact. Additionally, advancements in process engineering have resulted in more efficient application methods that reduce overall chemical consumption and emissions.
As global environmental awareness continues to rise, it is likely that regulations surrounding the use of ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing will become increasingly stringent. Companies in this industry must stay informed about evolving environmental policies and invest in technologies that ensure compliance while maintaining production efficiency. The future of rubber processing may see a shift towards greener alternatives and more environmentally friendly practices to address the challenges associated with ammonium hydroxide use.
Regulatory bodies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, have established strict guidelines for the handling and disposal of ammonium hydroxide in industrial settings. These regulations typically require proper ventilation systems, containment measures, and waste treatment protocols to minimize environmental impact. Companies engaged in rubber processing must adhere to air quality standards, which often include limits on ammonia emissions.
Water pollution is another critical aspect of environmental regulations concerning ammonium hydroxide use. Effluent from rubber processing facilities must be carefully monitored and treated to remove excess ammonia before discharge. Many jurisdictions have implemented stringent water quality standards that mandate the reduction of ammonia levels in wastewater to protect aquatic life and maintain the ecological balance of receiving water bodies.
Occupational health and safety regulations also play a crucial role in governing the use of ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing. Workers must be provided with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and trained in the safe handling of this chemical. Workplace exposure limits for ammonia are typically set by agencies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) to protect workers from harmful effects.
In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards more sustainable rubber processing methods. This has led to increased research into alternative compounds that can replace or reduce the use of ammonium hydroxide. Some companies have adopted closed-loop systems to recycle and reuse ammonium hydroxide, minimizing waste and environmental impact. Additionally, advancements in process engineering have resulted in more efficient application methods that reduce overall chemical consumption and emissions.
As global environmental awareness continues to rise, it is likely that regulations surrounding the use of ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing will become increasingly stringent. Companies in this industry must stay informed about evolving environmental policies and invest in technologies that ensure compliance while maintaining production efficiency. The future of rubber processing may see a shift towards greener alternatives and more environmentally friendly practices to address the challenges associated with ammonium hydroxide use.
Health and Safety Considerations in Rubber Manufacturing
Health and safety considerations are paramount in rubber manufacturing processes, particularly when using chemicals like ammonium hydroxide. The use of this compound introduces several potential hazards that must be carefully managed to ensure worker safety and environmental protection.
Inhalation of ammonium hydroxide vapors poses a significant risk to workers. Even at low concentrations, these vapors can cause irritation to the eyes, nose, and respiratory tract. Prolonged exposure or higher concentrations may lead to more severe respiratory issues, including pulmonary edema. To mitigate these risks, proper ventilation systems must be installed and maintained in all areas where ammonium hydroxide is used or stored.
Skin contact with ammonium hydroxide can result in chemical burns and dermatitis. Workers must be provided with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including chemical-resistant gloves, aprons, and eye protection. Emergency eyewash stations and safety showers should be readily accessible in case of accidental exposure.
The corrosive nature of ammonium hydroxide necessitates proper storage and handling procedures. Containers must be clearly labeled and stored in well-ventilated areas away from incompatible materials. Regular inspections of storage facilities and transfer equipment are essential to prevent leaks or spills that could lead to worker exposure or environmental contamination.
Training programs are crucial for ensuring that all employees understand the hazards associated with ammonium hydroxide and are proficient in safe handling procedures. This should include proper use of PPE, spill response protocols, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher courses and safety drills help maintain a high level of awareness and preparedness.
Environmental considerations are also important when using ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing. Proper waste management and disposal procedures must be implemented to prevent the release of ammonia or ammonium compounds into the environment. This may include neutralization processes for waste streams and the use of scrubbers to capture and treat emissions.
Monitoring systems should be in place to detect ammonia levels in the workplace atmosphere. These systems can provide early warning of potential leaks or excessive vapor concentrations, allowing for prompt corrective action. Regular air quality testing and record-keeping are essential for maintaining a safe working environment and demonstrating compliance with regulatory standards.
In conclusion, the use of ammonium hydroxide in rubber manufacturing requires a comprehensive approach to health and safety management. By implementing robust engineering controls, providing appropriate PPE, conducting thorough training, and maintaining vigilant monitoring practices, manufacturers can minimize risks to workers and the environment while leveraging the benefits of this chemical in their production processes.
Inhalation of ammonium hydroxide vapors poses a significant risk to workers. Even at low concentrations, these vapors can cause irritation to the eyes, nose, and respiratory tract. Prolonged exposure or higher concentrations may lead to more severe respiratory issues, including pulmonary edema. To mitigate these risks, proper ventilation systems must be installed and maintained in all areas where ammonium hydroxide is used or stored.
Skin contact with ammonium hydroxide can result in chemical burns and dermatitis. Workers must be provided with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including chemical-resistant gloves, aprons, and eye protection. Emergency eyewash stations and safety showers should be readily accessible in case of accidental exposure.
The corrosive nature of ammonium hydroxide necessitates proper storage and handling procedures. Containers must be clearly labeled and stored in well-ventilated areas away from incompatible materials. Regular inspections of storage facilities and transfer equipment are essential to prevent leaks or spills that could lead to worker exposure or environmental contamination.
Training programs are crucial for ensuring that all employees understand the hazards associated with ammonium hydroxide and are proficient in safe handling procedures. This should include proper use of PPE, spill response protocols, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher courses and safety drills help maintain a high level of awareness and preparedness.
Environmental considerations are also important when using ammonium hydroxide in rubber processing. Proper waste management and disposal procedures must be implemented to prevent the release of ammonia or ammonium compounds into the environment. This may include neutralization processes for waste streams and the use of scrubbers to capture and treat emissions.
Monitoring systems should be in place to detect ammonia levels in the workplace atmosphere. These systems can provide early warning of potential leaks or excessive vapor concentrations, allowing for prompt corrective action. Regular air quality testing and record-keeping are essential for maintaining a safe working environment and demonstrating compliance with regulatory standards.
In conclusion, the use of ammonium hydroxide in rubber manufacturing requires a comprehensive approach to health and safety management. By implementing robust engineering controls, providing appropriate PPE, conducting thorough training, and maintaining vigilant monitoring practices, manufacturers can minimize risks to workers and the environment while leveraging the benefits of this chemical in their production processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!