Understanding V8 Engine Role in Sports Cars
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V8 Engine Evolution
The V8 engine has been a cornerstone of high-performance sports cars for decades, evolving significantly since its inception. Initially developed in the early 20th century, V8 engines gained prominence in the automotive industry due to their compact design and impressive power output.
In the 1950s and 1960s, V8 engines became synonymous with American muscle cars, offering unprecedented power and acceleration. This era saw the introduction of iconic engines like the Chevrolet Small-Block V8, which set new standards for performance and reliability.
The 1970s brought challenges to V8 development with stricter emission regulations and fuel economy concerns. Manufacturers responded by downsizing engines and implementing electronic fuel injection systems. This period marked a transition from raw power to a more balanced approach, focusing on efficiency without sacrificing performance.
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed a resurgence in V8 technology. Advanced materials and manufacturing techniques allowed for lighter, more compact designs. Variable valve timing and multi-valve cylinder heads became common, significantly improving engine efficiency and power output.
The turn of the millennium saw V8 engines reach new heights of sophistication. Direct fuel injection, forced induction through supercharging and turbocharging, and cylinder deactivation technologies became prevalent. These advancements allowed V8 engines to deliver exceptional performance while meeting increasingly stringent emissions standards.
Recent years have seen a focus on hybridization and electrification. Many sports car manufacturers now pair V8 engines with electric motors, creating hybrid powertrains that offer both high performance and improved fuel efficiency. This trend represents a bridge between traditional internal combustion engines and the electric future of automotive propulsion.
Throughout its evolution, the V8 engine has maintained its status as a symbol of power and prestige in sports cars. Its distinctive sound, smooth power delivery, and robust torque characteristics continue to captivate enthusiasts. As the automotive industry moves towards electrification, the role of V8 engines in sports cars is evolving, with manufacturers exploring ways to preserve their appeal while meeting future environmental regulations.
In the 1950s and 1960s, V8 engines became synonymous with American muscle cars, offering unprecedented power and acceleration. This era saw the introduction of iconic engines like the Chevrolet Small-Block V8, which set new standards for performance and reliability.
The 1970s brought challenges to V8 development with stricter emission regulations and fuel economy concerns. Manufacturers responded by downsizing engines and implementing electronic fuel injection systems. This period marked a transition from raw power to a more balanced approach, focusing on efficiency without sacrificing performance.
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed a resurgence in V8 technology. Advanced materials and manufacturing techniques allowed for lighter, more compact designs. Variable valve timing and multi-valve cylinder heads became common, significantly improving engine efficiency and power output.
The turn of the millennium saw V8 engines reach new heights of sophistication. Direct fuel injection, forced induction through supercharging and turbocharging, and cylinder deactivation technologies became prevalent. These advancements allowed V8 engines to deliver exceptional performance while meeting increasingly stringent emissions standards.
Recent years have seen a focus on hybridization and electrification. Many sports car manufacturers now pair V8 engines with electric motors, creating hybrid powertrains that offer both high performance and improved fuel efficiency. This trend represents a bridge between traditional internal combustion engines and the electric future of automotive propulsion.
Throughout its evolution, the V8 engine has maintained its status as a symbol of power and prestige in sports cars. Its distinctive sound, smooth power delivery, and robust torque characteristics continue to captivate enthusiasts. As the automotive industry moves towards electrification, the role of V8 engines in sports cars is evolving, with manufacturers exploring ways to preserve their appeal while meeting future environmental regulations.
Sports Car Market Trends
The sports car market has been experiencing significant shifts in recent years, driven by changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and regulatory pressures. One of the most notable trends is the increasing demand for high-performance vehicles that offer both exhilarating driving experiences and improved fuel efficiency. This has led to a renewed focus on V8 engines, which continue to play a crucial role in the sports car segment.
Despite the growing popularity of electric and hybrid powertrains, V8 engines remain a staple in the sports car market due to their ability to deliver impressive power output and the distinctive sound that enthusiasts crave. However, manufacturers are now faced with the challenge of balancing performance with environmental concerns, leading to innovations in V8 engine design and technology.
The market has seen a surge in demand for sports cars equipped with advanced V8 engines that incorporate technologies such as direct injection, variable valve timing, and cylinder deactivation. These innovations allow for improved fuel economy without sacrificing the power and performance that define the sports car segment. As a result, many automakers are investing heavily in research and development to enhance their V8 offerings.
Another significant trend is the integration of V8 engines into hybrid powertrains, creating high-performance vehicles that can operate in both electric and combustion modes. This approach appeals to consumers who desire the best of both worlds – the thrilling performance of a V8 engine combined with the efficiency and environmental benefits of electric propulsion.
The sports car market is also witnessing a shift towards more exclusive and limited-edition models featuring specially tuned V8 engines. These vehicles cater to collectors and enthusiasts willing to pay premium prices for unique, high-performance machines. This trend has led to increased collaboration between sports car manufacturers and specialized tuning companies to create bespoke V8-powered vehicles.
Furthermore, the rise of track-focused sports cars has reinvigorated interest in naturally aspirated V8 engines, which offer linear power delivery and immediate throttle response prized by driving purists. This niche market segment continues to grow, with several manufacturers developing dedicated track-day specials powered by high-revving V8 engines.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, the sports car market is adapting by exploring alternative fuels and advanced materials to improve the efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of V8 engines. This includes research into synthetic fuels and lightweight engine components that can help maintain the performance characteristics of V8 engines while meeting future emissions standards.
Despite the growing popularity of electric and hybrid powertrains, V8 engines remain a staple in the sports car market due to their ability to deliver impressive power output and the distinctive sound that enthusiasts crave. However, manufacturers are now faced with the challenge of balancing performance with environmental concerns, leading to innovations in V8 engine design and technology.
The market has seen a surge in demand for sports cars equipped with advanced V8 engines that incorporate technologies such as direct injection, variable valve timing, and cylinder deactivation. These innovations allow for improved fuel economy without sacrificing the power and performance that define the sports car segment. As a result, many automakers are investing heavily in research and development to enhance their V8 offerings.
Another significant trend is the integration of V8 engines into hybrid powertrains, creating high-performance vehicles that can operate in both electric and combustion modes. This approach appeals to consumers who desire the best of both worlds – the thrilling performance of a V8 engine combined with the efficiency and environmental benefits of electric propulsion.
The sports car market is also witnessing a shift towards more exclusive and limited-edition models featuring specially tuned V8 engines. These vehicles cater to collectors and enthusiasts willing to pay premium prices for unique, high-performance machines. This trend has led to increased collaboration between sports car manufacturers and specialized tuning companies to create bespoke V8-powered vehicles.
Furthermore, the rise of track-focused sports cars has reinvigorated interest in naturally aspirated V8 engines, which offer linear power delivery and immediate throttle response prized by driving purists. This niche market segment continues to grow, with several manufacturers developing dedicated track-day specials powered by high-revving V8 engines.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, the sports car market is adapting by exploring alternative fuels and advanced materials to improve the efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of V8 engines. This includes research into synthetic fuels and lightweight engine components that can help maintain the performance characteristics of V8 engines while meeting future emissions standards.
V8 Performance Challenges
V8 engines have long been synonymous with high-performance sports cars, offering a unique combination of power, sound, and driving experience. However, as the automotive industry evolves, V8 engines face several significant challenges that threaten their dominance in the sports car segment.
One of the primary challenges is the increasing focus on fuel efficiency and environmental regulations. V8 engines are known for their high fuel consumption and emissions, which puts them at odds with stringent global emission standards. Manufacturers are under pressure to reduce carbon footprints, leading to a shift towards smaller, turbocharged engines or hybrid powertrains.
Another challenge is the rapid advancement of electric vehicle technology. Electric motors can deliver instant torque and impressive acceleration, often surpassing the performance of traditional V8 engines. As battery technology improves and costs decrease, electric sports cars are becoming increasingly viable alternatives, threatening the market share of V8-powered vehicles.
Weight reduction is a crucial factor in sports car performance, and V8 engines present a challenge in this regard. Their size and complexity often result in a heavier overall vehicle, which can negatively impact handling and agility. Engineers must find innovative ways to reduce weight while maintaining the power output that V8 enthusiasts expect.
The complexity of V8 engines also poses challenges in terms of maintenance and reliability. With more moving parts compared to smaller engines or electric motors, V8s require more frequent servicing and are potentially more prone to mechanical issues. This can increase the total cost of ownership, which may deter some buyers in the premium sports car segment.
Noise regulations present another hurdle for V8 engines. While the distinctive sound of a V8 is part of its appeal, increasingly strict noise pollution laws in many countries are forcing manufacturers to develop quieter exhaust systems, potentially diminishing the auditory experience that many enthusiasts cherish.
Lastly, the cost of developing and producing V8 engines in compliance with modern standards is becoming prohibitively expensive for some manufacturers. This economic pressure may lead to reduced investment in V8 technology, potentially limiting future innovations and improvements in this engine configuration.
Despite these challenges, many sports car manufacturers continue to invest in V8 technology, recognizing its enduring appeal among enthusiasts. The future of V8 engines in sports cars will likely depend on the industry's ability to address these performance challenges through technological advancements and innovative engineering solutions.
One of the primary challenges is the increasing focus on fuel efficiency and environmental regulations. V8 engines are known for their high fuel consumption and emissions, which puts them at odds with stringent global emission standards. Manufacturers are under pressure to reduce carbon footprints, leading to a shift towards smaller, turbocharged engines or hybrid powertrains.
Another challenge is the rapid advancement of electric vehicle technology. Electric motors can deliver instant torque and impressive acceleration, often surpassing the performance of traditional V8 engines. As battery technology improves and costs decrease, electric sports cars are becoming increasingly viable alternatives, threatening the market share of V8-powered vehicles.
Weight reduction is a crucial factor in sports car performance, and V8 engines present a challenge in this regard. Their size and complexity often result in a heavier overall vehicle, which can negatively impact handling and agility. Engineers must find innovative ways to reduce weight while maintaining the power output that V8 enthusiasts expect.
The complexity of V8 engines also poses challenges in terms of maintenance and reliability. With more moving parts compared to smaller engines or electric motors, V8s require more frequent servicing and are potentially more prone to mechanical issues. This can increase the total cost of ownership, which may deter some buyers in the premium sports car segment.
Noise regulations present another hurdle for V8 engines. While the distinctive sound of a V8 is part of its appeal, increasingly strict noise pollution laws in many countries are forcing manufacturers to develop quieter exhaust systems, potentially diminishing the auditory experience that many enthusiasts cherish.
Lastly, the cost of developing and producing V8 engines in compliance with modern standards is becoming prohibitively expensive for some manufacturers. This economic pressure may lead to reduced investment in V8 technology, potentially limiting future innovations and improvements in this engine configuration.
Despite these challenges, many sports car manufacturers continue to invest in V8 technology, recognizing its enduring appeal among enthusiasts. The future of V8 engines in sports cars will likely depend on the industry's ability to address these performance challenges through technological advancements and innovative engineering solutions.
Current V8 Configurations
01 V8 Engine Design and Configuration
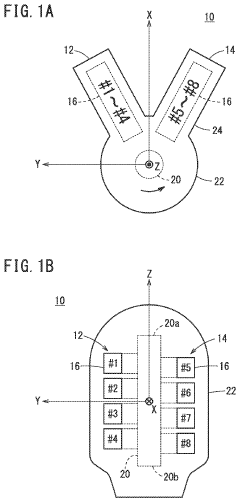
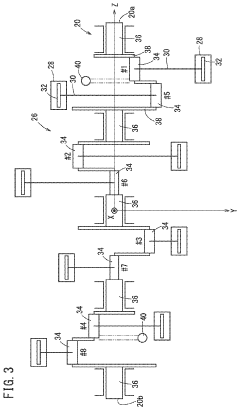
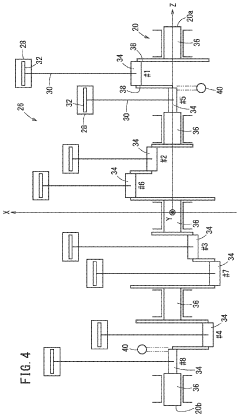
V8 engines are designed with eight cylinders arranged in two banks of four, forming a V-shape. This configuration allows for a compact design, improved balance, and higher power output compared to inline engines. Various aspects of V8 engine design, including cylinder arrangement, crankshaft configuration, and valve timing, are optimized for performance and efficiency.- V8 Engine Design and Configuration: V8 engines are designed with eight cylinders arranged in two banks of four, forming a V-shape. This configuration allows for a compact design, improved power output, and better balance compared to inline engines. Various aspects of V8 engine design, including cylinder arrangement, crankshaft configuration, and valve train systems, are continuously improved to enhance performance and efficiency.
- Fuel Efficiency and Emissions Control: Modern V8 engines incorporate technologies to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. These may include direct fuel injection, variable valve timing, cylinder deactivation, and advanced exhaust gas recirculation systems. Innovations in engine management systems and combustion chamber design also contribute to better fuel economy and lower emissions while maintaining high performance.
- Performance Enhancement and Tuning: Various methods and components are developed to enhance V8 engine performance. These include turbocharging, supercharging, intercooling, and high-flow intake and exhaust systems. Advanced engine tuning techniques, such as electronic control unit (ECU) remapping and variable geometry turbochargers, are employed to optimize power output and torque across different operating conditions.
- Cooling and Lubrication Systems: Efficient cooling and lubrication are crucial for V8 engine reliability and longevity. Innovations in coolant flow design, oil pump efficiency, and thermal management systems help maintain optimal operating temperatures and reduce friction. Advanced materials and coatings are also used to improve heat dissipation and reduce wear on engine components.
- Manufacturing and Assembly Techniques: Advancements in manufacturing processes and assembly techniques for V8 engines focus on improving precision, reducing weight, and enhancing durability. These may include the use of lightweight materials, such as aluminum alloys and composites, as well as advanced casting and machining techniques. Modular design approaches and automated assembly processes are also implemented to improve production efficiency and quality control.
02 Fuel Injection and Combustion Systems
Advanced fuel injection and combustion systems are crucial for V8 engine performance. These systems include direct injection, variable valve timing, and cylinder deactivation technologies. Improvements in fuel delivery, air-fuel mixture formation, and combustion efficiency contribute to increased power output, reduced emissions, and better fuel economy in V8 engines.Expand Specific Solutions03 Turbocharging and Supercharging
Forced induction systems, such as turbochargers and superchargers, are often employed in V8 engines to boost power output. These systems compress the intake air, allowing more fuel to be burned and increasing engine performance. Various designs and configurations of turbochargers and superchargers are used to optimize V8 engine performance across different operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Engine Block and Component Materials
The choice of materials for V8 engine blocks and components significantly impacts performance, durability, and weight. Advanced materials such as aluminum alloys, high-strength steel, and composite materials are used to reduce engine weight while maintaining strength and thermal efficiency. Innovations in material science and manufacturing processes contribute to improved V8 engine designs.Expand Specific Solutions05 Cooling and Lubrication Systems
Efficient cooling and lubrication systems are essential for V8 engine performance and longevity. Advanced cooling systems manage engine temperature across various operating conditions, while improved lubrication systems ensure proper oil distribution to critical components. Innovations in these areas focus on enhancing heat dissipation, reducing friction, and improving overall engine efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key V8 Manufacturers
The V8 engine market in sports cars is in a mature stage, with established players dominating the landscape. The global market size for V8-powered sports cars is significant, driven by demand for high-performance vehicles. Technologically, V8 engines are well-developed, with ongoing refinements focusing on efficiency and emissions. Key players like BMW, Toyota, and Ford continue to innovate, while niche manufacturers such as McLaren and Lamborghini push performance boundaries. Honda and Hyundai are also making strides in V8 technology, though they are not traditionally associated with this engine type. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of mainstream automakers and specialized sports car manufacturers, each leveraging their strengths in engine design and vehicle integration.
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG
Technical Solution: BMW's approach to V8 engines in sports cars combines performance with efficiency. Their latest S63 4.4-liter twin-turbocharged V8, used in M performance models, produces up to 617 horsepower in the M8 Competition[7]. BMW employs a "hot V" turbocharger layout, similar to Porsche, for compact packaging and reduced turbo lag. The engine features direct injection, variable valve timing, and a cross-bank exhaust manifold for improved exhaust gas flow. BMW has also implemented a water injection system in some high-performance applications to reduce knock and increase power output[8]. Their V8 engines are designed to deliver a balance of high-end performance and daily drivability, aligning with BMW's "Ultimate Driving Machine" philosophy.
Strengths: Balance of performance and efficiency, advanced technologies, versatility across different vehicle types. Weaknesses: Complexity of systems may lead to higher maintenance costs, potential reliability concerns with cutting-edge technologies.
Ford Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Ford's V8 engine development for sports cars, particularly in the Mustang lineup, focuses on both traditional naturally aspirated designs and modern turbocharged variants. The 5.0-liter Coyote V8 used in the Mustang GT produces up to 460 horsepower, featuring dual fuel injection (port and direct) for improved efficiency and power[9]. For higher performance applications, Ford has developed the 5.2-liter Voodoo V8 with a flat-plane crankshaft, used in the Shelby GT350, producing 526 horsepower and a distinctive high-revving character. Additionally, Ford's 5.2-liter Predator V8, a supercharged variant used in the Shelby GT500, delivers 760 horsepower[10]. Ford's V8 engines are designed to provide accessible performance and iconic American muscle car characteristics.
Strengths: Wide range of performance options, iconic muscle car sound, accessible performance. Weaknesses: Higher fuel consumption in some variants, less advanced in terms of downsizing and electrification compared to some European competitors.
V8 Innovations Analysis
V8 engine
PatentActiveUS20230109196A1
Innovation
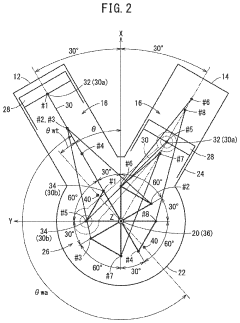
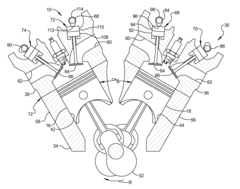
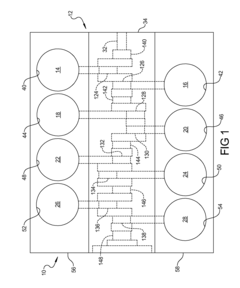
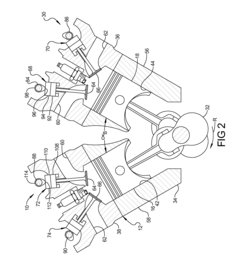
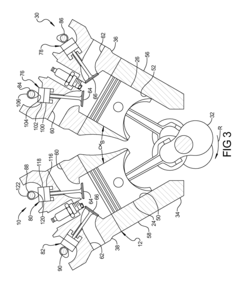
- The V8 engine configuration features crank pins arranged at 90° intervals on one bank and offset by 60° on the other bank, allowing for cancellation of primary inertia couples without additional specialized components by optimizing the arrangement of crank pins and connecting rods.
Engine assembly including crankshaft for v8 arrangement
PatentInactiveUS20120210958A1
Innovation
- A V8 engine crankshaft design with rotationally offset and aligned crank pins, allowing for primary balance without balance shafts and maintaining consistent firing intervals across all eight cylinders, as well as during operation with six or seven cylinders, through a specific arrangement of crank pins and bearing journals.
Emissions Regulations
Emissions regulations have become increasingly stringent for sports cars equipped with V8 engines, posing significant challenges for manufacturers. These regulations aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality, particularly in urban areas. The European Union's Euro 6d standards and the United States' EPA Tier 3 regulations have set strict limits on carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter emissions.
To comply with these regulations, sports car manufacturers have implemented various technologies and strategies. One common approach is the use of advanced engine management systems that optimize fuel injection, ignition timing, and exhaust gas recirculation. These systems help reduce emissions while maintaining performance. Additionally, many V8-powered sports cars now feature cylinder deactivation technology, which allows the engine to operate on fewer cylinders during low-load conditions, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
Turbocharging and direct fuel injection have also become prevalent in V8 engines for sports cars. These technologies enable manufacturers to downsize engines while maintaining power output, resulting in improved fuel economy and lower emissions. Some manufacturers have gone further by incorporating hybrid powertrains, combining V8 engines with electric motors to reduce overall emissions and meet regulatory requirements.
Exhaust aftertreatment systems play a crucial role in emissions reduction for V8-powered sports cars. Advanced catalytic converters, particulate filters, and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems are employed to treat exhaust gases before they are released into the atmosphere. These systems effectively reduce harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides.
The impact of emissions regulations on V8 engines in sports cars extends beyond technological adaptations. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on lightweight materials and aerodynamic designs to improve overall vehicle efficiency. This approach helps offset the additional weight and complexity introduced by emissions control systems, ensuring that performance remains a priority.
Despite these advancements, the future of V8 engines in sports cars faces uncertainty due to increasingly stringent emissions standards. Some regions, such as the European Union, have proposed plans to phase out internal combustion engines entirely in favor of electric vehicles. This shift presents a significant challenge for sports car manufacturers who have long relied on V8 engines as a cornerstone of their product offerings.
As a result, many manufacturers are exploring alternative powertrain options, including fully electric and hydrogen fuel cell technologies, to future-proof their sports car lineups. However, the unique characteristics of V8 engines, such as their distinctive sound and power delivery, remain highly valued by enthusiasts, creating a delicate balance between regulatory compliance and market demand.
To comply with these regulations, sports car manufacturers have implemented various technologies and strategies. One common approach is the use of advanced engine management systems that optimize fuel injection, ignition timing, and exhaust gas recirculation. These systems help reduce emissions while maintaining performance. Additionally, many V8-powered sports cars now feature cylinder deactivation technology, which allows the engine to operate on fewer cylinders during low-load conditions, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
Turbocharging and direct fuel injection have also become prevalent in V8 engines for sports cars. These technologies enable manufacturers to downsize engines while maintaining power output, resulting in improved fuel economy and lower emissions. Some manufacturers have gone further by incorporating hybrid powertrains, combining V8 engines with electric motors to reduce overall emissions and meet regulatory requirements.
Exhaust aftertreatment systems play a crucial role in emissions reduction for V8-powered sports cars. Advanced catalytic converters, particulate filters, and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems are employed to treat exhaust gases before they are released into the atmosphere. These systems effectively reduce harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides.
The impact of emissions regulations on V8 engines in sports cars extends beyond technological adaptations. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on lightweight materials and aerodynamic designs to improve overall vehicle efficiency. This approach helps offset the additional weight and complexity introduced by emissions control systems, ensuring that performance remains a priority.
Despite these advancements, the future of V8 engines in sports cars faces uncertainty due to increasingly stringent emissions standards. Some regions, such as the European Union, have proposed plans to phase out internal combustion engines entirely in favor of electric vehicles. This shift presents a significant challenge for sports car manufacturers who have long relied on V8 engines as a cornerstone of their product offerings.
As a result, many manufacturers are exploring alternative powertrain options, including fully electric and hydrogen fuel cell technologies, to future-proof their sports car lineups. However, the unique characteristics of V8 engines, such as their distinctive sound and power delivery, remain highly valued by enthusiasts, creating a delicate balance between regulatory compliance and market demand.
V8 vs Alternative Powertrains
The V8 engine has long been synonymous with high-performance sports cars, offering unparalleled power and a distinctive sound that enthusiasts crave. However, as the automotive industry evolves, alternative powertrains are emerging as viable competitors to the traditional V8. This shift is driven by a combination of factors, including environmental concerns, technological advancements, and changing consumer preferences.
Electric powertrains have made significant strides in recent years, challenging the dominance of V8 engines in the sports car segment. Electric motors offer instant torque delivery, providing rapid acceleration that can match or even surpass that of V8-powered vehicles. Additionally, the lower center of gravity achieved by placing battery packs in the floor of the vehicle can enhance handling and stability, key attributes for sports car performance.
Hybrid powertrains represent another alternative that combines the best of both worlds. By pairing a smaller internal combustion engine with electric motors, hybrid systems can deliver impressive performance while improving fuel efficiency. This technology has been successfully implemented in high-performance vehicles, demonstrating that environmental consciousness and exhilarating driving experiences are not mutually exclusive.
Hydrogen fuel cell technology, while still in its infancy for sports car applications, shows promise as a future alternative to V8 engines. Offering zero emissions and the potential for quick refueling, hydrogen-powered sports cars could address some of the range and charging time concerns associated with pure electric vehicles.
Despite these advancements, V8 engines continue to hold a significant place in the sports car market. Their raw power, emotional appeal, and heritage factor remain strong selling points for many enthusiasts. Manufacturers are also improving V8 efficiency through technologies like cylinder deactivation and advanced fuel injection systems, helping to extend their relevance in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
The competition between V8 engines and alternative powertrains is driving innovation across the board. As alternative technologies mature, they are pushing V8 development to new heights, resulting in more efficient and powerful engines. Conversely, the high bar set by V8 performance is challenging alternative powertrain engineers to create systems that can deliver comparable or superior driving experiences.
Looking ahead, the future of sports car powertrains is likely to be diverse. While alternative technologies will continue to gain market share, V8 engines are expected to evolve and maintain a presence, particularly in high-end and specialty vehicles. The key for manufacturers will be to balance performance, efficiency, and emotional appeal to meet the varied demands of sports car enthusiasts in an ever-changing automotive landscape.
Electric powertrains have made significant strides in recent years, challenging the dominance of V8 engines in the sports car segment. Electric motors offer instant torque delivery, providing rapid acceleration that can match or even surpass that of V8-powered vehicles. Additionally, the lower center of gravity achieved by placing battery packs in the floor of the vehicle can enhance handling and stability, key attributes for sports car performance.
Hybrid powertrains represent another alternative that combines the best of both worlds. By pairing a smaller internal combustion engine with electric motors, hybrid systems can deliver impressive performance while improving fuel efficiency. This technology has been successfully implemented in high-performance vehicles, demonstrating that environmental consciousness and exhilarating driving experiences are not mutually exclusive.
Hydrogen fuel cell technology, while still in its infancy for sports car applications, shows promise as a future alternative to V8 engines. Offering zero emissions and the potential for quick refueling, hydrogen-powered sports cars could address some of the range and charging time concerns associated with pure electric vehicles.
Despite these advancements, V8 engines continue to hold a significant place in the sports car market. Their raw power, emotional appeal, and heritage factor remain strong selling points for many enthusiasts. Manufacturers are also improving V8 efficiency through technologies like cylinder deactivation and advanced fuel injection systems, helping to extend their relevance in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
The competition between V8 engines and alternative powertrains is driving innovation across the board. As alternative technologies mature, they are pushing V8 development to new heights, resulting in more efficient and powerful engines. Conversely, the high bar set by V8 performance is challenging alternative powertrain engineers to create systems that can deliver comparable or superior driving experiences.
Looking ahead, the future of sports car powertrains is likely to be diverse. While alternative technologies will continue to gain market share, V8 engines are expected to evolve and maintain a presence, particularly in high-end and specialty vehicles. The key for manufacturers will be to balance performance, efficiency, and emotional appeal to meet the varied demands of sports car enthusiasts in an ever-changing automotive landscape.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!