Using Microfluidics for Efficient Metabolite Analysis in Studies
SEP 10, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Microfluidics Technology Background and Objectives
Microfluidics technology has evolved significantly over the past three decades, transforming from a conceptual laboratory technique to a powerful analytical platform with diverse applications. The fundamental principle of microfluidics involves manipulating fluids at the microscale level, typically within channels with dimensions ranging from tens to hundreds of micrometers. This technology emerged in the early 1990s, building upon advancements in microfabrication techniques originally developed for the semiconductor industry.
The evolution of microfluidics has been characterized by several key milestones, including the development of soft lithography techniques in the late 1990s, which dramatically reduced fabrication costs and increased accessibility. Subsequently, the integration of various functional components such as valves, pumps, and mixers enabled more complex fluid handling operations, expanding the technology's capabilities beyond simple channel networks.
In recent years, microfluidics has gained significant traction in metabolite analysis due to its inherent advantages in handling small sample volumes, providing precise control over reaction conditions, and enabling high-throughput screening. The miniaturization of analytical processes has led to reduced reagent consumption, faster analysis times, and enhanced sensitivity compared to conventional methods.
The primary objective of implementing microfluidics for metabolite analysis is to overcome the limitations of traditional analytical techniques, which often require substantial sample volumes and lengthy processing times. By leveraging the unique properties of microscale fluid dynamics, researchers aim to develop integrated platforms capable of rapid, sensitive, and comprehensive metabolite profiling from limited biological samples.
Current technological trends indicate a convergence of microfluidics with complementary technologies such as mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and advanced imaging techniques. This integration aims to create seamless analytical workflows that maintain the integrity of metabolite samples throughout the entire analysis process, from sample preparation to detection and quantification.
Looking forward, the field is moving toward fully automated, high-throughput microfluidic systems capable of parallel processing multiple samples with minimal human intervention. The development of standardized fabrication methods and modular design approaches is expected to facilitate wider adoption across various research domains and industrial applications.
The ultimate goal is to establish microfluidics as a cornerstone technology for metabolomics research, enabling comprehensive metabolite analysis with unprecedented speed, sensitivity, and reproducibility. This would significantly advance our understanding of metabolic processes in various biological systems and potentially revolutionize approaches to disease diagnosis, drug development, and personalized medicine.
The evolution of microfluidics has been characterized by several key milestones, including the development of soft lithography techniques in the late 1990s, which dramatically reduced fabrication costs and increased accessibility. Subsequently, the integration of various functional components such as valves, pumps, and mixers enabled more complex fluid handling operations, expanding the technology's capabilities beyond simple channel networks.
In recent years, microfluidics has gained significant traction in metabolite analysis due to its inherent advantages in handling small sample volumes, providing precise control over reaction conditions, and enabling high-throughput screening. The miniaturization of analytical processes has led to reduced reagent consumption, faster analysis times, and enhanced sensitivity compared to conventional methods.
The primary objective of implementing microfluidics for metabolite analysis is to overcome the limitations of traditional analytical techniques, which often require substantial sample volumes and lengthy processing times. By leveraging the unique properties of microscale fluid dynamics, researchers aim to develop integrated platforms capable of rapid, sensitive, and comprehensive metabolite profiling from limited biological samples.
Current technological trends indicate a convergence of microfluidics with complementary technologies such as mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and advanced imaging techniques. This integration aims to create seamless analytical workflows that maintain the integrity of metabolite samples throughout the entire analysis process, from sample preparation to detection and quantification.
Looking forward, the field is moving toward fully automated, high-throughput microfluidic systems capable of parallel processing multiple samples with minimal human intervention. The development of standardized fabrication methods and modular design approaches is expected to facilitate wider adoption across various research domains and industrial applications.
The ultimate goal is to establish microfluidics as a cornerstone technology for metabolomics research, enabling comprehensive metabolite analysis with unprecedented speed, sensitivity, and reproducibility. This would significantly advance our understanding of metabolic processes in various biological systems and potentially revolutionize approaches to disease diagnosis, drug development, and personalized medicine.
Market Demand for Metabolite Analysis Solutions
The global market for metabolite analysis solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by advancements in precision medicine and the increasing prevalence of metabolic disorders. Current market valuations indicate that the metabolomics market reached approximately 2.2 billion USD in 2022, with projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.5% through 2030, highlighting the robust demand for innovative analytical technologies.
Healthcare institutions represent the largest segment of end-users, accounting for nearly 45% of the market share. This dominance stems from the critical role metabolite analysis plays in disease diagnosis, particularly for conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and various metabolic disorders. The pharmaceutical industry follows closely, utilizing metabolite analysis extensively in drug discovery and development processes to understand drug metabolism and identify potential biomarkers.
Academic research institutions constitute another significant market segment, where metabolite analysis supports fundamental research in biochemistry, molecular biology, and systems biology. The demand from this sector is expected to grow at 15% annually as research funding for metabolomics studies increases globally.
Geographically, North America leads the market with approximately 40% share, followed by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific at 20%. However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 16% annually, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and expanding research infrastructure in countries like China, Japan, and India.
A key market trend is the growing demand for point-of-care testing solutions that enable rapid metabolite analysis in clinical settings. This trend aligns perfectly with microfluidic technologies, which offer miniaturization, automation, and reduced sample volume requirements. Industry surveys indicate that 78% of healthcare providers express interest in adopting microfluidic-based metabolite analysis systems that can deliver results within minutes rather than hours.
Cost-effectiveness represents another critical market driver, with healthcare facilities actively seeking solutions that reduce per-test costs while maintaining analytical accuracy. Current conventional metabolite analysis methods cost between 50-200 USD per sample, creating substantial market opportunity for microfluidic technologies that can potentially reduce these costs by 40-60%.
The market also shows increasing demand for integrated systems that combine sample preparation, separation, and detection in single platforms. This integration trend favors microfluidic approaches, which naturally lend themselves to such comprehensive solutions. Market research indicates that 65% of potential users prioritize workflow integration as a key purchasing factor for new metabolite analysis technologies.
Healthcare institutions represent the largest segment of end-users, accounting for nearly 45% of the market share. This dominance stems from the critical role metabolite analysis plays in disease diagnosis, particularly for conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and various metabolic disorders. The pharmaceutical industry follows closely, utilizing metabolite analysis extensively in drug discovery and development processes to understand drug metabolism and identify potential biomarkers.
Academic research institutions constitute another significant market segment, where metabolite analysis supports fundamental research in biochemistry, molecular biology, and systems biology. The demand from this sector is expected to grow at 15% annually as research funding for metabolomics studies increases globally.
Geographically, North America leads the market with approximately 40% share, followed by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific at 20%. However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 16% annually, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and expanding research infrastructure in countries like China, Japan, and India.
A key market trend is the growing demand for point-of-care testing solutions that enable rapid metabolite analysis in clinical settings. This trend aligns perfectly with microfluidic technologies, which offer miniaturization, automation, and reduced sample volume requirements. Industry surveys indicate that 78% of healthcare providers express interest in adopting microfluidic-based metabolite analysis systems that can deliver results within minutes rather than hours.
Cost-effectiveness represents another critical market driver, with healthcare facilities actively seeking solutions that reduce per-test costs while maintaining analytical accuracy. Current conventional metabolite analysis methods cost between 50-200 USD per sample, creating substantial market opportunity for microfluidic technologies that can potentially reduce these costs by 40-60%.
The market also shows increasing demand for integrated systems that combine sample preparation, separation, and detection in single platforms. This integration trend favors microfluidic approaches, which naturally lend themselves to such comprehensive solutions. Market research indicates that 65% of potential users prioritize workflow integration as a key purchasing factor for new metabolite analysis technologies.
Current Microfluidic Metabolite Analysis Challenges
Despite significant advancements in microfluidic technologies for metabolite analysis, several critical challenges continue to impede the full realization of their potential in research and clinical applications. Sample preparation remains a major bottleneck, as metabolites often exist in complex biological matrices requiring extensive purification before analysis. The integration of effective sample preparation steps directly onto microfluidic platforms without compromising sensitivity or throughput presents significant engineering challenges.
Detection sensitivity constitutes another persistent limitation. Many metabolites of interest exist at extremely low concentrations in biological samples, sometimes in the picomolar to femtomolar range. Current microfluidic detection methods often struggle to achieve these detection limits without incorporating bulky external equipment, which contradicts the miniaturization advantages of microfluidic systems.
Standardization across platforms represents a substantial hurdle for widespread adoption. The field currently suffers from fragmentation, with various research groups developing proprietary systems with unique specifications and protocols. This lack of standardization complicates cross-laboratory validation and hinders the establishment of reliable reference values for metabolite concentrations in different biological contexts.
Multiplexing capabilities, while improving, still face considerable technical barriers. The simultaneous detection of multiple metabolites with diverse chemical properties requires sophisticated detection systems and intricate channel designs. Current multiplexed systems often compromise on either the number of detectable metabolites or the sensitivity of detection.
Integration with downstream analytical techniques presents ongoing challenges. While microfluidic platforms excel at sample handling and preparation, their connection to sophisticated analytical instruments like mass spectrometers often involves complex interfaces that can introduce sample loss or contamination, reducing overall system performance.
Reproducibility issues persist due to manufacturing variations in microfluidic chips. Even minor differences in channel dimensions, surface properties, or material composition can significantly affect flow dynamics and analytical performance. These variations become particularly problematic when scaling up production for commercial applications.
Real-time analysis capabilities remain limited for many metabolite classes. The ideal microfluidic platform would provide immediate feedback on metabolite concentrations, but current systems often require time-consuming separation steps or complex detection mechanisms that introduce delays between sample introduction and result generation.
Biofouling and sample carryover represent practical challenges in continuous or repeated analyses. Metabolites and other biomolecules can adsorb to channel surfaces, leading to cross-contamination between samples and degradation of analytical performance over time. Developing effective surface treatments or cleaning protocols that maintain system integrity remains an active area of research.
Detection sensitivity constitutes another persistent limitation. Many metabolites of interest exist at extremely low concentrations in biological samples, sometimes in the picomolar to femtomolar range. Current microfluidic detection methods often struggle to achieve these detection limits without incorporating bulky external equipment, which contradicts the miniaturization advantages of microfluidic systems.
Standardization across platforms represents a substantial hurdle for widespread adoption. The field currently suffers from fragmentation, with various research groups developing proprietary systems with unique specifications and protocols. This lack of standardization complicates cross-laboratory validation and hinders the establishment of reliable reference values for metabolite concentrations in different biological contexts.
Multiplexing capabilities, while improving, still face considerable technical barriers. The simultaneous detection of multiple metabolites with diverse chemical properties requires sophisticated detection systems and intricate channel designs. Current multiplexed systems often compromise on either the number of detectable metabolites or the sensitivity of detection.
Integration with downstream analytical techniques presents ongoing challenges. While microfluidic platforms excel at sample handling and preparation, their connection to sophisticated analytical instruments like mass spectrometers often involves complex interfaces that can introduce sample loss or contamination, reducing overall system performance.
Reproducibility issues persist due to manufacturing variations in microfluidic chips. Even minor differences in channel dimensions, surface properties, or material composition can significantly affect flow dynamics and analytical performance. These variations become particularly problematic when scaling up production for commercial applications.
Real-time analysis capabilities remain limited for many metabolite classes. The ideal microfluidic platform would provide immediate feedback on metabolite concentrations, but current systems often require time-consuming separation steps or complex detection mechanisms that introduce delays between sample introduction and result generation.
Biofouling and sample carryover represent practical challenges in continuous or repeated analyses. Metabolites and other biomolecules can adsorb to channel surfaces, leading to cross-contamination between samples and degradation of analytical performance over time. Developing effective surface treatments or cleaning protocols that maintain system integrity remains an active area of research.
Current Microfluidic Platforms for Metabolite Detection
01 Microfluidic channel design optimization
Optimizing the design of microfluidic channels can significantly improve efficiency in microfluidic systems. This includes considerations for channel geometry, surface treatments, and flow path configurations that minimize resistance and enhance fluid transport. Advanced channel designs can reduce dead volumes, prevent clogging, and enable more efficient mixing or separation processes, ultimately improving the overall performance of microfluidic devices.- Microfluidic channel design optimization: Optimizing the design of microfluidic channels can significantly improve efficiency in microfluidic systems. This includes considerations for channel geometry, surface treatments, and flow dynamics to reduce resistance and enhance fluid transport. Advanced channel designs incorporate features that minimize dead volumes, prevent clogging, and ensure uniform flow distribution, resulting in improved overall system performance and reduced processing time.
- Integration of sensing and control systems: Incorporating sensing and control systems into microfluidic devices enables real-time monitoring and adjustment of operational parameters. These integrated systems can detect flow rates, pressure, temperature, and chemical compositions, allowing for automated feedback control. This integration enhances process reliability, reduces human intervention, and optimizes resource utilization, leading to improved efficiency in microfluidic applications.
- Novel materials and fabrication techniques: The development of new materials and fabrication techniques has revolutionized microfluidic efficiency. Advanced polymers, glass formulations, and hybrid materials offer improved chemical resistance, optical clarity, and biocompatibility. Modern fabrication methods such as 3D printing, laser ablation, and soft lithography enable the creation of complex microstructures with high precision, resulting in more efficient and reliable microfluidic devices.
- Droplet-based microfluidics for enhanced throughput: Droplet-based microfluidic systems compartmentalize reactions into discrete droplets, functioning as individual micro-reactors. This approach enables high-throughput processing, parallel operations, and reduced reagent consumption. The controlled generation, manipulation, and analysis of these droplets allow for increased processing speed, improved reaction efficiency, and enhanced analytical sensitivity compared to conventional continuous-flow systems.
- Energy-efficient pumping and fluid manipulation: Innovations in pumping mechanisms and fluid manipulation techniques have significantly improved energy efficiency in microfluidic systems. These include electrokinetic methods, acoustic actuation, magnetic manipulation, and passive capillary-driven flows that require minimal external power. Advanced valve designs and flow control strategies further optimize fluid handling while reducing energy consumption, making microfluidic systems more sustainable and suitable for portable applications.
02 Integration of sensing and control systems
Incorporating advanced sensing and control systems into microfluidic platforms enables real-time monitoring and adjustment of operational parameters. These integrated systems can detect flow rates, pressure, temperature, and other critical variables, allowing for automated feedback control to maintain optimal conditions. This integration enhances process reliability, reproducibility, and efficiency by minimizing manual interventions and enabling precise control over microfluidic operations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Novel materials and fabrication techniques
The development and application of novel materials and advanced fabrication techniques are improving microfluidic efficiency. Materials with specific properties such as enhanced hydrophobicity, reduced surface adsorption, or improved thermal conductivity can be selected for particular applications. Modern fabrication methods including 3D printing, laser ablation, and nanoimprinting allow for more complex and precise microstructures that optimize fluid handling and processing capabilities.Expand Specific Solutions04 Droplet-based microfluidics optimization
Droplet-based microfluidic systems offer enhanced efficiency through compartmentalization of reactions and processes. By optimizing droplet generation, manipulation, and analysis techniques, these systems can achieve higher throughput, reduced reagent consumption, and improved reaction kinetics. Advanced droplet handling methods including electrowetting, acoustic actuation, and passive sorting mechanisms contribute to more efficient microfluidic operations for applications in diagnostics, drug discovery, and chemical synthesis.Expand Specific Solutions05 Energy-efficient microfluidic pumping and mixing
Developing energy-efficient methods for fluid pumping and mixing in microfluidic systems is crucial for overall efficiency. Innovative approaches include passive mixing structures, inertial microfluidics, electrokinetic techniques, and magnetically-actuated systems that require minimal external power. These methods reduce energy consumption while maintaining or improving fluid handling performance, making microfluidic systems more sustainable and suitable for portable or point-of-care applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Microfluidics
Microfluidics for metabolite analysis is in a growth phase, with the market expanding due to increasing applications in life sciences research. The technology is maturing rapidly, evidenced by significant advancements from key players across academic and commercial sectors. Tsinghua University, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, and University of Washington are leading academic research, while companies like Agilent Technologies, Applied Biosystems (Thermo Fisher), and Roche Diagnostics are commercializing sophisticated platforms. Fluigent and Cellix are specializing in microfluidic pumping solutions, while pharmaceutical companies like Piramal Enterprises are integrating these technologies into their R&D pipelines. The convergence of microfluidics with AI and automation, driven by collaborations between technology firms like Intel and life science specialists, is accelerating market growth and technological sophistication.
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics Chinese Academy of Sci
Technical Solution: The Dalian Institute has developed an innovative microfluidic platform for comprehensive metabolite analysis that integrates multiple separation modes with high-sensitivity detection. Their system employs a hybrid approach combining electrophoresis-driven and pressure-driven flow control, allowing dynamic adjustment based on sample properties. The platform features multilayer microfluidic chips fabricated using advanced nanolithography techniques, creating channel structures with precisely controlled dimensions (5-20 μm) and specialized surface properties. Their technology incorporates on-chip solid-phase extraction columns with functionalized nanoparticles, achieving enrichment factors of 50-200× for low-abundance metabolites. The institute's microfluidic system includes integrated electrochemical detection arrays with multiplexed electrodes modified with specific recognition elements, enabling simultaneous quantification of over 40 metabolites with detection limits in the nanomolar range. Their platform supports two-dimensional separations combining chromatographic and electrophoretic principles, dramatically improving resolution for complex biological samples. Recent innovations include integration with ambient ionization mass spectrometry techniques and development of machine learning algorithms for automated peak identification with accuracy exceeding 90% for common metabolic pathways.
Strengths: Exceptional separation capabilities for complex biological matrices through innovative hybrid separation technologies. Advanced on-chip sample preparation techniques enable analysis of challenging samples with minimal pretreatment. Weaknesses: Less commercialized than competing platforms, potentially limiting accessibility and support. Higher complexity in operation requires specialized training and expertise.
Applied Biosystems LLC
Technical Solution: Applied Biosystems has developed an advanced microfluidic platform specifically optimized for metabolite analysis in biological studies. Their system utilizes digital microfluidics technology that manipulates discrete droplets (50-500 nL) through electrowetting principles, eliminating the need for complex pumping systems. The platform features integrated sample preparation modules including on-chip extraction, derivatization, and concentration capabilities that reduce sample processing time by approximately 70% compared to conventional methods. Their proprietary microchip design incorporates multiple parallel reaction chambers with temperature control precision of ±0.1°C, enabling simultaneous processing of up to 96 samples. The system employs fluorescence detection with sensitivity down to picomolar concentrations for labeled metabolites, while also supporting seamless integration with external mass spectrometry systems. Applied Biosystems' technology includes automated calibration protocols that reduce inter-assay variability to less than 5%, and their software platform provides comprehensive metabolite identification against curated databases containing over 20,000 compounds.
Strengths: Exceptional throughput capabilities with parallel processing architecture ideal for large-scale metabolomic studies. Highly automated workflow reduces operator intervention and improves reproducibility. Weaknesses: Limited flexibility for customization of experimental parameters compared to some competing platforms. Higher initial investment cost though offset by reduced per-sample analysis expenses.
Key Innovations in Microfluidic Metabolite Separation
A microfluidic device, a microfluidic system and a method for the capture and controllable release of single biological cells
PatentWO2025068547A1
Innovation
- A microfluidic device with a capturing surface functionalized with an immobilizer bonded by an electrochemically dissociable bond, allowing for the capture, monitoring, and controlled release of single biological cells, enabling their analysis and further assessments.
Microfluidic device for pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic study of drugs and uses thereof
PatentActiveUS20120135452A1
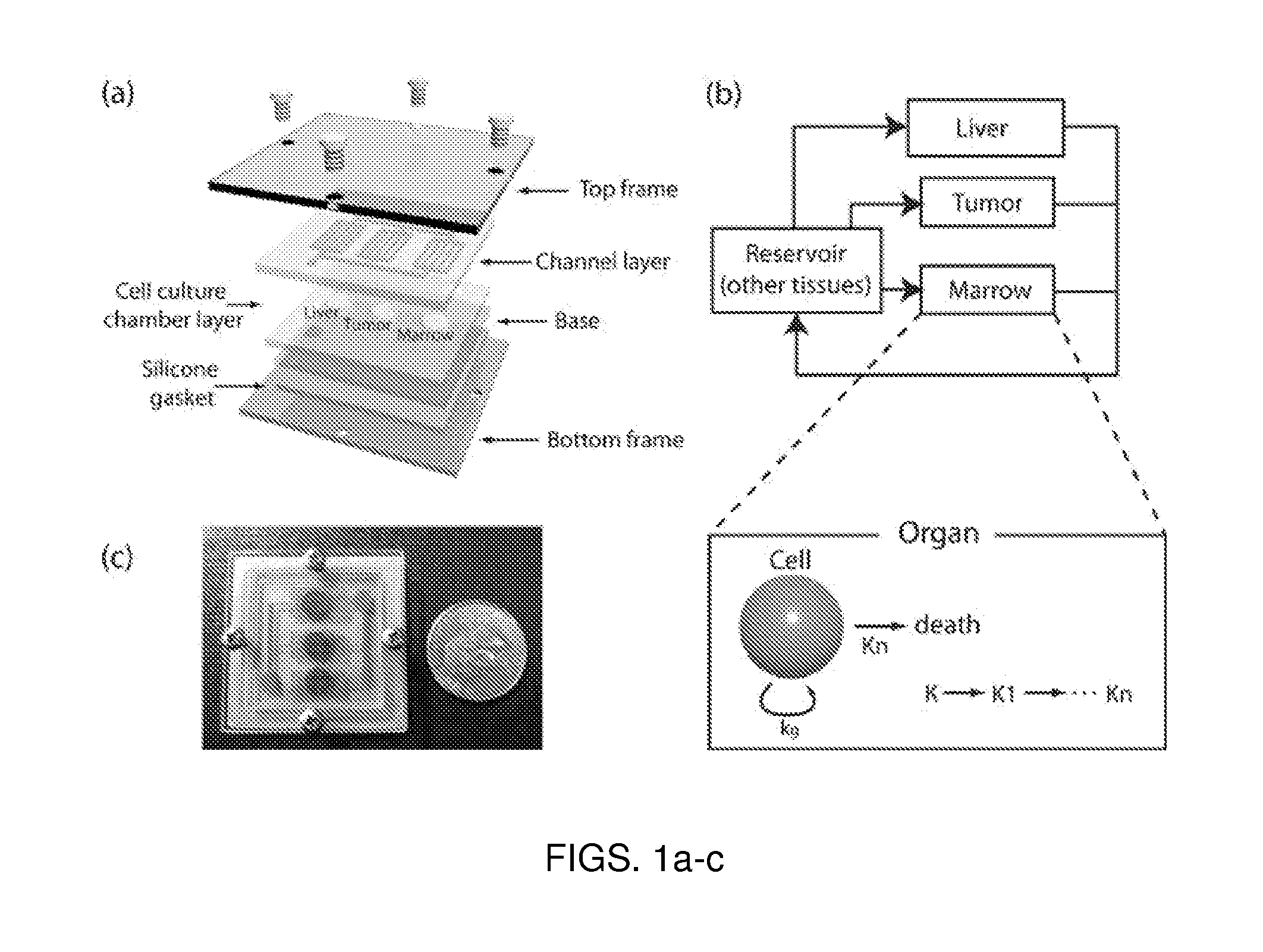
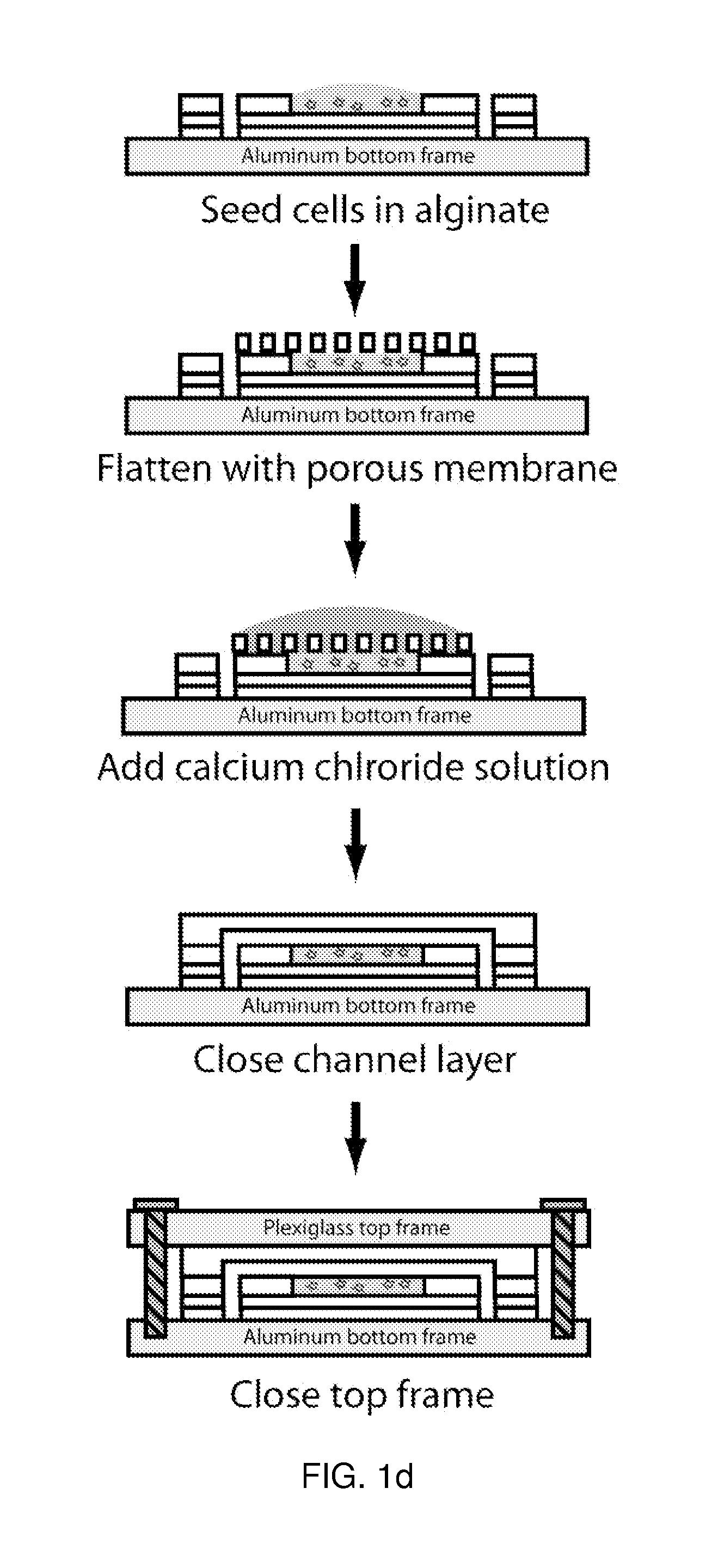
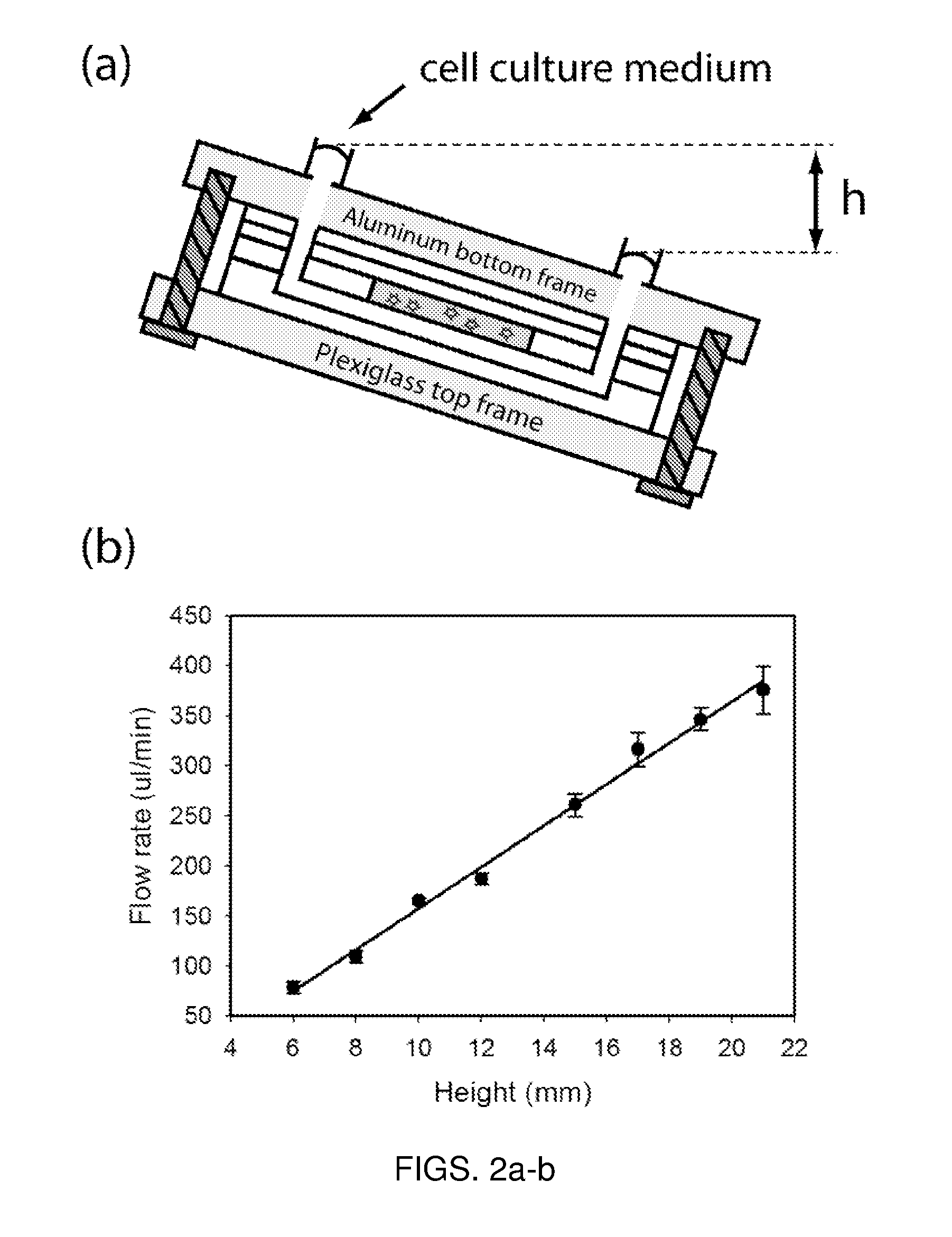
Innovation
- A microfluidic device with a layered design featuring a cell culture chamber layer and fluidic channel layer, allowing for controlled fluid flow to simulate physiological environments and conditions, enabling pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis of drugs in a multi-organ interaction setting.
Integration with Mass Spectrometry and Other Analytical Methods
The integration of microfluidics with mass spectrometry (MS) represents a powerful analytical approach for metabolite analysis. This combination leverages the high-throughput sample processing capabilities of microfluidic platforms with the exceptional sensitivity and specificity of mass spectrometry. Recent advancements have focused on developing seamless interfaces between these technologies, addressing challenges related to flow rate compatibility and sample transfer efficiency.
Direct coupling of microfluidic devices with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) has emerged as a particularly effective strategy. This integration enables real-time analysis of metabolites with minimal sample loss and contamination risks. Innovations in chip-based ESI emitters have significantly improved ionization efficiency and stability, allowing for detection of metabolites at femtomole levels or lower. These developments have proven especially valuable for studies involving limited sample volumes, such as single-cell metabolomics.
Beyond mass spectrometry, microfluidic platforms have been successfully integrated with various other analytical techniques. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy integration offers complementary structural information about metabolites, though miniaturization challenges remain. Raman spectroscopy integration provides label-free detection capabilities with minimal sample preparation requirements. Fluorescence-based detection methods, when combined with microfluidics, enable high-sensitivity monitoring of specific metabolites through targeted fluorescent probes or enzymatic assays.
Multi-modal integration approaches are gaining traction, where microfluidic devices incorporate several detection methods simultaneously. These systems can perform parallel analyses using optical detection for rapid screening followed by MS for detailed characterization. Such integrated platforms significantly enhance the information density obtained from a single sample, providing both quantitative and qualitative data on complex metabolite mixtures.
Data integration represents another crucial aspect of these hybrid analytical systems. Advanced software solutions have been developed to process and correlate data from multiple detection modalities, enabling comprehensive metabolite profiling. Machine learning algorithms are increasingly employed to identify patterns and relationships across different analytical outputs, enhancing the interpretative power of multi-modal analyses.
The miniaturization of these integrated systems continues to advance, with recent developments focusing on portable devices capable of field deployment. These systems maintain analytical performance comparable to laboratory-based equipment while offering significant advantages in terms of mobility and rapid on-site analysis capabilities, particularly valuable for environmental metabolomics studies and point-of-care diagnostics.
Direct coupling of microfluidic devices with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) has emerged as a particularly effective strategy. This integration enables real-time analysis of metabolites with minimal sample loss and contamination risks. Innovations in chip-based ESI emitters have significantly improved ionization efficiency and stability, allowing for detection of metabolites at femtomole levels or lower. These developments have proven especially valuable for studies involving limited sample volumes, such as single-cell metabolomics.
Beyond mass spectrometry, microfluidic platforms have been successfully integrated with various other analytical techniques. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy integration offers complementary structural information about metabolites, though miniaturization challenges remain. Raman spectroscopy integration provides label-free detection capabilities with minimal sample preparation requirements. Fluorescence-based detection methods, when combined with microfluidics, enable high-sensitivity monitoring of specific metabolites through targeted fluorescent probes or enzymatic assays.
Multi-modal integration approaches are gaining traction, where microfluidic devices incorporate several detection methods simultaneously. These systems can perform parallel analyses using optical detection for rapid screening followed by MS for detailed characterization. Such integrated platforms significantly enhance the information density obtained from a single sample, providing both quantitative and qualitative data on complex metabolite mixtures.
Data integration represents another crucial aspect of these hybrid analytical systems. Advanced software solutions have been developed to process and correlate data from multiple detection modalities, enabling comprehensive metabolite profiling. Machine learning algorithms are increasingly employed to identify patterns and relationships across different analytical outputs, enhancing the interpretative power of multi-modal analyses.
The miniaturization of these integrated systems continues to advance, with recent developments focusing on portable devices capable of field deployment. These systems maintain analytical performance comparable to laboratory-based equipment while offering significant advantages in terms of mobility and rapid on-site analysis capabilities, particularly valuable for environmental metabolomics studies and point-of-care diagnostics.
Standardization and Validation Protocols for Microfluidic Metabolomics
The standardization and validation of microfluidic platforms for metabolomics analysis represents a critical challenge in the field. Current protocols exhibit significant variability across laboratories, hindering reproducibility and limiting widespread adoption of microfluidic technologies in metabolite studies. Establishing robust standardization frameworks requires addressing multiple technical parameters that influence analytical performance.
Sample preparation protocols must be rigorously standardized, including consistent methods for cell lysis, metabolite extraction, and sample storage. These procedures significantly impact metabolite stability and recovery rates, with temperature control being particularly crucial for preserving labile metabolites. Standardized protocols should specify optimal buffer compositions, centrifugation parameters, and storage conditions tailored to different sample types.
Microfluidic device calibration demands systematic approaches to ensure consistent performance across different instruments and laboratories. This includes standardized procedures for channel conditioning, flow rate validation, and detector response calibration. Regular quality control measures using certified reference materials are essential for maintaining analytical integrity and enabling cross-laboratory comparisons.
Validation metrics must be clearly defined and universally adopted to enable meaningful assessment of microfluidic metabolomics platforms. These metrics should include limits of detection and quantification, linear dynamic range, precision (intra- and inter-day), accuracy, and robustness. Recovery experiments using isotopically labeled internal standards provide critical information about matrix effects and extraction efficiency across different sample types.
Data processing and analysis represent another crucial area requiring standardization. Automated peak detection, alignment algorithms, and normalization methods significantly impact the final metabolite profiles. Establishing consensus approaches for data preprocessing, feature extraction, and statistical analysis would greatly enhance comparability between studies and facilitate meta-analyses across different research groups.
Interlaboratory ring trials constitute an essential component of validation protocols. These collaborative studies, where identical samples are analyzed across multiple facilities using standardized methods, reveal systematic biases and variability sources. Results from such trials can inform refinement of protocols and establish realistic performance expectations for microfluidic metabolomics platforms.
Documentation standards must be developed to ensure comprehensive reporting of experimental conditions. This includes detailed descriptions of microfluidic device specifications, operational parameters, sample handling procedures, and data processing workflows. Such documentation facilitates method transfer between laboratories and supports troubleshooting when performance issues arise.
Sample preparation protocols must be rigorously standardized, including consistent methods for cell lysis, metabolite extraction, and sample storage. These procedures significantly impact metabolite stability and recovery rates, with temperature control being particularly crucial for preserving labile metabolites. Standardized protocols should specify optimal buffer compositions, centrifugation parameters, and storage conditions tailored to different sample types.
Microfluidic device calibration demands systematic approaches to ensure consistent performance across different instruments and laboratories. This includes standardized procedures for channel conditioning, flow rate validation, and detector response calibration. Regular quality control measures using certified reference materials are essential for maintaining analytical integrity and enabling cross-laboratory comparisons.
Validation metrics must be clearly defined and universally adopted to enable meaningful assessment of microfluidic metabolomics platforms. These metrics should include limits of detection and quantification, linear dynamic range, precision (intra- and inter-day), accuracy, and robustness. Recovery experiments using isotopically labeled internal standards provide critical information about matrix effects and extraction efficiency across different sample types.
Data processing and analysis represent another crucial area requiring standardization. Automated peak detection, alignment algorithms, and normalization methods significantly impact the final metabolite profiles. Establishing consensus approaches for data preprocessing, feature extraction, and statistical analysis would greatly enhance comparability between studies and facilitate meta-analyses across different research groups.
Interlaboratory ring trials constitute an essential component of validation protocols. These collaborative studies, where identical samples are analyzed across multiple facilities using standardized methods, reveal systematic biases and variability sources. Results from such trials can inform refinement of protocols and establish realistic performance expectations for microfluidic metabolomics platforms.
Documentation standards must be developed to ensure comprehensive reporting of experimental conditions. This includes detailed descriptions of microfluidic device specifications, operational parameters, sample handling procedures, and data processing workflows. Such documentation facilitates method transfer between laboratories and supports troubleshooting when performance issues arise.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!