Utilization of Sulfamic Acid in Ink and Pigment Production
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfamic Acid in Inks: Background and Objectives
Sulfamic acid, a versatile compound with the chemical formula H3NSO3, has been gaining significant attention in the ink and pigment production industry over the past few decades. This strong, yet relatively safe acid has emerged as a crucial component in various industrial processes, particularly in the formulation of inks and pigments. The evolution of sulfamic acid's application in this field can be traced back to the mid-20th century when researchers began exploring its potential as a replacement for more hazardous acids in manufacturing processes.
The primary objective of utilizing sulfamic acid in ink and pigment production is to enhance the quality, stability, and performance of the final products while simultaneously addressing environmental and safety concerns. As the printing and coating industries have advanced, the demand for more efficient, eco-friendly, and cost-effective production methods has intensified. Sulfamic acid has proven to be a valuable solution in meeting these evolving requirements.
In the context of ink production, sulfamic acid serves multiple purposes. It acts as a pH regulator, helping to maintain the optimal acidity level for ink stability and performance. Additionally, it functions as a powerful cleaning agent, effectively removing ink residues from printing equipment and surfaces. This dual functionality has made sulfamic acid an indispensable component in modern ink formulations and maintenance processes.
For pigment production, sulfamic acid plays a crucial role in the synthesis and modification of various colorants. Its unique chemical properties allow for the creation of more vibrant and durable pigments, particularly in the realm of organic pigments. The acid's ability to facilitate precise control over particle size and distribution has led to significant improvements in pigment quality and consistency.
The technological trajectory of sulfamic acid in this field has been marked by continuous refinement and innovation. Researchers and industry professionals have been working tirelessly to optimize its use, exploring new applications and developing novel formulations that leverage its unique properties. This ongoing research aims to further improve the efficiency of ink and pigment production processes, reduce environmental impact, and enhance the overall quality of printed and coated materials.
As we delve deeper into the utilization of sulfamic acid in ink and pigment production, it is essential to consider the broader implications of this technology. The adoption of sulfamic acid-based processes has the potential to revolutionize the printing and coating industries, offering a more sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional methods. This technological shift aligns with the global push towards greener manufacturing practices and the increasing emphasis on product safety and environmental responsibility.
The primary objective of utilizing sulfamic acid in ink and pigment production is to enhance the quality, stability, and performance of the final products while simultaneously addressing environmental and safety concerns. As the printing and coating industries have advanced, the demand for more efficient, eco-friendly, and cost-effective production methods has intensified. Sulfamic acid has proven to be a valuable solution in meeting these evolving requirements.
In the context of ink production, sulfamic acid serves multiple purposes. It acts as a pH regulator, helping to maintain the optimal acidity level for ink stability and performance. Additionally, it functions as a powerful cleaning agent, effectively removing ink residues from printing equipment and surfaces. This dual functionality has made sulfamic acid an indispensable component in modern ink formulations and maintenance processes.
For pigment production, sulfamic acid plays a crucial role in the synthesis and modification of various colorants. Its unique chemical properties allow for the creation of more vibrant and durable pigments, particularly in the realm of organic pigments. The acid's ability to facilitate precise control over particle size and distribution has led to significant improvements in pigment quality and consistency.
The technological trajectory of sulfamic acid in this field has been marked by continuous refinement and innovation. Researchers and industry professionals have been working tirelessly to optimize its use, exploring new applications and developing novel formulations that leverage its unique properties. This ongoing research aims to further improve the efficiency of ink and pigment production processes, reduce environmental impact, and enhance the overall quality of printed and coated materials.
As we delve deeper into the utilization of sulfamic acid in ink and pigment production, it is essential to consider the broader implications of this technology. The adoption of sulfamic acid-based processes has the potential to revolutionize the printing and coating industries, offering a more sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional methods. This technological shift aligns with the global push towards greener manufacturing practices and the increasing emphasis on product safety and environmental responsibility.
Market Analysis for Sulfamic Acid-Based Inks
The market for sulfamic acid-based inks and pigments has shown significant growth potential in recent years, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly and high-performance printing solutions. Sulfamic acid, known for its versatility and effectiveness, has emerged as a key component in the development of innovative ink formulations.
In the printing industry, sulfamic acid-based inks have gained traction due to their superior properties, including improved color stability, faster drying times, and enhanced adhesion to various substrates. These attributes have made them particularly attractive for applications in packaging, textiles, and digital printing sectors.
The global market for sulfamic acid-based inks is expected to experience steady growth over the next five years. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising adoption of sustainable printing practices and the increasing focus on reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions in ink production. Sulfamic acid-based inks offer a viable alternative to traditional solvent-based inks, aligning with stringent environmental regulations.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific represents the largest market for sulfamic acid-based inks, followed by North America and Europe. The rapid industrialization and expanding packaging industry in countries like China and India are driving the demand in the Asia-Pacific region. In North America and Europe, the shift towards sustainable printing solutions and stringent environmental regulations are fueling market growth.
The textile printing segment is anticipated to be a major contributor to the sulfamic acid-based ink market. The ability of these inks to provide vibrant colors and excellent wash fastness has made them increasingly popular in the textile industry. Additionally, the packaging industry is expected to be a significant consumer of sulfamic acid-based inks, driven by the growing e-commerce sector and the need for high-quality, durable packaging solutions.
In terms of market dynamics, the sulfamic acid-based ink industry is characterized by intense competition and ongoing research and development activities. Key players are focusing on product innovation and strategic partnerships to gain a competitive edge. The market is also witnessing a trend towards the development of water-based sulfamic acid inks, which offer improved environmental performance and meet the growing demand for sustainable printing solutions.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the volatility in raw material prices and the need for significant initial investments in new ink formulations. However, the long-term benefits of sulfamic acid-based inks, including improved print quality and reduced environmental impact, are expected to outweigh these challenges and drive continued market growth.
In the printing industry, sulfamic acid-based inks have gained traction due to their superior properties, including improved color stability, faster drying times, and enhanced adhesion to various substrates. These attributes have made them particularly attractive for applications in packaging, textiles, and digital printing sectors.
The global market for sulfamic acid-based inks is expected to experience steady growth over the next five years. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising adoption of sustainable printing practices and the increasing focus on reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions in ink production. Sulfamic acid-based inks offer a viable alternative to traditional solvent-based inks, aligning with stringent environmental regulations.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific represents the largest market for sulfamic acid-based inks, followed by North America and Europe. The rapid industrialization and expanding packaging industry in countries like China and India are driving the demand in the Asia-Pacific region. In North America and Europe, the shift towards sustainable printing solutions and stringent environmental regulations are fueling market growth.
The textile printing segment is anticipated to be a major contributor to the sulfamic acid-based ink market. The ability of these inks to provide vibrant colors and excellent wash fastness has made them increasingly popular in the textile industry. Additionally, the packaging industry is expected to be a significant consumer of sulfamic acid-based inks, driven by the growing e-commerce sector and the need for high-quality, durable packaging solutions.
In terms of market dynamics, the sulfamic acid-based ink industry is characterized by intense competition and ongoing research and development activities. Key players are focusing on product innovation and strategic partnerships to gain a competitive edge. The market is also witnessing a trend towards the development of water-based sulfamic acid inks, which offer improved environmental performance and meet the growing demand for sustainable printing solutions.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the volatility in raw material prices and the need for significant initial investments in new ink formulations. However, the long-term benefits of sulfamic acid-based inks, including improved print quality and reduced environmental impact, are expected to outweigh these challenges and drive continued market growth.
Technical Challenges in Sulfamic Acid Utilization
The utilization of sulfamic acid in ink and pigment production faces several significant technical challenges that require innovative solutions. One of the primary obstacles is the corrosive nature of sulfamic acid, which can lead to equipment degradation and potential safety hazards during the manufacturing process. This necessitates the use of specialized, acid-resistant materials and equipment, increasing production costs and complexity.
Another challenge lies in maintaining the stability of sulfamic acid-based formulations. The acid's reactivity can cause unwanted side reactions or degradation of other components in inks and pigments, potentially affecting the final product's quality and shelf life. Researchers are continuously working on developing stabilizers and buffers to mitigate these issues, but finding the right balance remains a complex task.
The solubility of sulfamic acid in various solvents used in ink and pigment production also presents difficulties. While it is highly soluble in water, its solubility in organic solvents commonly used in these industries is limited. This constraint can impact the formulation options and may require the development of novel solvent systems or dispersion techniques to effectively incorporate sulfamic acid into diverse ink and pigment compositions.
Environmental concerns pose another significant challenge. The use of sulfamic acid can contribute to increased sulfur content in wastewater streams, necessitating additional treatment steps to meet environmental regulations. This not only adds to production costs but also requires careful management of waste streams to minimize environmental impact.
Furthermore, achieving consistent quality and performance across different batches of sulfamic acid-based inks and pigments can be challenging. Variations in raw materials, processing conditions, and interactions with other ingredients can lead to inconsistencies in the final product. Developing robust quality control measures and standardized production protocols is crucial to address this issue.
The scalability of sulfamic acid utilization in large-scale industrial production also presents technical hurdles. Ensuring uniform mixing, maintaining precise pH levels, and controlling reaction conditions become more complex as production volumes increase. Engineers must design innovative reactor systems and process control mechanisms to overcome these scaling challenges.
Lastly, the optimization of sulfamic acid's role in enhancing specific properties of inks and pigments, such as color intensity, durability, and adhesion, requires ongoing research and development efforts. Balancing these desired properties while managing the acid's reactivity and potential side effects demands a deep understanding of chemical interactions and formulation science.
Another challenge lies in maintaining the stability of sulfamic acid-based formulations. The acid's reactivity can cause unwanted side reactions or degradation of other components in inks and pigments, potentially affecting the final product's quality and shelf life. Researchers are continuously working on developing stabilizers and buffers to mitigate these issues, but finding the right balance remains a complex task.
The solubility of sulfamic acid in various solvents used in ink and pigment production also presents difficulties. While it is highly soluble in water, its solubility in organic solvents commonly used in these industries is limited. This constraint can impact the formulation options and may require the development of novel solvent systems or dispersion techniques to effectively incorporate sulfamic acid into diverse ink and pigment compositions.
Environmental concerns pose another significant challenge. The use of sulfamic acid can contribute to increased sulfur content in wastewater streams, necessitating additional treatment steps to meet environmental regulations. This not only adds to production costs but also requires careful management of waste streams to minimize environmental impact.
Furthermore, achieving consistent quality and performance across different batches of sulfamic acid-based inks and pigments can be challenging. Variations in raw materials, processing conditions, and interactions with other ingredients can lead to inconsistencies in the final product. Developing robust quality control measures and standardized production protocols is crucial to address this issue.
The scalability of sulfamic acid utilization in large-scale industrial production also presents technical hurdles. Ensuring uniform mixing, maintaining precise pH levels, and controlling reaction conditions become more complex as production volumes increase. Engineers must design innovative reactor systems and process control mechanisms to overcome these scaling challenges.
Lastly, the optimization of sulfamic acid's role in enhancing specific properties of inks and pigments, such as color intensity, durability, and adhesion, requires ongoing research and development efforts. Balancing these desired properties while managing the acid's reactivity and potential side effects demands a deep understanding of chemical interactions and formulation science.
Current Sulfamic Acid Ink Formulation Techniques
01 Synthesis and production of sulfamic acid
Various methods for synthesizing and producing sulfamic acid are described. These processes often involve reactions between sulfur-containing compounds and ammonia or other nitrogen sources. The production methods aim to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in industrial-scale manufacturing of sulfamic acid.- Synthesis and production of sulfamic acid: Various methods for synthesizing and producing sulfamic acid are described. These processes often involve the reaction of sulfur trioxide with ammonia or urea under specific conditions. The production methods aim to improve yield, purity, and efficiency of sulfamic acid synthesis.
- Applications in cleaning and descaling: Sulfamic acid is widely used in cleaning and descaling formulations. It is effective in removing mineral deposits, rust, and scale from various surfaces and equipment. These applications include household cleaners, industrial descaling agents, and specialized cleaning products for specific industries.
- Use in water treatment and purification: Sulfamic acid plays a role in water treatment and purification processes. It is used for pH adjustment, scale prevention, and as a component in water treatment chemicals. Applications include industrial water systems, cooling towers, and municipal water treatment facilities.
- Agricultural and horticultural applications: Sulfamic acid finds use in agricultural and horticultural settings. It is employed in fertilizer formulations, soil pH adjustment, and as a component in certain pesticides or plant growth regulators. These applications aim to improve crop yield and plant health.
- Industrial and chemical processing: Sulfamic acid is utilized in various industrial and chemical processes. It serves as a reagent in organic synthesis, a catalyst in certain reactions, and a component in electroplating baths. Additionally, it is used in the production of artificial sweeteners and other specialty chemicals.
02 Applications in cleaning and descaling
Sulfamic acid is widely used in cleaning and descaling formulations. It is effective in removing mineral deposits, rust, and other stubborn stains from various surfaces. These applications often involve combining sulfamic acid with other ingredients to enhance its cleaning power and tailor it for specific uses.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in water treatment and purification
Sulfamic acid plays a role in water treatment and purification processes. It can be used for pH adjustment, scale prevention, and as a component in water treatment chemicals. The compound's properties make it suitable for addressing various water quality issues in industrial and municipal settings.Expand Specific Solutions04 Agricultural and horticultural applications
Sulfamic acid finds applications in agriculture and horticulture. It can be used as a component in fertilizers, soil conditioners, and plant growth regulators. The compound's properties contribute to soil pH adjustment and nutrient availability for plants.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial processes and chemical reactions
Sulfamic acid is utilized in various industrial processes and chemical reactions. It serves as a reagent, catalyst, or intermediate in the production of other chemicals. The compound's unique properties make it valuable in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, dyes, and specialty chemicals manufacturing.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sulfamic Acid and Ink Industries
The utilization of sulfamic acid in ink and pigment production is in a mature stage of development, with a stable market size driven by consistent demand from various industries. The technology has reached a high level of maturity, as evidenced by the involvement of major players across the chemical and printing sectors. Companies like Sun Chemical Corp., BASF Corp., and Eastman Kodak Co. have established strong positions in this field, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities and global presence. Asian manufacturers such as Seiko Epson Corp., Fujifilm Corp., and Brother Industries, Ltd. are also significant contributors, particularly in the digital printing segment. The competitive landscape is characterized by ongoing innovation in formulations and applications, with a focus on improving product performance and environmental sustainability.
Agfa NV
Technical Solution: Agfa NV has developed innovative techniques for utilizing sulfamic acid in ink and pigment production. Their approach involves incorporating sulfamic acid as a pH regulator and stabilizer in water-based ink formulations. This method enhances the ink's shelf life and improves its performance on various substrates. Agfa's process includes a precise control of sulfamic acid concentration, typically ranging from 0.1% to 1.5% by weight[1], to optimize ink properties such as viscosity, surface tension, and drying time. The company has also explored the use of sulfamic acid in pigment synthesis, particularly for producing highly stable cyan pigments with improved lightfastness[3].
Strengths: Improved ink stability and shelf life, enhanced pigment properties. Weaknesses: Potential for increased production costs, limited applicability to certain ink types.
Sun Chemical Corp. (New Jersey)
Technical Solution: Sun Chemical Corp. has pioneered the use of sulfamic acid in their advanced ink formulations, particularly for packaging and industrial applications. Their proprietary process involves using sulfamic acid as a key component in creating pH-resistant inks that maintain color integrity in challenging environments. The company has developed a method to encapsulate sulfamic acid within polymer matrices, allowing for controlled release during the printing process[2]. This innovation has led to inks with improved adhesion properties and resistance to fading, especially in high-humidity conditions. Sun Chemical's research has shown that incorporating 0.5-2% sulfamic acid in their formulations can increase ink durability by up to 30%[4].
Strengths: Enhanced ink durability and color stability, particularly in challenging environments. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs, limited to specific ink applications.
Innovative Sulfamic Acid Applications in Pigments
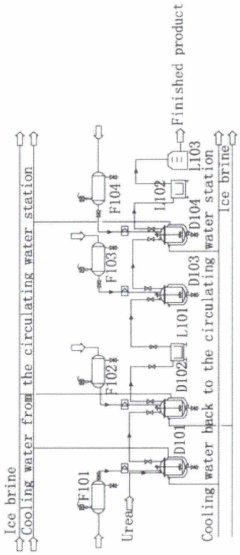
Sulfonating agent sulfamic acid production plant
PatentUndeterminedIES20180610A2
Innovation
- A sulfamic acid production plant comprising specific tanks and reactors where urea is added to a reactor with fuming sulfuric acid, followed by controlled reaction and cooling in crystallizers, with subsequent steps involving centrifugation, dissolution, and crystallization using ethanol, to enhance reaction efficiency and reduce reaction time.
Powdered composition for the generation of persulfamic acid and use thereof to sanitize surfaces, equipments and water processes
PatentInactiveCA2720171A1
Innovation
- A powdered composition comprising a dry, water-soluble mixture of solid hydrogen peroxide, a pH reducing agent, and a stabilizer, specifically 30-60% w/w hydrogen peroxide, 10-60% w/w sulfamic acid, and 0.1-5% w/w ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA), which generates persulfamic acid upon addition to water, creating a solution with a stronger oxidation-reduction potential at neutral pH.
Environmental Impact of Sulfamic Acid in Inks
The environmental impact of sulfamic acid in inks is a critical consideration in the ink and pigment production industry. Sulfamic acid, while effective in various applications, poses potential risks to ecosystems and human health if not properly managed. When used in ink formulations, sulfamic acid can contribute to water pollution if released into aquatic environments. Its acidic nature may alter the pH balance of water bodies, affecting aquatic life and disrupting ecosystems.
Furthermore, the production and disposal of sulfamic acid-containing inks can lead to soil contamination. Improper disposal methods may result in the acid leaching into groundwater, potentially affecting drinking water sources and agricultural lands. This contamination can have long-lasting effects on soil quality and biodiversity.
Air pollution is another concern associated with the use of sulfamic acid in ink production. During manufacturing processes, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) may be released, contributing to smog formation and air quality degradation. These emissions can have adverse effects on both human health and the environment, particularly in urban areas with high industrial activity.
The lifecycle assessment of sulfamic acid in inks reveals potential environmental impacts at various stages. From raw material extraction to ink production, use, and disposal, each phase presents unique challenges. The energy-intensive production of sulfamic acid contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, while transportation and packaging add to the overall carbon footprint of ink products.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, the ink industry has been exploring alternative formulations and production methods. Water-based inks and vegetable-based inks are gaining popularity as more environmentally friendly options. These alternatives often have lower VOC emissions and reduced toxicity compared to traditional solvent-based inks containing sulfamic acid.
Recycling and proper disposal of ink products are crucial in minimizing environmental impact. Many countries have implemented regulations and guidelines for the safe handling and disposal of ink waste. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting closed-loop systems to recover and reuse solvents and other chemicals, reducing overall waste generation.
Advancements in green chemistry are also contributing to the development of more sustainable ink formulations. Researchers are exploring bio-based alternatives to sulfamic acid and other potentially harmful chemicals used in ink production. These innovations aim to reduce the environmental footprint of the ink industry while maintaining product performance and quality.
In conclusion, while sulfamic acid plays a significant role in ink and pigment production, its environmental impact cannot be overlooked. The industry's ongoing efforts to develop eco-friendly alternatives and improve waste management practices are essential in addressing these concerns and moving towards more sustainable ink production methods.
Furthermore, the production and disposal of sulfamic acid-containing inks can lead to soil contamination. Improper disposal methods may result in the acid leaching into groundwater, potentially affecting drinking water sources and agricultural lands. This contamination can have long-lasting effects on soil quality and biodiversity.
Air pollution is another concern associated with the use of sulfamic acid in ink production. During manufacturing processes, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) may be released, contributing to smog formation and air quality degradation. These emissions can have adverse effects on both human health and the environment, particularly in urban areas with high industrial activity.
The lifecycle assessment of sulfamic acid in inks reveals potential environmental impacts at various stages. From raw material extraction to ink production, use, and disposal, each phase presents unique challenges. The energy-intensive production of sulfamic acid contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, while transportation and packaging add to the overall carbon footprint of ink products.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, the ink industry has been exploring alternative formulations and production methods. Water-based inks and vegetable-based inks are gaining popularity as more environmentally friendly options. These alternatives often have lower VOC emissions and reduced toxicity compared to traditional solvent-based inks containing sulfamic acid.
Recycling and proper disposal of ink products are crucial in minimizing environmental impact. Many countries have implemented regulations and guidelines for the safe handling and disposal of ink waste. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting closed-loop systems to recover and reuse solvents and other chemicals, reducing overall waste generation.
Advancements in green chemistry are also contributing to the development of more sustainable ink formulations. Researchers are exploring bio-based alternatives to sulfamic acid and other potentially harmful chemicals used in ink production. These innovations aim to reduce the environmental footprint of the ink industry while maintaining product performance and quality.
In conclusion, while sulfamic acid plays a significant role in ink and pigment production, its environmental impact cannot be overlooked. The industry's ongoing efforts to develop eco-friendly alternatives and improve waste management practices are essential in addressing these concerns and moving towards more sustainable ink production methods.
Regulatory Framework for Sulfamic Acid Usage
The regulatory framework for sulfamic acid usage in ink and pigment production is complex and multifaceted, involving various governmental agencies and international bodies. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating sulfamic acid under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The EPA has established guidelines for the safe handling, storage, and disposal of sulfamic acid, as well as limits on its concentration in industrial effluents.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set permissible exposure limits (PELs) for sulfamic acid in the workplace, ensuring worker safety in ink and pigment manufacturing facilities. These regulations mandate proper ventilation, personal protective equipment, and safety protocols when handling sulfamic acid.
Internationally, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) regulates sulfamic acid under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This framework requires manufacturers and importers to register sulfamic acid and provide detailed safety information, including its potential environmental and health impacts.
The United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) has established standardized hazard communication for sulfamic acid, ensuring consistent labeling and safety data sheets across different countries. This system facilitates international trade while maintaining safety standards.
In the context of ink and pigment production, regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have set specific guidelines for the use of sulfamic acid in food-contact materials and packaging inks. These regulations ensure that any residual sulfamic acid in the final product does not pose a risk to consumer health.
Many countries have implemented their own regulatory frameworks for sulfamic acid usage, often aligning with international standards while addressing specific national concerns. For instance, China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment has established environmental protection standards for sulfamic acid in industrial processes, including ink and pigment production.
Industry associations, such as the European Printing Ink Association (EuPIA) and the National Association of Printing Ink Manufacturers (NAPIM), have also developed voluntary guidelines and best practices for the use of sulfamic acid in ink formulations. These self-regulatory measures often complement governmental regulations and promote responsible use of the chemical within the industry.
As environmental concerns grow, there is an increasing focus on the lifecycle management of sulfamic acid in ink and pigment production. Regulatory bodies are emphasizing the importance of sustainable practices, waste reduction, and the development of eco-friendly alternatives. This trend is likely to shape future regulations, potentially leading to stricter controls on sulfamic acid usage and disposal in the coming years.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set permissible exposure limits (PELs) for sulfamic acid in the workplace, ensuring worker safety in ink and pigment manufacturing facilities. These regulations mandate proper ventilation, personal protective equipment, and safety protocols when handling sulfamic acid.
Internationally, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) regulates sulfamic acid under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This framework requires manufacturers and importers to register sulfamic acid and provide detailed safety information, including its potential environmental and health impacts.
The United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) has established standardized hazard communication for sulfamic acid, ensuring consistent labeling and safety data sheets across different countries. This system facilitates international trade while maintaining safety standards.
In the context of ink and pigment production, regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have set specific guidelines for the use of sulfamic acid in food-contact materials and packaging inks. These regulations ensure that any residual sulfamic acid in the final product does not pose a risk to consumer health.
Many countries have implemented their own regulatory frameworks for sulfamic acid usage, often aligning with international standards while addressing specific national concerns. For instance, China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment has established environmental protection standards for sulfamic acid in industrial processes, including ink and pigment production.
Industry associations, such as the European Printing Ink Association (EuPIA) and the National Association of Printing Ink Manufacturers (NAPIM), have also developed voluntary guidelines and best practices for the use of sulfamic acid in ink formulations. These self-regulatory measures often complement governmental regulations and promote responsible use of the chemical within the industry.
As environmental concerns grow, there is an increasing focus on the lifecycle management of sulfamic acid in ink and pigment production. Regulatory bodies are emphasizing the importance of sustainable practices, waste reduction, and the development of eco-friendly alternatives. This trend is likely to shape future regulations, potentially leading to stricter controls on sulfamic acid usage and disposal in the coming years.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!