What is Zirconia Crown?
Zirconia Crown Overview and Objectives
Zirconia crowns represent a significant advancement in dental restoration technology, offering a blend of aesthetic appeal and durability that has revolutionized the field of prosthodontics. These crowns are fabricated from zirconium dioxide, a ceramic material known for its exceptional strength and biocompatibility. The development of zirconia crowns can be traced back to the late 20th century, with continuous improvements in manufacturing processes and material properties leading to their widespread adoption in modern dentistry.
The evolution of zirconia crowns has been driven by the dental industry's pursuit of materials that can withstand the demanding conditions of the oral environment while providing natural-looking results. Initially, zirconia was primarily used in industrial applications due to its high strength and resistance to wear. However, as dental professionals sought alternatives to traditional metal-based restorations, zirconia emerged as a promising candidate for dental prosthetics.
The primary objectives of zirconia crown technology are multifaceted. Firstly, these crowns aim to provide superior aesthetics, closely mimicking the appearance of natural teeth. This is achieved through the material's translucency and the ability to color-match it to surrounding dentition. Secondly, zirconia crowns are designed to offer exceptional durability and longevity, with the potential to withstand the forces of mastication for many years without chipping or fracturing.
Another crucial goal of zirconia crown technology is to ensure biocompatibility and minimize the risk of allergic reactions or adverse tissue responses. Zirconia's inert nature makes it an excellent choice for patients with metal sensitivities or those seeking metal-free restorations. Additionally, the technology aims to improve the overall patient experience by reducing the need for extensive tooth preparation and potentially preserving more natural tooth structure.
The ongoing development of zirconia crowns focuses on enhancing their optical properties, improving their fit and marginal adaptation, and optimizing the manufacturing process. Researchers and dental material scientists are continuously exploring ways to refine the crystalline structure of zirconia, balance its translucency with strength, and develop more efficient production methods such as CAD/CAM technology.
As the dental industry moves towards more personalized and minimally invasive treatments, zirconia crown technology is expected to play a pivotal role. Future objectives include the development of multi-layered zirconia materials that better replicate the natural gradation of tooth color and translucency, as well as the integration of zirconia with other advanced materials to create hybrid restorations with optimized properties.
Market Demand Analysis for Dental Prosthetics
The global dental prosthetics market has been experiencing significant growth, driven by an aging population, increasing prevalence of dental diseases, and growing awareness of oral health. Zirconia crowns, as a subset of this market, have gained substantial traction due to their superior aesthetics, durability, and biocompatibility.
Market research indicates that the dental prosthetics market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with zirconia-based products playing a crucial role. The demand for zirconia crowns has been particularly strong in developed countries, where patients are willing to pay a premium for more natural-looking and longer-lasting dental restorations.
One of the key factors driving the demand for zirconia crowns is the shift towards metal-free dentistry. Patients and dentists alike are increasingly favoring materials that do not contain metals, due to concerns about allergies and aesthetic considerations. Zirconia, being a ceramic material, aligns perfectly with this trend.
The cosmetic dentistry sector has also contributed significantly to the growing demand for zirconia crowns. As more people seek to improve their smiles, the need for aesthetically pleasing dental solutions has surged. Zirconia crowns, with their ability to mimic natural tooth color and translucency, have become a preferred choice for patients looking for cosmetic dental improvements.
Another factor influencing market demand is the increasing adoption of digital dentistry technologies. CAD/CAM systems have made the production of zirconia crowns more efficient and cost-effective, allowing dental laboratories to meet the growing demand more easily. This technological advancement has also improved the precision and fit of zirconia crowns, further enhancing their appeal to both dentists and patients.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the dental prosthetics market. While it initially led to a decline in elective dental procedures, the subsequent backlog of cases and increased awareness of oral health have contributed to a rebound in demand. Zirconia crowns, being a more hygienic option due to their non-porous nature, have seen renewed interest in the post-pandemic landscape.
Looking ahead, the market for zirconia crowns is expected to expand further, driven by technological advancements, increasing disposable incomes in emerging markets, and a growing emphasis on preventive and aesthetic dentistry. However, challenges such as the high cost of zirconia crowns compared to traditional alternatives and the need for specialized training for dentists may moderate growth in some regions.
Current State and Challenges in Zirconia Crown Technology
Zirconia crown technology has made significant strides in recent years, establishing itself as a prominent option in dental restorations. The current state of zirconia crowns is characterized by their high strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal. These crowns are fabricated from zirconium dioxide, a ceramic material known for its exceptional mechanical properties and biocompatibility.
One of the primary advantages of zirconia crowns is their superior strength, which allows for thinner restorations and preservation of more natural tooth structure. The material's flexural strength ranges from 900 to 1200 MPa, significantly higher than other ceramic options. This strength also contributes to their longevity, with studies showing high survival rates of over 90% after 5 years.
Aesthetically, zirconia crowns have improved dramatically. Modern zirconia materials offer increased translucency, closely mimicking natural teeth. Multi-layered zirconia blanks have been developed to replicate the gradual color transition found in natural dentition, enhancing the overall appearance of restorations.
Despite these advancements, zirconia crown technology faces several challenges. One significant issue is the potential for chipping or fracturing of veneering porcelain when applied to zirconia frameworks. This has led to the development of monolithic zirconia crowns, which eliminate the need for veneering but may compromise aesthetics in highly visible areas.
Another challenge is the high sintering temperature required for zirconia, which can lead to dimensional changes and affect the fit of the final restoration. Manufacturers and researchers are working on developing low-temperature sintering techniques to address this issue.
The opacity of zirconia, while improved, still presents a challenge in achieving optimal aesthetics, particularly in anterior restorations. Ongoing research focuses on enhancing the optical properties of zirconia without compromising its strength.
Additionally, the bonding of zirconia to tooth structure remains a concern. Traditional bonding techniques are less effective on zirconia due to its inert surface. New surface treatment methods and specialized primers are being developed to improve bond strength and long-term stability of zirconia restorations.
The digital workflow in zirconia crown fabrication, while advancing rapidly, still faces challenges in terms of accuracy and efficiency. Improving CAD/CAM technologies and streamlining the digital process are areas of ongoing development in the field.
Lastly, the cost of zirconia crowns, while competitive, is still higher than some traditional options. Efforts are being made to optimize production processes and reduce material costs to make zirconia crowns more accessible to a broader patient population.
Existing Zirconia Crown Production Techniques
01 Zirconia crown manufacturing techniques
Various techniques are employed in the manufacturing of zirconia crowns, including CAD/CAM technology, milling processes, and sintering methods. These techniques aim to improve the precision, strength, and aesthetic qualities of the final product. Advanced manufacturing processes can enhance the fit, durability, and overall performance of zirconia crowns.- Zirconia crown manufacturing techniques: Various methods and techniques for manufacturing zirconia crowns, including CAD/CAM systems, milling processes, and sintering procedures. These techniques aim to improve the precision, strength, and aesthetic qualities of zirconia crowns.
- Zirconia crown composition and structure: Innovations in the composition and structure of zirconia crowns, including multi-layered designs, gradient coloration, and incorporation of other materials to enhance strength and aesthetics. These advancements aim to improve the overall performance and natural appearance of the crowns.
- Surface treatment and coating of zirconia crowns: Methods for treating and coating the surface of zirconia crowns to enhance their properties, such as improving bonding strength, increasing wear resistance, and enhancing aesthetics. These treatments may include chemical etching, sandblasting, or application of specialized coatings.
- Customization and color matching of zirconia crowns: Techniques for customizing zirconia crowns to match the patient's natural teeth, including color matching, shade selection, and translucency adjustments. These methods aim to create more natural-looking and aesthetically pleasing dental restorations.
- Zirconia crown fixation and bonding methods: Advancements in fixation and bonding techniques for zirconia crowns, including improved cement formulations, surface preparation methods, and bonding protocols. These innovations aim to enhance the long-term stability and durability of zirconia crown restorations.
02 Zirconia crown composition and structure
The composition and structure of zirconia crowns are crucial for their performance. This includes the use of specific zirconia materials, layering techniques, and the incorporation of other materials to enhance properties such as strength, translucency, and color matching. The structural design of the crown, including thickness and contour, plays a significant role in its functionality and aesthetics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Surface treatment and finishing of zirconia crowns
Various surface treatment and finishing techniques are applied to zirconia crowns to improve their appearance, durability, and integration with natural teeth. These may include polishing, glazing, coloring, and texturing methods. Surface treatments can enhance the crown's resistance to wear, staining, and bacterial adhesion while improving its aesthetic appeal.Expand Specific Solutions04 Zirconia crown customization and fitting
Techniques for customizing and fitting zirconia crowns to individual patients are essential for optimal performance. This includes methods for precise measurements, digital impressions, and adjustments to ensure proper occlusion and alignment. Customization processes may involve software-aided design, virtual try-ons, and chairside modifications to achieve the best possible fit and patient comfort.Expand Specific Solutions05 Zirconia crown maintenance and longevity
Strategies for maintaining zirconia crowns and extending their lifespan are crucial for long-term success. This includes proper care instructions for patients, periodic professional assessments, and techniques for repairing or refurbishing crowns if necessary. Additionally, research into improving the material properties of zirconia to enhance its resistance to chipping, fracturing, and wear contributes to the overall longevity of the crowns.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Zirconia Crown Manufacturing
The zirconia crown market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for aesthetic dental solutions. The global market size is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, zirconia crowns are reaching maturity, with ongoing innovations focused on improving aesthetics and durability. Key players like 3M Innovative Properties Co., Kuraray Noritake Dental, Inc., and GC Corp. are leading the field with advanced materials and manufacturing processes. Emerging companies such as Aidite Technology Co., Ltd. and Sagemax Bioceramics, Inc. are also making strides in product development, intensifying competition and driving further technological advancements in the zirconia crown sector.
Kuraray Noritake Dental, Inc.
Aidite (Qinhuangdao) Technology Co., Ltd.
Core Innovations in Zirconia Crown Design
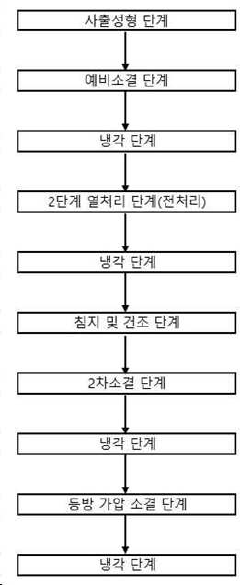
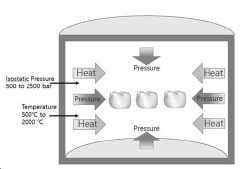
- A manufacturing process involving yttria-stabilized zirconia powder, combined with controlled heating and immersion in a metal chloride solution, followed by isostatic pressure sintering, to achieve a dense and aesthetically pleasing zirconia crown suitable for mass production.
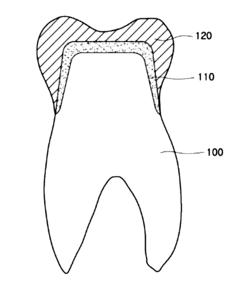
- A surface treatment process using a solution comprising nitric acid, hydrofluoric acid, hydrogen peroxide, and optionally acetyl chloride or oxalyl chloride, combined with ultrasonic impact treatment, is applied to zirconia-based crowns to enhance surface roughness and adhesion, allowing for improved bonding with porcelain layers and abutment teeth, thereby increasing the durability and aesthetic appeal of dental restorations.
Biocompatibility and Safety Considerations
Zirconia crowns have gained significant popularity in dentistry due to their excellent biocompatibility and safety profile. The material's inherent properties make it highly suitable for use in dental restorations, with minimal risk of adverse reactions or complications.
One of the primary advantages of zirconia crowns is their exceptional biocompatibility. Zirconia is a bioinert material, meaning it does not interact chemically with living tissues or fluids in the oral cavity. This characteristic significantly reduces the likelihood of allergic reactions or inflammatory responses, making zirconia crowns suitable for patients with metal sensitivities or allergies.
The safety of zirconia crowns is further enhanced by their resistance to corrosion and degradation. Unlike some metal-based dental materials, zirconia does not release ions or particles into the oral environment, minimizing the risk of systemic toxicity or local tissue irritation. This stability ensures long-term safety and durability of the dental restoration.
Zirconia's low thermal conductivity is another crucial safety feature. It provides excellent insulation, protecting the underlying tooth structure from temperature extremes and reducing the risk of pulpal irritation or sensitivity. This property contributes to patient comfort and helps maintain the vitality of the restored tooth.
The smooth surface of zirconia crowns inhibits plaque accumulation, promoting better oral hygiene and reducing the risk of secondary caries or periodontal issues. This characteristic not only enhances the longevity of the restoration but also supports overall oral health.
Clinical studies have consistently demonstrated the safety and biocompatibility of zirconia crowns. Long-term follow-up studies have shown minimal adverse effects and high patient satisfaction rates. The material's ability to integrate seamlessly with surrounding tissues without causing irritation or inflammation further supports its safety profile.
However, it is essential to note that proper manufacturing and handling of zirconia crowns are crucial to maintain their biocompatibility and safety. Strict adherence to quality control measures during production and careful clinical procedures during placement are necessary to ensure optimal outcomes and minimize potential risks.
In conclusion, zirconia crowns offer a highly biocompatible and safe option for dental restorations. Their bioinert nature, resistance to corrosion, low thermal conductivity, and smooth surface properties contribute to their excellent safety profile. As research continues and long-term clinical data accumulates, the biocompatibility and safety of zirconia crowns remain a significant advantage in modern dentistry.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Zirconia Crowns
The cost-effectiveness analysis of zirconia crowns reveals a compelling case for their adoption in dental practices. Initial costs for zirconia crowns are typically higher than traditional alternatives, such as porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) crowns. However, when considering long-term durability and patient satisfaction, zirconia crowns often prove to be more economical.
Zirconia crowns demonstrate superior longevity, with studies indicating a lifespan of 10-15 years or more under proper care. This extended durability translates to fewer replacements over time, reducing the overall cost burden on patients and healthcare systems. In contrast, PFM crowns may require replacement every 5-7 years, incurring additional expenses and patient discomfort.
The aesthetic qualities of zirconia crowns contribute to their cost-effectiveness by enhancing patient satisfaction and reducing the likelihood of premature replacement due to dissatisfaction with appearance. The natural look and biocompatibility of zirconia also minimize the risk of allergic reactions or gum irritation, potentially saving on additional medical interventions.
From a dental practice perspective, the efficiency of zirconia crown production using CAD/CAM technology can lead to reduced chair time and improved workflow. This efficiency allows dentists to see more patients and potentially increase revenue, offsetting the higher material costs of zirconia.
Insurance coverage for zirconia crowns has been expanding, recognizing their long-term benefits. This trend further improves the cost-effectiveness for patients, making zirconia a more accessible option. Additionally, the reduced need for adjustments and repairs compared to other crown types contributes to overall cost savings for both patients and dental practices.
While the initial investment in zirconia crowns may be higher, the long-term financial benefits are significant. Patients experience fewer dental visits, reduced discomfort from frequent replacements, and improved oral health outcomes. Dental practices benefit from increased patient satisfaction, potentially leading to better retention and referrals.
In conclusion, the cost-effectiveness of zirconia crowns extends beyond mere price comparisons. When factoring in longevity, aesthetic value, patient satisfaction, and overall health benefits, zirconia crowns present a compelling economic argument for their use in modern dentistry.